Top Closure Tension-relief System with Regulated Oxygen-enriched Negative Pressure-assisted Wound Therapy for the Treatment of Refractory Wounds
-
摘要:
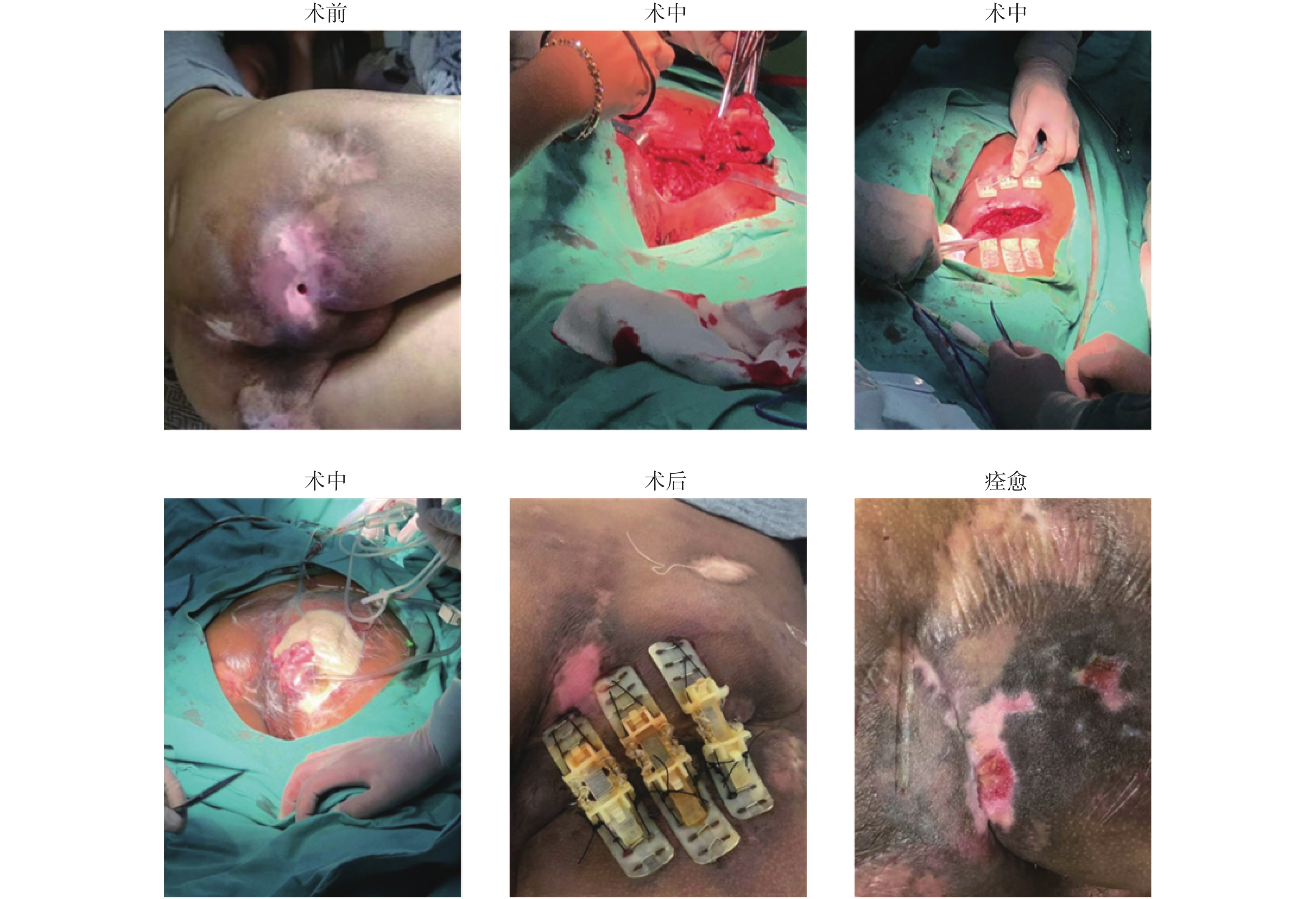
目的 探讨Top Closure皮肤牵拉闭合器联合富氧可调节负压辅助疗法治疗难治性创面的临床疗效。 方法 选取2018年8月至2020年7月昆明医科大学第一附属医院胃肠与疝外科收治的不同部位难治性创面患者36例,回顾性分析Top Closure皮肤牵拉闭合器与富氧可调节负压辅助疗法的治疗效果。 结果 35例患者经Top Closure皮肤牵拉闭合器与富氧可调节负压辅助疗法治疗后,创面均愈合良好,无愈合不良或不愈合。1例患者因为术后严重的心肺功能衰竭死亡。 结论 Top Closure皮肤持续牵张技术联合富氧可调节负压辅助疗法相对简单,大大降低了手术难度,术后伤口愈合良好,可应用于治疗难治性创面。 -
关键词:
- Top Closure皮肤持续牵张技术 /
- 富氧可调节负压辅助疗法 /
- 难治性创面 /
- 褥疮 /
- 糖尿病足
Abstract:Objective To investigate the clinical efficacy of Top Closure tension-relief system combined with regulated oxygen-enriched negative pressure-assisted wound therapy in the treatment of refractory wounds. Methods From August 2018 to July 2020, 36 patients with refractory wounds at different sites were selected from the Department of Gastroenterology and hernia surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University. We retrospectively analyzed the therapeutic effects of Top Closure tension-relief system combined with regulated oxygen-enriched negative pressure-assisted wound therapy. Results After 35 patients were treated with Top Closure skin traction occluder and oxygen-enriched adjustable negative pressure therapy, the wounds healed well and there was no malunion or nonunion. One patient died of severe cardiopulmonary failure after operation. Conclusion Top Closure tension-relief system combined with regulated oxygen-enriched negative pressure-assisted wound therapy in the treatment of refractory wounds is relatively simple, it can greatly reduce the difficulty of operation, and make the wound heal well after operation, so it can be used to treat refractory wounds. -
表 1 36例患者创面疗效分析(
$\bar x \pm s$ )Table 1. Analysis of curative effect of 36 cases of wounds (
$\bar x \pm s$ )疾病类型 人数(n) 年龄(岁) 疤痕质量评分(分) 褥疮愈合质量评分(分) 创面愈合情况 住院时间(周) 褥疮 5 19~50 2.0 ± 1.0 5.0 ± 2.0 痊愈 5.0 ± 1.2 25 51~90 3.0 ± 1.0 6.0 ± 1.0 24例痊愈
1例死亡7.0 ± 2.1 糖尿病足 5 65~80 3.0 ± 1.0 痊愈 10 ± 1.5 巨大缺损 1 35 3 痊愈 3 -
[1] Reinke J,Sorg H. Wound repair and regeneration[J]. European surgical research Europaische chirurgische Forschung Recherches chirurgicales europeennes,2012,49(1):35-43. doi: 10.1159/000339613 [2] Lyder CH. Pressure ulcer prevention and management[J]. JAMA,2003,289(2):223-236. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.2.223 [3] Govea-Camacho L H,Astudillo-Carrera A,Hermosillo-Sandoval JM,et al. Impact of vacuum-assisted closure management in deep neck abscesses[J]. Cirugia y Cirujanos,2016,84(4):275-281. doi: 10.1016/j.circir.2015.12.004 [4] Xing D,Yang Z,Cao C,et al. A modified negative pressure wound therapy for the treatment of refractory wounds:A preliminary study[J]. Medicine,2020,99(28):e21148. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021148 [5] Qu J,Yan R,Wang L,et al. Free dermatoplasty combined with vacuum sealing drainage for the treatment of large-area soft tissue defects accompanied by bone exposure in the lower leg[J]. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine,2013,5(5):1375-1380. doi: 10.3892/etm.2013.999 [6] Shrestha B,Nathan V,Delbridge M,et al. Vacuum-assisted closure(VAC)therapy in the management of wound infection following renal transplantation[J]. Kathmandu University Medical Journal(KUMJ),2007,5(1):4-7. [7] Li Y,Hu X,Lai X,et al. Improvement of wound healing by regulated oxygen-enriched negative pressure-assisted wound therapy in a rabbit model[J]. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology,2018,43(1):11-18. doi: 10.1111/ced.13225 [8] Zhu Z,Tong Y,Wu T,et al. TopClosure® tension-relief system for immediate primary abdominal defect repair in an adult patient with bladder exstrophy[J]. The Journal of International Medical Research,2020,48(1):30-36. [9] Topaz M,Carmel N,Topaz G,et al. Stress-relaxation and tension relief system for immediate primary closure of large and huge soft tissue defects:an old-new concept:new concept for direct closure of large defects[J]. Medicine,2014,93(28):e234. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000234 [10] Baryza M J,Baryza G A. The Vancouver Scar Scale:an administration tool and its interrater reliability[J]. The Journal of Burn care & Rehabilitation,1995,16(5):535-538. [11] Marongiu F,Buggi F,Mingozzi M,et al. A rare case of primary necrotising fasciitis of the breast:combined use of hyperbaric oxygen and negative pressure wound therapy to conserve the breast. Review of literature[J]. International Wound Journal,2017,14(2):349-354. doi: 10.1111/iwj.12607 [12] Suh H,Lee A Y,Park E J,et al. Negative pressure wound therapy on closed surgical wounds with dead space:Animal study using a swine model[J]. Annals of Plastic Surgery,2016,76(6):717-722. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000000231 [13] Li Z,Wu W,Liu S,et al. Effect of vacuum sealing drainage in dermatoplasty of large area of cutaneous defects[J]. International Journal of Surgery(London,England),2017,42:143-146. [14] Huang Q,Wang J T,Gu H C,et al. Comparison of vacuum sealing drainage and traditional therapy for treatment of diabetic foot ulcers:A meta-analysis[J]. The Journal of foot and ankle surgery:official publication of the American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons,2019,58(5):954-958. [15] Topaz M. Improved wound management by regulated negative pressure-assisted wound therapy and regulated,oxygen- enriched negative pressure-assisted wound therapy through basic science research and clinical assessment[J]. Indian Journal of Plastic Surgery:Official Publication of the Association of Plastic Surgeons of India,2012,45(2):291-301. doi: 10.4103/0970-0358.101301 [16] Sugihara F, Inoue N, Venkateswarathirukumara S. Ingestion of bioactive collagen hydrolysates enhanced pressure ulcer healing in a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical study[J]. Scientific Reports,2018,8(1):11403. [17] Iizaka S,Kaitani T,Nakagami G,et al. Clinical validity of the estimated energy requirement and the average protein requirement for nutritional status change and wound healing in older patients with pressure ulcers:A multicenter prospective cohort study[J]. Geriatrics & Gerontology International,2015,15(11):1201-1209. [18] Mullins M,Thomason S S,Legro M. Monitoring pressure ulcer healing in persons with disabilities[J]. Rehabilitation Nursing:the Official Journal of the Association of Rehabilitation Nurses,2005,30(3):92-99. doi: 10.1002/j.2048-7940.2005.tb00369.x [19] Choi E P,Chin W Y,Wan E Y,et al. Evaluation of the internal and external responsiveness of the Pressure Ulcer Scale for Healing(PUSH)tool for assessing acute and chronic wounds[J]. Journal of Advanced Nursing,2016,72(5):1134-1143. doi: 10.1111/jan.12898 -






 下载:
下载: