Effect and Mechanism of Puerarin on Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis in Mice
-
摘要:
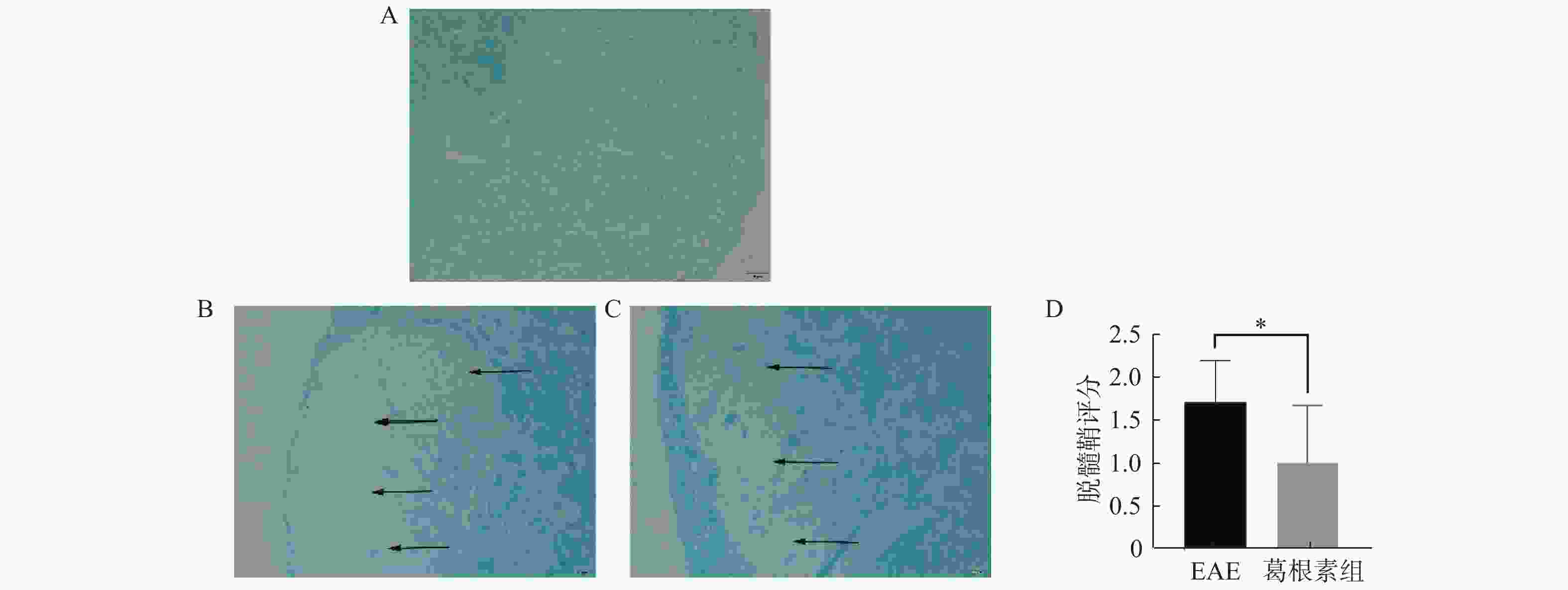
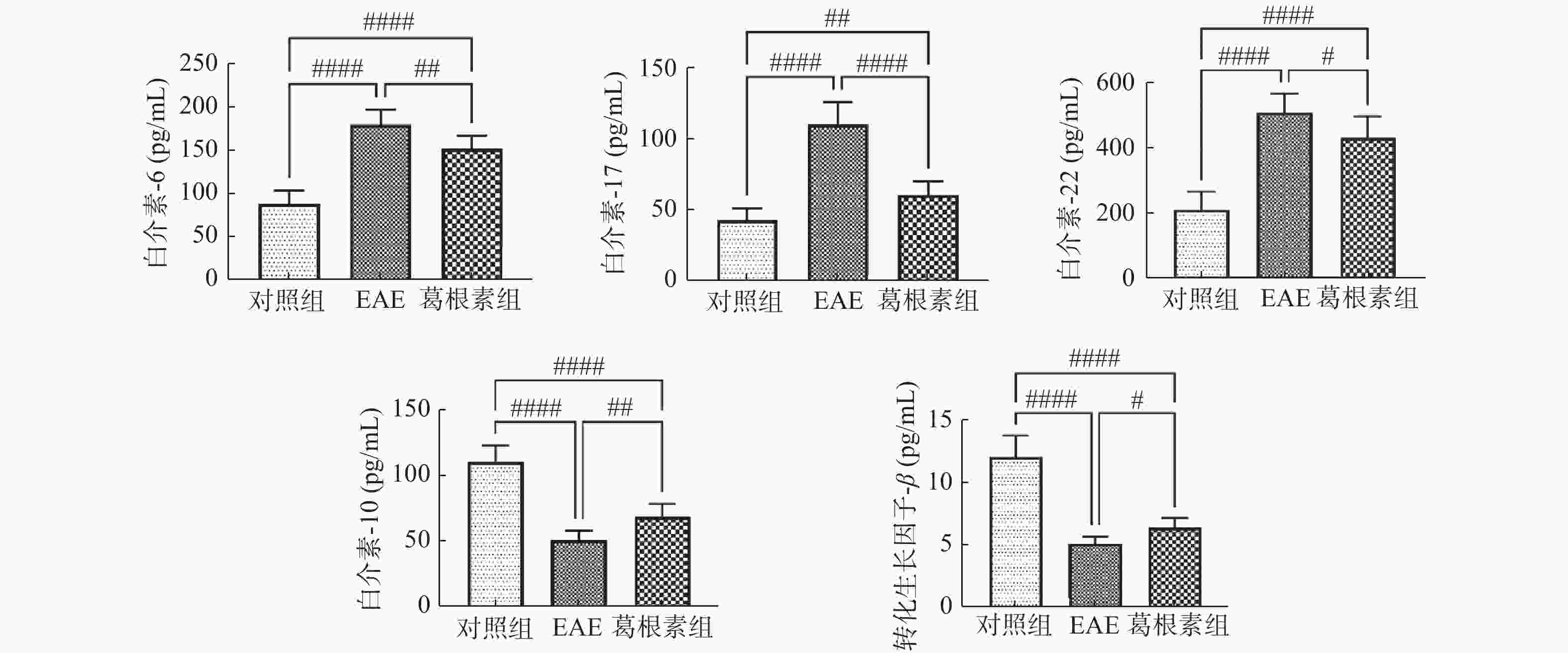
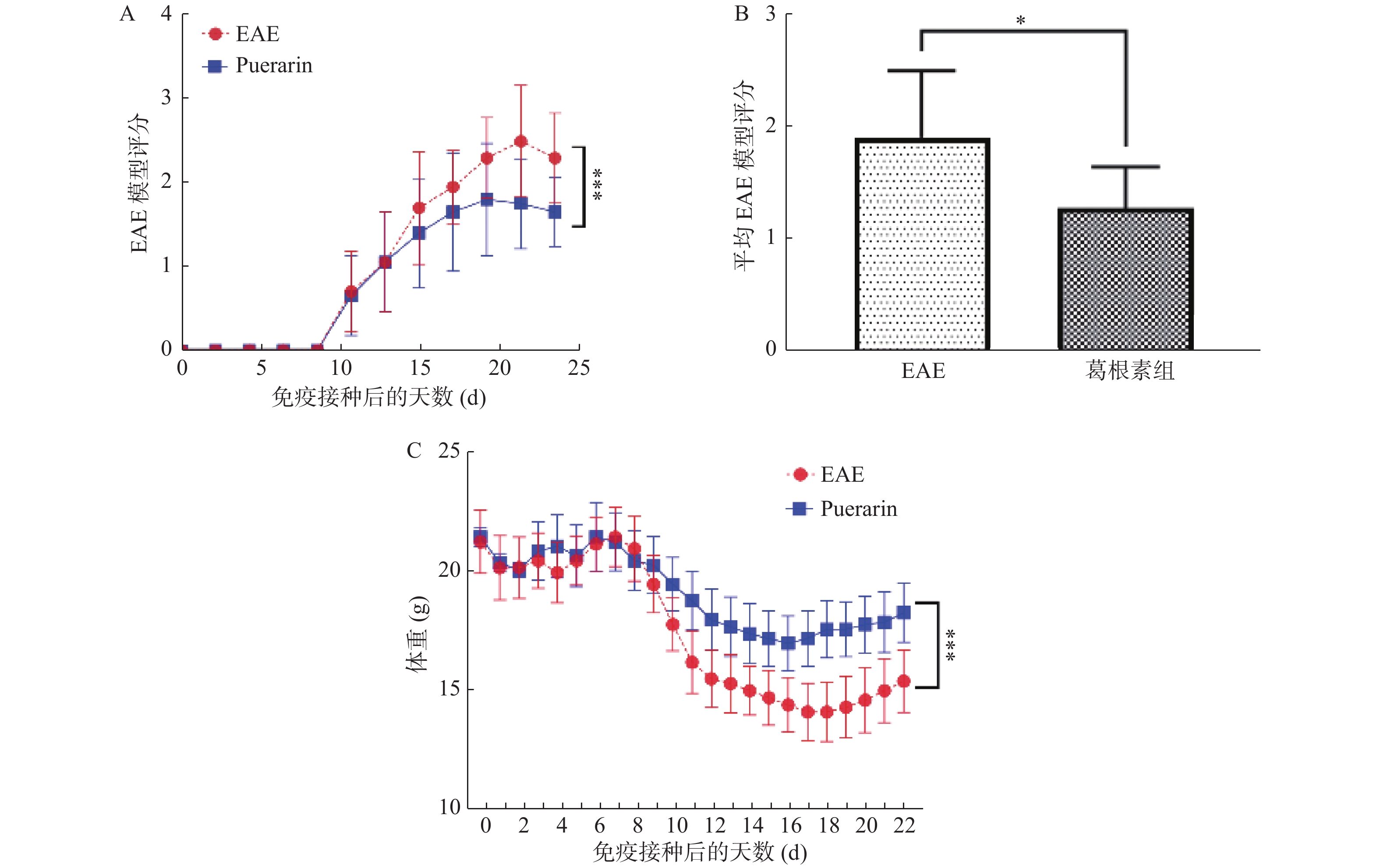
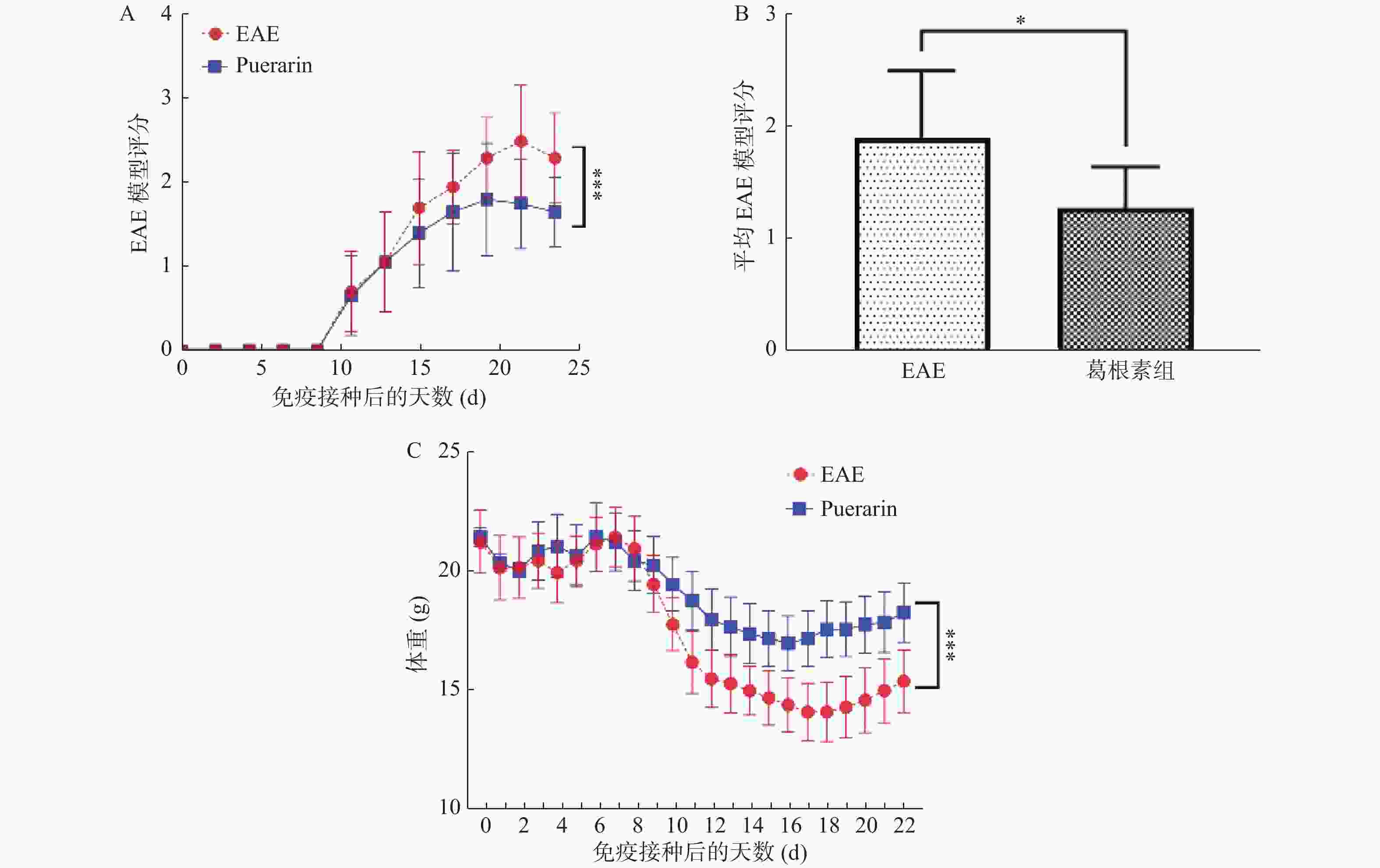
目的 探索葛根素(Puerarin)治疗小鼠实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, EAE)的作用和机制。 方法 将C57BL/6小鼠随机分为对照组、EAE组、Puerarin处理EAE组(Puerarin组)。从诱导EAE当日开始,Puerarin组用葛根素(80 mg/kg)灌胃,其余2组用同体积生理盐水灌胃,每日1次。每天记录神经功能评分及体重变化;劳克坚劳蓝(luxol fast bBlue,LFB)髓鞘染色检测脊髓脱髓鞘情况;ELISA法检测血清中IL-6、IL-10、IL-17、IL-22和TGF-β的水平;Western 印迹法检测脊髓组织NF-κB、IκBα、IL-17、Foxp3等蛋白表达。 结果 Puerarin组小鼠神经功能评分及平均分均较EAE组明显降低(P < 0.01),而体重明显增加(P < 0.01)。应用葛根素后,EAE小鼠脱髓鞘面积(P < 0.01)及病理评分(P < 0.05)均明显下降。Puerarin组小鼠促炎因子IL-6、IL-17和IL-22水平显著降低(P < 0.01),抑炎因子IL-10和TGF-β显著增加(P < 0.05)。应用葛根素后:NF-κB及IL-17表达明显减少(P < 0.05);IκBα及Foxp3表达显著增加(P < 0.01)。 结论 葛根素可缓解EAE小鼠症状,减少脱髓鞘。作用机制是抑制NF-κB通路,调节IL17/Tregs平衡,实现对免疫功能的调节。 -
关键词:
- 实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎 /
- 葛根素 /
- 辅助性T细胞17 /
- 调节性T细胞 /
- NF-κB通路
Abstract:Objective To explore the effect and mechanism of Puerarin on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) in mice. Methods C57BL / 6 mice were randomly divided into control group, EAE group and purearin treated EAE group. From the first day of EAE induction, puerarin group was gavaged with Puerarin (80 mg/kg), and the other two groups were given the same volume of normal saline once a day. The neurological function score and weight changes were recorded every day; the demyelination of spinal cord was detected by LFB myelination staining; the levels of IL-6, IL-10, IL-17, IL-22 and TGF-β in serum were detected by ELISA; the protein expression of NF-κB, IκBα, IL-17, Foxp3 in spinal cord tissue were detected by Western blot. Results Compared with EAE group, the neurological function score and average score of purearin group were significantly decreased (P < 0.01), while the body weight was significantly increased (P < 0.01). The demyelinating area (P < 0.01) and pathological score (P < 0.05) of EAE mice were significantly decreased after puerarin treatment. The levels of proinflammatory cytokines IL-6, IL-17 and IL-22 were significantly decreased in puerarin group (P < 0.01), while IL-10 and TGF-β were significantly increased (P < 0.05). After puerarin treatment, the expressions of NF-κB and IL-17 significantly decreased (P < 0.05), and the expressions of IκBα and Foxp3 significantly increased (P < 0.01). Conclusion Puerarin can alleviate the symptoms of EAE mice and reduce demyelination. The mechanism of action is to inhibit NF-κB pathway, to balance of IL-17/Tregs, and to regulate of immune function. -
Key words:
- Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis /
- Puerarin /
- Th17 /
- Treg /
- NF-κB pathway
-
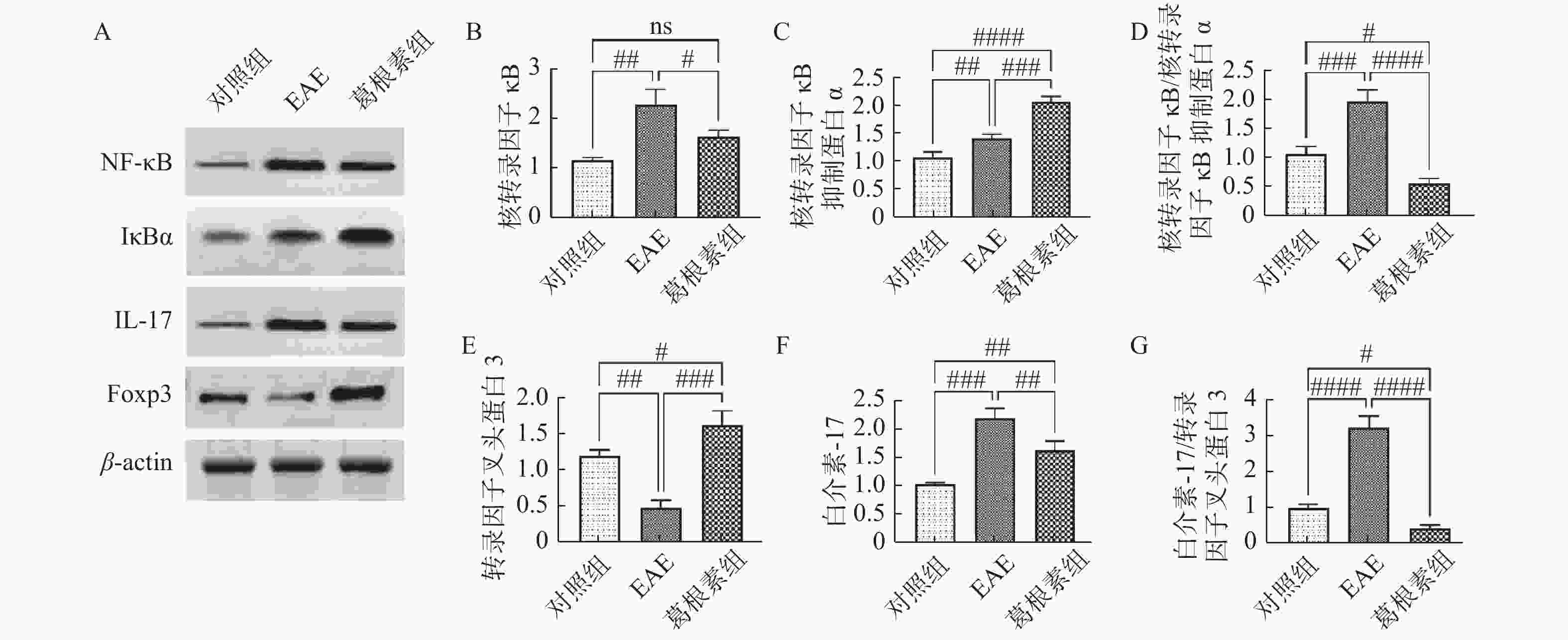
图 4 各组小鼠脊髓组织NF-κB信号通路及IL-17、Foxp3表达的变化
A:各组小鼠Western印迹蛋白表达;B:核转录因子κB相对表达水平;C:核转录因子κB抑制蛋白α相对表达水平;D:核转录因子κB与核转录因子κB抑制蛋白α表达比值;E:转录因子叉头蛋白3相对表达水平;F:白介素-17相对表达水平;G:转录因子叉头蛋白3与白介素-17表达比值。与对照组比较,#P < 0.05,##P < 0.01,###P < 0.001,####P < 0.0001;与EAE组比较,#P < 0.05,##P < 0.01,###P < 0.001,####P < 0.0001。
Figure 4. Changes of NF - κ B signaling pathway and expression of IL-17 and Foxp3 in spinal cord of mice in each group
表 1 各组小鼠血清IL-6、IL-17、IL-22、IL-10和TGF-β水平的变化(
$ \bar x \pm s$ )(pg/mL)Table 1. Changes of serum levels of IL-6,IL-17,IL-22,IL-10 and TGF-β in mice (
$\bar x \pm s $ )(pg/mL)项目 对照组 EAE 葛根素 IL-6 87.4 ± 15.4 179.3 ± 17.4# 151.7 ± 14.5##△ IL-17 42.7 ± 8.4 110.0 ± 15.5# 60.1 ± 9.9##△ IL-22 209.2 ± 54.8 507.4 ± 57.3# 429.4 ± 64.2##△ IL-10 110.4 ± 12.5 50.5 ± 7.5# 68.7 ± 9.5##△ TGF-β 12.02 ± 1.71 5.10 ± 0.56# 6.39 ± 0.73##△ 与对照组相比较,#P < 0.05,##P < 0.01;与EAE组比较,△P < 0.05。 表 2 各组小鼠脊髓组织NF-κB信号通路及IL-17、Foxp3表达的变化(
$\bar x \pm s $ )(蛋白相对表达水平)Table 2. Changes of NF-κB signaling pathway and expression of IL-17 and Foxp3 in spinal cord of mice (
$\bar x \pm s $ )(Relative protein expression level)项目 对照组 EAE 葛根素 NF-κB 1.15 ± 0.06 2.27 ± 0.36# 1.64 ± 0.13△ IκBα 1.09 ± 0.09 1.43 ± 0.07# 2.08 ± 0.10##△ NF-κB/IκBα 1.08 ± 0.13 1.98 ± 0.20# 0.58 ± 0.09##△ IL-17 1.03 ± 0.03 2.19 ± 0.09# 1.62±0.21##△ Foxp3 1.20 ± 0.08 0.49 ± 0.10# 0.41±0.09##△ IL-17/Foxp3 0.97 ± 0.11 3.21 ± 0.34# 与对照组比较,#P < 0.05,##P < 0.01;与EAE组比较,△P < 0.05。 -
[1] Denrou C A,Fugger L,FriseR M A. Immunopathology of multiple sclerosis[J]. Nature reviews. Immunology,2015,15(9):545-558. doi: 10.1038/nri3871 [2] Correale J,Gaitan M I,Ysrraelit M C,et al. Progressive multiple sclerosis:from pathogenic mechanisms to treatment[J]. Brain:A journal of neurology,2017,140(3):527-546. [3] Cai Y,Shen H,Qin C,et al. The Spatio-Temporal Expression Profiles of CD4+T Cell Differentiation and Function-Related Genes During EAE Pathogenesis[J]. Inflammation,2017,40(1):195-204. [4] Luckel C,Picard F,Raifer H,et al. IL-17 CD8 T cell suppression by dimethyl fumarate associates with clinical response in multiple sclerosis[J]. Nature communications,2019,10(1):5722. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13731-z [5] Eggert M,Goertsches R,Seeck U,et al. Changes in the activation level of NF-kappa B in lymphocytes of MS patients during glucocorticoid pulse therapy[J]. Journal of the neurological sciences,2008,264(1-2):145-150. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2007.08.026 [6] Kipp M,Nyamoya S,Hochstrasser T,et al. Multiple sclerosis animal models:a clinical and histopathological perspective[J]. Brain Pathol,2017,27(2):123-137. [7] Chao C C,Gutierrez-Vazquez C,Rothhammer V,et al. Metabolic Control of Astrocyte Pathogenic Activity via cPLA2-MAVS[J]. Cell,2019,179(7):1483-1498 e1422. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.11.016 [8] Correa J O,Aarestrup B J,Aarestrup F M. Effect of thalidomide and pentoxifylline on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE)[J]. Exp Neurol,2010,226(1):15-23. [9] Toyama M,Kudo D,Aoyagi T,et al. Attenuated accumulation of regulatory T cells and reduced production of interleukin 10 lead to the exacerbation of tissue injury in a mouse model of acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Microbiol Immunol,2018,62(2):111-123. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12564 [10] Wang N,Liang S,Jin J,et al. CD226 attenuates Treg suppressive capacity via CTLA-4 and TIGIT during EAE[J]. Immunol Res,2019,67(6):486-496. doi: 10.1007/s12026-019-09112-9 [11] Hou H,Cao R,Quan M,et al. Rapamycin and fingolimod modulate Treg/Th17 cells in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by regulating the Akt-mTOR and MAPK/ERK pathways[J]. J Neuroimmunol,2018,324(1):26-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2018.08.012 [12] Lin X,Liu Y,Ma L,et al. Amelioration of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by Rhodiola rosea,a natural adaptogen[J]. Biomed Pharmacother,2020,125(1):109960. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109960 [13] Li J,Chen Y,Chen Z,et al. Therapeutic effects of human adipose tissue-derived stem cell (hADSC) transplantation on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) mice[J]. Scientific reports,2017,7(2):42695. [14] Zhan T,Wang X,Ouyang Z,et al. Rotating magnetic field ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by promoting T cell peripheral accumulation and regulating the balance of Treg and Th1/Th17[J]. Aging,2020,12(7):6225-6239. doi: 10.18632/aging.103018 [15] Mc Guire C,Volckaert T,Wolke U,et al. Oligodendrocyte-specific FADD deletion protects mice from autoimmune-mediated demyelination[J]. Journal of immunology (Baltimore,Md.:1950),2010,185(12):7646-7653. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000930 [16] Wang Z-K,Chen R-R,Li J-H,et al. Puerarin protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting inflammation and the NLRP3 inflammasome:The role of the SIRT1/NF-κB pathway[J]. International immunopharmacology,2020,89(Pt B):107086. [17] Jeon Y-D,Lee J-H,Lee Y-M,et al. Puerarin inhibits inflammation and oxidative stress in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis mice model[J]. Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie,2020,124(1):109847. -





 下载:
下载: