Efficacy of Multiple Non-invasive Diagnostic Models in the Diagnosis of Hepatic Fibrosis in Patients with Chronic Liver Diseases
-
摘要:
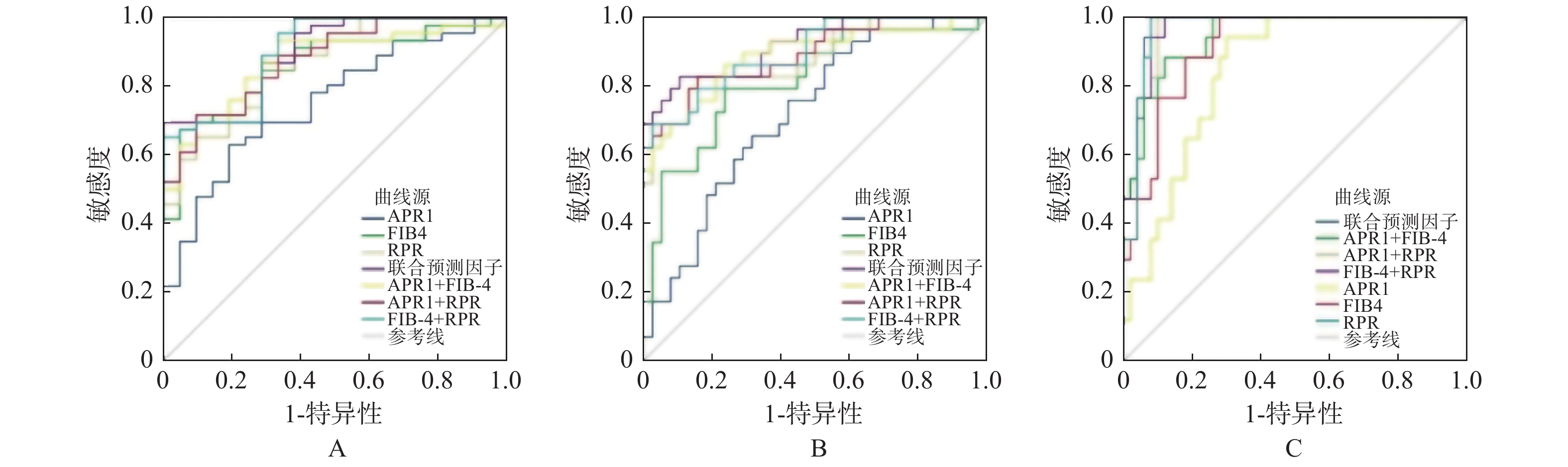
目的 探讨APRI、FIB-4、Forns、GPR、S指数、King、RPR无创模型在慢性肝病患者肝纤维化中的诊断价值。 方法 回顾性收集2016年1月至2020年12月在昆明医科大学附属甘美医院接受肝穿刺活检的67例慢性肝病患者的临床资料,计算不同模型得分,与肝组织活检病理分期做对照研究和统计学分析。 结果 7种无创模型中,GPR与肝纤维化分期相关性最弱(r = 0.259),RPR最强(r = 0.769);RPR诊断肝纤维化价值相对最高,诊断显著肝纤维化(≥S2)、进展期肝纤维化(≥S3)和肝硬化(S4)AUROC分别为0.866、0.883、0.967;构建联合预测因子RPR + FIB-4 + APRI,诊断显著肝纤维化、进展期肝纤维化和肝硬化能力均提高(AUROC = 0.896、0.919、0.973)。 结论 7种无创模型中RPP诊断性能相对最佳,无创模型联合诊断可提高诊断肝纤维化的准确性。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the diagnostic value of APRI, FIB-4, Forns, GPR, S-index, King, RPR non-invasive models in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic liver disease. Methods The clinical data of 67 patients with chronic liver disease who received liver biopsy in Ganmei Hospital Affiliated to Kunming Medical University from January 2016 to December 2020 were retrospectively collected. The scores of different models were calculated and compared with the pathological stages of liver biopsy for statistical analysis. Results Among the 7 non-invasive models, the correlation between GPR and liver fibrosis stage was the weakest (r = 0.259), while RPR was the strongest (r = 0.769). The value of RPR in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis was the highest, and the AUROC of significant liver fibrosis (≥S2), advanced liver fibrosis (≥S3) and cirrhosis (S4) were 0.866, 0.883 and 0.967, respectively. The combined predictor RPR + FIB-4 + APRI was established to improve the ability to diagnose significant liver fibrosis, advanced liver fibrosis and cirrhosis (Auroc = 0.896, 0.919, 0.973). Conclusion The diagnostic performance of RPP is the best among the seven non-invasive models, and the combined diagnosis of non-invasive model can improve the accuracy of the diagnosis of liver fibrosis. -
Key words:
- Liver fibrosis /
- Non-invasive indexes /
- Serum biomarker
-
表 1 纳入患者临床资料特征比较[
$\bar x \pm s$ /M(P25,P75)]Table 1. Comparison of clinical data characteristics of included patients [
$\bar x \pm s$ /M(P25,P75)]指标 S1(n = 21) S2(n = 17) S3(n = 12) S4(n = 17) χ2/F/H P 男性 11(52.4) 9(52.9) 8(66.7) 8(47.1) 1.13 0.769 年龄(岁) 45.1 ± 14.0 50.4 ± 12.1 52.2 ± 12.8 50.5 ± 8.4 1.15 0.335 ALB(g/L) 48.9 ± 7.1 44.2 ± 4.0 43.0 ± 5.5 31.4 ± 4.2 33.67 < 0.001* ALT(U/L) 64
(39.5,97.5)83(27.5,202.5) 41.5(28.5,99.25) 40(28,102) 2.79 0.425 AST(U/L) 44(31,52.5) 71(26.5,140.5) 35.5(25.5,47.5) 76(43.5,171.5) 7.97 0.047* TBil(mol/L) 15.2(11.3,22.6) 13.5(11.1,20.4) 13.5(9.4,28.6) 35.5(21.4,314.0) 17.80 < 0.001* GGT(U/L) 80(29,401.5) 112(26.5,426.5) 40(22.5,170.5) 88(64,141.5) 1.47 0.69 ALP(U/L) 95(84,135.5) 149(83,264.5) 92.5(56.8,174.3) 187(139,249) 14.15 0.003* TC(mmol/L) 4.7 ± 1.1 4.9 ± 1.8 4.3 ± 0.8 3.3 ± 1.2 4.42 0.007* PLT(×109/L) 247.5 ± 68.0 200.0 ± 60.0 162.8 ± 58.3 104.5 ± 54.2 18.08 < 0.001* RDW(%) 13(12.1,13.6) 13.2(12.1,15.4) 13.4(12.4,14.1) 17.6(15.2,24.4) 26.60 < 0.001* 注:*P < 0.05;ALB = 白蛋白,ALT = 丙氨酸氨基转氨酶,AST = 天冬氨酸氨基转氨酶,TBiL = 总胆红素,ALP = 碱性磷酸酶,GGT = γ-谷氨酰转移酶,TC = 总胆固醇,PLT = 血小板计数,RDW%为红细胞分布宽度。 表 2 不同肝纤维化分期患者无创诊断模型得分[M(P25,P75)]
Table 2. Comparison of non-invasive diagnostic model scores for patients in different stages of liver fibrosis [M(P25,P75)]
无创模型 S1(n = 21) S2(n = 17) S3(n = 12) S4(n = 17) H P APRI 0.46(0.3,0.7) 0.77(0.4,2.5) 0.52(0.5,1.2) 2.13(1.0,5.2) 21.2 < 0.001* FIB-4 0.96(0.8,1.5) 1.82(1.2,3.2) 1.71(1.2,4.7) 5.46(3.6,16.8) 34.281 < 0.001* Forns 7.24(6.2,8.3) 8.71(6.9,9.9) 8.81(7.4,9.6) 10.25(9.2,13.0) 23.479 < 0.001* GPR 0.65(0.3,3.8) 1.13(0.3,4.1) 0.69(0.4,3.3) 2.50(1.3,5.6) 6.488 0.09 S指数 0.15(0.06,0.51) 0.35(0.07,0.98) 0.19(0.07,0.80) 1.06(0.67,2.47) 17.815 < 0.001* King评分 8.43(4.8,13.8) 20.23(7.4,43.2) 10.40(7.7,27.3) 49.10(26.5,132.4) 26.293 < 0.001* RPR 0.055(0.045,0.064) 0.067(0.059,0.090) 0.087(0.060,0.111) 0.193(0.131,0.317) 40.991 < 0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 3 各模型与炎症分级(G)肝纤维化分期(F)的相关性
Table 3. Correlation between each model and inflammation grade (G) and liver fibrosis stage (F)
无创模型 相关系数(G) P 相关系数(F) P APRI 0.623 < 0.001 0.512 < 0.001 FIB-4 0.669 < 0.001 0.692 < 0.001 Forns 0.539 < 0.001 0.58 < 0.001 GPR 0.425 0.003 0.259 0.034 S指数 0.554 < 0.001 0.45 < 0.001 King 0.660 < 0.001 0.578 < 0.001 RPR 0.609 < 0.001 0.769 < 0.001 表 4 各模型诊断肝纤维化的AUROC比较
Table 4. Comparison of AUROC in liver fibrosis diagnosis of each model
模型 显著肝纤维化(≥S2) 进展期肝纤维化(≥S3) 肝硬化(S4) AUROC 95%置信区间 P AUROC 95%置信区间 P AUROC 95%置信区间 P APRI 0.754 0.633~0.851 0.001* 0.719a 0.596~0.822 0.002* 0.842a 0.733~0.920 < 0.001* FIB4 0.86b 0.754~0.933 < 0.001* 0.815 0.701~0.899 < 0.001* 0.913 0.818~0.968 < 0.001* Forns 0.784 0.666~0.875 < 0.001* 0.78a 0.663~0.872 < 0.001* 0.852a 0.744~0.927 < 0.001* GPR 0.609 0.482~0.726 0.154 0.611 0.484~0.728 0.121 0.701 0.577~0.807 0.019* S指数 0.692 0.567~0.799 0.012* 0.703a 0.579~0.809 0.005* 0.834a 0.723~0.914 < 0.001* King 0.879 0.776~0.946 < 0.001* 0.75a 0.630~0.848 < 0.001* 0.789a 0.672~0.879 < 0.001* RPR 0.866 0.761~0.937 < 0.001* 0.883 0.781~0.949 < 0.001* 0.967 0.892~0.995 < 0.001* 注:*P < 0.05。与RPR比较,aP < 0.05;与King比较,bP < 0.05;GPR未纳入比较;S4期:RPR与APRI、Forns、S、King比较的Z值分别为2.596、2.434、2.488、2.088;≥S3期:与APRI、Forns、S、King比较的Z值分别为2.895、1.96、2.736、2.415;≥S2期:King与FIB-4比较Z值为2.34。 表 5 APRI、FIB-4、RPR联合诊断肝纤维化效能比较
Table 5. Comparison of efficacy of APRI,FIB-4 and RPR in the combined diagnosis of liver fibrosis
无创模型 AUROC 95%置信区间 敏感度 NLR 特异度 PLR APRI + FIB-4 ≥S2 0.872 0.786~0.957 0.935 0.113 0.571 2.179 ≥S3 0.887 0.803~0.971 0.862 0.181 0.763 3.637 S4 0.944 0.891~0.996 0.882 0.134 0.88 7.35 APRI + RPR ≥S2 0.879 0.798~0.96 0.717 0.349 0.81 3.774 ≥S3 0.891 0.812~0.97 0.828 0.204 0.842 5.241 S4 0.961 0.919~1 1 / 0.9 10 FIB-4 + RPR ≥S2 0.903 0.829~0.977 0.674 0.342 0.952 14.04 ≥S3 0.898 0.825~0.972 0.69 0.318 0.974 26.54 S4 0.967 0.93~1 1 / 0.88 8.333 RPR + FIB-4 + APRI ≥S2 0.896 0.822~0.971 0.696 0.304 1 / ≥S3 0.919 0.853~0.985 0.897 0.23 0.447 1.622 S4 0.973 0.940~1.000 1 / 0.92 12.5 注:NLR:阴性似然比;PLR:阳性似然比。 -
[1] Wai C T,Greenson J K,Fontana R J,et al. A simple noninvasive index can predict both significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C[J]. Hepatology,2003,38(2):518-526. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2003.50346 [2] Sterling R K,Lissen E,Clumeck N,et al. Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection[J]. Hepatology,2006,43(6):1317-1325. doi: 10.1002/hep.21178 [3] Forns X,Ampurdanès S,Llovet J M,et al. Identification of chronic hepatitis C patients without hepatic fibrosis by a simple predictive model[J]. Hepatology,2002,36(4 Pt 1):986-992. [4] Lemoine M,Shimakawa Y,Nayagam S,et al. The gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase to platelet ratio(GPR)predicts significant liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic HBV infection in West Africa[J]. Gut,2016,65(8):1369-1376. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309260 [5] Zhou K,Gao C F,Zhao Y P,et al. Simpler score of routine laboratory tests predicts liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol,2010,25(9):1569-1577. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06383.x [6] Cross T J,Rizzi P,Berry P A,et al. King’s Score:an accurate marker of cirrhosis in chronic hepatitis C[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol,2009,21(7):730-738. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e32830dfcb3 [7] Chen B,Ye B,Zhang J,et al. RDW to platelet ratio:a novel noninvasive index for predicting hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis in chronic hepatitis B[J]. PLoS One,2013,8(7):e68780. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068780 [8] 陆伦根,尤红,谢渭芬,等. 肝纤维化诊断及治疗共识(2019年)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志,2019,35(10):2163-2172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.10.007 [9] 王贵强,段钟平,王福生,等. 慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2019年版)[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志,2020,23(01):9-32. [10] Xiao G,Yang J,Yan L. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index and fibrosis-4 index for detecting liver fibrosis in adult patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection:a systemic review and meta-analysis[J]. Hepatology,2015,61(1):292-302. doi: 10.1002/hep.27382 [11] Yuyun D,Zhihua T,Haijun W,et al. Predictive value of the red blood cell distribution width-to-platelet ratio for hepatic fibrosis[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol,2019,54(1):81-86. doi: 10.1080/00365521.2018.1558786 [12] 蔡莹,刘迪娜,崔静,等. 红细胞分布宽度与血小板比值在慢性肝病纤维化的预测价值[J]. 中国医药导刊,2021,23(3):161-167. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0959.2021.03.001 [13] 桂志兵,汪文生. 红细胞分布宽度与血小板计数比值在乙型肝炎肝硬化患者病情评估中的作用[J]. 医学信息,2018,31(20):65-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2018.20.019 [14] Wang R,Zhang Q,Zhao S,et al. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase to platelet ratio index is a good noninvasive biomarker for predicting liver fibrosis in Chinese chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. J Int Med Res,2016,44(6):1302-1313. doi: 10.1177/0300060516664638 [15] Liu D P,Lu W,Zhang Z Q,et al. Comparative evaluation of GPR versus APRI and FIB-4 in predicting different levels of liver fibrosis of chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Viral Hepat,2018,25(5):581-589. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12842 [16] Huang R,Wang G,Tian C,et al. Gamma-glutamyl-transpeptidase to platelet ratio is not superior to APRI,FIB-4 and RPR for diagnosing liver fibrosis in CHB patients in China[J]. Sci Rep,2017,7(1):8543. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09234-w [17] Schiavon L L,Narciso-schiavon J L,Ferraz M,et al. The γ-glutamyl transpeptidase to platelet ratio(GPR)in HBV patients:just adding up?[J]. Gut,2017,66(6):1169-1170. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312658 [18] Yanchao H,Hao L,Xiaoyan L,et al. Value of gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase-to-platelet ratio in diagnosis of hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. World J Gastroenterol,2017,23(41):7425-7432. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i41.7425 [19] 王海莉,贾因棠. APRI、GPRI、FIB-4在诊断慢乙肝肝脏纤维化及肝癌中的临床应用价值[J]. 山西医科大学学报,2018,49(6):650-654. -






 下载:
下载: