Evaluation of Analysis Performance of Automatic Biochemical Analyzer in Detecting Serum Lipoprotein A
-
摘要:
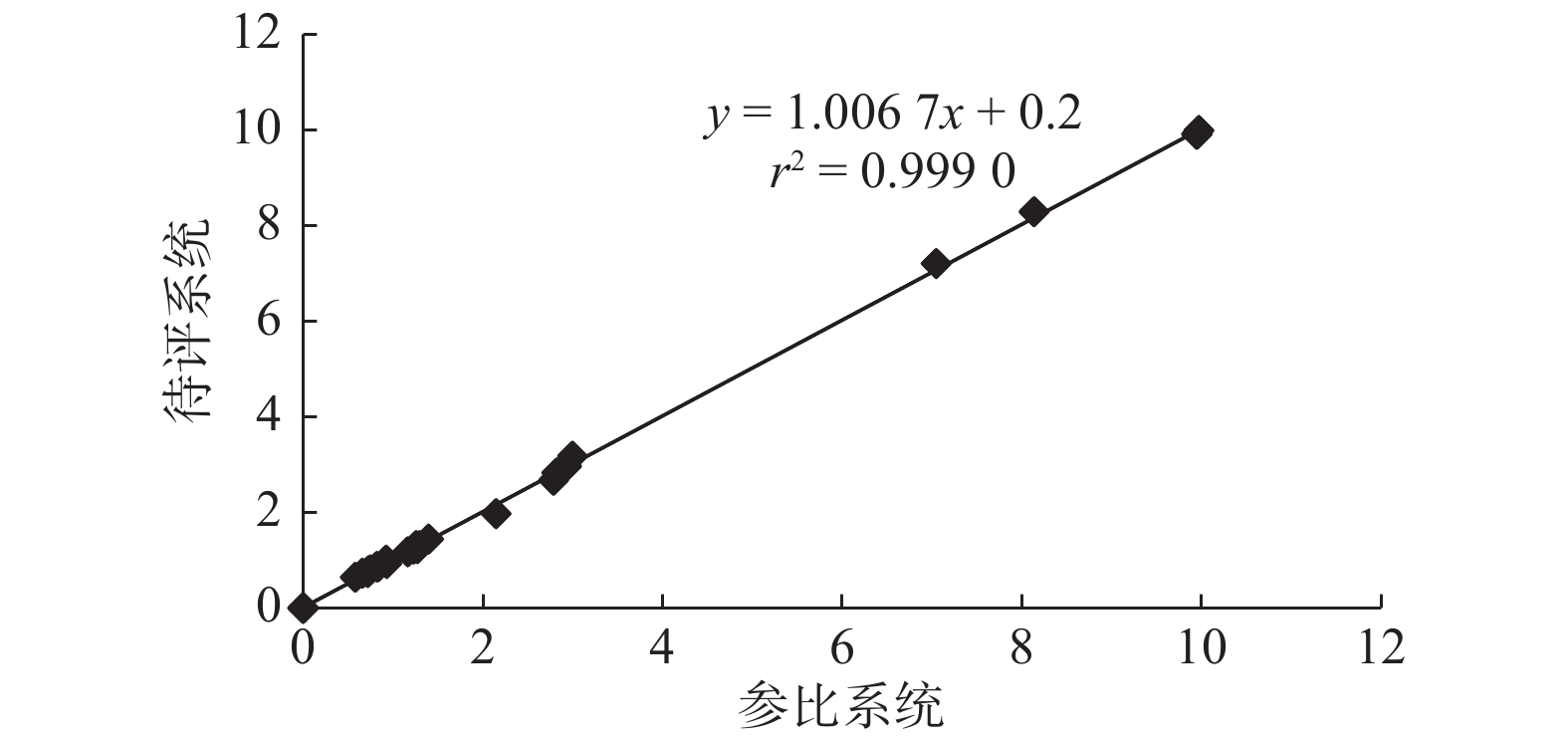
目的 对在雅培C16000全自动生化分析仪上用胶乳凝集比浊法检测血清脂蛋白a[LP(a)]的分析性能进行评价,判断其是否能满足临床需求。 方法 参考国际、国内有关性能评价的文件和行业标准,结合工作实际从精密度、正确度、分析测量范围、临床可报告范围、抗干扰性能以及生物参考区间几个方面进行评价。 结果 LP(a)在质控水平1、2和混合血清样本中的批内不精密度分别为1.44%、0.45%、0.91%,批间不精密度分别为1.67%、0.81%、1.23%,都低于厂商声明的标准;与已通过ISO15189实验室认可的其他实验室相同检测系统进行样本的比对,相关系数r2为0.9990;分析测量范围在11.0~919.0 mg/L之间;最大允许稀释倍数为10倍,最高可报告范围可扩展到9 190.0 mg/L;采用商品化的干扰物质检测结果显示,游离胆红素20 mg/dL以下、结合胆红素20 mg/dL以下、乳糜浊度3 000 FTU以下、血红蛋白500 mg/dL以下对LP(a)测定结果检测干扰的偏移量都小于10%,这些浓度的物质对LP(a)的检测结果干扰很小;以40例健康体检人群样本验证实验室引用的参考区间,验证通过。 结论 雅培全自动生化分析仪测定LP(a)的分析性能与厂家声明基本一致,能够满足临床需求,可以应用于临床。 Abstract:Objective To evaluate the assay performance of automatic biochemical analyzer in detecting serum lipoprotein A [LP(a)] by using latex agglutination-turbidimetry on a(Abbott C16000), so as to evaluate whether it can meet clinical requirements. Methods According to international and domestic performance evaluation documents and industry standards, the evaluation was carried out from the aspects of precision, accuracy a, analytical measurement range, clinical reportable range, anti-interference performance and biological reference range. Results The intra-batch imprecisions of LP(a)were 1.44%, 0.45% and 0.91% at quality control level 1, 2 and mixed serum samples, and the inter-batch imprecisions were 1.67%, 0.81% and 1.23%, respectively, which were lower than the standard declared by the manufacturer. The correlation coefficient R2 was 0.9990 when comparing the samples with the same testing system approved by ISO15189 laboratory. The analytical measurement range was 11.0-919.0 mg/L. The maximum allowable dilution was 10 times, and the maximum reportable range was extended to 9190.0 mg/L. Commercial interference substance detection results showed that the deviation of free bilirubin was less than 20 mg/dL, binding bilirubin was less than 20 mg/dL, chylous turbidity was less than 3 000 FTU, hemoglobin was less than 500 mg/dL on the detection result of LP(a)was less than 10%, indicating that these concentrations of substances had little interference on the detection result of LP(a). The reference interval cited by the laboratory was verified by 40 healthy population samples. Conclusion The analytical performance of automatic biochemical analyzer in detecting LP(A)is basically consistent with the manufacturer's statement, which can meet the clinical requirements and can be applied in clinical practice. -
Key words:
- Lipoprotein A /
- Automatic biochemical analyzer /
- Performance evaluation
-
表 1 精密度实验结果(
$\bar x \pm s$ )Table 1. Precision test results(
$\bar x \pm s$ )样本 批内不精密度 批间不精密度 均值 ± 标准差
(mg/L)变异系数
(%)均值 ± 标准差
(mg/L)变异系数
(%)质控1 124.8 ± 1.8 1.44 124.7 ± 2.08 1.67 质控2 425.8 ± 1.9 0.45 422.2 ± 3.42 0.81 混合血清 229.9 ± 2.1 0.91 230.3 ± 2.84 1.23 表 2 定值校准品测定结果(mg/L)
Table 2. Determination results of fixed calibrators (mg/L)
校准品水平 定值 测定均值 偏差(%) 允许偏差(%) S1 122 124.00 1.63 12.5 S2 420 425.67 1.35 12.5 S3 940 932.38 −0.81 12.5 表 3 临床可报告范围实验结果(mg/L)
Table 3. Clinical report range of experimental results (mg/L)
稀释倍数 结果1 结果2 结果3 均值 实测值 理论值 偏差(%) 2 374 382 374 376.7 753.4 795.0 5.23 4 184 168 68 173.3 693.3 795.0 12.8 8 92 90 86 89.3 714.4 795.0 10.1 10 72 72 76 73.3 733.3 795.0 7.8 20 30 32 33 31.7 634.0 795.0 20.3 表 4 不同浓度干扰物对正常浓度LP(a)检测的干扰(%)
Table 4. Interference of different concentration interferences to the detection of normal concentration LP(a)(%)
干扰物质 浓度1 浓度2 浓度3 浓度4 浓度5 游离型胆红素 0.0 −0.7 0.5 0.8 1.0 结合型胆红素 0.3 −0.3 0.8 0.3 0.5 血红蛋白 0.8 1.8 2.1 1.3 0.8 乳糜 1.3 0.7 1.7 0.5 0.8 表 5 不同浓度干扰物对异常浓度LP(a)检测的干扰(%)
Table 5. Interference of different concentration interferences on detection of abnormal concentration LP(a)(%)
干扰物质 浓度1 浓度2 浓度3 浓度4 浓度5 游离型胆红素 0.8 0.3 0.6 0.4 1.1 结合型胆红素 0.5 0.9 −0.4 0.1 0.2 血红蛋白 0.4 0.1 0.0 0.4 0.5 乳糜 0.4 1.1 0.1 0.2 0.5 -
[1] Kronenberg F. Human genetics and the causal role of lipoprotein(a)for various diseases[J]. Cardiovasc Drugs and Ther,2016,30(1):87-100. doi: 10.1007/s10557-016-6648-3 [2] Franchini M,Capuzzo E,Liumbruno G M. Lipoprotein apheresis for the treatment of elevated circulating levels of lipoprotein(a):A critical literature review[J]. Blood Transfus,2016,14(5):413-418. [3] Bucci M,Tana C,Giamberardino M A,et al. Lp(a)and cardiovascular risk:investigating the hidden side of the moon[J]. Nutr Metab and Cardiovasc Dis,2016,26(11):980-986. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2016.07.004 [4] 乔蕊,张捷. 脂蛋白(a)-血脂家族的重要一员[J]. 检验医学,2017,32(7):561-565. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8640.2017.07.002 [5] WS/T 420-2013. 临床实验室对商品定量试剂盒分析性能的验证[S]. 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 2013. [6] CNAS-CL02: 2012. 医学实验室质量和能力认可准则[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 中国合格评定国家认可委员会, 2012. [7] ISSN: 0273-3099. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Evaluation of precision performance of quantitative measurement methods: EP5-A2[S]. Wayne, PA, USA: CLSI, 2004. [8] WS/T 492-2016. 临床检验定量测定项目精密度与正确度性能验证[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 2016. [9] ISSN: 0273-3099. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Evaluation of the linearity of quantitative measurement procedures: EP6-A2[S]. Wayne, PA, USA: CLSI, 2003. [10] 张秀明. 浅析定量检验程序分析性能验证实验方案设计[J]. 中华检验医学杂志,2015,38(6):428-430. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-9158.2015.06.017 [11] WS/T 402-2012. 临床实验室检验项目参考区间的制定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 中华人民共和国卫生部, 2012. [12] 张秀明,范勇利,温冬梅,等. 临床化学自建检测系统分析性能确认的分析测量范围和临床可报告范围[J]. 中华检验医学杂志,2016,39(12):946-952. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-9158.2016.12.016 [13] WS/T 416-2013. 干扰实验指南[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 中华人民共和国卫生部, 2013. [14] 王明富. CLIA'88推荐精密度目标在生化室内质控中的应用价值[J]. 实用检验医师杂志,2018,10(1):30-31,35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7151.2018.01.010 [15] 杨俊英. 多项生化项目参考区间验证分析[J]. 国际检验医学杂志,2015,36(10):1435-1436. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2015.10.051 -






 下载:
下载: