Effects of Different Doses of Gastrodin on Conditioned Place Preference and Microglia Activation in Hippocampus of Methamphetamine Dependent Rats
-
摘要:
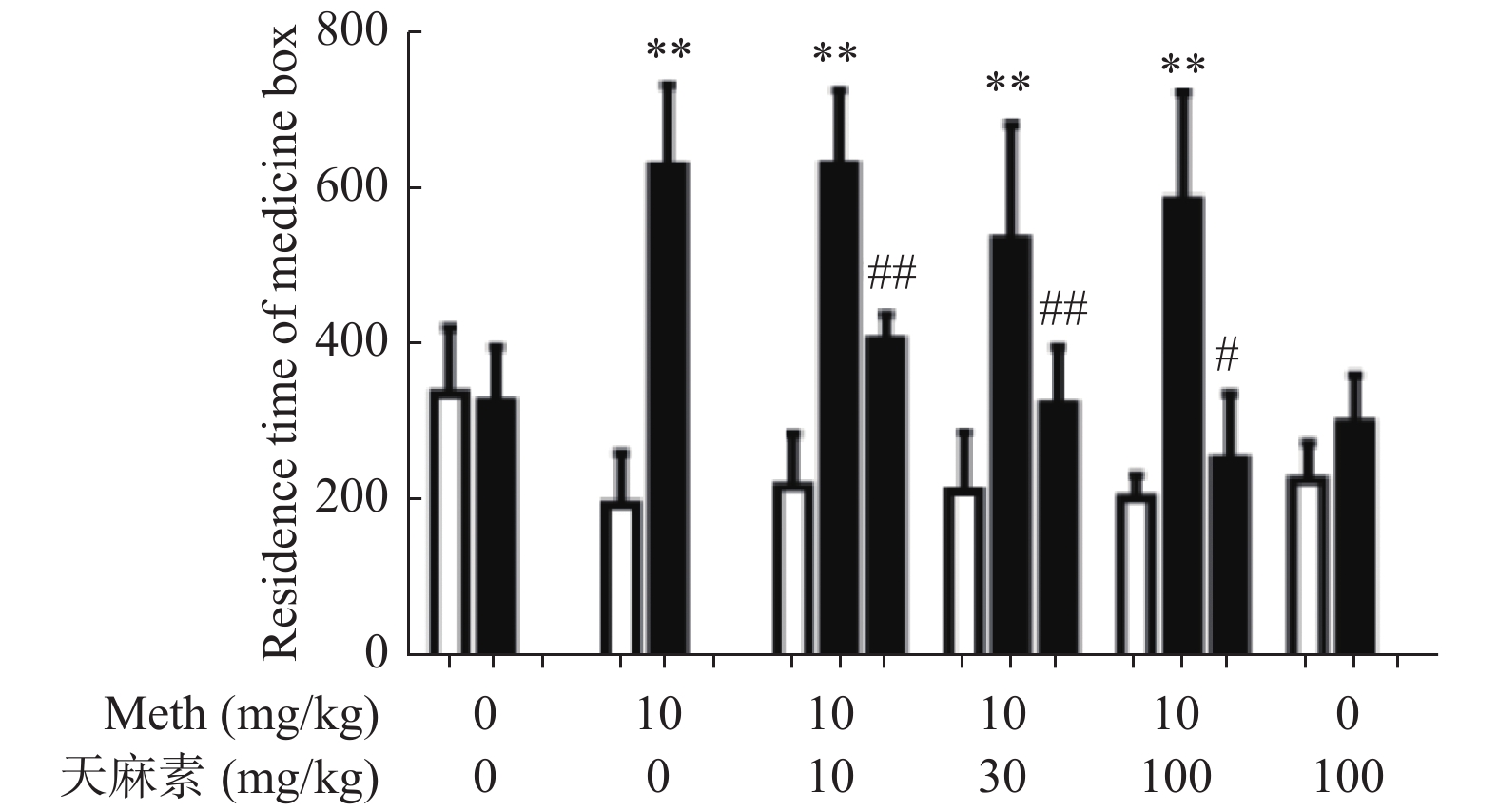
目的 研究不同剂量天麻素(gastrodin,Gas)对甲基苯丙胺(methamphetamine,Meth)依赖大鼠条件性位置偏爱(conditioned place preference,CPP)的影响及海马小胶质细胞激活状态的改变。 方法 腹腔注射Meth(10 mg/kg,qd,14 d)建立Meth依赖大鼠CPP模型,然后采用10 mg/kg、30 mg/kg、100 mg/kg不同剂量的天麻素治疗14 d,测定不同剂量天麻素对Meth依赖大鼠CPP效应的影响;用免疫荧光技术检测不同剂量天麻素对海马小胶质细胞激活的影响。 结果 Meth依赖大鼠CPP模型建立成功。与生理盐水组相比,Meth组的CPP效应明显增强,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);天麻素治疗可使大鼠在伴药箱停留时间明显缩短;与Meth组相比,10 mg/kg、30 mg/kg、100 mg/kg的天麻素治疗后,可呈剂量依赖性地降低Meth诱导的CPP效应,且100 mg/kg的天麻素可基本消除Meth诱导的CPP效应。免疫荧光检测结果显示,与生理盐水组相比,Meth组大鼠海马小胶质细胞明显被激活;经10 mg/kg、30 mg/kg、100 mg/kg的天麻素治疗后,小胶质细胞激活被明显抑制,且30 mg/kg、100 mg/kg两组剂量的天麻素治疗后抑制效果更明显。 结论 天麻素可呈剂量依赖性降低Meth依赖大鼠的CPP效应,天麻素对Meth成瘾具有改善作用。不同剂量的天麻素可抑制Meth依赖CPP大鼠海马组织小胶质细胞的激活状态。 Abstract:Objective To study the effects of different dosages of gastrodin on conditioned place preference and hippocampal microglia activation in methamphetamine (Meth)-dependent rats. Methods Meth dependent CPP model was established by intraperitoneal injection of meth (10 mg/kg, QD, 14 d) and then gastrodin (10 mg/kg, 30 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg) was used for 14 d to determine the effect of gastrodin on CPP in meth dependent rats. After that, the immunofluorescence technique was used to detect the effect of different doses of gastrodin on the activation of microglia in hippocampus. Results The Meth-dependent rat CPP model was successfully established. Gastrodin treatment could shorten the time of the rats stayed in the drug-paired chamber. Compared with the saline group, the CPP effect of the Meth group was significantly enhanced, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Compared with Meth group, 10 mg/kg, 30 mg/kg, and 100 mg/kg gastrodin treated groups showed a dose-dependent reduction of Meth-induced CPP effect, and 100 mg/kg of gastrodin could basically eliminate the CPP effect induced by Meth. The results of immunofluorescence showed that, compared with the normal saline group, the hippocampal microglia of the Meth group was significantly activated. After the treatment with 10 mg/kg, 30 mg/kg, or 100 mg/kg gastrodin, the microglia cell activation was inhibited by gastrodin, and the performance was more obvious after the treatment with 30 mg/kg and 100 mg/kg gastrodin. Conclusion Gastrodin can reduce the CPP effect of Meth-dependent rat in a dose-dependent manner; gastrodin has a potential effect on methamphetamine dependence. Gastrodin can inhibit the activation of hippocampal microglia in hippocampus region of Meth-dependent rat. -
Key words:
- Methamphetamine (Meth) /
- Gastrodin /
- Conditional position preference (CPP) /
- Hippocampus /
- Microglia
-
表 1 各组大鼠在伴药箱的停留时间[n = 6,(
$ \bar x \pm s$ )]Table 1. The time of each group of rats in the drug-paired chamber [n = 6,(
$ \bar x \pm s$ )]组别 适应期(s) 训练期(s) 治疗期(s) t/F P 生理盐水组 336.9 ± 85.2 327.9 ± 69.5 − 1.5 0.7 Meth组 194.7 ± 66.9 629.8 ± 103.2** − 20.3 < 0.01 天麻素100 mg/kg组 226.1± 48.2 299.9 ± 61.1 − 2.5 0.06 Meth+天麻素10 mg/kg组 218.2 ± 67.8 630.9 ± 95.7** 406.1 ± 33.7## 51.5 < 0.01 Meth+天麻素30 mg/kg组 212.2 ± 76.3 535.2 ± 148.3** 322.9 ± 74.5## 14.5 < 0.01 Meth+天麻素100 mg/kg组 203.3 ± 29.5 585.6 ± 138.6*** 253.3 ± 84.2# 28.6 < 0.01 与适应期比较,*P < 0.05、**P < 0.01、***P < 0.001;与训练期比较,#P < 0.05、##P < 0.01。 表 2 各组大鼠给药前后在伴药箱停留时间的差值[n = 6,(
$ \bar x \pm s$ )]Table 2. Comparison of the difference of times that the rat stayed in the drug-paired chamber before and after Meth administration [n = 6,(
$\bar x \pm s$ )]分组 伴药箱停留时间的差值(s) 生理盐水组 38.9 ± 29.5 Meth组 435.1 ± 52.6** 天麻素100 mg/kg组 94.6 ± 31.2 Meth + 天麻素10 mg/kg组 187.9 ± 76.5**## Meth + 天麻素30 mg/kg组 110.7 ± 27.3*## Meth + 天麻素100 mg/kg组 78.1 ± 36.4## F 59.9 P < 0.01 与生理盐水组比较,*P < 0.05、**P < 0.01;与Meth组比较,#P < 0.05、##P < 0.01。 -
[1] Mizoguchi H,Yamada K. Methamphetamine use causes cognitive impairment and altered decision-making[J]. Neurochemistry International,2019,12(4):106-113. [2] Papageorgiou M,Raza A,Fraser S,et al. Methamphetamine and its immune modulating effects[J]. Maturitas,2018,8(3):45-52. [3] Xue Y,Yong W,Li Q Y,et al. The main molecular mechanisms underlying methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity and implications for pharmacological treatment[J]. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience,2018,11(6):186-192. [4] Shaerzadeh F,Streit W J,Heysieattalab S,et al. Methamphetamine neurotoxicity,microglia,and neuroinflammation[J]. Journal of Neuroinflammation,2018,15(1):34-39. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1072-1 [5] Wang Z Y,Guo L,Han X,et al. Naltrexone attenuates methamphetamine induced behavioral sensitization and conditioned place preference in mice[J]. Behavioral Brain Research,2020,6(1):45-51. [6] Zhao Z L,Kim Y W,Yang Y P,et al. Glycyrrhizae radix methanol extract attenuates methamphetamine-induced locomotor sensitization and conditioned place preference[J]. Evidence-based Complementary & Alternative Medicine(eCAM),2014,11(3):152-157. [7] Yang G M,Li L,Xue F L,et al. The potential role of PKA/CREB signaling pathwaycon-cerned with gastrodin administration on methamphetamine-induced conditioned place preference rats and SH-SY5Y Cell line[J]. Neurotoxicity Research,2020,7(12):1-10. [8] Ma C L,Li L,Yang G M,et al. Neuroprotective effect of gastrodin in methamphetamine induced apoptosis through regulating cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway in cortical neuron[J]. Human & Experimental Toxicology,2020,39(8):1118-1129. [9] 黄兆奎,石振金,吴亚梅,等. 甲基苯丙胺不同给药时程及天麻素的干预对建立大鼠条件性位置偏爱模型的影响[J]. 昆明医科大学学报,2019,40(3):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4706.2019.03.001 [10] Andoh M,Ikegaya Y,Koyama R,et al. Microglia modulate the structure and function of the hippocampus after early-life seizures[J]. Journal of Pharmacolo -gical Sciences,2020,144(4):212-217. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2020.09.003 [11] Wolf S A,Boddeke H W,Kettenmann H,et al. Microglia in physiology and disease[J]. Annual Review of Physiology,2017,7(9):619-643. [12] Chao J,Zhang Y,Du L,et al. Molecular mechanisms underlying the involvement of the sigma-1 receptor in methamphetamine-mediated microglial polarization[J]. Sci Rep,2017,7(1):115-121. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00091-1 [13] Yang T,Zang S,Wang Y,et al. Methamphetamine induced neuroinflammation in mouse brain and microglial cell line BV2:Roles of the TLR4/TRIF/Peli1 signaling axis[J]. Toxicology Letters,2020,9(3):150-158. [14] Sekine Y,Ouchi Y,Sugihara G,et al. Methamphetamine causes microglial activation in the brains of human abusers[J]. Journal of Neuroscience the Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience,2008,28(22):5756-5761. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1179-08.2008 -








 下载:
下载: