The Prevalence and Related Factors of Malocclusion on 3-to 5 Years-old Children with Primary Dentition in Kunming
-
摘要:
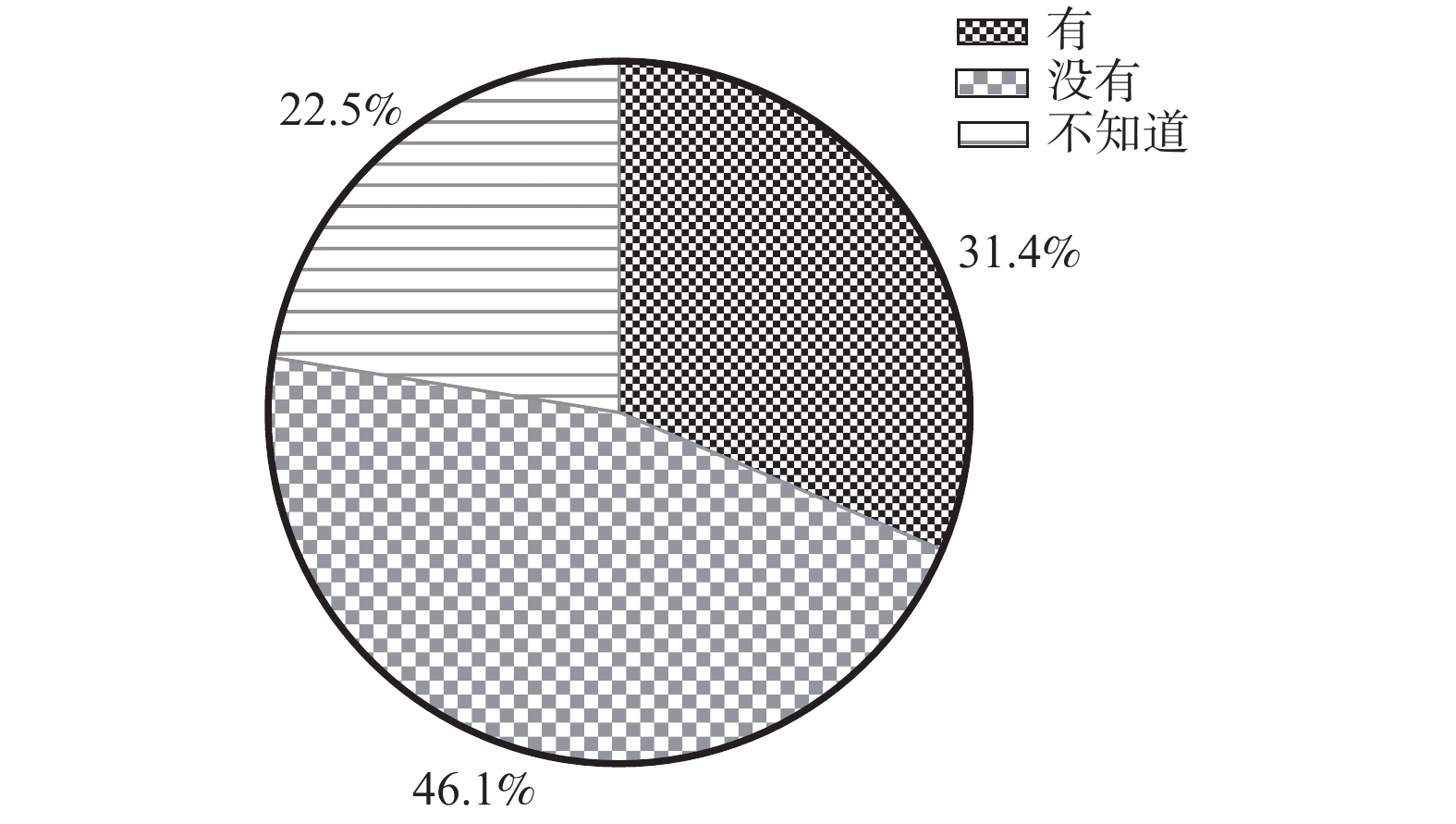
目的 调查昆明市3~5岁儿童乳牙列错畸形患病状况,了解家长对儿童乳牙列错畸形的认知及态度,探讨昆明市儿童乳牙列错畸形患病状况及相关因素。 方法 采用多阶段分层随机抽样的方法,随机抽取昆明市3~5岁480名儿童进行咬合检查及龋病状况检查,并通过问卷调查,了解家长对儿童错畸形的认知和态度。采用SPSS 25.0统计软件对数据进行描述性分析、单因素χ2分析,并将单因素分析中具有统计学意义的因素进行二元Logistic回归分析,分析其影响因素。 结果 共430名3~5岁儿童纳入调查。错畸形患病率为69.3%,其中错畸形中深覆占比最高(82.2%),其次为深覆盖(24.5%),切占比最低(0.7%)。单因素分析中,喂养方式、遗传因素与乳牙列错畸形患病间存在相关性(P < 0.05),夜磨牙、咬物不良习惯分别与深覆、深覆盖患病存在相关性( P < 0.05)。二元Logistic回归分析结果中夜磨牙是乳牙列错畸形患病的危险因素(OR = 1.256, P < 0.05)。家长问卷结果显示仅有31.4%家长关注儿童咬合问题。 结论 昆明市3~5岁儿童乳牙列错畸形患病率高,多种因素与乳牙列错畸形患病相关,家长对儿童咬合问题关注不足。 Abstract:Objective The aim of this study is to assess the malocclusion status, the risk factors and the parental awareness about deciduous malocclusion among 3-to-5-year-old children in Kunming. Methods Multistage stratified random sampling method was conducted to examine the occlusion and caries status of 480 3-to-5-year-old children in Kunming. Information of the parental awareness on malocclusion was collected using a questionnaire. Data were analyzed by the Chi-square test and binary logistic regression analysis. Results 430 children were recruited, the prevalence of malocclusion was 69.3%. Among them, the most common type of malocclusion was deep overbite(82.2%), followed by deep overjet(24.5%), and the minimum prevalence was the edge-to-edge occlusion(0.7%). And there was a significant difference between the feeding methods and the prevalence of malocclusion(P < 0.05). In genetic, there was a significant difference between crossbite and genetic( P < 0.05). As to oral bad habits, there was a correlation between the biting habit and deep overjet, and between the bruxism and deep overbite( P < 0.05). The results of binary logistic regression analysis showed that the bruxism was a risk factor of deciduous malocclusion(OR = 1.256, P < 0.05). The result of parental questionnaire showed that merely 31.4% of parents payed attention to children's occlusal problem. Conclusion The prevalence of malocclusion is high among 3-to-5-year-old childrein with primary dentition in Kunming. Many factors are related to malocclusion of primary dentition. And parents pay less attention to the children's occlusion. -
Key words:
- Primary dentition /
- Malocclusion /
- Related factors /
- Attention
-
表 1 昆明市3~5岁儿童乳牙列不同类型错畸形构成情况
Table 1. Composition of malocclusion in different types of primary dentition in aged 3-5 years children in Kunming
类型 患病人数(n) 构成比(%) 深覆 245 82.2 深覆盖 73 24.5 前牙反覆 39 13.1 后牙反覆 6 2.0 反覆盖 45 15.1 开 6 2.0 切 2 0.7 表 2 乳牙列错畸形与相关因素单因素分析[n(%)]
Table 2. Chi-square analysis between malocclusion of primary dentition and related factors[n(%)]
变量 分类 n 错畸形 χ2/z P 性别 男 220 159(37.0) 1.868 0.172 女 210 139(32.3) 经济发展区 一级区 255 171(39.8) 1.591 0.451 二级区 128 92(21.4) 三级区 47 35(8.1) 年龄组 3岁 163 115(26.7) 0.204 0.903 4岁 180 123(28.6) 5岁 87 60(14.0) 孩子父亲学历 大学以下 177 115(26.7) 2.652 0.103 大学或以上 253 183(42.6) 孩子母亲学历 大学以下 181 118(27.4) 2.481 0.115 大学或以上 249 180(41.9) 家庭月收入 9000元以下 267 181(42.1) 0.757 0.384 9001元以上 163 117(27.1) 喂养方式 母乳喂养 148 94(21.9) 8.048 0.018 * 奶瓶喂养 73 60(14.0) 两者都有 209 144(33.5) 龋齿 无 174 129(30.0) 3.212 0.073 有 256 169(39.3) 口腔不良习惯 有 192 141(73.4) 2.788 0.058 没有 238 157(66.0) 夜磨牙 有 48 34(7.9) 4.232 0.027* 没有 382 211(49.1) 家人是否地反 有 26 23(5.3) 4.775 0.029* 没有 404 275(64.0) 组间比较,*P < 0.05。 -
[1] Shen L,He F,Zhang C,et al. Prevalence of malocclusion in primary dentition in Mainland of China,1988-2017:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Sci Rep,2018,8(1):1-10. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17765-5 [2] Santos P M,Gonçalves A R,Marega T. Validity of the psychosocial impact of dental aesthetics questionnaire for use on Brazilian adolescents[J]. Dental Press J Orthod,2016,21(3):67-72. doi: 10.1590/2177-6709.21.3.067-072.oar [3] Woon S C,Thiruvenkatachari B. Early orthodontic treatment for class III malocclusion:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop,2017,151(1):28-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2016.07.017 [4] 杨灵,谭泽飞. 昆明区域经济发展问题研究[J].农业开发与装备,2017,4(1):62. [5] Zhou Z,Liu F,Shen S,et al. Prevalence of and factors affecting malocclusion in primary dentition among children in Xi’ an,China[J]. BMC Oral Health,2016,16(1):91-102. doi: 10.1186/s12903-016-0285-x [6] Björk A,Krebs A,Solow B. A Method for epidemiological registration of malocculusion[J]. Acta Odontologica Scandinavica,1964,22(1):27-41. doi: 10.3109/00016356408993963 [7] Foster T,Hamilton M. Occlusion in the primary dentition. Study of children at 2 and one-half to 3 years of age[J]. Br Dent J,1969,126(2):76-79. [8] Organization W H. Oral health surveys: basic methods: World Health Organization[M]. France: World Health Organization, 2013: 43. [9] Charchut S W,Allred E N,Needleman H L. The effects of infant feeding patterns on the occlusion of the primary dentition[J]. J Dent Child (Chic),2003,70(3):197-203. [10] G ó is E G,Vale M P,Paiva Sm,et al. Incidence of malocclusion between primary and mixed dentitions among Brazilian children:A 5-year longitudinal study[J]. Angle Orthod,2012,82(3):495-500. doi: 10.2319/033011-230.1 [11] Kirzioglu Z,Simsek S,Yilmaz Y. Longitudinal occlusal changes during the primary dentition and during the passage from primary dentition to mixed dentition among a group of Turkish children[J]. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent,2013,14(2):97-103. doi: 10.1007/s40368-013-0014-y [12] Dimberg L,Lennartsson B,Arnrup K,et al. Prevalence and change of malocclusions from primary to early permanent dentition:a longitudinal study[J]. Angle Orthod,2015,85(5):728-734. doi: 10.2319/080414-542.1 [13] Bilgiç F,Gelgör İ E. Prevalence of temporomandibular dysfunction and its association with malocclusion in children:An epidemiologic study[J]. J Clin Pediatr Dent,2017,41(2):161-165. doi: 10.17796/1053-4628-41.2.161 [14] 傅民魁,张丁,王邦康,等. 中国 25392 名儿童与青少年错畸形患病率的调查[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2002,37(5):371-373. doi: 10.3760/j.issn:1002-0098.2002.05.017 [15] 黄桂月,刘波,陈梅红,等. 昆明市乳牙列错牙合畸形发病率的调查研究[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2017,44(2):141-143. doi: 10.7518/gjkq.2017.02.004 [16] Baccetti T,Franchi L,Mc Namara Jr J A. Longitudinal growth changes in subjects with deepbite[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop,2011,140(2):202-209. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2011.04.015 [17] Stahl F,Grabowski R. Orthodontic findings in the deciduous and early mixed dentition-inferences for a preventive strategy[J]. J Orofac Orthop,2003,64(6):401-416. doi: 10.1007/s00056-003-0313-8 [18] Silveira L M D,Prade L S,Ruedell A M,et al. Influence of breastfeeding on children's oral skills[J]. Rev Saude Publica,2013,47(1):37-43. doi: 10.1590/S0034-89102013000100006 [19] 傅民魁. 口腔正畸学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2012: 47-48. [20] Yu-lou T,Jie L,Fang Y. A study on the relationship between OTX1 and hereditary bone crossbite deformity[J]. Journal of China Medical University,2011,40(8):715-718. [21] De Oliveira B F,Seraidarian P I,de Oliveira S G,et al. Tooth displacement in shortened dental arches:A three-dimensional finite element study[J]. J Prosthet Dent,2014,111(6):460-465. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2013.07.022 [22] Zhang S,Lo E C M,Chu C H. Occlusal features and caries experience of Hong Kong chinese preschool children:A cross-sectional study[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health,2017,14(6):621-629. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14060621 [23] Zhou X,Zhang Y,Wang Y et al. Prevalence of Malocclusion in 3-to 5-year-old children in Shanghai,China[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health,2017,14(3):328-338. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14030328 -






 下载:
下载: