Analysis of the Risk Factors Associated with Vascular Crisis after the Digits Replantation
-
摘要:
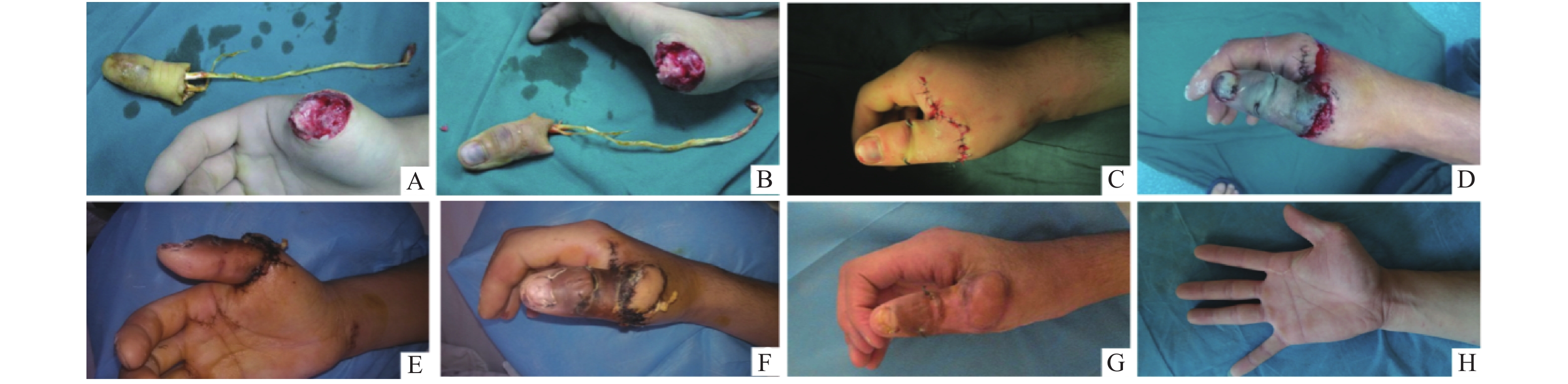
目的 探讨断指再植术后血管危象的相关危险因素,为提高断指再植成活率提供参考。 方法 自2016年1月至2018年12月,对延安大学咸阳医院收治的26例(29指)断指再植患者进行回顾性分析,总结再植成活率并进行功能评估;同时,利用统计学方法对断指再植后血管危险相关危险因素进行分析。 结果 25例(28指)患者获得随访,随访时间9~28月(平均18.4月)。28指中25指成活,末次随访时采用中华医学会手外科学分会断指再植功能评定标准评估优16,良5,可4,差3,优良率75%。未发生血管危象和发生血管危象两组间在受伤-手术时间、有无静脉移植及功能评估方面对比有统计学差异(P < 0.05)。 结论 影响断指再植成活的因素众多,严格缩短受伤至手术的时间并提高静脉移植的质量可降低术后血管危象的发生,提高再植指体成活率。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the risk factors associated with the vascular crisis after the digits replantation and provide the evidence for the improvement of the replantation survival rate. Methods From Jan. 2016 to Dec. 2018, 26 cases(29 digits)suffered by digit amputation were collected and analyzed retrospectively. Survival rate of replantation was summarized and functional evaluation was performed at the last follow-up. Statistical methods were used to analyze the risk factors associated with vascular crisis after digits replantation. Results 25 cases(28 digits)were followed up and the follow-up period raged from 9 to 28 months(mean 18.4 months). 25 cases(28 digits)survived during the last follow-up, and the standard evaluation of digits replantation function of Chinese medical association hand surgery branch was used to evaluate the function. 16 digits function was excellent, 5 digits good, 4 digits better and 3 digits poor, and the rate of excellent and good was 75%. There were statistically significant differences between the vascular crisis group and non-vascular crisis group during the process of injury-operation time, vein transplantation and functional evaluation(P < 0.05). Conclusion There are many factors affecting the survival of digits replantation. Strictly shortening the time interval from injury to operation and improving the quality of vein transplantation can reduce the occurrence of vascular crisis and finally improve the survival rate of the replanted digit. -
Key words:
- Digit amputation /
- Replantation /
- Vascular crisis /
- Survival rate /
- Risk factor
-
表 1 危险因素单因素分析( $\bar{x}\pm s$)
Table 1. Single factor analysis of risk factors( $\bar{x}\pm s$)
项目 危险因素 未发生血管危象 发生血管危象 χ2/t/Z P 性别(n) 男 14 8 0.266 0.606 女 2 2 年龄(岁) − 36.50 ± 12.28 40.10 ± 12.31 0.712 0.483 损伤原因 切割伤 13 7 1.706 0.426 挤压伤 3 2 撕脱伤 0 1 受伤-手术时间(h) ≤6 12 1 10.798 0.005* ≤12 3 5 > 12 1 4 有无静脉移植 有 4 10 5.811 0.016* 无 11 4 离断指体 拇指 4 2 1.203 0.878 示指 5 3 中指 3 3 环指 1 2 小指 3 3 功能评估 优 12 4 −3.397 0.001* 良 3 2 可 0 4 差 1 2 两组间危险因素进行比较,*P < 0.05。 -
[1] Chung K C,Yoon A P,Malay S,et al. Patient-reported and functional outcomes after revision amputation and replantation of digit amputations:The franchise multicenter international retrospective cohort study[J]. JAMA surg,2019,154(7):1-10. [2] Shaterian A,Sayadi LR,Tiourin E,et al. Predictors of hand function following digit replantation:Quantitative review and meta-analysis[J]. Hand(NY),2019,4(2):1-7. [3] Reavey PL,Stranix JT,Muresan H,et al. Disappearing digits:Analysis of national trends in amputation and replantation in the United States[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg,2018,141(6):857e-867e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000004368 [4] Tatebe M,Urata S,Tanaka K,et al. Survival rate of limb replantation in different age groups[J]. J Hand Microsurg,2017,9(2):92-94. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1605353 [5] 俆凌锋,伍辉国,张文正. 手部多指完全离断再植的临床应用与体会[J].中华显微外科杂志,2018,41(1):88-90. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-2036.2018.01.024 [6] Cho H E,Zhong L,Kotsis S V,et al. Finger replantation optimization study(FRONT):Update on national trends[J]. J Hand Surg Am,2018,43(10):903-912. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2018.07.021 [7] De Putter C E,Selles R W,Polinder S,et al. Economic impact of hand and wrist injuries:Health-care costs and productivity costs in a population-based study[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Am,2012,94(9):1-7. [8] Bamba R,Malhotra G,Bueno R A,et al. Ring avulsion injuries:A systematic review[J]. Hand(NY),2017,13(1):15-22. [9] 詹倩,贾铮. 断指再植术中血管危象防治的研究现状[J].中外医学研究,2011,09(31):159-160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6805.2011.31.129 [10] 彭俊才,马传亮. 断指再植成活率的影响因素分析[J].海南医学,2013,24(24):3693-3695. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6350.2013.24.1531 [11] 刘飞,梁定顺,张成武,等. 末节断指再植手术成活率的影响因素分析[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2016,38(8):935-938. [12] 苏广炎,张飞. 断指再植手术成活相关因素分析及临床分析[J].中国继续医学教育,2016,8(7):91-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9308.2016.07.061 [13] Shaterian A,Rajaii R,Kanack M,et al. Predictors of digit survival following replantation:Quantitative review and meta-analysis[J]. J Hand Microsurg,2018,10(2):66-73. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1626689 [14] 何雨生,石武祥,翁雨雄,等. 断指再植成活率影响因素的Logistic回归分析[J].中华手外科杂志,2015,31(5):369-372. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1005-054X.2015.05.022 [15] 王昌义,汪翔. 断指再植手术成活相关因素分析及临床对策[J].医学专业,2013,15(1):92-93. [16] 孙迎放,杜振翠,杨金章,等. 断指再植术后局部镇痛、抗痉挛的临床应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2004,6(11):1315-1316. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-7600.2004.11.041 -






 下载:
下载: