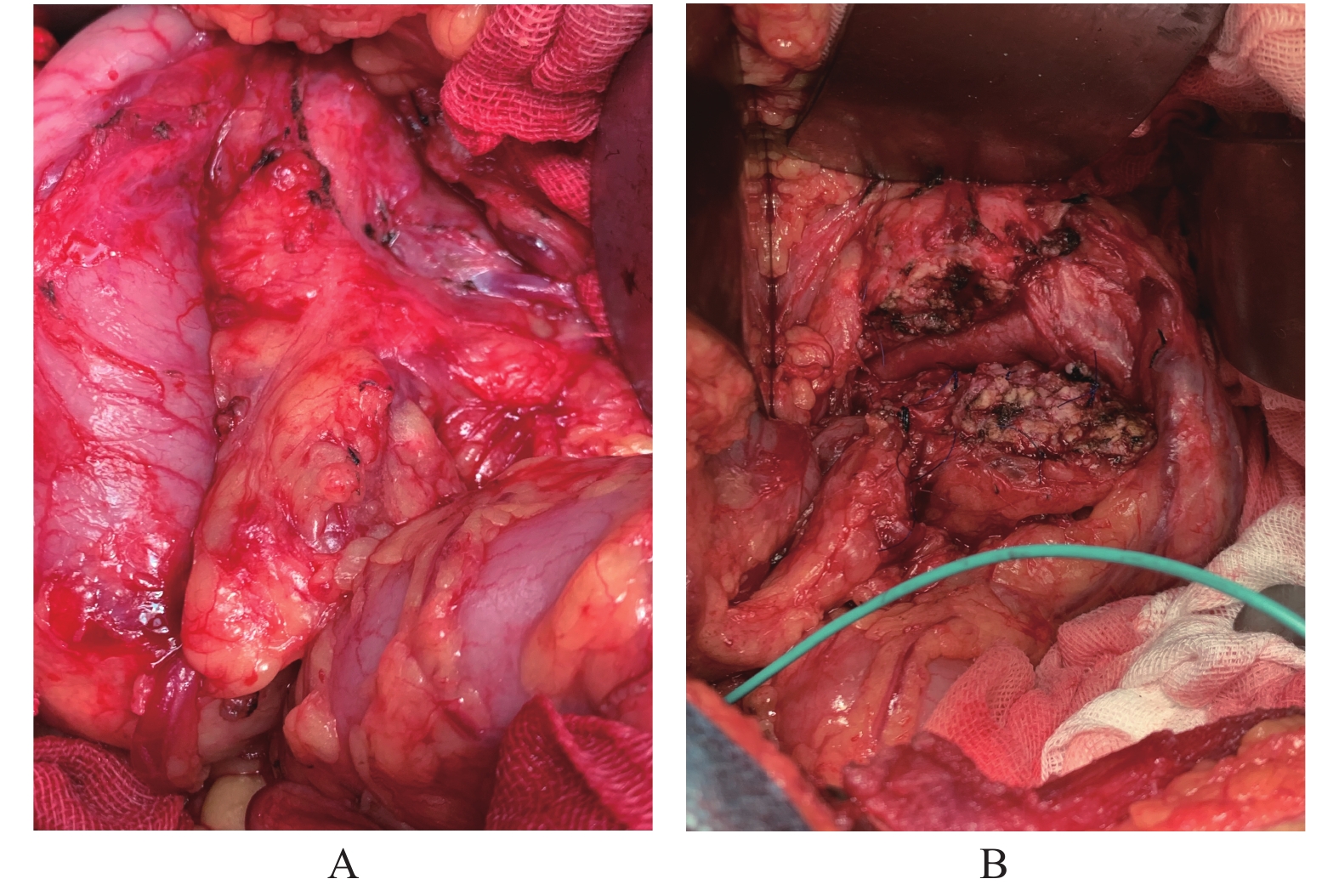
Clinical Application of Modified Beger Operation
-
摘要:
目的 探讨改良Beger手术的临床应用价值。 方法 回顾性分析2014年1月至2020年1月临沧市人民医院肝胆外科收治行手术治疗的59例慢性胰腺炎、胰头良性及低度恶性肿瘤患者的临床资料,其中胰头肿块型慢性胰腺炎49例,胰头囊肿合并胰管结石3例,胰头实性假乳头状瘤2例,导管内乳头状黏液性肿瘤2例,胰头浆液性囊腺瘤2例,胰头黏液性囊腺瘤1例。随机分为改良Beger手术组和胰十二指肠切除术(PD)组,其中行改良Beger手术31例,胰十二指肠切除术(PD)28例。比较两组的手术时间、术中出血、术后住院时间并发证发生率、疼痛缓解有效率行装。 结果 改良Beger手术组和PD组比较,手术时间、术中出血、术后住院时间、术后并发症发生率、疼痛缓解有效率分别为(231.4±42.3/268.1±52.5)min、(405.5±64.1/449.9±61.2)mL、(17.1±3.4/28.5±4.1)d、(12.9/42.9)%、(89.7/88.9)%。56例(Beger组29例,PD组27例)患者,差异无统计学意义(P < 0.05)术后获随访6个月~5 a,无肿瘤或结石复发。 结论 改良Beger手术切除胰腺组织少、手术创伤小、能缩短术后住院埋间,减少术后并发症、对缓解顽固性腹痛确切、患者术后生存质量及营养状况明显改善。是一种可选择的手术方式。 -
关键词:
- 慢性胰腺炎 /
- 保留十二指肠胰头切除术 /
- 胰十二指肠切除术
Abstract:Objective To investigate the clinical application value of modified Beger operation. Methods The clinical data of 59 patients with chronic pancreatitis, benign and low-grade malignant tumor of pancreatic head treated by surgery from January 2014 to January 2020 were retrospectively analyzed, Among them, there were 49 cases of mass type chronic pancreatitis in the head of pancreas, 3 cases of cyst with pancreatic duct stones, 2 cases of solid pseudopapillary tumor, 2 cases of intraductal papillary mucinous tumor, 2 cases of serous cystadenoma and 1 case of mucinous cystadenoma. They were randomly divided into modified beger operation group and pancreatoduodenectomy (PD) group. Among them, 31 cases underwent modified beger operation and 28 cases underwent pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD). Results For patients in the modified beger operation group and PD group, the operation time, intraoperative bleeding, postoperative hospital stay, incidence of postoperative complications and pain relief efficiency were(231.4 ± 42.3/268.1 ± 52.5)min, (405.5 ± 64.1 / 449.9 ± 61.2)mL, (17.1 ± 3.4 / 28.5 ± 4.1)d, (12.9 / 42.9)% and (89.7 / 88.9)%, respectively. 56 cases (29 cases in Beger group and 27 cases in PD group) were followed up for 6 months to 5 years without recurrence of tumor or stone. Conclusion The modified Beger operation has the advantages of less pancreatic tissue resection, less surgical trauma, safer operation, faster recovery, more accurate relief of intractable abdominal pain, and significant improvement of postoperative quality of life and nutritional status of patients. -
表 1 两组一般资料比较(
$ \bar x \pm s$ )Table 1. Comparison of the general data between two groups (
$\bar x \pm s $ )项目 Beger组(n = 31) PD组(n = 28) t/χ2 P 男/女(n) 23/8 21/7 210.06 0.25 年龄(岁) 43.7 ± 3.1 44.2 ± 2.7 0.843 0.20 疾病谱[n(%)] 胰头肿块型慢性胰腺炎 26(83.9) 23(82.1) 202.21 0.11 胰头囊肿合并胰管结石 2(6.5) 1(3.6) 18.34 0.19 胰头实性假乳头状瘤 1(3.2) 1(3.6) 45.54 0.33 导管内乳头状黏液瘤 1(3.2) 1(3.6) 3.19 0.46 胰头浆液性囊腺瘤 1(3.2) 1(3.6) 11.51 0.29 长期酗酒史(n) 27 25 146.04 0.27 并存疾病(n) 2.96 0.31 糖尿病 16 17 高血压病 7 9 冠心病 7 5 表 2 两组手术相关指标比较(
$\bar x \pm s $ )Table 2. Comparison of surgical indicators between the two groups (
$ \bar x \pm s$ )指标 Beger组(n = 31) PD组(n = 28) t/χ2 P 手术时间(min) 231.4 ± 42.3 268.1 ± 52.5 2.98 0.06 术中出血量(mL) 405.5 ± 64.1 449.9 ± 61.2 13.18 0.08 术后住院时间(d) 17.1 ± 3.4 28.5 ± 4.1 −17.85 < 0.001 术后并发症[n(/%)] 4/12.9 12/42.9 5.31 0.01 术后出血 0 2 胰漏 3 2 胆漏 1 1 不全性肠梗阻 0 3 非计划再次手术 0 2 胃瘫 0 2 新发脂肪泻(n) 2 3 0.77 0.07 新发糖尿病(n) 2 2 0.85 0.92 疼痛缓解(n) 有效 26 24 1.68 0.79 无变化 3 3 0.91 0.83 -
[1] 庄岩,杨尹默. Beger手术—回顾与展望[J]. 中华肝脏外科手术学电子杂志,2017,6(1):6-9. doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3232.2017.01.002 [2] Beger H G,Mayer B,Rau B M. Parenchyma-sparing,limited pancreatic head resection for benign tumors and low-risk periampullary cancera systematic review[J]. J Gastrointest Surg,2016,20(1):206-217. doi: 10.1007/s11605-015-2981-2 [3] 崔铭,廖泉. 胰腺假性囊肿治疗方式选择[J]. 中华肝脏外科手术学电子杂志,2016,5(6):355-357. doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3232.2016.06.004 [4] Beger H G,Krautzberger W,Bittner R,et al. Duodenum-preserving resection of the head of the pancreas in patients with severe chronic pancreatitis[J]. Surgery,1985,97(4):467-473. [5] Beger H G,Nakao A,Mayer B,et al. Duodenum- preserving total and partial pancreatic head resection for benign tumors-systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Pancreatology,2015,15(2):167-178. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2015.01.009 [6] Beger H G,Siech M,Poch B,et al. Limited surgery for benign tumours of the pancreas:A systematic review[J]. World J Surg,2015,39(6):1557-1566. doi: 10.1007/s00268-015-2976-x [7] 刘万伟,李恩亮,邬林. Beger手术治疗胰头部浆液性微囊腺瘤1例[J]. 南昌大学学报医学版,2016,56(2):102-103. [8] 王坚,王伟. 胆胰肠结合部疾病的诊治策略[J]. 世界华人消化杂志,2018,26(22):1329-1333. [9] 吴艳艳译. 《2019年国际共识指南:慢性胰腺炎的手术治疗及干预时机》摘译[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志,2020,36(4):764-765. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.04.010 [10] Majumder S,Chari S T. Chronic pancreatitis[J]. Lancet,2016,387(10031):1957-1966. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00097-0 [11] 程坤,孙永辉,林海. 保留胰头的十二指肠切除术与胰十二指肠切除术的远期临床疗效比较:单中心经验分析[J]. 中国普外基础与临床杂志,2020,27(5):1-5. [12] 周松强,田毅峰,赖智德. 保留十二指肠胰头切除术的临床应用探讨[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志,2018,34(1):157-159. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.01.032 [13] 刘嘉哲,黄新余. 保留十二指肠胰头切除术[J]. 肝胆胰外科杂志,2010,22(4):342-348. -






 下载:
下载: