Negative Regulation of hTERT Expression in Cervical Cancer Hela Cell Line by miR-21
-
摘要:
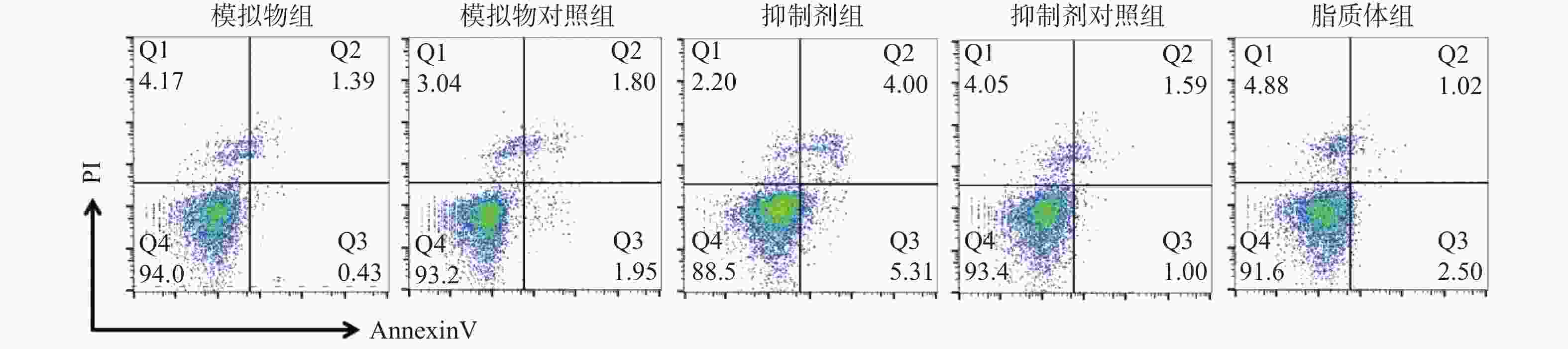
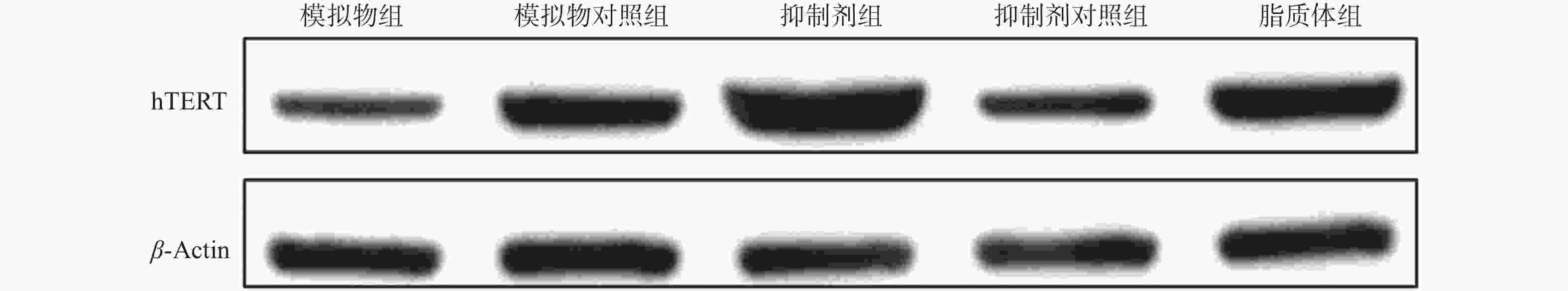
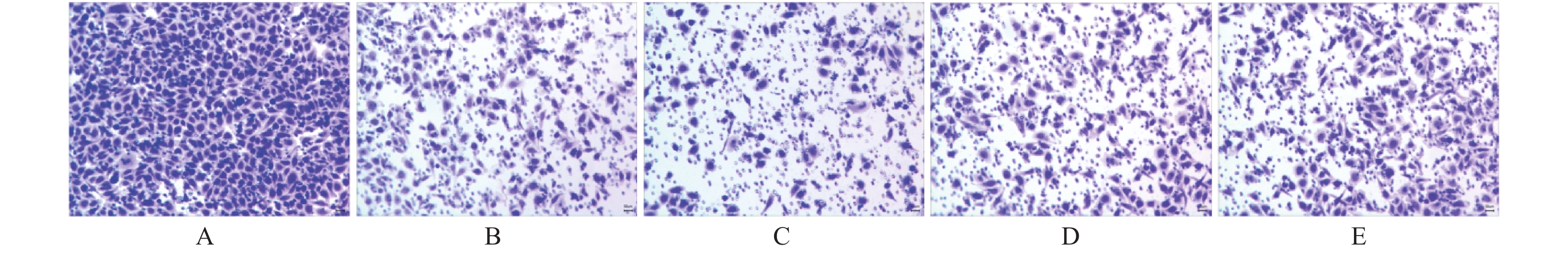
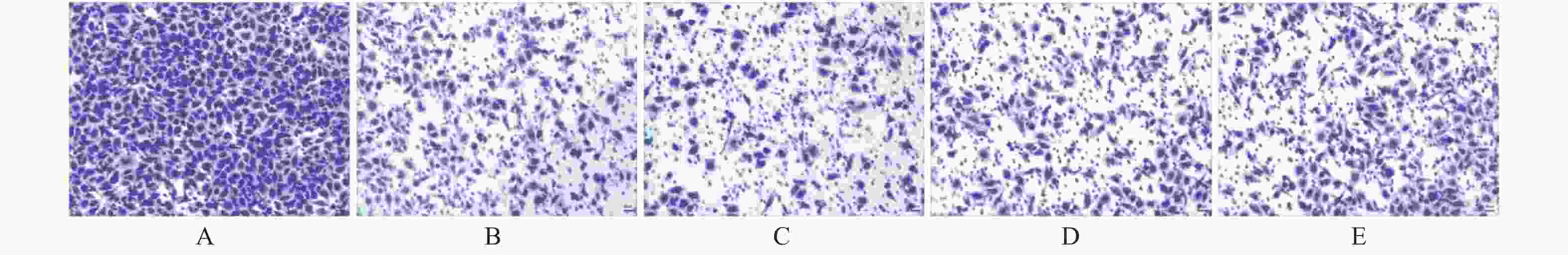
目的 通过观察在miR-21作用下hTERT的表达情况,探讨在宫颈癌HeLa细胞中miR-21对hTERT的调控作用。 方法 利用RT-PCR 法及West Blot 法分别检测HeLa中miR-21 的表达,以及hTERT蛋白的表达情况;通过实验设计,生成miR-21模拟物和 miR-21抑制剂,并分别设立两组的空白对照序列;将空转liposome2000 (lipo2000)设为对照组,利用脂质体 liposome2000包裹宫颈癌细胞株 HeLa并予以转染。在转染后24 h及时检测hTERT及蛋白的表达量。 结果 HeLa细胞株中miR-21及hTERT表达阳性;转染后24 h模拟物组、模拟物对照组、抑制剂组、抑制剂对照组、脂质体组 hTERT mRNA相对表达水平分别为(0.51±0.33)、(0.69±0.19)、(1.33±0.39)、(0.83±0.26)和(0.58±0.16);蛋白相对表达水平分别为(0.41±0.18)、(0.62±0.18)、(1.45±0.60)、(0.83±0.15)和(0.82±0.30);模拟物组与其对照组及脂质体组相比较,hTERT mRNA及蛋白表达情况均较低且差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);相反,在抑制剂组与其对照组及脂质体组相比较中,hTERT mRNA及蛋白表达情况明显升高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。 结论 通过检测发现miR-21及hTERT基因在HeLa细胞株中均呈现高表达状态;miR- 21可以调节hTERT mRNA 和蛋白表达水平,从而发挥负向调控hTERT的作用。 Abstract:Objective To observe the effect of miR-21 on hTERT expression in human cervical cancer Hela cell line, explore the regulatory effect of miR-21 on hTERT. Methods RT-PCR was used to detect the expressions of miR-21 and hTERT mRNA in human cervical cancer Hela cell line. West Blot was used to detect the expression of hTERT protein; miR-21 mimics, miR-21 inhibitor, mimics control and inhibitor control were designed and synthesized, then they were transfected into human cervical cancer Hela cell line after parceled by liposome 2000, blank liposome 2000 was designed as control group. The changes of expressions of hTERT mRNA and protein at 24 hours after transfection were detected. Results miR-21 and hTERT were positive in human cervical cancer Hela cell line; the relative expression levels of hTERT mRNA in mimics group, mimics control group, inhibitor group, inhibitor control group and liposome group at 24 hours after transfection were (0.51±0.33), (0.69±0.19), (1.33±0.39), (0.83±0.26) and (0.58±0.16), respectively; the relative expression levels of hTERT protein were (0.41±0.18), (0.62±0.18), (1.45±0.60), (0.83±0.15) and (0.82±0.30), respectively. The relative expression levels of hTERT mRNA and protein in mimics group were statistically significantly lower than those in mimics control group and liposome group (P < 0.05). The relative expression levels of hTERT mRNA and protein in inhibitor group were statistically significantly higher than those in inhibitor control group and liposome group (P < 0.05). Conclusions miR-21 and hTERT genes are highly expressed in HeLa cell lines. MiR-21 can regulate hTERT mRNA and protein expression levels, thus negatively regulating hTERT. -
Key words:
- miR-21 /
- hTERT /
- Cervical carcinoma /
- Hela /
- Negative regulation
-
表 1 hTERT mRNA 在各组别细胞中的表达情况(
$\bar{x}\pm s$ )Table 1. Expression of hTERT mRNA in different groups of cells (
$\bar{x}\pm s$ )组别 hTERT mRNA t P 模拟物组 0.51 ± 0.33 4.478 0.011 模拟物对照组 0.69 ± 0.19 抑制剂组 1.33 ± 0.39 5.387 0.005 抑制剂对照组 0.83 ± 0.26 脂质体组 0.58 ± 0.16 注:单因素多组间比较(F = 5.403,P = 0.002)。 表 2 hTERT 蛋白在各组别细胞中的表达情况(
$\bar{x}\pm s$ )(1)Table 2. hTERT protein expression in each group of cells (
$\bar{x}\pm s$ )(1)组别 实验结果 t P 模拟物组 0.41 ± 0.18 5.072 0.0071 模拟物对照组 0.62 ± 0.18 抑制剂组 1.45 ± 0.60 5.85 0.0043 抑制剂对照组 0.83 ± 0.15 脂质体组 0.82 ± 0.30 表 2 hTERT 蛋白在各组别细胞中的表达情况(
$\bar{x}\pm s$ )(2)Table 2. hTERT protein expression in each group of cells (
$\bar{x}\pm s$ )(2)组别 hTERT蛋白 t P 模拟物组 0.41 ± 0.18 5.072 0.007 模拟物对照组 0.62 ± 0.18 抑制剂组 1.45 ± 0.60 5.85 0.004 抑制剂对照组 0.83 ± 0.15 脂质体组 0.82 ± 0.30 -
[1] 梁静,张慧杰,张淑兰,等. 妊娠期宫颈上皮内瘤变筛查57例临床分析[J]. 中国计划生育和妇产科,2020,12(1):78-82,88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4020.2020.01.17 [2] 韩钦,郭红燕,耿力. 宫颈癌机会性筛查人群中高危型HPV感染状况及其与宫颈病变关系的研究[J]. 实用妇产科杂志,2018,34(3):194-197. [3] 陈静,刘红敏,居艳梅,等. 氢氧化钠预处理宫颈粘液性标本检测HPV的优越性[J]. 河北医药,2019,41(23):3578-3580,3584. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2019.23.014 [4] Wang F,Huang W,Hu X,et al. Transc-ription factor AP-2β suppresses cervical ca-ncer cell proliferation by promoting the de-gradation of its interaction partner β-catenin[J]. Molecular Carcinogenesis,2017,56(8):1909-1923. doi: 10.1002/mc.22646 [5] Hao M,Zang M,Zhao L,et al. Serum high expression of miR-214 and miR-135b as novel predictor for myeloma bone disease development and prognosis[J]. Oncotarget,2016,7(15):19589-19600. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7319 [6] 陈光治,王晓娟,何燕,等. FOXM1、hTERC与C-myc在HPV阳性宫颈癌筛查意义[J]. 中国计划生育学杂志,2018,26(3):198-201. [7] Maojun Liu,Zining Li,Biao Liang,et al. Hydrogen sulfide ameliorates rat myocardial fibrosis induced by thyroxine through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Endocrine Journal,2018,65(7):769-781. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ17-0445 [8] 袁敏,黄焜,姚立丽,等. 高危型人乳头瘤病毒对宫颈病变治疗后监测临床意义研究[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志,2017,24(4):268-272. [9] Yao T,Lu R,Zhang J,et al. Growth arrest-specific 5 attenuates cisplatin-induced apoptosis in cervica cancer by regulating STAT3 signaling via miR-21[J]. J Cell Physiol,2019,234(6):9605-9615. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27647 [10] Wang Y,Zhou S,Fan K,et al. MicroRNA-21 and its impact on signaling pathways in cervical cancer[J]. Oncol Lett,2019,17(3):3066-3070. [11] 李民,李东儒,孙关,等. 反义miR-21 通过调控hTERT 表达抑制胶质瘤细胞生长[J]. 临床神经外科杂志,2013,10(5):277-280. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7770.2013.05.008 [12] 魏丽惠. 面向加速消除宫颈癌的挑战[J]. 中国妇产科临床杂志,2021,22(1):1-2. [13] 张小燕,黄娟,李晓丽. 宫颈癌组织中miRNA-21表达与其发展及预后的关系[J]. 实用癌症杂志,2020,35(11):1790-1792,1796. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5930.2020.11.013 [14] 徐建萍,叶丽君,喻长法,等. miR-34a和miR-21在宫颈癌中的表达及其临床意义[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志,2020,30(11):1281-1283. [15] 郑永波,刘佳渝,段李梅,等. miR-199b-3p通过靶向PLCε抑制前列腺癌细胞的恶性增殖[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报,2020,42(05):803-811. [16] Hammou R A,Kasmi Y,Ennaji M M. A computational approach to the study of interactions between proteins and miR10-b,miR-335,and miR-21 involved in breast cancer[J]. Contemp Oncol(Pozn),2019,23(4):220-225. [17] Bica-Pop C,Cojocneanu-Petric R,Magdo L,et al. Overview upon miR-21 in lung cancer:focus on NSCLC[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci,2018,75(19):3539-3551. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2877-x [18] Choi P J,Oskouian R J,Tubbs R S. The current understanding of microRNA's therapeutic,diagnostic,and prognostic role in chordomas: A review of the literature[J]. Cureus,2018,10(12):e3772. [19] Qiu Y F,Wang M X,Meng L N,et al. MiR-21 regulates proliferation and apoptosis of oral cancer cells through TNF-alpha[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci,2018,22(22):7735-7741. [20] 苏俊玲,乌云,杨文静,等. miR-21通过负调节CYLD表达促进宫颈癌增殖[J]. 中国生育健康杂志,2019,30(06):534-540. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-878X.2019.06.008 [21] Xu L,Wu Z,Chen Y,et al. Micro RNA-21(miR-21)regulates cellular proliferation,invasion,migration,and apoptosis by targeting pten,reck and Bcl-2 in lung squamous carcinoma,gejiu city,China[J]. PLoS One,2014,9(8):e103698. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103698 [22] Yao Q,Xu H,Zhang Q Q,et al. MicroRNA-21 promotes cell proliferation and down-regulates the expression of programmed cell death 4(PDCD4)in HeLa cervical carcinoma cells[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2009,388(3):539-542. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.08.044 [23] 王金华. 膀胱癌诊断及预后相关肿瘤标志物的研究进展[D]. 重庆: 重庆医科大学硕士学位论文, 2018. [24] Zhao Y,Cheng D,et al. Dual roles of c-Myc in the regulation of hTERT gene[J]. Nucleic Acids Res,2014,42(16):10385-10398. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku721 [25] 李春琳,张红平,王应海,等. hTERT基因多态性与宫颈癌前病变关联性研究[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志,2019,26(18):1323-1328. [26] Bachand F,Autexier C. Functional regions of human telomerase reverse transcriptase and human telomerase RNA required for telomerase activity and RNA-protein interactions[J]. Molecular and Cellular Biology,2001,21(5):1888-1897. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.5.1888-1897.2001 -





 下载:
下载: