A Retrospective CBCT Analysis of the Characteristics of Root Canal Systems of Mandibular Molars in a Kunming Population
-
摘要:
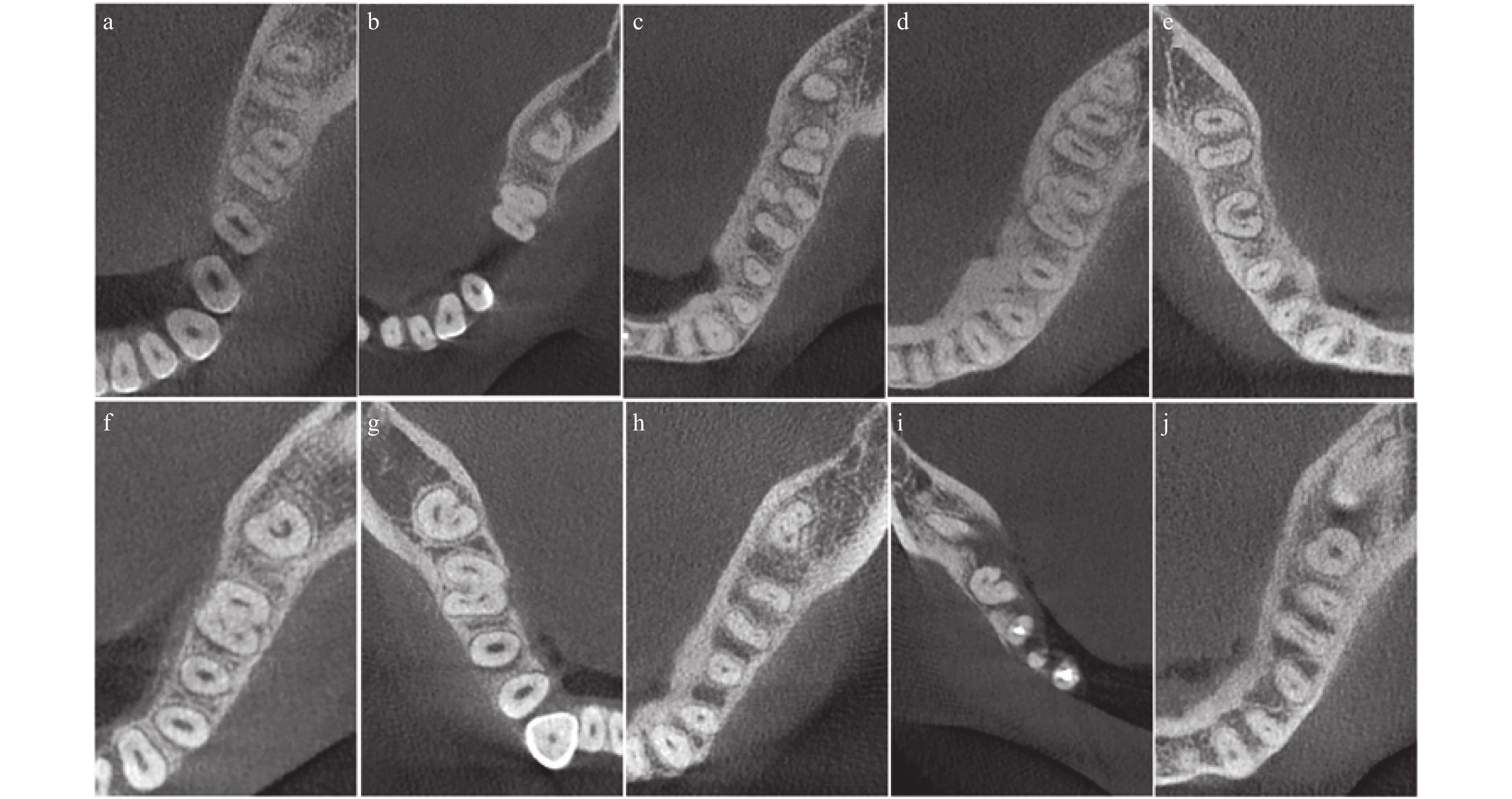
目的 回顾性分析昆明地区人群下颌第1和第2磨牙根管系统的CBCT资料,研究其根管形态的规律。 方法 收集云南省第一人民医院口腔医学中心358名患者总共1229颗下颌第1和第2磨牙的CBCT资料,计算根管数量和类型、远舌根管和C形根管发生率,分析根管形态特征。 结果 下颌第1磨牙73.96%为4根管,19.73%为3根管,4.48%为5根管,0.33%为2根管,远舌根平均发生率为14.43%。下颌第2磨牙C形根管平均发生率为30.83%,女性高于男性(34.95% > 26.81%,P < 0.05),牙位或各年龄间无显著性差异(P > 0.05)。C形根管在根管口水平面81.35%表现为C1和C2型,根中水平70.47%为C2和C3型,根尖3 mm水平83.42%为C3和C4型。 结论 昆明地区人群下颌第1磨牙远舌根管和第2磨牙C形根管发生率较高,治疗时需特别注意。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the characteristics of root canal system of mandibular first and second molars ina Kunming population with cone-beam computed tomography technology. Methods CBCT dada of 1229 mandibular first and second molar from 358 patients were collected. The root canal number, classification and incidence of radix entomolaris and C-shaped canalswere calculated to conclude their characteristics. Results The majority of mandibular first molars (73.96%) showed 4 canals, 19.73% with 3 canals, 4.48% with 5 canals, 0.33% with 2 canals. The incidence of radix entomolaris was 14.43%. The incidence of C-shaped canals in mandibular second molars was 30.83%.There was a significant difference of incidence in female than that in male (34.95% > 26.81%, P < 0.05). The incidence of C-shaped canals in group 1 and 2 was higher than that in group 3 and 4 (P < 0.05). Most of the C-shaped canals were C1 and C2 type at the level of orifice (81.35%), 70.47% being C2 and C3 type at the level of middle and 83.42% being C3 and C4 type at the level of apical 3mm. Conclusion More attention must be paid when treating mandibular first and second molars in Kunming population bucause there is a high incidence of radix entomolaris and C-shaped canal. -
表 1 昆明地区人群下颌磨牙牙根及根管数量构成比[n(%)]
Table 1. Number and distribution of roots and root canals of mandibular molars in a Kunming population [n(%)]
牙位 牙根 根管 1 2 3 2 3 4 5 6 下颌第一磨牙 0(0) 516(85.57) 87(14.43) 2(0.33) 119(19.73) 446(73.96) 27(4.48) 9(1.49) 下颌第二磨牙 193(30.83) 420(67.09) 13(2.08) 56(8.94) 360(57.51) 17(2.72) − − 表 2 昆明地区人群下颌第二磨牙C形根管发生率[n(%)]
Table 2. Incidence of C-shaped canalsin mandibular second molars in a Kunming population [n(%)]
项目 总数 C形根管
数量C形根管
发生率n(%)检验统计值 P值 性别 男 317 85 26.81 4.529 0.033 女 309 108 34.95 牙位 左 320 99 30.94 0.000 0.987 右 306 94 30.72 年龄
(岁)17~19 19 9 47.37 20~39 321 114 35.51 40~59 208 48 23.08 > 60 78 22 28.21 注:各年龄组比较:17~19岁与20~39岁比较,χ2 = 0.682,P = 0.409;17~19岁与40~59岁比较,χ2 = 2.576,P = 0.109;17~19岁与 > 60岁比较,χ2 = 2.469,P = 0.116;20~39岁与40~59岁比较,χ2=:3.562,P=0.059;20~39岁与 > 60岁比较,χ2 = 2.370,P = 0.124;40~59岁与 > 60岁比较,χ2 = 0.016,P = 0.899。 表 3 昆明地区人群下颌第二磨牙C形根管构成比分析[n(%)]
Table 3. Distribution of the C-shaped canals at different level in mandibular second molarsin a Kunming population [n(%)]
部位 C1 C2 C3c C3d C4 合计 根管口 112(58.03) 45(23.32) 13(6.74) 19(9.84) 4(2.07) 193 根中部 16(8.29) 75(38.86) 61(31.61) 33(17.10) 8(4.14) 193 根尖3 mm 0(0.00) 7(3.63) 25(12.95) 92(47.67) 69(35.75) 193 -
[1] Ren H Y,Zhao Y S,Yoo Y J,et al. Mandibular molar C-shaped root canals in 5th millennium BC China[J]. Arch Oral Biol,2020,117:104773. [2] Zhang X,Xu N,Wang H,et al. A cone-beam computed tomographic study of apical surgery-related morphological characteristics of the distolingual root in 3-rooted mandibular first molars in a Chinese population[J]. J Endod,2017,43(12):2020-2024. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2017.07.022 [3] Zhang R,Wang H,Tian Y Y,et al. Use of cone-beam computed tomography to evaluate root and canal morphology of mandibular molars in Chinese individuals[J]. Int Endod J,2011,44(11):990-999. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2011.01904.x [4] Fan B,Cheung G S,Fan M,et al. C-shaped canal system in mandibular second molars:Part I--Anatomical features[J]. J Endod,2004,30(12):899-903. doi: 10.1097/01.don.0000136207.12204.e4 [5] Qiao X,Zhu H,Yan Y,et al. Prevalence of middle mesial canal and radix entomolaris of mandibular first permanent molars in a western Chinese population:an in vivo cone-beam computed tomographic study[J]. BMC Oral Health,2020,20(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s12903-020-01218-z [6] Al-Alawi H,Al-Nazhan S,Al-Maflehi N,et al. The prevalence of radix molaris in the mandibular first molars of a Saudi subpopulation based on cone-beam computed tomography[J]. Restor Dent Endod,2019,45(1):e1. [7] Nosrat A,Deschenes R J,Tordik P A,et al. Middle mesial canals in mandibular molars:incidence and related factors[J]. J Endod,2015,41(1):28-32. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2014.08.004 [8] Yang Y,Wu B,Zeng J,et al. Classification and morphology of middle mesial canals of mandibular first molars in a southern Chinese subpopulation:a cone-beam computed tomographic study[J]. BMC Oral Health,2020,20(1):358. doi: 10.1186/s12903-020-01339-5 [9] Zheng Q,Zhang L,Zhou X,et al. C-shaped root canal system in mandibular second molars in a Chinese population evaluated by cone-beam computed tomography[J]. Int Endod J,2011,44(9):857-862. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2011.01896.x -






 下载:
下载: