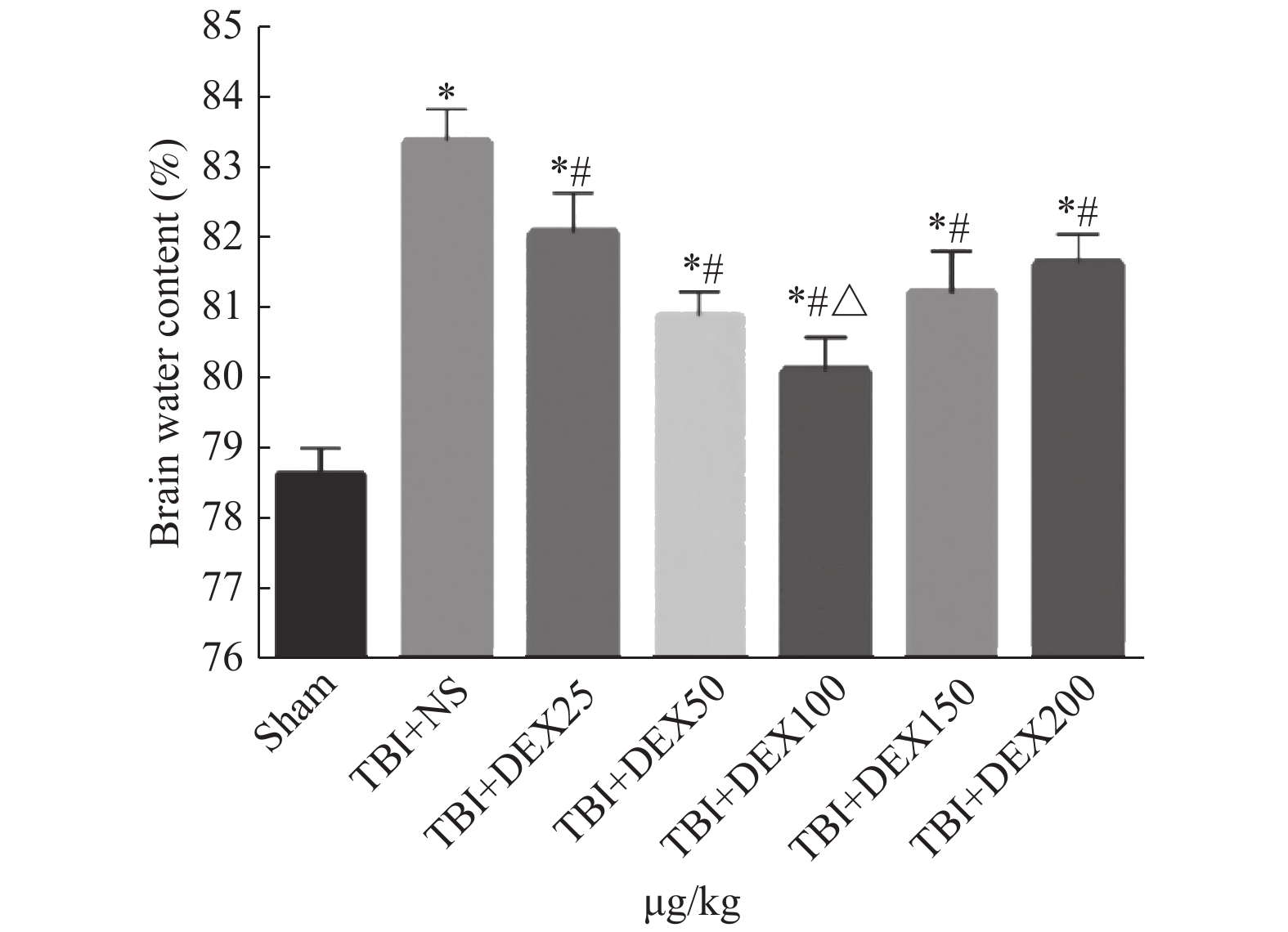
|
[1]
|
Liu J, Xiong X, Sui Y. Isoliquiritigenin attenuates neuroinflammation in traumatic brain injury in young rats[J]. Neuroimmunomodulation,2019,26(2):102-110. doi: 10.1159/000495467
|
|
[2]
|
Ghaffarpasand F, Torabi S, Rasti A, et al. Effects of cerebrolysin on functional outcome of patients with traumatic brain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment,2019,15(1):127-135.
|
|
[3]
|
Pearn M L, Niesman I R, Egawa J, et al. Pathophysiology associated with traumatic brain injury: current treatments and potential novel therapeutics[J]. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology,2017,37(4):571-585. doi: 10.1007/s10571-016-0400-1
|
|
[4]
|
Li G, Yang Y, Dong H J, et al. The research progress of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of traumatic brain injury[J]. Turkish Neurosurgery,2017,28(3):696-702.
|
|
[5]
|
Jha R M, Kochanek P M, Simard J M. Pathophysiology and treatment of cerebral edema in traumatic brain injury[J]. Neuropharmacology,2019,145(Pt B):230-246.
|
|
[6]
|
刘瑞宁, 金晓晴, 赵剡. 创伤性脑损伤继发性损伤机制研究进展[J]. 临床急诊杂志,2017,18(11):875-879.
|
|
[7]
|
Xu X, Jiang R, Gong P, et al. Up-regulation of FOS-like antigen 1 contributes to neuronal apoptosis in the cortex of rat following traumatic brain injury[J]. Metabolic Brain Disease,2018,33(1):115-125. doi: 10.1007/s11011-017-0129-7
|
|
[8]
|
Anderson M A, Huang D, Roberts A. Targeting BCL2 for the treatment of lymphoid malignancies[J]. Seminars in Hematology,2014,51(3):219-227. doi: 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2014.05.008
|
|
[9]
|
Keating G M. Dexmedetomidine: A review of its use for sedation in the intensive care setting[J]. Drugs,2015,75(10):1119-1130. doi: 10.1007/s40265-015-0419-5
|
|
[10]
|
Jiang W W, Wang Q H, Liao Y J, et al. Effects of dexmedetomidine on TNF-α and interleukin-2 in serum of rats with severe craniocerebral injury[J]. BMC Anesthesiology,2017,17(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12871-017-0410-7
|
|
[11]
|
Cai Y, Xu H, Yan J, et al. Molecular targets and mechanism of action of dexmedetomidine in treatment of ischemia/reperfusion injury[J]. Molecular Medicine Reports,2014,9(5):1542-1550. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2034
|
|
[12]
|
Jiang T, Yang W, Zhang H, et al. Hydrogen sulfide ameliorates lung ischemia-reperfusion injury through sirt1 signaling pathway in type 2 diabetic rats[J]. Frontiers in Physiology,2020,11(1):596.
|
|
[13]
|
Kida Y, Goligorsky M S. Sirtuins, cell Senescence, and vascular aging[J]. The Canadian Journal of Cardiology,2016,32(5):634-641. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2015.11.022
|
|
[14]
|
Han D, Wang J, Ma S, et al. SIRT1 as a promising novel therapeutic target for myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury and cardiometabolic disease[J]. Current Drug Targets,2017,18(15):1746-1753.
|
|
[15]
|
Feeney D M, Boyeson M G, Linn R T, et al. Responses to cortical injury: i. methodology and local effects of contusions in the rat[J]. Brain Research,1981,211(1):67-77. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90067-6
|
|
[16]
|
Shen M, Wang S, Wen X, et al. Dexmedetomidine exerts neuroprotective effect via the activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in rats with traumatic brain injury[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy Biomedecine & Pharmacotherapie,2017,95(11):885-893.
|
|
[17]
|
Zhang X, Chen Y, Jenkins L W, et al. Bench-to-bedside review: Apoptosis/programmed cell death triggered by traumatic brain injury[J]. Critical Care (London, England),2005,9(1):66-75.
|
|
[18]
|
Stoica B A, Faden A I. Cell death mechanisms and modulation in traumatic brain injury[J]. Neurotherapeutics: the Journal of the American Society for Experimental NeuroTherapeutics,2010,7(1):3-12. doi: 10.1016/j.nurt.2009.10.023
|
|
[19]
|
Shamas-Din A, Brahmbhatt H, Leber B, et al. BH3-only proteins: Orchestrators of apoptosis[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta,2011,1813(4):508-520. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.11.024
|
|
[20]
|
王艳雪. 右美托咪定通过SIRT1信号通路抑制创伤性脑损伤大鼠神经细胞凋亡的研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明医科大学硕士论文, 2019.
|






 下载:
下载: