Domestication and Biological Characteristics of a Vero Cell line in Suspension Culture
-
摘要:
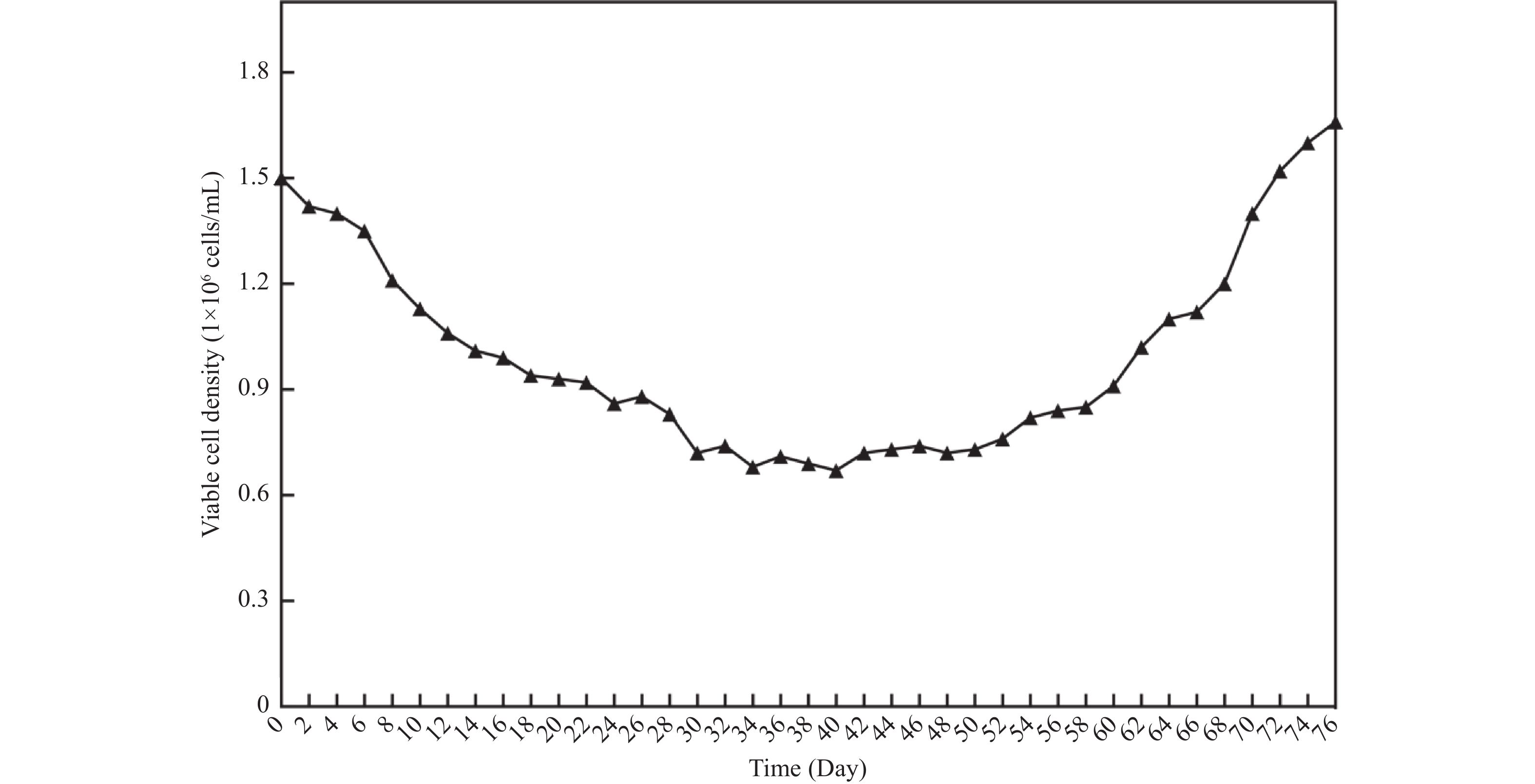
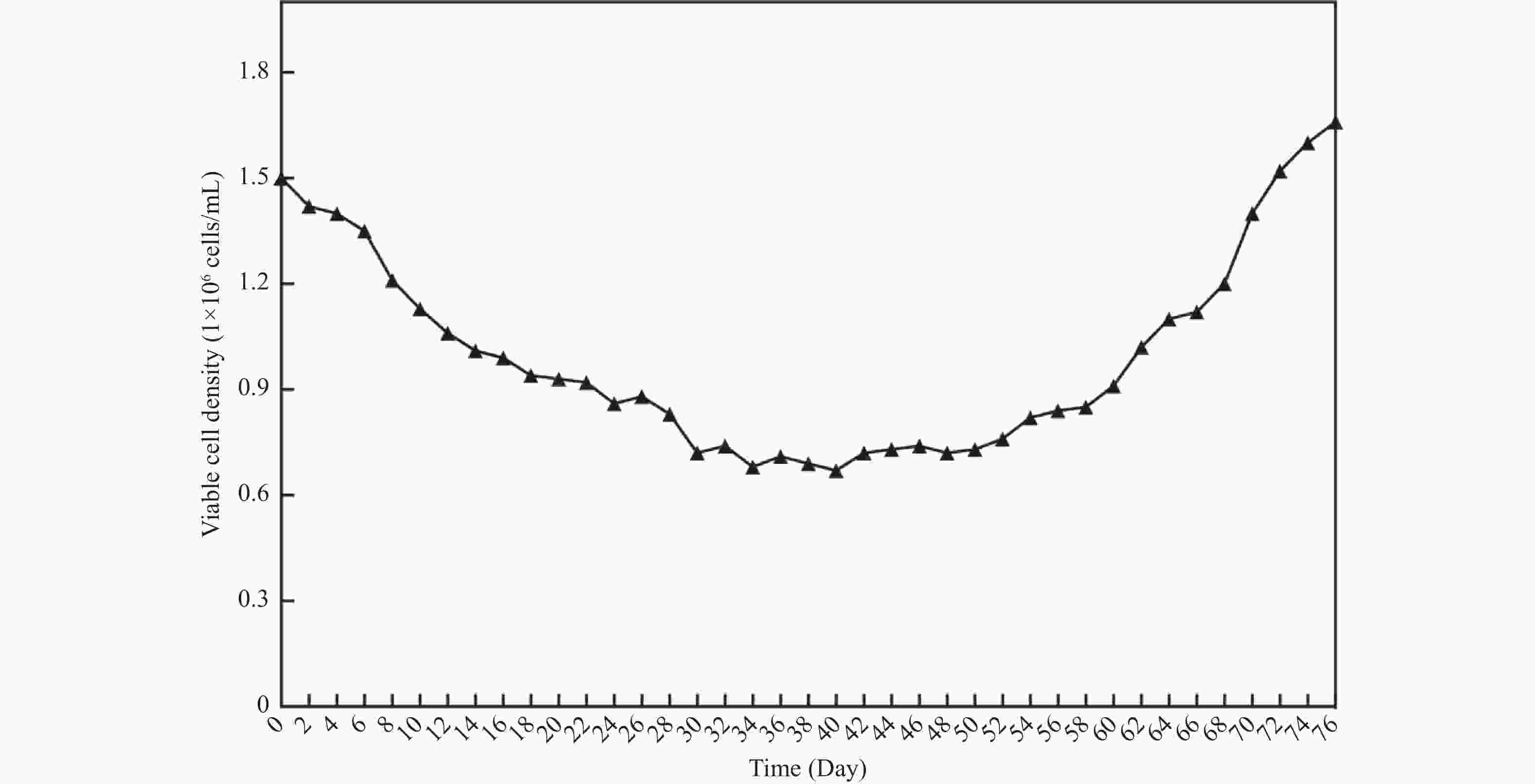
目的 将贴壁培养的Vero细胞驯化成悬浮培养细胞,并对其生物学特性进行研究。 方法 采用无血清培养和“摇床适应法”对细胞进行培养优化,对其进行成瘤性、短串联重复序列(short tandem repeat,STR)分析、透射电子显微镜形态,以及对流感病毒敏感性检测。 结果 成功建立悬浮细胞系Vero-S,Vero-S细胞生长期在24~72 h,平台期在108~144 h之间,衰退期在144 h以后,细胞PDT为36 h,细胞密度在14.01~14.88×108个/L之间,细胞平均圆度在0.73~0.75之间,细胞直径在12.12~14.44 µm之间。Vero-S细胞在裸鼠皮下形成肿瘤,而悬浮培养前的Vero细胞不具有成瘤性;STR显示为猴源细胞系;电镜下细胞结构完整;Vero-S细胞对流感病毒感染不敏感。 结论 悬浮细胞系Vero-S细胞的生长经历与贴壁细胞类似的生长期、平台期、衰退期,且细胞大小均一,建立的悬浮培养基能够支持Vero-S细胞高密度生长。STR结果表明悬浮Vero细胞具有完全的遗传稳定性,透射电镜下与贴壁Vero细胞无明显区别。为细胞悬浮驯化培养技术提供参考价值,并可用于细胞致肿瘤的机理研究。 Abstract:Objective To domesticate adherently cultured Vero cells into suspension-cultured cells and investigate their biological characteristics. Methods Cell culture was optimized using serum-free media and the "shaker adaptation method." Additionally, tumorigenicity, short tandem repeat (STR) profiles, morphological characters under transmission electron microscope (TEM), and influenza virus sensitivity were analyzed in these cells. Results Suspension cell line Vero-S was successfully established. The growth period of Vero-S cells ranged from 24 to 72 hours, with a plateau phase between 108 and 144 hours, and a decline phase after 144 hours. The population doubling time (PDT) was 36 hours, and cell density ranged from 14.01 to 14.88 × 108 cells/L. Average cell roundness ranged from 0.73 to 0.75, and cell diameter ranged from 12.12 to 14.44 µm. Vero-S cells formed tumors subcutaneously in nude mice, while Vero cells before suspension culture did not exhibit tumorigenicity. STR analysis indicated a primate origin of the cell line. Under electron microscopy, cell structure appeared intact. Vero-S cells showed insensitivity to influenza virus infection. Conclusion The established suspension cell line Vero-S exhibiting growth patterns similar to adherent cells, with uniform cell size and high-density growth supported by the established suspension culture medium. STR results demonstrated complete genetic stability of suspended Vero cells, with no apparent differences observed under transmission electron microscopy compared to adherent Vero cells. This study provides reference for suspension culture domestication techniques and can be applied in mechanistic studies of cell tumorigenicity. -
表 1 Vero-S细胞的STR位点基因分型结果
Table 1. Results of STR loci genotyping for Vero-S cells
STR位点 等位基因1 等位基因2 重复次数 重复次数 D1S518 191.04 194.99 15 16 D4S2408 346.03 349.93 16 17 D5S1467 180.06 10 D6S1017 354.84 358.7 10 11 D8S1106 134.07 12 D17S1304 210.15 214.31 14 15 D19S245 245.76 21 DYS389 328.29 12 -
[1] Ahmad N,Nawi A M,Jamhari M N,et al. Post-exposure prophylactic vaccination against rabies: A systematic review[J]. Iran J Public Health,2022,51(5):967-977. [2] Hu L,Sun J,Wang Y,et al. A review of inactivated COVID-19 vaccine development in China: Focusing on safety and efficacy in special populations[J]. Vaccines,2023,11(6):1045. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11061045 [3] Wang L,Li J,Mu Q,et al. Study on immune persistence of the CTN-1V strain rabies vaccine in humans[J]. Journal of Virus Eradication,2024,10(1):100365. doi: 10.1016/j.jve.2024.100365 [4] Liang C,Hui N,Liu Y,et al. Insights into forsythia honeysuckle (Lianhuaqingwen) capsules: A Chinese herbal medicine repurposed for COVID-19 pandemic[J]. Phytomed Plus,2021,1(2):100027. doi: 10.1016/j.phyplu.2021.100027 [5] Someya K,Okemoto-Nakamura Y,Kurata T,et al. Establishment of measles virus receptor-expressing Vero cells lacking functional poliovirus receptors[J]. Microbiol Immunol,2023,67(3):166-170. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.13047 [6] Todesco H M,Gafuik C,John C M,et al. High-titer manufacturing of SARS-CoV-2 Spike-pseudotyped VSV in stirred-tank bioreactors[J]. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev,2024,32(1):101189. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2024.101189 [7] Guo M,Zheng R,Wu H L,et al. Inhibition of enterovirus 71 infection by polysaccharides extracted from Picochlorum sp. 122 via the AKT and ATM/ATR signaling pathways[J]. Arch Virol,2021,166(12):3269-3274. doi: 10.1007/s00705-021-05229-1 [8] 赵彩红,王美皓,李自良,等. 无血清悬浮培养MDCK细胞系的建立及生物反应器高密度培养[J]. 中国生物制品学杂志,2021,34(11):1362-1369. [9] 刘丽,郭骐源,郝建丽,等. 无血清悬浮MDCK细胞培养流感病毒纯化工艺的初步建立[J]. 中国生物制品学杂志,2021,34(9):1100-1104. [10] 李政蓉,金宏丽,黄培,等. BHK-21细胞悬浮培养狂犬病病毒(rCVS-11-dG株)工艺的建立及病毒免疫原性评价[J]. 中国生物制品学杂志,2021,34(2):129-134. [11] 陈丽,倪敏舒,徐悦,等. 伪狂犬病毒在BHK-21悬浮细胞中的增殖特性[J]. 江苏农业科学,2022,50(10):166-170. [12] Göbel S,Pelz L,Silva C A T,et al. Production of recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus-based vectors by tangential flow depth filtration[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,2024,108(1):240. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13078-6 [13] Cui W,Liu S. Optimization of adaptation parameters from adhesion cell culture in serum-containing media to suspension in chemically defined media by superlative box design[J]. Cytotechnology,2024,76(1):39-52. doi: 10.1007/s10616-023-00596-w [14] Du Q,Zhang X,Wang T,et al. Effects and mechanisms of animal-free hydrolysates on recombination protein yields in CHO cells[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,2022,106(22):7387-7396. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-12229-x [15] Huang Z,Habib A,Zhao G,et al. CRISPR-Cas9 mediated stable expression of exogenous proteins in the CHO cell line through site-specific integration[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2023,24(23):16767. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316767 [16] 国家药典委员会编. 中华人民共和国药典 三部 2020年版 [M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社,2020: 11-13. [17] Kiesslich S,Kim G N,Shen C F,et al. Bioreactor production of rVSV-based vectors in Vero cell suspension cultures[J]. Biotechnol Bioeng,2021,118(7):2649-2659. doi: 10.1002/bit.27785 [18] Kim J,Kwon E J,Kim Y J,et al. Epigenetic repression of CHCHD2 enhances survival from single cell dissociation through attenuated Rho A kinase activity[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci,2024,81(1):38. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-05060-8 [19] Wu K,El Zowalaty A E,Sayin V I,et al. The pleiotropic functions of reactive oxygen species in cancer[J]. Nat Cancer,2024,5(3):384-399. doi: 10.1038/s43018-024-00738-9 [20] Sato Y,Bando H,Di Piazza M,et al. Tumorigenicity assessment of cell therapy products: The need for global consensus and points to consider[J]. Cytotherapy,2019,21(11):1095-1111. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2019.10.001 [21] Yang Z,Yu S,Xu Y,et al. The screening and mechanism of influenza-virus sensitive MDCK cell lines for influenza vaccine production[J]. Diseases,2024,12(1):20. doi: 10.3390/diseases12010020 [22] Ulengin-Talkish I,Parson M A H,Jenkins M L,et al. Palmitoylation targets the calcineurin phosphatase to the phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase complex at the plasma membrane[J]. Nat Commun,2021,12(1):6064. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26326-4 [23] Logan M,Rinas K,McConkey B,et al. Vero cells gain renal tubule markers in low-calcium and magnesium chemically defined media[J]. Sci Rep,2022,12(1):6180. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-10221-z [24] V á zquez-Ram í rez D,Jordan I,Sandig V,et al. High titer MVA and influenza A virus production using a hybrid fed-batch/perfusion strategy with an ATF system[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,2019,103(7):3025-3035. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-09694-2 [25] Kalle. S R M Z H. Adaptation of Vero cells to suspension growth for rabies virus production in different serum free media[J]. Vaccine,2019,37(47):6987-6995. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.05.092 -





 下载:
下载: