The Expression and Significance of Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor-5A2 in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
-
摘要:
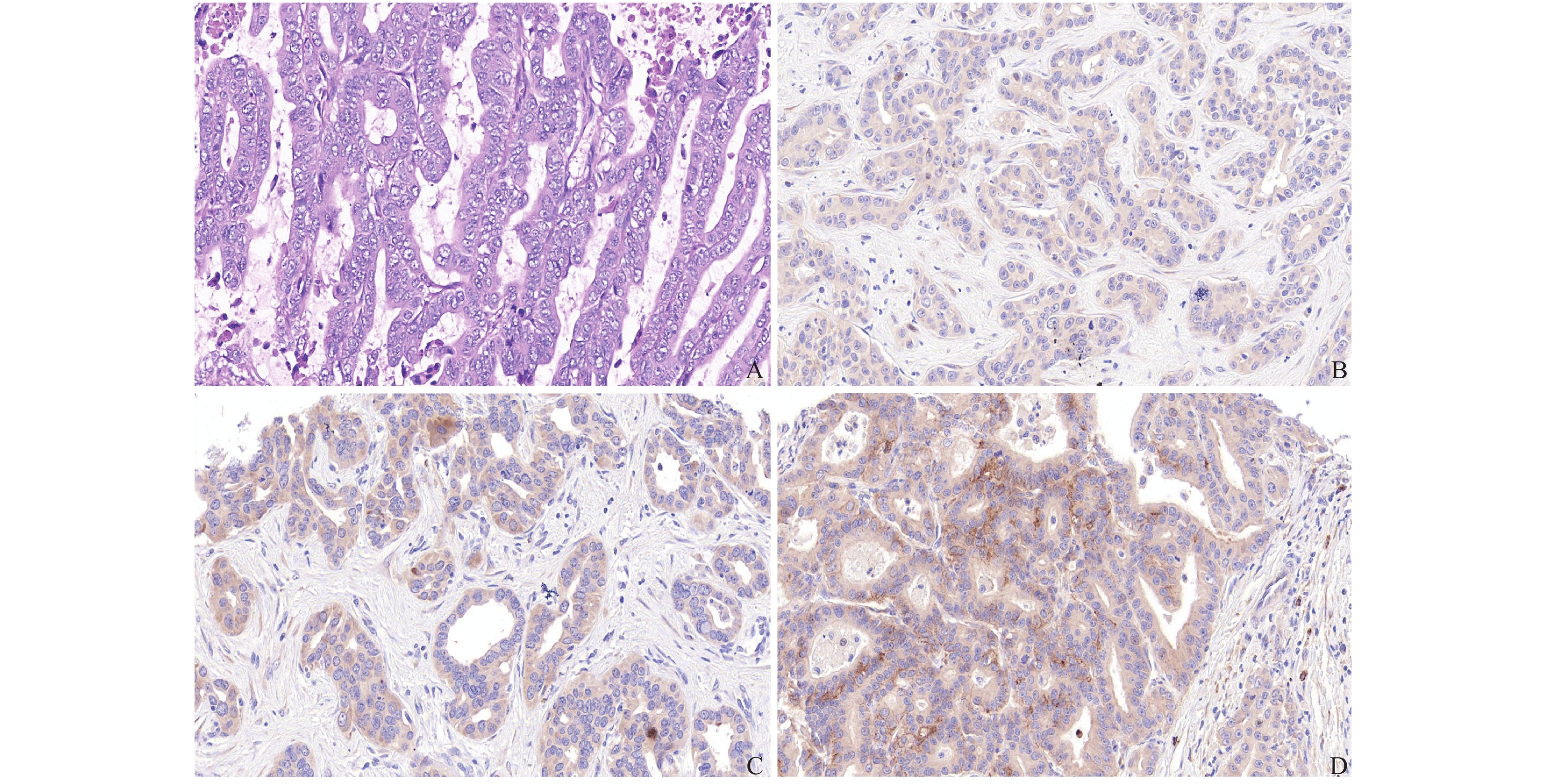
目的 研究真核翻译起始因子-5A2(eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2,eIF5A2)在肝内胆管癌中的表达及与神经侵犯和周围脂肪组织浸润的相关性。 方法 收集昆明医科大学第二附属医院肝胆胰外科2013年10月至2020年10月156例肝内胆管癌患者术后石蜡切块,收集同期30例肝血管瘤患者部分肝切除的正常肝组织作为对照组,采用免疫组化的方法检测eIF5A2的表达水平,并收集病理资料,分析eIF5A2与神经侵犯和周围脂肪组织浸润的相关性。 结果 156例肝内胆管癌组织切片中eIF5A2高表达95例(60.9%),其在正常肝组织胆管上皮高表达率为13.3%,eIF5A2的表达与神经侵犯和周围脂肪组织浸润显著相关(P < 0.05)。 结论 eIF5A2在肝内胆管癌中高表达,与神经侵犯和周围脂肪组织浸润显著相关。 -
关键词:
- 肝内胆管癌 /
- 真核翻译起始因子-5A2 /
- 免疫组织化学染色
Abstract:Objective To study the expression of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 (eIF5A2) in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and its correlation with nerve invasion and peripheral adipose tissue infiltration. Methods Paraffin sections from 156 patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma were collected from October 2013 to October 2020 in the Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, and the normal liver tissues from 30 cases of hepatic hemangioma undergoing partial hepatectomy were collected during the same period. In the control group, the immunohistochemical methods were used to detect the expression level of eIF5A2, and pathological data were collected to analyze the correlation between eIF5A2 and nerve invasion and peripheral adipose tissue infiltration. Results In 156 cases of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma tissue sections, 95 cases (60.9%) had high expression of eIF5A2. The high expression rate of eIF5A2 in normal liver tissue bile duct epithelium was 13.3%. The expression of eIF5A2 was significantly related to nerve invasion and peripheral adipose tissue infiltration (P < 0.05). Conclusion eIF5A2 is highly expressed in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and is significantly related to nerve invasion and surrounding adipose tissue infiltration. -
表 1 eIF5A2在肝内胆管癌组织与正常肝组织表达的比较[n(%)]
Table 1. Comparison of eIF5A2 expression in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma tissues and normal liver tissues [n(%)]
项目 n eIF5A2
高表达eIF5A2
低表达χ2 P 肝内胆管癌 156 95(60.9) 61(39.1) 22.865 < 0.001 正常肝组织 30 4(13.3) 26(86.7) 表 2 eIF5A2的表达与神经侵犯、周围脂肪组织浸润的相关性比较[n(%)]
Table 2. Correlation between the expression of eIF5A2 and nerve invasion and peripheral adipose tissue infiltration [n(%)]
项目 n(例) 神经侵犯n(%) 周围脂肪组织浸润n(%) eIF5A2高表达 95 53(55.8)* 30(31.6)* eIF5A2低表达 61 22(36.1) 9(14.8) χ2 5.789 5.608 P 0.016 0.018 与eIF5A2低表达组相比,*P < 0.05。 -
[1] De Jong M C,Nathan H,Sotiropoulos G C,et al. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma:An international multi-institutional analysis of prognostic factors and lymph node assessment[J]. J Clin Oncol,2011,29(23):3140-3145. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.35.6519 [2] Guan X Y,Sham J S,Tang T C,et al. Isolation of a novel candidate oncogene within a frequently amplified region at 3q26 in ovarian cancer[J]. Cancer Res,2001,61(9):3806-3809. [3] Meng Q B,Peng J J,Qu Z W,et al. Eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 and human digestive system neoplasms[J]. World J Gastrointest Oncol,2019,11(6):449-458. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i6.449 [4] Bao Y,Lu Y L,Wang X,et al. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 (eIF5A2) regulates chemoresistance in colorectal cancer through pithelial mesenchymal transition[J]. Cancer Cell Int,2015,15(2):1-7. doi: 10.1186/s12935-015-0250-9 [5] Tang D J,Dong S S,Ma N F,et al. Overexpression of eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 enhances cell motility and promotes tumor metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology,2010,51(4):1255-1263. doi: 10.1002/hep.23451 [6] Tsang F H,Au V,Lu W J,et al. Prognostic marker microRNA-125b inhibits tumorigenic properties of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via suppressing tumorigenic molecule eIF5A2[J]. Dig Dis Sci,2014,59(10):2477-2487. doi: 10.1007/s10620-014-3184-5 [7] Wu Y,Tang Y,Xie S,et al. Chimeric peptide supramolecular nanoparticles for plectin-1 targeted miRNA-9 delivery in pancreatic cancer[J]. Theranostics,2020,10(3):1151-1165. doi: 10.7150/thno.38327 [8] Wei Y X,Chen G,You L,et al. Expression of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 in pancreatic adenocarcinoma and its correlation with the prognosis[J]. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao,2013,35(6):634-638. [9] Meng Q B,Kang W M,Yu J C,et al. Overexpression of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 (EIF5A2) correlates with cell aggressiveness and poor survival in gastric cancer[J]. PLoS One,2015,10(3):e0119229. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119229 [10] Patel T. Increasing incidence and mortality of primary intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States[J]. Hepatology,2001,33(6):1353-1357. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2001.25087 [11] 吴孟超, 吴在德. 黄家驷外科学[M]. 第7版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2008: 1695. [12] Lu J,Zhao H W,Chen Y,et al. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 is highly expressed in prostate cancer and predicts poor prognosis[J]. Exp Ther Med,2019,17(5):3741-3747. [13] Yang H,Li X D,Zhou Y,et al. Stemness and chemotherapeutic drug resistance induced by EIF5A2 overexpression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Oncotarget,2015,6(28):26079-26089. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4581 [14] Chen W,Luo J H,Hua W F,et al. Overexpression of EIF-5A2 is an independent predictor of outcome in patients of urothelial carcinoma of the bladder treated with radical cystectomy[J]. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev,2009,18(2):400-408. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-08-0754 [15] Wang F W,Guan X Y,Xie D. Roles of eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 in human cancer[J]. Int J Biol Sci,2013,9(10):1013-1020. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.7191 [16] 韦颍昕,陈革,由磊,等. 真核翻译起始因子5A2在胰腺癌中的表达及与预后的相关性[J]. 中国医学科学院学报,2013,35(06):634-638. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2013.06.009 [17] 孟庆彬. EIF5A2促进胃癌细胞增殖、侵袭的分子机制研究[D]. 北京: 北京协和医学院博士论文, 2013. [18] Marchet A,Mocellin S,Belluco C,et al. Gene expression profile of primary gastric cancer:Towards the prediction of lymph node status[J]. Ann Surg Oncol,2007,14(3):1058-1064. doi: 10.1245/s10434-006-9090-0 [19] Xie D,Ma N F,Pan Z Z,et al. Overexpression of EIF-5A2 is associated with metastasis of human colorectal carcinoma[J]. Hum Pathol,2008,39(1):80-86. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2007.05.011 [20] Liu R R,Lv Y S,Tang Y X,et al. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 regulates the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via pathways involving reactive oxygen species[J]. Oncotarget,2016,7(17):24348-24360. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8324 [21] Fujimura K,Wright T,Strnadel J,et al. A hypusine-eIF5A-PEAK1 switch regulates the pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer[J]. Cancer Res,2014,74(22):6671-6681. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-1031 [22] Zhu W,Cai M Y,Tong Z T,et al. Overexpression of EIF5A2 promotes colorectal carcinoma cell aggressiveness by upregulating MTA1 through C-myc to induce epithelial-mesenchymaltransition[J]. Gut,2012,61(4):562-575. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300207 [23] Li Y,Fu L,Li J B,et al. Increased expression of EIF5A2,via hypoxia or gene amplification,contributes to metastasis and angiogenesis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Gastroenterology,2014,146(7):1701-1713. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.02.029 [24] Luo J H,Hua W F,Rao H L,et al. Overexpression of EIF-5A2 predicts tumor recurrence and progression in pTa/pT1 urothelial carcinoma of the bladder[J]. Cancer Sci,2009,100(5):896-902. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01126.x [25] Dong J S,Wu B,Zha Z L,et al. MicroRNA-588 regulates migration capacity and invasiveness of renal cancer cells by targeting EIF5A2[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci,2019,23(23):10248-10256. [26] Zhao K,Ye Z,Li Y,et al. LncRNA FTX contributes to the progression of colorectal cancer through regulating miR-192-5p/EIF5A2 axis[J]. Onco Targets Ther,2020,13(3):2677-2688. [27] Li X,He J,Ren X,Zhao H,et al. Circ_0003998 enhances doxorubicin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating miR-218-5p/EIF5A2 pathway[J]. Diagn Pathol,2020,15(1):141-154. doi: 10.1186/s13000-020-01056-1 -






 下载:
下载: