Progress in Clinical Research on Drug Resistance and Reversal of Endocrine Therapy in Breast Cancer
-
摘要: 激素受体阳性HR + 乳腺癌临床治疗初始阶段依靠内分泌治疗常取得较好的预后,但一旦出现复发和转移,总的预后并不理想,因此近年来内分泌治疗的疗效因耐药性的产生而受到各种限制,内分泌耐药的逆转被认为是让早期激素受体阳性乳腺癌回归慢性疾病治疗的新的方法和希望,延缓和逆转内分泌耐药的策略也逐渐受到临床和科研工作密切的关注。对延缓和逆转内分泌治疗以及应对策略的研究进展作一综述。Abstract: In the initial stage of clinical treatment of hormone receptor positive HR + breast cancer, good prognosis is often achieved by endocrine therapy. Once recurrence and metastasis occur, the overall prognosis is not ideal. Therefore, the efficacy of endocrine therapy is limited by the emergence of drug resistance these years. The reversal of endocrine resistance is considered to be a new method and hope for early hormone receptor positive breast cancer to return to chronic disease treatment. The strategy of delaying and reversing endocrine drug resistance has been paid close attention by clinical and scientific research work. This article will review the research progress and strategies of delaying and reversing endocrine therapy.
-
Key words:
- Breast cancer /
- Endocrine therapy /
- Drug resistance /
- Reversal
-
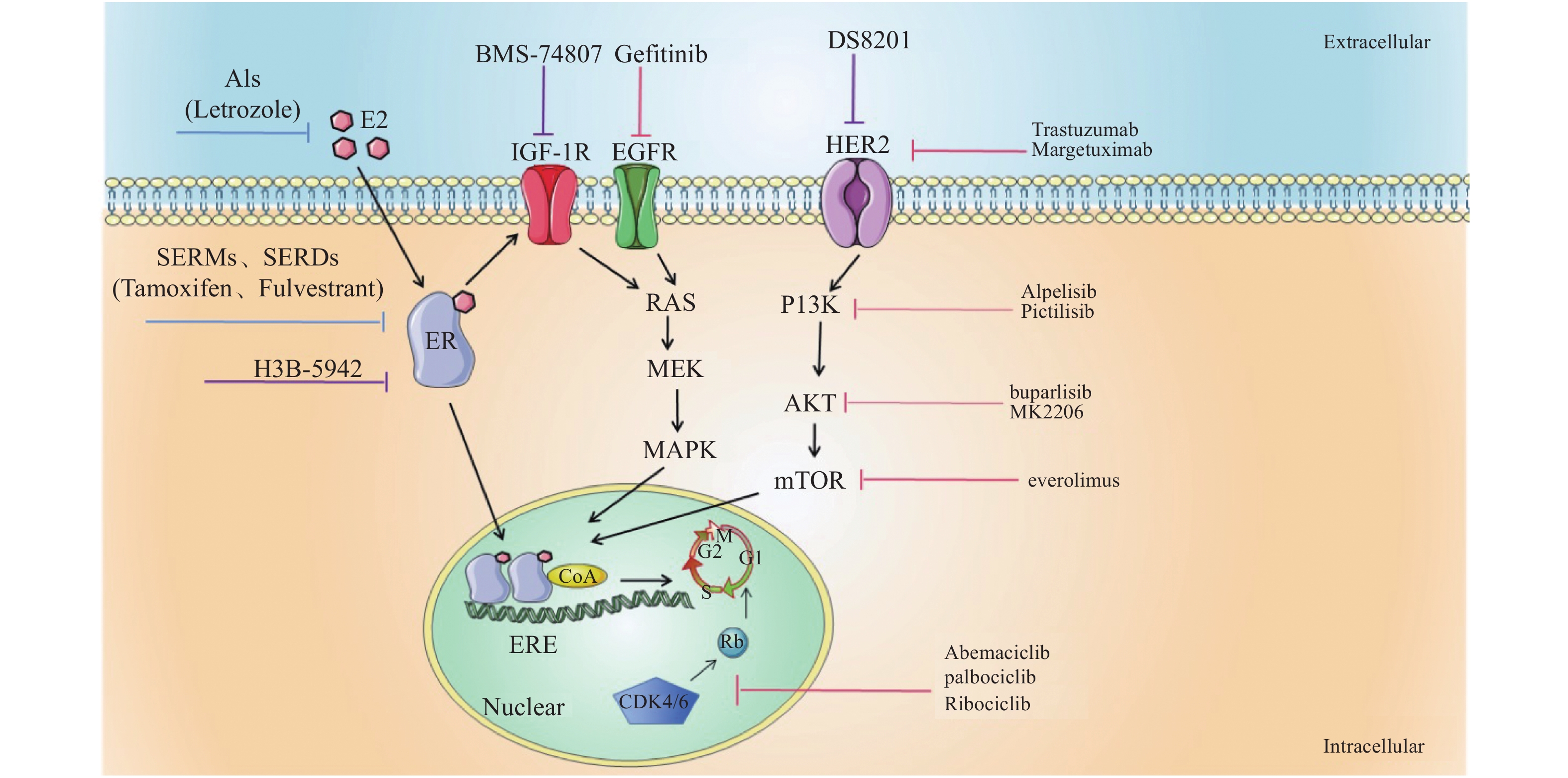
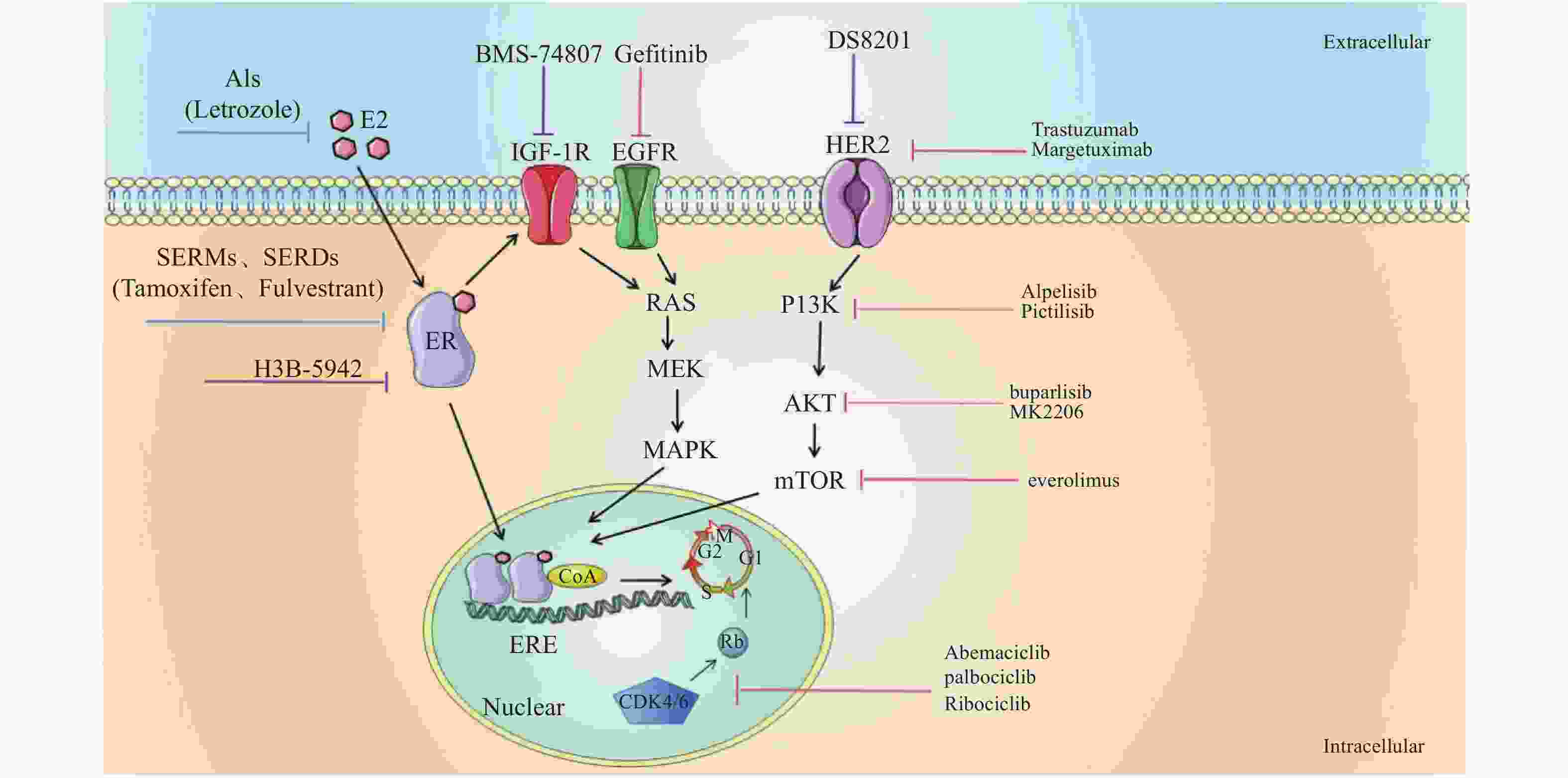
表 1 HR+乳腺癌的内分泌联合治疗
Table 1. Endocrine combined therapy for HR + breast cancer
药物类别/靶点 药物名称 临床研究 研究设计 无进展生存时间/月 EGFR inhibitors Gefitinib NCT00229697[2] Tamoxifen + Gefitinib vs placebo 10.9 vs 8.8 NCT00057941[5] Gefitinib + Anastrozole vs
Gefitinib + Fulvestrant5.3 vs 5.2 Molecular targeted agents Trastuzumab TAnDEM-3[3] Trastuzumab + Anastrozole vs anastrozole 4.8 vs 2.4
5.6 vs 3.8Margetuximab SOPHIA-3[4] Margetuximab + chemotherapy vs
Trastuzumab+ chemotherapy6.9 vs 5.1 CDK4/6 inhibitors Abemaciclib MONARCH-3[7] Abemaciclib/placebo+
non-steroidal drugs28.18 vs 14.76 palbociclib NCT02549430[8] Palbociclib + ET vs palbociclib 10.8 vs 6.5 Ribociclib MalAlESA-2[9] Ribociclib + Letrozole vs
ribociclib + placebo25.3 vs 16.0 PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors buparlisib BELLE-2[10] Buparlisib + Fulvestrant vs placebo 6.9 vs 5.0;
6.8 vs 4.5;
6.8 vs 4.0Pictilisib NCT01437566[11] Pictilisib + Fulvestrant vs placebo 6.5 vs 5.1 Alpelisib BYL719-1b[12] Alpelisib + Letrozole vs placebo -N/A MK-2206 NCT01344031[14] MK-2206 + Fulvestrant vs placebo N/A- -
[1] Wu Y L,Zhang L,Kim D W,et al. Phase Ib/II study of capmatinib (INC280) plus gefitinib after failure of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor therapy in patients with EGFR-mutated, MET factor-dysregulated non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol,2018,36(31):3101-3109. [2] Osborne C K,Neven P,Dirix L Y,et al. Gefitinib or placebo in combination with tamoxifen in patients with hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer:a randomized phase II study[J]. Clin Cancer Res,2011,17(5):1147-1159. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1869 [3] Kaufman B,Mackey J R,Clemens M R,et al. Trastuzumab plus anastrozole versus anastrozole alone for the treatment of postmenopausal women with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive,hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer:results from the randomized phase III TAnDEM study[J]. J Clin Oncol,2009,27(33):5529-5537. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.20.6847 [4] Rugo H S, Im S A, Cardoso F, et al. Efficacy of Margetuximab vs trastuzumab in patients with pretreated ERBB2-positive advanced breast cancer: A phase 3 randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA Oncol,2021,7(4):573-584. [5] Carlson R W,O’Neill A,Vidaurre T,et al. A randomized trial of combination anastrozole plus gefitinib and of combination fulvestrant plus gefitinib in the treatment of postmenopausal women with hormone receptor positive metastatic breast cancer[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat,2012,133(3):1049-1056. doi: 10.1007/s10549-012-1997-5 [6] Li Y,Guo Q,Zhang C,Huang Z,et al. Discovery of a highly potent,selective and novel CDK9 inhibitor as an anticancer drug candidate[J]. Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2017,27(15):3231-3237. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.06.041 [7] Johnston S,Martin M,Di Leo A,et al. MONARCH 3 final PFS:a randomized study of abemaciclib as initial therapy for advanced breast cancer[J]. NPJ Breast Cancer,2019,5:5. doi: 10.1038/s41523-018-0097-z [8] Malorni L,Curigliano G,Minisini A M,et al. Palbociclib as single agent or in combination with the endocrine therapy received before disease progression for estrogen receptor-positive,HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer:TREnd trial[J]. Ann Oncol,2018,29(8):1748-1754. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy214 [9] Hortobagyi G N,Stemmer S M,Burris H A,et al. Updated results from MONALEESA-2,a phase III trial of first-line ribociclib plus letrozole versus placebo plus letrozole in hormone receptor-positive,HER2-negative advanced breast cancer[J]. Ann Oncol,2018,29(7):1541-1547. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy155 [10] Baselga J,Im S A,Iwata H,et al. Buparlisib plus fulvestrant versus placebo plus fulvestrant in postmenopausal,hormone receptor-positive,HER2-negative,advanced breast cancer(BELLE-2):A randomised,double-blind,placebo-controlled,phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol,2017,18(7):904-916. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30376-5 [11] Krop I E,Mayer I A,Ganju V,et al. Pictilisib for oestrogen receptor-positive,aromatase inhibitor-resistant,advanced or metastatic breast cancer(FERGI):a randomised,double-blind,placebo-controlled,phase 2 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol,2016,17(6):811-821. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)00106-6 [12] Mayer I A,Abramson V G,Formisano L,et al. A phase Ib study of alpelisib(BYL719),a PI3Kalpha-specific inhibitor,with letrozole in ER+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res,2017,23(1):26-34. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0134 [13] Hortobagyi G N,Chen D,Piccart M,et al. Correlative analysis of genetic alterations and everolimus benefit in hormone receptor-positive,human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer:Results from BOLERO-2[J]. J Clin Oncol,2016,34(5):419-426. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.60.1971 [14] Ma C X,Sanchez C,Gao F,et al. A Phase I study of the AKT inhibitor MK-2206 in combination with hormonal therapy in postmenopausal women with estrogen receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res,2016,22(11):2650-2658. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2160 [15] Kim H J,Kwon H,Lee J W,et al. Metformin increases survival in hormone receptor-positive,HER2-positive breast cancer patients with diabetes[J]. Breast Cancer Res,2015,17(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s13058-015-0574-3 [16] Sonnenblick A,Agbor-Tarh D,Bradbury I,et al. Impact of diabetes,insulin,and metformin use on the outcome of patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive primary breast cancer:Analysis from the ALTTO phase III randomized trial[J]. J Clin Oncol,2017,35(13):1421-1429. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.69.7722 [17] Goedert J J,Hua X,Bielecka A,et al. Postmenopausal breast cancer and oestrogen associations with the IgA-coated and IgA-noncoated faecal microbiota[J]. Br J Cancer,2018,118(4):471-479. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2017.435 [18] Hou X,Huang F,Macedo L F,et al. Dual IGF-1R/InsR inhibitor BMS-754807 synergizes with hormonal agents in treatment of estrogen-dependent breast cancer[J]. Cancer Res,2011,71(24):7597-7607. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1080 [19] Tamura K,Tsurutani J,Takahashi S,et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan(DS-8201a)in patients with advanced HER2-positive breast cancer previously treated with trastuzumab emtansine:a dose-expansion,phase 1 study[J]. Lancet Oncol,2019,20(6):816-826. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30097-X [20] Toy W,Shen Y,Won H,et al. ESR1 ligand-binding domain mutations in hormone-resistant breast cancer[J]. Nat Genet,2013,45(12):1439-1445. doi: 10.1038/ng.2822 [21] Puyang X,Furman C,Zheng G Z,et al. Discovery of selective estrogen receptor covalent antagonists for the treatment of ERα WT and ERα MUT breast cancer[J]. Cancer Discovery,2018,8(9):1176-1193. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-1229 [22] Piggott L,Silva A,Robinson T,et al. Acquired Resistance of ER-Positive Breast Cancer to Endocrine Treatment Confers an Adaptive Sensitivity to TRAIL through Posttranslational Downregulation of c-FLIP[J]. Clin Cancer Res,2018,24(10):2452-2463. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1381 [23] Malorni L,Biagioni C,Luca F D,et al. Abstract 4416:Plasma thymidine kinase activity in patients with luminal metastatic breast cancer treated with Palbociclib within the phase II TREnd trial[J]. Cancer Research,2019,79(9):4416-4416. [24] Demark-Wahnefried W,Schmitz K H,Alfano C M,et al. Weight management and physical activity throughout the cancer care continuum[J]. CA Cancer J Clin,2018,68(1):64-89. doi: 10.3322/caac.21441 -





 下载:
下载: