Predictive Value of KIAA1199 and Linc00673 Genes on Chemotherapy Efficacy in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
-
摘要:
目的 探讨KIAA1199基因和Linc00673基因在非小细胞肺癌患者化疗前后的表达变化,并进一步评估这两个基因作为分子标志物在预测化疗疗效方面的潜在价值。 方法 选取2019年8月至2021年8月石家庄市第三医院和华北医疗健康集团峰峰总医院收治的58 例Ⅲ-Ⅳ期非小细胞肺癌患者,分别在治疗前2 d和治疗两个周期后获取患者外周血PBMC细胞,检测KIAA1199基因、Linc00673基因表达水平,统计患者化疗疗效,并通过ROC曲线分析KIAA1199基因、Linc00673基因作为分子标志物预测化疗疗效的价值。 结果 经两个周期化疗后,58例患者中20例出现病情进展,占比34.48%。qPCR结果显示,治疗前,进展与未进展患者间KIAA1199基因、Linc00673基因表达水平比较,差异均无统计学意义(P > 0.05);治疗后,相比于进展患者,未进展患者KIAA1199基因、Linc00673基因表达水平均显著降低(P < 0.01)。ROC曲线分析结果显示,联合检测的AUC均显著高于KIAA1199基因和Linc00673基因(Z = 3.054、5.178,P < 0.05)。 结论 在非小细胞肺癌化疗患者中,KIAA1199基因、Linc00673基因的表达因疗效不同而呈现显著差异,其中KIAA1199基因更适宜作为预测化疗疗效的生物标志物。 Abstract:Objective To explore the expression changes of KIAA1199 and Linc00673 genes in non-small cell lung cancer patients before and after chemotherapy, and to further evaluate the potential value of these two genes as molecular markers in predicting chemotherapy efficacy. Methods A total of 58 patients with stage Ⅲ-Ⅳ NSCLC admitted to the Third Hospital of Shijiazhuang and Fengfeng General Hospital of North China Medical Health Group from August 2019 to August 2021 were selected. Peripheral blood PBMCs were collected from patients 2 days before treatment and after two cycles of treatment to detect the expression levels of KIAA1199 and Linc00673 genes. The chemotherapy efficacy of patients was statistically analyzed, and the value of KIAA1199 and Linc00673 genes as molecular markers in predicting chemotherapy efficacy was assessed using ROC curve analysis. Results After 2 cycles of chemotherapy, 20 out of 58 patients showed disease progression, accounting for 34.48%. qPCR results showed no statistically significant difference in the expression levels of KIAA1199 and Linc00673 genes between progressed and non-progressed patients before treatment (P > 0.05). After treatment, the expression levels of KIAA1199 and Linc00673 genes were significantly lower in non-progressed patients compared to progressed patients (P < 0.01). ROC curve analysis showed that the AUC of combined detection was significantly higher than that of KIAA1199 gene and Linc00673 gene alone (Z = 3.054, 5.178, P < 0.05). Conclusion In NSCLC patients undergoing chemotherapy, the expression of KIAA1199 and Linc00673 genes shows significant differences based on therapeutic efficacy, with KIAA1199 being more suitable as a biomarker for predicting chemotherapy efficacy. -
Key words:
- Linc00673 /
- KIAA1199 /
- Non small cell lung cancer /
- Expression level /
- Efficacy prediction
-
喙尾琵甲(Blaps rhynchoptera Fairmaire)是鞘翅目(Coleoptera)拟步甲科(Tenebrionidae)琵甲属(Blaps)昆虫,主要分布在我国西南地区,云南省内各地区均有分布,以滇中、滇东高原较为集中,俗名臭壳虫、小黑虫、打屁虫等[1-3]。其性辛辣、温、有毒,具有解表祛风、镇痉止痛、抗菌消炎等功效,可用于治疗发烧、咳嗽、胃炎、疔疮、肿痛,以及心血管、类风湿和肿瘤等疾病。喙尾琵甲在云南民间应用历史悠久,彝族、壮族、苗族等少数民族治疗各种疑难病症的处方中80%以上都含有该昆虫,有很好的民间药用基础[4]。
喙尾琵甲成虫能分泌具有药用价值的防御液,近年来研究表明其防御液的主要化学成分为2-甲基-1,4-苯醌、2 -乙基-1,4-苯醌和1-十三烯,这些小分子物质具有潜在的抗肿瘤、抑菌等活性[5-6],而喙尾琵甲虫体的化学成分主要是酚类 、环肽类以及氨基酸类化合物[7-9],其虫体本身也具有浓烈的刺激性气味,提示其可能含有大量的挥发性成分。然而目前针对喙尾琵甲虫体挥发性成分的研究不多,仅有罗建蓉等[10-11]对全虫的正己烷和石油醚提取物进行分析,指出不饱和脂肪酸类化合物是其油脂的主要化学成分。本文以喙尾琵甲虫体为研究对象,采用顶空固相微萃取方法,结合气相色谱-质谱联用技术对其中挥发性成分进行了分析鉴定,并利用面积归一化法确定各组分的相对含量,旨在为合理开发利用这一重要的药用昆虫资源提供科学依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 仪器与试剂
喙尾琵甲样品购自云南大理,标本保存在昆明医科大学药学院。HP6890GC/5973MS气相色谱-质谱联用仪(美国Agilent Technologies公司),Supelco 65 μm PDMS/DVB手动固相微萃取头(美国SUPELCO公司),BSA224S型电子天平(上海梅特勒托利多公司)。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 GC-MS条件
Agilent HP-5MS石英毛细管柱(30 m×0.25 mm,0.25 μm);柱温:起始温度40 ℃,程序升温3 ℃/min至80 ℃,再5 ℃/min升温至280 ℃,保持20 min;柱流量为1.0 mL/min;进样口温度250 ℃;柱前压100 kPa;分流比5∶1;载气为高纯氦气;分析检测时间共40 min。
1.2.2 质谱条件
电离方式EI;电子能量70 eV;传输线温度250 ℃;离子源温度230 ℃;四极杆温度150 ℃;扫描质量范围35~500 amu。
1.2.3 样品处理
称取0.5 g粉碎后的喙尾琵甲粉末置于10 mL顶空瓶中,压盖密封。插入装有萃取纤维头的手动进样器,室温下顶空萃取50 min后移出萃取头,然后立即插入气相色谱仪进样口进行解析,解析温度为250 ℃,解析时间为 5 min。
2. 结果
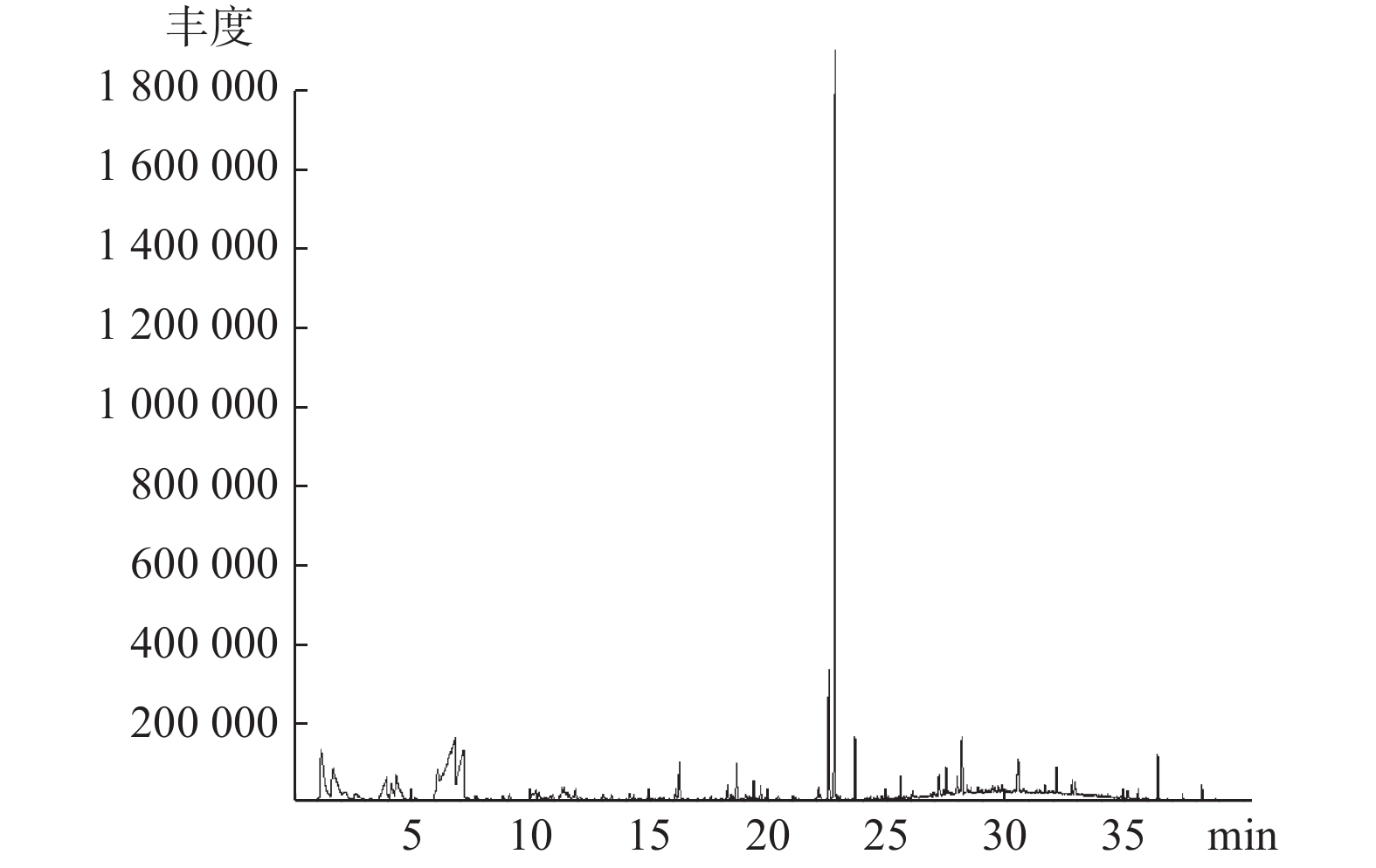
喙尾琵甲虫体挥发性成分GC-MS总离子流图,见图 1,经质谱扫描结合wiley7n.l和NIST98.L标准谱库检索对比,并采用面积归一化法计算出各成分的相对百分含量,共鉴定出其中40个成分,占总峰面积的92.80%,见表1。成分分析结果显示,其挥发性成分中含有烃类成分16种,占总含量的35.73%;脂肪酸类成分8种,占总含量的35.87%,其中7种为短链脂肪酸;胺类成分3种,占总含量的7.29%;醇类成分4种,占总含量的5.54%;酯类成分4种,占总含量的3.87%;醛类成分2种,占总含量的2.83%;此外,还检测到酚类、酮类和醚类成分各1种,分别占总含量的0.80%、0.54%和0.33%。含量在5%以上的成分有5种,分别是十三烷(21.47%)、3-甲基丁酸(16.88%)、2-甲基丁酸(7.67%)、三甲胺(6.59%)和乙酸(5.47%),占总含量的58.08%;含量在1%~5%之间的有11种,占总含量的22.52%;其余成分含量均在1%以下,共24种,占总含量的12.20%。此外,虫体中含有10种C12~C20的直链和支链烷烃,占总含量的28.86%。
表 1 喙尾琵甲挥发性成分分析结果Table 1. Volatile components from Blaps rhynchoptera序号 保留时间(min) 化合物名称 分子式 分子量 含量(%) 1 1.16 三甲胺 N,N-Dimethylmethylamine C3H9N 59.11 6.59 2 1.67 乙酸 Acetic acid C2H4O2 60.05 5.47 3 2.15 异戊醛 3-Methylbutanal C5H10O 86.13 1.25 4 2.63 丙酸 Propanoic acid C3H6O2 74.08 0.96 5 3.92 异丁酸 Isobutyric acid C4H8O2 88.11 2.92 6 4.11 2,3-丁二醇 2,3-Butanediol C4H10O2 90.12 1.34 7 4.32 1,3-丁二醇 1,3-Butanediol C4H10O2 90.12 2.99 8 6.06 异戊酸乙酯 Ethyl isopentanoate C7H14O2 130.18 2.69 9 6.81 3-甲基丁酸 Isovaleric acid C5H10O2 102.13 16.88 10 7.17 2-甲基丁酸 2-Methyl butyric acid C5H10O2 102.13 7.67 11 9.10 二乙二醇单甲醚 Ethanol,2-(2-methoxyethoxy)- C5H12O3 120.15 0.33 12 10.22 4-甲基戊酸 4-Methylvaleric acid C6H12O2 116.16 1.10 13 10.32 4-甲基戊酸乙酯 Ethyl 4-methylvalerate C8H16O2 144.21 0.51 14 11.30 苯酚 Phenol C6H6O 94.11 0.54 15 11.39 1,2,4-三甲基苯 1,2,4-trimethyl-benzene C9H12 120.19 0.62 16 11.52 己酸 Hexanoic acid C6H12O2 116.16 0.37 17 13.04 N-(2-甲基丙基)乙酰胺 N-(2-Methylpropyl)acetamide C6H13NO 115.17 0.38 18 13.38 泛酰内酯 Pantolactone C6H10O3 130.14 0.29 19 14.15 γ-己内酯 4-Hexalactone C6H10O2 114.14 0.38 20 14.95 2-吡咯烷酮 2-Pyrrolidinone C4H7NO 85.10 0.32 21 16.09 芳樟醇 Linalool C10H18O 154.25 0.47 22 16.25 壬醛 Nonanal C9H18O 142.24 1.58 23 18.66 3,5,5-三甲基环己烯 3,5,5-Trimethy-cyclohexene C9H16 124.22 1.13 24 19.03 萘 Naphthalene C10H8 128.17 0.29 25 19.37 α-松油醇α-Terpineol C10H18O 154.25 0.74 26 19.67 十二烷 Dodecane C12H26 170.33 0.54 27 22.11 壬酸 Nonanoic acid C9H18O2 158.24 0.50 28 22.54 1-十三烯 1-Tridecene C13H26 182.34 3.55 29 22.8 十三烷 Tridecane C13H28 184.36 21.47 30 25.56 十四烷 Tetradecane C14H30 198.39 0.59 31 27.18 2,6,10-三甲基十二烷 2,6,10-Trimethyldodecane C15H32 212.41 0.78 32 27.49 2,6-二(叔丁基)-4-羟基-4-甲基-2,5-环己二烯-1-酮
2,6-Di(tert-butyl)-4-hydroxy-4-methyl-2,5-cyclohexadien-1-oneC15H24O2 236.35 0.80 33 27.94 1-十五烯 1-Pentadecene C15H30 210.40 0.83 34 28.14 十五烷 Pentadecane C15H32 212.41 2.60 35 28.37 α-法尼烯 α-Farnesene C15H24 204.35 0.45 36 30.52 十六烷 Hexadecane C16H34 226.44 1.37 37 31.65 2,6,10-三甲基十五烷2,6,10-Trimethylpentadecane C18H38 254.49 0.35 38 32.78 十七烷 Heptadecane C17H36 240.47 0.41 39 32.91 姥鲛烷 pentadecane,2,6,10,14-tetramethyl- C19H40 268.52 0.40 40 35.12 植烷 Hexadecane,2,6,10,14-tetramethyl- C20H42 282.55 0.35 3. 讨论
喙尾琵甲干燥虫体中含有大量的高级脂肪酸和脂肪酸酯等油脂类成分,如亚油酸、棕榈酸、亚油酸乙酯、油酸甲酯、棕榈酸甲酯、硬脂酸甲酯等,含量很高[10-12]。本研究首次采用顶空固相微萃取法结合气质联用技术对喙尾琵甲虫体中的挥发性成分进行了分析,有效避免了因溶剂提取导致的大量油脂类成分的干扰,更真实的反应了喙尾琵甲中的挥发性成分的种类和含量。
研究结果显示喙尾琵甲虫体的挥发性物质中烷烃类和短链脂肪酸类化合物相对较多,以十三烷和3-甲基丁酸为代表。十三烷等烷烃属于昆虫告警信息素,对昆虫的行为活动起着至关重要的作用[13-14],本研究首次揭示了喙尾琵甲虫体中含有大量的十三烷。除烃类化合物以外,其他24种成分(酸类、胺类、醇类、酯类、醛类、酚类、酮类、醚类等)均首次从该虫体中发现。3-甲基丁酸等7种酸类成分为短链脂肪酸,这类成分主要由肠道菌群以膳食纤维为底物发酵产生,是肠道微生物群及宿主肠上皮细胞的重要能量来源,能够维持肠道酸碱平衡,抑制有害病原菌生长,调节宿主肠道免疫,降低肠道炎症反应并增强肠道屏障功能[15-16]。短链脂肪酸还具有神经活性,能够直接或间接参与微生物群-肠-脑轴的交流,对免疫和内分泌系统产生广泛的影响[17-18]。分析结果显示了喙尾琵甲虫体的挥发性物质与其臀腺分泌的防御性物质在化学成分上有很大差异,文献报道[4-5]的防御性分泌物中主要含有苯醌类、1-十三烯、烯酰胺等成分,本研究从虫体中仅检测到少量的1-十三烯,并未分离得到分泌物中的两个主要物质2-甲基苯醌和2-乙基苯醌,也未发现其他苯醌衍生物,进一步证实了取代苯醌可能主要富集于喙尾琵琶甲的防御腺,其他组织中分布极少[11]。对喙尾琵甲虫体中挥发性成分的分析和鉴定,可为该药用昆虫资源的进一步开发利用提供参考。
-
表 1 qPCR检测中不同基因的引物序列
Table 1. The primer sequences of different genes in qPCR detection
基因名 引物序列(5'-3') KIAA1199 正向序列:5′-GCCTGTGGCCTATGCAGTCA-3′ 反向序列:5′-TGCTGTGGCCTGTTCCCACTGCTTAC-3' Linc00673 正向序列: 5′-AATATTAAACGGTCCAGTCCTACAA-3′ 反向序列: 5′-TAGGACTGCCCATTACAGAGGA-3′ GAPDH 正向序列: 5′-CGACTTATACATGGCCTTA-3′ 反向序列: 5′-TTCCGATCACTGTTGGAAT-3′ 表 2 患者一般资料比较
Table 2. Comparison of general data of patients
临床病理特征 无进展组
(n = 38)进展组
(n = 20)χ2 P 年龄(岁) 1.277 0.258 < 65 15(39.47) 11(55.00) ≥ 65 23(60.53) 9(45.00) 性别 0.043 0.836 男 32(84.21) 18(90.00) 女 6(15.79) 2(10.00) 吸烟史 0.547 0.460 有 27(71.05) 16(80.00) 无 11(28.95) 4(20.00) TNM分期 3.471 0.062 Ⅲ期 21(55.26) 11(55.00) Ⅳ期 17(44.74) 9(45.00) 病理类型 鳞癌 18(47.37) 10(50.00) 0.036 0.849 腺癌 17(44.74) 9(45.00) 0.000 0.985 其他 3(7.89) 1(5.00) 0.017 0.895 表 3 患者化疗疗效分析
Table 3. Analysis of the efficacy of chemotherapy in patients
临床病理特征 n 百分比(%) CR 0 0 PR 13 22.4 SD 25 43.1 PD 20 34.4 表 4 ROC曲线分析KIAA1199基因和Linc00673基因对化疗疗效的预测价值
Table 4. ROC curve analysis of the predictive value of KIAA1199 gene and Linc00673 gene for chemotherapy efficacy
指标 曲线下面积(95%CI) 敏感度(%) 特异度(%) 截断值 约登指数 KIAA1199基因 0.829(0.726~0.932) 90.0(18/20) 31.6(12/38) > 1.270 0.584 Linc00673基因 0.758(0.637~0.878) 100.0(20/20) 52.6(20/38) > 0.955 0.474 联合检测 0.880(0.793~0.966) 100.0(20/20) 26.3(10/38) − 0.737 -
[1] Tang A,Ahmad U,Toth A J,et al. Non-small cell lung cancer in never- and ever-smokers: Is it the same disease? [J]. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg,2021,161(6): 1903-1917. e9. [2] Alexander M,Kim S Y,Cheng H Y. Update 2020: Management of non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Lung,2020,198(6):897-907. doi: 10.1007/s00408-020-00407-5 [3] Zhou C C,Chen G Y,Huang Y C,et al. Camrelizumab plus carboplatin and pemetrexed versus chemotherapy alone in chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (CameL): A randomised,open-label,multicentre,phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Respir Med,2021,9(3):305-314. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30365-9 [4] Imyanitov E N,Iyevleva A G,Levchenko E V. Molecular testing and targeted therapy for non-small cell lung cancer: Current status and perspectives[J]. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol,2021,157:103194. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2020.103194 [5] Redman M W,Papadimitrakopoulou V A,Minichiello K,et al. Biomarker-driven therapies for previously treated squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (Lung-MAP SWOG S1400): A biomarker-driven master protocol[J]. Lancet Oncol,2020,21(12):1589-1601. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30475-7 [6] Ito K,Nishida Y,Ikuta K,et al. Overexpression of KIAA1199,a novel strong hyaluronidase,is a poor prognostic factor in patients with osteosarcoma[J]. J Orthop Surg Res,2021,16(1):439. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02590-4 [7] Liu J M,Yan W,Han P,et al. The emerging role of KIAA1199 in cancer development and therapy[J]. Biomed Pharmacother,2021,138:111507. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111507 [8] Qiao K,Ning S P,Wan L,et al. LINC00673 is activated by YY1 and promotes the proliferation of breast cancer cells via the miR-515-5p/MARK4/Hippo signaling pathway[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res,2019,38(1):418 doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1421-7 [9] Lu W,Zhang H H,Niu Y Q,et al. Long non-coding RNA linc00673 regulated non-small cell lung cancer proliferation,migration,invasion and epithelial mesenchymal transition by sponging miR-150-5p[J]. Mol Cancer,2017,16(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0685-9 [10] Guan H Y,Zhu T,Wu S S,et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00673-v4 promotes aggressiveness of lung adenocarcinoma via activating WNT/β-catenin signaling[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,2019,116(28):14019-14028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1900997116 [11] Schrank B R,Colbert L E. Genomic biomarkers predict response to combined ATR inhibition and radiotherapy[J]. Clin Cancer Res,2024,30(24):5505-5507. [12] Ebrahimpour L, Lemaréchal Y, Yolchuyeva S, et al. Sensitivity of CT-derived radiomic features to extraction libraries and gray-level discretization in the context of immune biomarker discovery[J]. Br J Radiol,2024,97(1164):1982-1991. [13] Tang Z Y,Ding Y,Shen Q,et al. KIAA1199 promotes invasion and migration in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) via PI3K-Akt mediated EMT[J]. J Mol Med (Berl),2019,97(1):127-140. doi: 10.1007/s00109-018-1721-y [14] Baran K,Kordiak J,Jabłoński S,et al. Panel of miR-150 and linc00673,regulators of CCR6/CCL20 may serve as non-invasive diagnostic marker of non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Scientific Reports,2023,13(1):9642. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36485-7 [15] Yao Y,Zhao Q,Xu F,et al. Enhanced anti-tumor therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma via sorafenib and KIAA1199-siRNA co-delivery liposomes[J]. Saudi Pharm J,2024,32(9):102153. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2024.102153 [16] Zhu Y R,Zhang Z F,Peng H,et al. Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of LINC00673 in human malignancy: A review and meta-analysis[J]. Biosci Rep,2021,41(7):BSR20211175. doi: 10.1042/BSR20211175 [17] Shen X J,Mo X C,Tan W D,et al. KIAA1199 correlates with tumor microenvironment and immune infiltration in lung adenocarcinoma as a potential prognostic biomarker[J]. Pathol Oncol Res,2022,28:1610754. doi: 10.3389/pore.2022.1610754 [18] Zhang Y B,Yu H L,Guo Z. Circ_KIAA1199 inhibits MSI1 degradation by targeting miR-34c-5p to drive the malignant cell behaviors and tumor growth of colorectal cancer[J]. Anticancer Drugs,2022,33(1):e134-e144. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001164 [19] Zhu K J,Gong Z J,Li P C,et al. A review of linc00673 as a novel lncRNA for tumor regulation[J]. Int J Med Sci,2021,18(2):398-405. doi: 10.7150/ijms.48134 [20] Shen S Y,Yang C Q,Liu X B,et al. RBFOX1 regulates the permeability of the blood-tumor barrier via the LINC00673/MAFF pathway[J]. Mol Ther Oncolytics,2020,17:138-152. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.03.014 [21] Li N,Cui Z G,Huang D Y,et al. Association of LINC00673 rs11655237 polymorphism with cancer susceptibility: A meta-analysis based on 23478 subjects[J]. Genomics,2020,112(6):4148-4154. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.07.015 [22] Wang S S,Chao J S,Wang H,et al. Effectiveness,safety,and biomarker analysis of lenvatinib plus toripalimab as chemo-free therapy in advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A real-world study[J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother,2024,73(12):249. doi: 10.1007/s00262-024-03841-z [23] Zhou C C,Hu Y P,Arkania E,et al. 152P Exploratory biomarker analysis of phase Ⅲ ASTRUM-004 study: Serplulimab plus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for advanced squamous non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Annals of Oncology,2024,35(S2):S276. [24] Solomon B,Wu L Y,Dziadziuszko R,et al. 1206MO ALINA: Exploratory biomarker analyses in patients (pts) with resected ALK+ non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with adjuvant alectinib vs chemotherapy (chemo)[J]. Annals of Oncology,2024,35(S2):S775. -






 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:


