The Effect of Peptide-prolinyl Isomerase(Pin1)on Lipid Metabolism in Cervical Cancer Cells
-
摘要:
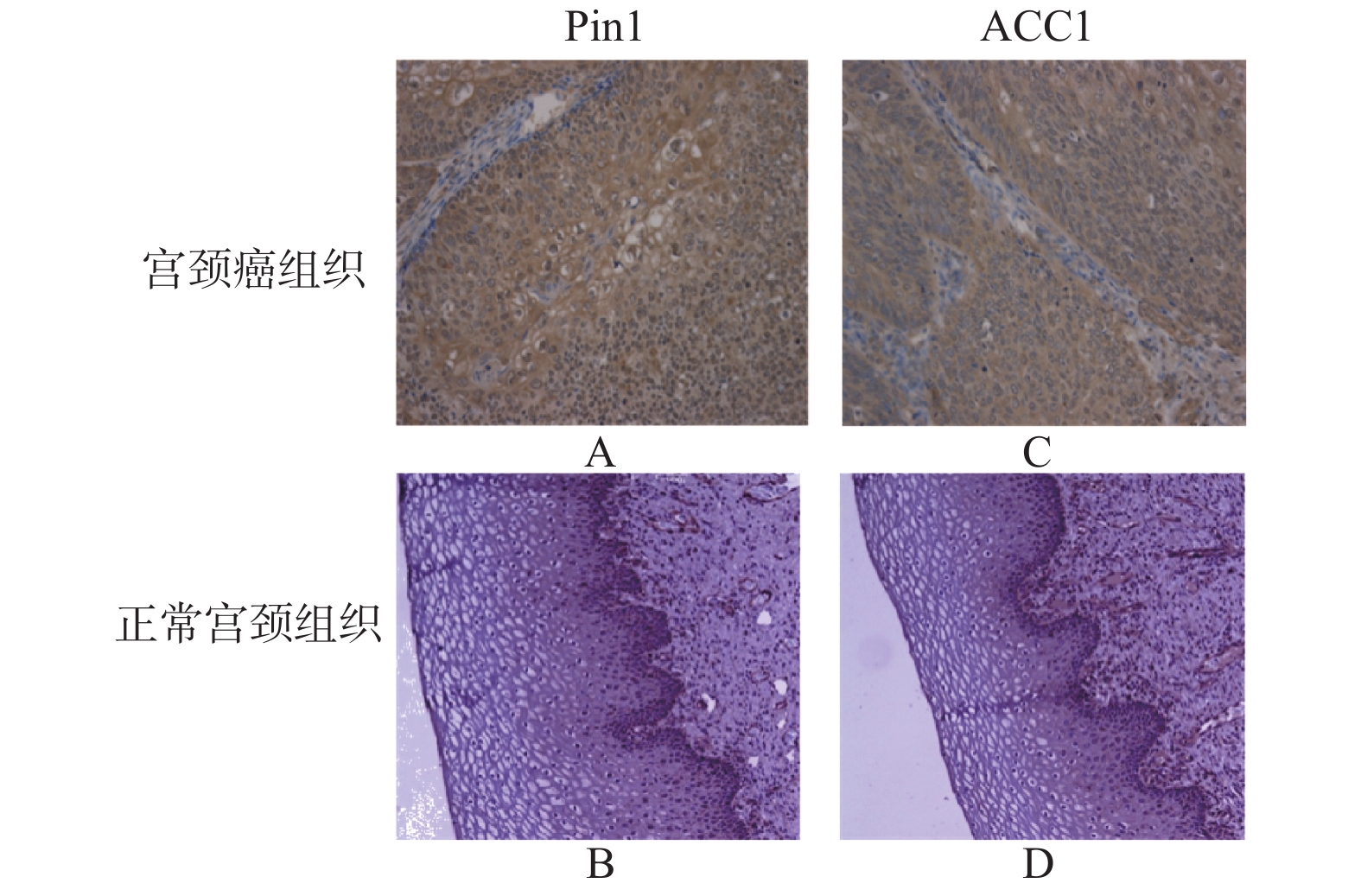
目的 探讨肽基脯氨酰同分异构酶(Pin1)蛋白对宫颈癌细胞脂质代谢的作用。 方法 应用免疫组织化学方法检测Pinl和ACC1蛋白在女性慢性宫颈癌及宫颈癌组织的表达;Western blotting技术和RT-PCR技术检测Pin1基因在宫颈癌SiHa、C33a及H8细胞中的蛋白本底表达情况,采用RNA干扰技术下调子宫颈癌C33a细胞中Pin1的表达;Western blotting技术检测宫颈癌细胞中Pin1蛋白表达水平变化对ACC1蛋白表达的影响;脂溶性荧光染色(BODIPY493/503)观察转染Pin1低表达慢病毒前后宫颈癌细胞中性脂肪含量的变化。 结果 与慢性宫颈炎相比,宫颈癌组织中Pin1和ACC1蛋白表达明显上调(P < 0.05),两者在宫颈癌组织中的表达呈正相关( χ2 = 6.02,P < 0.05)。与C33a细胞相比,SiHa细胞中Pin1蛋白的表达水平较低,故选用C33a细胞转染Pin1低表达慢病毒。C33a细胞转染Pin1低表达慢病毒后,Pin1及ACC1蛋白表达水平明显降低( P < 0.05),与正常对照组和阴性对照组比,转染Pin1低表达慢病毒的细胞内中性脂肪酸含量降低。 结论 Pin1蛋白的表达参与宫颈癌细胞内的脂质代谢,具体调控机制尚待研究。 -
关键词:
- 宫颈癌 /
- 肽基脯氨酰同分异构酶 /
- 脂肪酸合成酶
Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of peptide-based prolinyl isomerase(Pin1)protein on lipid metabolism in cervical cancer cells. Methods The expression of Pinl and ACC1 protein in chronic cervical cancer and cervical cancer tissues was detected by immunohistochemistry. Western blotting and RT-PCR were used to detect the background expression of Pin1 gene in SiHa, C33a and H8 cells of cervical cancer, and RNA interference was used to detect the expression of Pin1 in C33a cells of cervical cancer. The influence of Pin1 protein expression on ACC1 protein expression in cervical cancer cells was detected by Western blotting. Lipid-soluble fluorescence staining(bodipy493/503)was used to observe the changes in the content of neutral fat in cervical cancer cells before and after transfection with low expression of lentivirus Pin1. Results Compared with chronic cervicitis, the expression of Pin1 and ACC1 in cervical cancer tissues was significantly up-regulated(P < 0.05), and the expression of Pin1 and ACC1 in cervical cancer tissues was positively correlated(r = 4.45, P < 0.05). Compared with C33a cells, the expression level of Pin1 protein in SiHa cells was relatively low, so C33a cells were selected for transfection with lentivirus with low Pin1 expression. After the transfection with lentivirus with low Pin1 expression in C33a cells, the protein expression levels of Pin1 and ACC1 were significantly decreased( P < 0.05). Compared with normal control group and negative control group, the content of intracellular neutral fatty acids transfected with lentivirus with low Pin1 expression was decreased. Conclusion The expression of Pin1 protein is involved in lipid metabolism in cervical cancer cells, and the specific regulatory mechanism remains to be studied. -
Key words:
- Cervical cancer /
- Peptide-prolinyl isomerase /
- Fatty acid synthetase
-
表 1 Pinl和ACC蛋白在宫颈相应组织中的表达情况[n(%)]
Table 1. The expression of Pinl and ACC proteins in corresponding cervical tissues[n(%)]
分类 n Pin1 ACC1 阳性 χ2 P 阳性 χ2 P 慢性宫颈组织 30 9(30) 94.471 0.0000 11(36.67) 45.274 0.000 CSCC组织 64 59(92.18)* 50(78.13)* 与慢性宫颈炎组织比较,*P < 0.05。 表 2 Pin1与ACC1表达水平的相关性分析
Table 2. Correlation analysis of expression levels of Pin1 and ACC1
Pin1 ACC1 χ2 P + − + 10 45 6.02 0.014 − 5 4 表 3 宫颈癌细胞中Pin1 mRNA的相对表达量(
$\bar x \pm s $ )Table 3. The relative expression of Pin1 mRNA in cervical cancer cells(
$\bar x \pm s $ )基因名 H8 SiHa C33a F P Pin1 0.17 ± 0.069* 1.0 ± 0.67 1.43 ± 0.26 91.997 0.000 与正常宫颈上皮细胞比较,*P < 0.05。 -
[1] Lu K,Hanes S,Hunter T. A human peptidyl-prolyl isomerase essential for regulation of mitosis[J]. Nature,1996,380(6574):544-547. doi: 10.1038/380544a0 [2] Cheng C,Tse E. PIN1 in Cell Cycle Control and Cancer[J]. Frontiers in pharmacology,2018,9(26):1367. [3] Yun H,Kim J,Kim G,et al. Prolyl-isomerase Pin1 impairs trastuzumab sensitivity by up-regulating fatty acid synthase expression[J]. Anticancer Research,2014,34(3):1409-1416. [4] Hanahan D,Weinberg R. Hallmarks of cancer:the next generation[J]. Cell,2011,144(5):646-674. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013 [5] Huang F,Han S,Xing B,et al. Targeted inhibition of fascin function blocks tumour invasion and metastatic colonization[J]. Nature Communications,2015,6(17):7465. [6] Takahashi K,Uchida C,Shin R,et al. Prolyl isomerase,Pin1:new findings of post-translational modifications and physiological substrates in cancer,asthma and Alzheimer's disease[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences:CMLS,2008,65(3):359-375. doi: 10.1007/s00018-007-7270-0 [7] Bao L,Kimzey A,Sauter G,et al. Prevalent overexpression of prolyl isomerase Pin1 in human cancers[J]. The American Journal of Pathology,2004,164(5):1727-1737. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63731-5 [8] Suen K,Lin C,Seiler C,et al. Phosphorylation of threonine residues on Shc promotes ligand binding and mediates crosstalk between MAPK and Akt pathways in breast cancer cells[J]. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology,2018,94(1):89-97. [9] Kozono S,Lin Y,Seo H,et al. Arsenic targets Pin1 and cooperates with retinoic acid to inhibit cancer-driving pathways and tumor-initiating cells[J]. Nature Communications,2018,9(1):3069. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05402-2 [10] Chen Y,Wu Y,Yang H,et al. Prolyl isomerase Pin1:a promoter of cancer and a target for therapy[J]. Cell Death & Disease,2018,9(9):883. [11] Li X,Jiang Y,Meisenhelder J,et al. Mitochondria-Translocated PGK1 Functions as a Protein Kinase to Coordinate Glycolysis and the TCA Cycle in Tumorigenesis[J]. Molecular Cell,2016,61(5):705-719. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.02.009 [12] Han Y,Lee S,Bahn M,et al. Pin1 enhances adipocyte differentiation by positively regulating the transcriptional activity of PPARγ[J]. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology,2016,4369(28):150-158. -






 下载:
下载: