Clinical Features of Rhupus Syndrome
-
摘要:
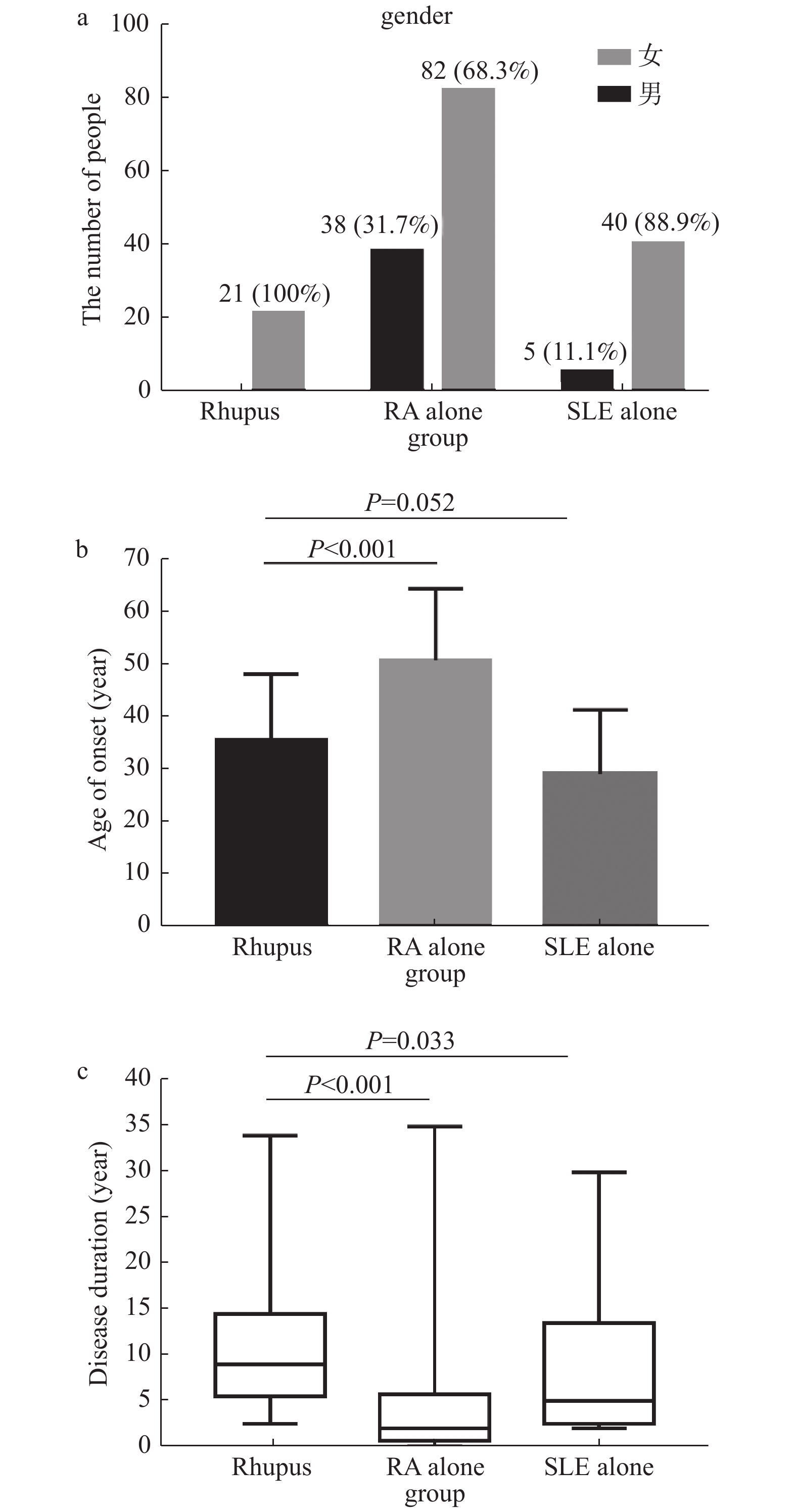
目的 探讨Rhupus综合征的临床特点。 方法 收集2015年1月至2019年12月昆明医科大学第二附属医院风湿免疫科21例Rhupus综合征患者(Rhupus组)资料,并随机抽取同期住院的无合并SLE的120例RA患者(RA组)及无合并RA的45例SLE患者(SLE组)作为对照组,比较三组临床特点。 结果 21例Rhupus综合征患者均为女性,61.9%以RA起病,起病年龄小于RA组,与SLE组比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),病程均长于对照组。与RA组相比,手关节炎、多关节炎、对称性关节炎的发生率和RF阳性率的差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);骨侵蚀、关节畸形、类风湿结节的发生率高于RA组,抗CCP、AKA、APF抗体的阳性率则低于RA组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。与SLE组相比,Rhupus组面部红斑的发生率低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);多浆膜腔积液、肾脏及血液系统受累的发生率及ANA、抗dsDNA抗体的阳性率的差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。 结论 Rhupus综合征多以RA起病,关节炎表现重,ANA、抗CCP抗体及RF阳性率较高,有助于诊断。 Abstract:Objective To analyse the clinical features of Rhupus syndrome. Methods The medical records of 21 Rhupus syndrome patients who were admitted to the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from 2015 to 2019 were analysed retrospectively. One hundred and twenty RA patients and 45 SLE patients from our Unit were randomly selected as the controls. The data of patients in the three groups were compared. Results Twenty-one patients with Rhupus syndrome were female, 61.9% patients were initiallypresented with RA. The age of onset was significantly younger than that of RA (P < 0.05), but similar to that of SLE. Rhupus patients had longer diseaseduration than control groups.As compared with RA patients, Rhupus patients had higher incidence of bone erosion, joint defornlity and rheumatoid nodules, lower anti-CCP, AKA and APF antibodies positivity (P < 0.05). There were no significant differences in the incidence of hand arthritis, polyarthritis, symmetrical arthritis and RF positivity (P > 0.05). As compared with SLE patients, Rhupus patients had less malar erythema while no differences were observed in serositis, kidney, hematological involvement and ANA, anti-dsDNA antibody positivity (P > 0.05). Conclusions Most of the Rhupus patients are firstly presented with RA and with severe arthritis. The positivity of ANA, anti-CCP and RF arehigh, are helpful to the diagnosis. -
Key words:
- Rhupus syndrome /
- Systemic lupus erythematosus /
- Rheumatoid arthritis /
- Overlap syndrome
-
表 1 Rhupus与未合并系统性红斑狼疮的类风湿关节炎患者临床特点比较[n(%)]
Table 1. Comparison of the clinical featurs between rhupus and RA alone[n(%)]
项目 Rhupus组(n = 21) RA组(n = 120) χ2 P 手关节炎 21(100) 117(97.5) − 1.000 多关节炎 21(100) 119(99.1) − 1.000 对称性关节炎 21(100) 109(90.8) − 0.370 关节肿胀 14(66.7) 101(84.2) 3.639 0.056 晨僵 2(9.5) 42(35) 5.403 0.021 关节畸形 8(38.1) 20(16.7) 5.157 0.023 骨侵蚀 21(100) 70(58.3) 13.558 < 0.001 类风湿结节 2(9.5) 1(0.8) 6.482 0.011 肺间质病变 3(14.3) 11(9.1) 0.524 0.694 肺动脉高压 1(4.8) 10(8.3) 0.317 0.701 抗CCP阳性 13(62.0) 107(89.2) 10.479 0.001 抗AKA阳性 4(19.0) 56(46.7) 5.577 0.018 抗APF阳性 6(28.6) 68(56.7) 5.657 0.017 RF阳性 16(76.2) 97(80.8) 0.242 0.623 RF-IgG阳性 4(19.0) 24(20) 0.010 0.920 RF-IgM阳性 17(81.0) 88(73.3) 0.546 0.460 红细胞沉降率升高 17(81.0) 110(91.7) 2.294 0.130 C反应蛋白升高 8(38.1) 97(80.8) 17.170 < 0.001 注:RA:类风湿关关节炎,AKA:抗角蛋白抗体,CCP:抗环瓜氨酸多肽,APF:抗核周因子,RF:类风湿因子。 表 2 Rhupus与未合并类风湿关节炎的系统性红斑狼疮患者临床特点比较[n(%)]
Table 2. Comparison of the clinical featurs between rhupus and SLE alone[n(%)]
项目 Rhupus组(n = 21) SLE组(n = 45) χ2 P 面部红斑 3(14.3) 18(40.0) 4.364 0.037 口腔溃疡 6(28.6) 5(11.1) 2.011 0.156 脱发 2(9.5) 14(31.1) 3.633 0.057 多浆膜腔积液 5(23.8) 15(33.3) 0.615 0.433 肾功能不全 3(14.3) 1(2.4) 1.565 0.211 狼疮性肾炎 8(38.1) 19(42.2) 0.101 0.751 肾病综合征 1(4.8) 5(11.1) − 0.656 神经系统损害 0(0) 8(17.8) 2.743 0.098 白细胞降低 10(47.6) 12(26.7) 2.829 0.093 贫血 14(66.7) 19(42.2) 3.422 0.064 血小板降低 4(19.0) 7(15.6) − 0.733 ANA阳性 20(95.2) 44(97.8) − 0.538 抗dsDNA阳性 8(38.1) 17(37.8) 0.001 0.980 抗Sm阳性 6(28.6) 13(28.9) 0.001 0.979 抗心磷脂抗体阳性 2(9.5) 7(15.6) 0.078 0.779 抗β2糖蛋白抗体阳性 3(14.3) 6(13.3) 0.011 0.916 抗核糖体P蛋白抗体阳性 4(19.0) 19(42.2) 3.387 0.066 补体C3降低 12(57.1) 37(82.2) 4.709 0.030 注:SLE:系统性红斑狼疮;ANA:抗核抗体;dsDNA:双链DNA;Sm:Smith。 -
[1] As J,Lupus H S J. The definition for coexistent rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Lupus,1995,4(2):166-168. [2] Iaccarino L,Gatto M,Bettio S,et al. Overlap connective tissue disease syndromes[J]. Autoimmunity Reviews,2013,12(3):363-373. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2012.06.004 [3] Petri M,Orbai A M,Alarc¨®N G S,et al. Derivation and validation of the systemic lupus international collaborating Clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Arthritis Rheum,2012,64(8):2677-2686. doi: 10.1002/art.34473 [4] Aletaha D,Neogi T,Silman A J,et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria:an american college of rheumatology/european league against rheumatism collaborative initiative[J]. Arthritis Rheum,2010,62(9):2569-2581. doi: 10.1002/art.27584 [5] Aletaha D,Wang X,Zhong S,et al. Differences in disease activity measures in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who achieved DAS,SDAI,or CDAI remission but not boolean remission[J]. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism,2020,50(2):276-284. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2019.09.005 [6] Bajema I M,Wilhelmus S,Alpers C E,et al. Revision of the International society of nephrology/renal pathology society classification for lupus nephritis:clarification of definitions,and modified national institutes of health activity and chronicity indices[J]. Kidney International,2018,93(4):789-796. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2017.11.023 [7] Shovman O,Langevitz P,SHOENFELD Y. Rhupus;unusual presentations[J]. Clin Rheumatol,2015,34(12):2041-2046. doi: 10.1007/s10067-015-2978-y [8] J L,H W,X H,et al. Clinical analysis of 56 patients with rhupus syndrome:manifestations and comparisons with systemic lupus erythematosus:a retrospective case-control study[J]. Medicine(Baltimore),2014,93(10):e49. [9] Liu T,Li G,MU R,et al. Clinical and laboratory profiles of rhupus syndrome in a Chinese population:a single-centre study of 51 patients[J]. Lupus,2014,23(9):958-963. doi: 10.1177/0961203314526439 [10] Tani C,D'aniello D,Dellesedie A,et al. Rhupus syndrome:assessment of its prevalence and its clinical and instrumental characteristics in a prospective cohort of 103 SLE patients[J]. Autoimmunity Teviews,2013,12(4):537-541. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2012.09.004 [11] S G,S D,TA K,et al. Organising pneumonia in rhupus syndrome[J]. BMJ Case Rep,2019,12(12):e232326. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2019-232326 [12] Panagopoulos P K,Lambrou G I. Bone erosions in rheumatoid arthritis:recent developments in pathogenesis and therapeutic implicatio ns[J]. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact,2018,18(3):304-319. [13] Aurell Y,Andersson M,Forslind K. Cone-beam computed tomography,a new low-dose three-dimensional imaging technique for assessment of bone erosions in rheumatoid arthritis:reliability assessment and comparison with conventional radiography - a BARFOT study[J]. Scand J Rheumatol,2018,47(3):173-177. doi: 10.1080/03009742.2017.1381988 [14] Hallert E,Björk M,Dahlström O,et al. Disease activity and disability in women and men with early rheumatoid arthritis(RA):an 8-year foll owup of a Swedish early RA project[J]. Arthritis Care Res(Hoboken),2012,64(8):1101-1107. [15] Tian M,Song X,Dong L,et al. Systematic evaluation of different doses of cyclophosphamide induction therapy for lupus nephritis[J]. Medicine(Baltimore),2017,96(51):e9408. [16] 张桌莉. 吗替麦考酚酯在自身免疫病治疗中应用的风湿病专家共识[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志,2019,23(7):436-440. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-7480.2019.07.002 [17] Zengin O,Onder M E,Sarica M A,et al. Systemic vasculitis in a patient with rhupus syndrome[J]. Reumatismo,2015,67(4):161-164. [18] Zaman S,Rahim M A,Sayami L A,et al. Libman-sacks endocarditis in a Bangladeshi patient suffering from rhupus[J]. Trop Doct,2019,49(4):309-311. doi: 10.1177/0049475519854623 [19] Nizami M F,Sharma C B,Guria R T,et al. A rare case of rhupus syndrome with hashimoto's thyroiditis,associated adverse effect of drugs and i ncidental findings[J]. J Family Med Prim Care,2019,8(9):3048-3050. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_568_19 -






 下载:
下载: