Advantages of 3D-DSA in Neurointervention
-
摘要:
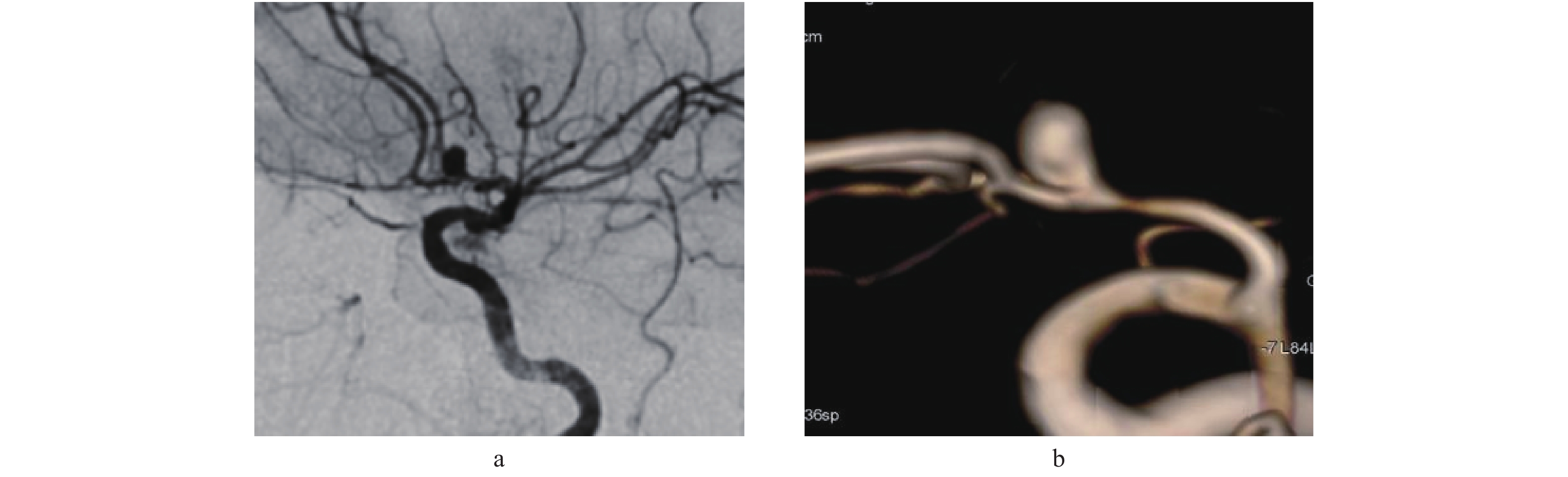
目的 浅析“金标准”内3D-DSA技术较常规2D-DSA在神经介入中的诊断优势和治疗中的应用价值。 方法 收集昆明医科大学附属延安医院2018年1月至2019年12月使用2D及3D-DSA技术行神经介入患者277例。其中:脑血栓取栓111例、动脉瘤106例137个(普通囊状动脉瘤75例97个、巨大型动脉瘤5例6个、宽颈动脉瘤21例29个、夹层动脉瘤等2例2个、梭形动脉瘤2例2个、复杂型动脉瘤1例1个)、动静脉畸形45例、颈动脉狭窄支架置入15例。由工作经验丰富的2位副高以上阅片者采用双盲法对2D和3D的图像进行回顾性分析与测量,进而比较2D、3D图像测量数据差异及疾病检出率。 结果 2D-DSA在普通脑血栓对各段血管的显示率与3D-DSA,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);2D-DSA检出动脉瘤93例(122个),3D-DSA检出106例(137个)( P < 0.05),不含假阳性2例;2D-DSA检出动静脉畸形44例,3D-DSA检出45例( P > 0.05);2D-DSA显示颈动脉狭窄15例,3D-DSA检出15例,差异无统计学意义( P > 0.05)。3D-DSA在颅内动脉瘤检出率、瘤颈、瘤体形态、瘤径、载瘤血管、穿支血管显示等方面显示效果明显优于2D-DSA。 结论 3D-DSA技术提高了对神经性疾病的检出率;同时也提高了对疾病的定性、定量诊断准确率;并且对疾病的进一步治疗有重要的指导意义。 Abstract:Objective To analyse the diagnostic advantages and therapeutic value of 3D-DSA compared with conventional 2D-DSA in nerointervention in the “Gold Standard”. Methods A total of 277 cases who underwent neurointerventional therapy using 2D and 3D-DSA were collected from the Affiliated Yan’ an Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 2018 to December 2019, including 111 cases of cerebral thrombectomy, 106 cases/137 aneurysms (97 common cystic aneurysms in 75 cases, 6 giant aneurysms in 5 cases, 29 wide neck aneurysms in 21 cases, 2 dissecting aneurysms in 2 cases, 2 spindle aneurysms in 2 cases, 1 complex aneurysm in 1 case), 45 cases of arteriovenous malformation and 15 cases of carotid artery stenosis stent implantation. The 2D and 3D images were retrospectively analyzed and measured by two experienced radiologists using double-blind method, and then the difference of the measured data and the detection rate of the disease were compared. Results There was no significant difference between 2D-DSA and 3D-DSA in the detection rate of each segment of cerebral thrombosis (P > 0.05). 122 aneurysms (93 cases) were detected by 2D-DSA, 137 aneurysms (106 cases) were detected by 3D-DSA ( P < 0.05), excepted 2 false positive cases. 44 cases of AVM were detected by 2D-DSA and 45 cases were detected by 3D-DSA ( P > 0.05). 2D-DSA showed carotid artery stenosis in 15 cases and 3D-DSA showed carotid artery stenosis in 15 cases, the difference was not statistically significant ( P > 0.05). 3D-DSA is significantly better than 2D-DSA in the detection rate of intracranial aneurysm, tumor neck, tumor shape, tumor diameter, tumor tumor-bearing vessels, perforator vessel, etc. Conclusion 3D-DSA technology improves the detection rate of neurological diseases, improves the accuracy of qualitative and quantitative diagnosis of neurological diseases; therefore it has important guiding significance for the further treatment of diseases. -
Key words:
- 3D-DSA /
- Neurointervention /
- Cerebral angiography
-
表 1 2D-DSA、3D-DSA在脑血栓取栓后远端血管显示及分支显示统计[n(%)]
Table 1. Comparison of 2D-DSA and 3D-DSA in displaying distal vessels and branches after thrombectomy [n(%)]
项目 2D-DSA 3D-DSA P − 15(13.9) 15(13.5) 1.000 + 15(13.9) 19(17.1) 0.835 ++ 78(72.2) 77(69.4) 0.731 总计 108 111 0.679 表 2 2D-DSA、3D-DSA在脑动脉瘤颈与载瘤动脉关系统计[n(%)]
Table 2. Comparison of 2D-DSA and 3D-DSA in aneurysm neck and parent artery [n(%)]
项目 2D-DSA 3D-DSA P 普通囊状动脉瘤 71(51.8) 97(70.8) 0.012* 巨大型动脉瘤 2(1.5) 2(1.5) 1.000 宽颈动脉瘤 25(18.2) 29(21.2) 0.042* 夹层动脉瘤 2(1.5) 2(1.5) 1.000 梭形动脉瘤 2(1.5) 2(1.5) 1.000 复杂型动脉瘤 1(0.7) 1(0.7) 1.000 总计 122 137 0.009* *P < 0.05。 表 3 不同形态动脉瘤显示统计[n(%)]
Table 3. Comparison of different shapes of aneurysms [n(%)]
项目 2D-DSA 3D-DSA P − 5(16.1) 0 − + 5(16.1) 3(9.6) < 0.001* ++ 14(45.1) 27(87.1) < 0.001* 总计 24(77.4) 31(100) 0.019* *P < 0.05。 -
[1] 陆军,王大明. 中国神经介入发展略览[J]. 中国神经免疫学和神经病学杂志,2019,26(4):237-239. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2963.2019.04.001 [2] 董富山,史帅涛,姜喜峰,等. 3D-DSA脑血管造影诊断脑动脉瘤技术中的质量控制[J]. 实用诊断与治疗杂志,2008,22(8):612-613. [3] Lauric A,Heller RS,Schimansky S,et al. Benefit of cone-beam CT angiography in visualizing aneurysm shape and identification of exact rupture site.[J]. J Neuroimaging,2015,25(1):56-61. doi: 10.1111/jon.12120 [4] Choi J H,Park H S. The incidence and characteristics of patients with small ruptured aneurysms (< 5 mm) in subarachnoid hemorrhage[J]. J Korean Neurosurg Soc,2017,60(4):424-432. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2016.0910.003 [5] 中国医师协会神经介入专业委员会出血性脑血管病神经介入专业委员会(学组),中国医师协会神经外科医师分会神经介入专业委员会,中国医师协会介入医师分会神经介入专业委员会. 血流导向装置治疗颅内动脉瘤的中国专家共识[J]. 中华神经外科杂志,2020,36(5):433-445. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112050-20200229-00089 [6] 中华医学会神经病学分会,中华医学会神经病学分会神经血管介入协作组. 介入神经病学导管室构建与管理中国专家共识[J]. 中华神经科杂志,2019,52(4):247-251. [7] 唐晓平,段军伟,赵龙,等. 小脑上动脉动脉瘤的诊断和治疗(附16例报道)[J]. 中华神经医学杂志,2019,18(4):357-362. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-8925.2019.04.006 [8] 李强,朱敏,姜华,等. CTA与2D DSA、3D DSA在颅内动脉瘤检出率和动脉瘤颈可见度中的应用价值[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2018,38(5):1084-1086. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2018.05.023 [9] 申杰,姜建昌,李蓉晖,等. 血管三维影像融合技术在硬脑(脊)膜动静脉瘘治疗中的应用[J]. 中华神经外科杂志,2019,35(2):186-189. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-2346.2019.02.018 [10] 王童,刘阳,徐剑峰,等. 3D-DSA双容积重建技术在复杂动脉瘤中的应用价值[J]. 重庆医学,2019,48(2):255-258,262. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2019.02.019 [11] 程佳,刘朝,谢珊珊,等. 三维可变反转角快速自旋回波序列在颅内动脉支架术后随访中的价值[J]. 中华放射学杂志,2019,53(3):224-228. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1005-1201.2019.03.012 [12] 周选民,黄宽明,李小力,等. 三维DSA与常规DSA在颅内动脉瘤诊断中的对比研究[J]. 郧阳医学院学报,2009,28(3):208-209. [13] 顾红波,李冰,张二朋,等. 颅底颈内动脉瘤15例临床分析[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2021,56(1):18-25. [14] 秦汉,胡军民,秦海林,等. 血管检查在自发性脑内出血或脑室出血病因诊断中的应用价值[J]. 中国临床神经外科杂志,2021,26(1):1-4. [15] 蒋孝先,罗光华,周飞,等. 4D-CTA在颅内动脉瘤诊断中的应用价值[J]. 中国医科大学学报,2020,49(4):336-341. [16] 杨威威,梁奕,凡娜,等. 4D-CT血管成像评估前交通动脉瘤破裂的形态学定量研究[J]. 实用放射学杂志,2020,36(10):1588-1592. -






 下载:
下载: