Clinical Effects of Posterior Decompression Combined with Unilateral Fixation in Treatment of Single-segmentalcervical Spondylotic Radiculopathy
-
摘要:
目的 探讨后路单侧减压固定治疗单节段神经根型颈椎病的初期临床疗效。 方法 回顾性分析昆明市第一人民医院甘美医院骨科自2016年1月至2018年12月收治的26例经后路单侧减压固定治疗的神经根型颈椎病患者的临床资料。其中,男16例,女10例,年龄39~62岁,平均50.5岁,手术节段C6/77例、C5/612例、C4/57例。评估手术时间、术中出血量,术前及末次随访时颈椎神经根性疼痛视觉模拟(VAS)评分,术前及末次随访时颈椎功能残障指数量表(NDI)评分、术后颈椎病疗效Odom评级、术后2 d及末次随访时颈椎椎间隙高度(DH)、手术并发症情况、术后影像学检查神经受压改善情况。 结果 26例患者均获得随访,随访16~25个月,平均(18.1±4.8)个月。平均手术时间(76.9±12.8) min;术中出血量(87.3±14.3) mL;术前根性疼痛VAS评分平均(6.9±0.8)分,术后末次随访时间根性疼痛VAS评分平均(1.4±0.6)分,术前与术后根性疼痛VAS评分比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);术前NDI评分平均(32.4±4.3)分,末次随访时间NDI评分平均(16.3±6.7)分;术后2 d平均DH为(5.8±0.6) mm,末次随访平均DH为(5.7±0.4) mm,两者比较差异无统计学意义( P > 0.05);术后颈椎病疗效Odom评级优8例(30.8%),良14例(53.8%),可4例(15.4%),优良率为84.6%。术后未出现感染、固定物松动、椎动脉损伤等并发症。 结论 经后路单侧减压固定治疗单节段神经根型颈椎病初期疗效良好,对于侧方椎间盘突出并有神经根管狭窄的神经根型颈椎病,可以作为除前路手术外的另一选择。 Abstract:Objective To explore the initial clinical effect of posterior unilateral decompression and fixation for single-segment cervical spondylosis. Methods We retrospectively analyzed the clinical data of 26 patients with cervical spondylotic radiculopathy treated by unilateral decompression and fixation by posterior approach from January 2016 to December 2018. Among them, there were 16 males and 10 females, aged 39-62 years old, with an average age of 50.5 years. The surgical segment included 7 cases in C6/7, 12 cases in C5/6, and 7 cases in C4/5. Then we evaluated the operation time, intraoperative blood loss, visual analogue (VAS) score of cervical radiculopathy before operation and last follow-up, cervical spine functional disability index (NDI) score before operation and last follow-up, and Odom rating of postoperative cervical spondylopathy, 2 days after operation and at the last follow-up, the height of the cervical intervertebral space (DH), surgical complications, and the improvement of postoperative imaging examination of nerve compression. Results All 26 patients were followed up for 16-25 months, with an average of (18.1±4.8) months. The average operation time was (76.9±12.8) min; intraoperative blood loss was (87.3±14.3) mL; average preoperative radicular pain VAS score was (6.9±0.8) points, average postoperative radicular pain VAS score was (1.4±0.6). There were significant differences in radicular pain VAS scores between the preoperation and postoperation (P < 0.05); the preoperative NDI score was (32.4±4.3) points, and (16.3±6.7) points at the last follow-up. After operation 2 days, the DH average was (5.8±0.6) mm, and (5.7±0.4) mm at the last follow-up. There was no statistically significant difference between the two groups ( P > 0.05). The postoperative cervical spondylosis efficacy Odom rating was excellent in 8 cases (30.8%), 14 cases were good (53.8%), 4 cases were fair (15.4%), and the excellent and good rate was 84.6%. There were no complications such as infection, internal fixation loose, and vertebral artery injury. Conclusions The posterior unilateral decompression and fixation has a good initial effect in the treatment of single-segment cervical spondylotic radiculopathy. For cervical radiculopathy with lateral disc herniation and nerve root canal stenosis, it can be used as an alternative excluding the anterior surgery. -
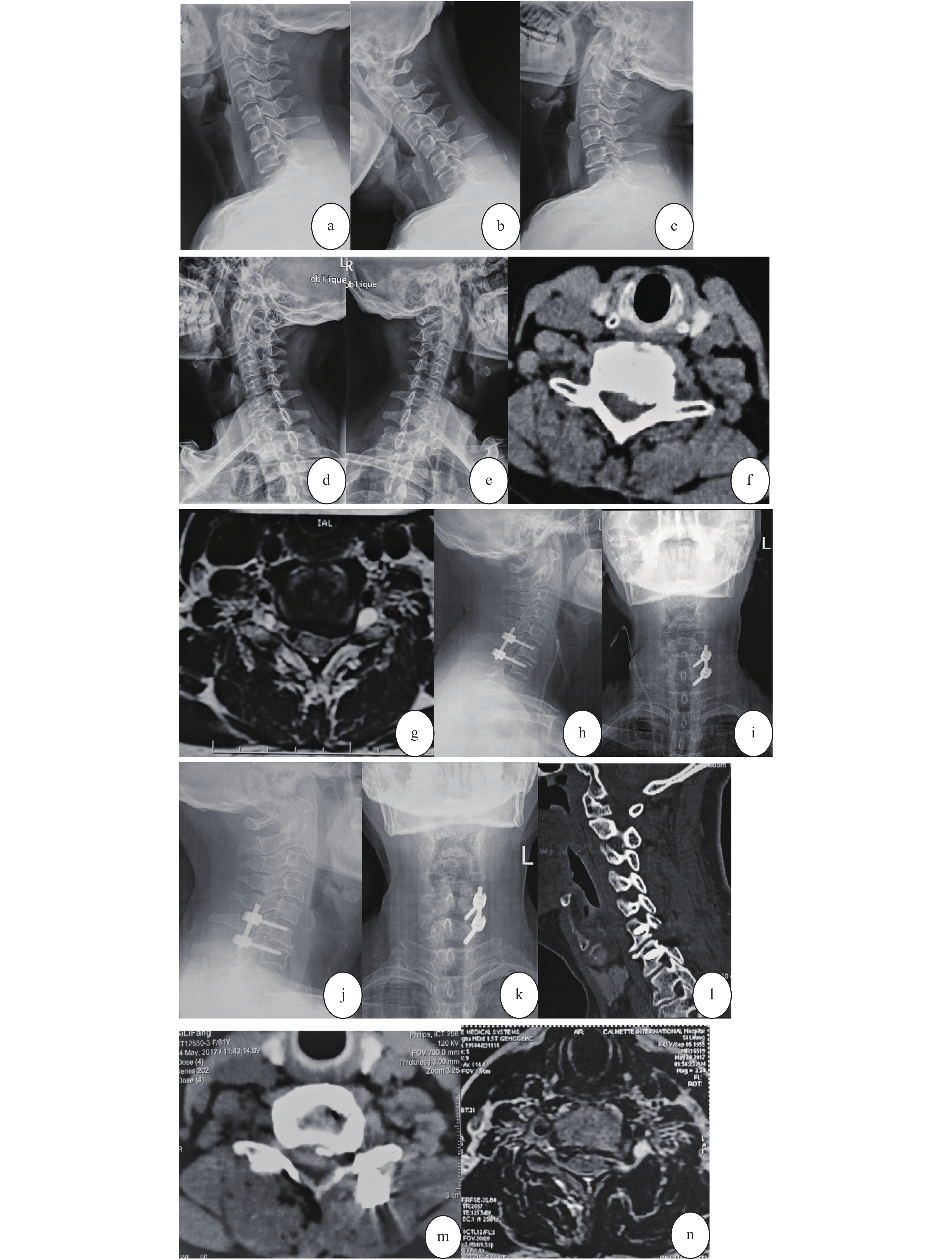
图 1 女,61岁。反复颈肩痛3 a加重伴左手麻木、无力2周入院。诊断:神经根型颈椎病(C6/7)
a~e:术前颈椎侧位、过屈过伸位及左右斜位X线片示:颈椎生理屈度变直;C6/7节段失稳,左侧后方钩锥关节处骨赘形成并椎间孔狭窄;f~g:术前颈椎CT、MRI示:C6/7左侧神经根明显受压;h~i:术后2 d颈椎正侧位X线示:颈椎生理曲度恢复正常,C6/7椎间高度及椎弓根钉固定良好;j~n:术后18个月颈椎正侧位X线、二维CT重建及横轴位CT、MRI示:颈椎生理曲度正常,C6/7椎间高度及内固定良好,同术后2 d;C6/7左侧减压充分,神经根管通畅。
Figure 1. Female,61 years old. She had repeated neck and shoulder pain for 3 years,and was admitted to hospital for 2 weeks with aggravated left hand numbness and weakness. Diagnosis:Cervical Spondylopathy of Nerve Root Type (C6/7)
表 1 术前、末次随访神经根性疼痛VAS评分、颈部疼痛NDI评分[(
$ \bar x \pm s$ ),n = 26]Table 1. VAS score for radiculopathy and NDI score for neck pain before operation and last follow-up[(
$ \bar x \pm s$ ),n = 26]指标 术前 末次随访 t P VAS评分 6.9 ± 0.76 1.4 ± 0.9△ 20.6 < 0.05 NDI评分 32.4 ± 4.3 16.3 ± 6.7△ 9.4 < 0.05 与术前比较,△P < 0.05。 -
[1] Balasa A, Bielecki M, Prokopienko M, et al. Lateral approach for recurrent unilateral cervical radiculopathy after anterior discectomy with fusion report of two cases[J]. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne,2019,14(2):348-352. [2] Foster M T, Carleton Bland N P, Lee M K, et al. Comparison of clinical outcomes in anterior cervical discectomy versus foraminotomy for brachialgia[J]. Br J Neurosurg,2019,33(1):3-7. doi: 10.1080/02688697.2018.1527013 [3] Scholz T, Geiger M F, Mainz V, et al. Anterior cervical decompression and fusion or posterior foraminotomy for cervical radiculopathy: Results of a single-center series[J]. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg,2018,79(3):211-217. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1607225 [4] Zheng X, Chaudhari R, Wu C, et al. Subaxial cervicalpedicle screw insertion with newly defined entry point and trajectory: accuracyevaluation in cadavers[J]. Eur Spine J,2010,19(1):105-120. doi: 10.1007/s00586-009-1213-4 [5] 王铭麒, 陈旭, 高浩然, 等. 经皮内镜下颈椎间盘切除术治疗颈椎病的研究进展[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2019,29(2):174-179. [6] 吕京懋. 颈椎后路椎间孔切开减压术治疗神经根型颈椎病的研究进展[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019,34(5):553-555. doi: 10.7531/j.issn.1672-9935.2019.05.042 [7] Peolsson A, Peolsson M. Predictive factors for long-term outcome of anterior cervical decompression and fusion: a multivariate data analysis[J]. Eur Spine J,2008,17(3):406-414. doi: 10.1007/s00586-007-0560-2 [8] Korinth M C, Krüger A, Oertel M F, et al. Posterior foraminotomy or anterior discectomy with polymethyl methacrylate interbody stabilization for cervical soft disc disease: results in 292 patients with monoradiculopathy[J]. Spine (Phila Pa 1976),2006,31(11):1207-1214. doi: 10.1097/01.brs.0000217604.02663.59 [9] 韩伟峰, 林欣, 李小光, 等. 颈椎病前路手术减压范围标志的解剖学研究[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2009,27(4):375-378. [10] Matsumoto M, Okada E, Ichihara D, et al. Anterior cervical decompression and fusion accelerates adjacent segment degeneration: comparison with asymptomatic volunteers in a ten-year magnetic resonance imaging follow-up study[J]. Spine (Phila Pa 1976),2010,35(1):36-43. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181b8a80d [11] Koç R K, Menkü A, Tucer B, et al. Anterior cervical foraminotomy for unilateral spondylotic radiculopathy[J]. Minim Invasive Neurosurg,2004,47(3):186-189. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-818497 [12] Suh B K, You K H, Park M S. Can axial pain be helpful to determine surgical level in the multilevel cervical radiculopathy[J]. J Orthopaedic Surgery,2017,25(1):309-405. [13] Chang J C, Park H K, Choi S K. Posterior cervical inclinatory foraminotomy for spondylotic radiculopathy preliminary[J]. J Korean Neurosurg Soc,2011,49(5):308-313. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2011.49.5.308 -






 下载:
下载: