Clinical Effect of Dexmedetomidine and Dexamethasone as Adjuvants for Brachial Plexus Block
-
摘要:
目的 探讨添加右美托咪定(dexmedetomidine,DEX)或地塞米松(dexamethasone,DXM)对肌间沟臂丛神经阻滞临床效果的影响。 方法 随机将拟行超声引导下肌间沟臂丛阻滞的患者50例,按局麻药配方不同分为5组:R组(对照组,0.5%罗哌卡因20 mL,n = 10);R+LDEX组(0.5%罗哌卡因 + 1 μg/kg DEX共20 mL,n = 10);R + HDEX组(0.5%罗哌卡因 + 2 μg/kg DEX共20 mL,n = 10);R + LDXM组(0.5%罗哌卡因 + 4 mg DXM共20 mL,n = 10);R + HDXM组(0.5%罗哌卡因 + 8 mg DXM共20 mL,n = 10)。 结果 与其他组比较,R + LDEX组和R + HDEX组阻滞起效时间显著缩短(P < 0.05);与R组比较,4个实验组均显著延长阻滞作用时间(P < 0.01);术后12、24 h VAS评分和自控镇痛使用次数4个实验组明显低于R组,(P < 0.001);阻滞后5 min R + HDEX组患者HR降低,并持续至30 min(P < 0.05);R + LDEX和R + HDEX组在阻滞后5、10、15 min SBP、DBP和MAP升高(P < 0.05);注射局麻药后5 min,R + LDEX和R + HDEX组患者出现BIS降低并持续至30 min(P < 0.001),R + HDEX组BIS降低较R + LDEX组更为明显。 结论 局麻药添加DEX和DXM均能显著延长臂丛神经阻滞作用时间;DEX可以缩短肌间沟臂丛阻滞起效时间并引起血压一过性升高;DEX呈剂量依赖性的产生中枢镇静作用。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of adding dexmedetomidine (DEX) or dexamethasone (DXM) on the effect of interscalene brachial plexus block. Methods Fifty patients who underwent ultrasound-guided interscalene brachial plexus block were randomly selected, and randomly divided into 5 groups according to different local anesthetic formulations: R group (control group, 0.5% ropivacaine 20 ml, n = 10); R + LDEX group (0.5% ropivacaine + 1 μg/kg DEX total 20 mL, n = 10); R + HDEX group (0.5% ropivacaine + 2 μg/kg DEX total 20 mL, n = 10); R + LDXM group (0.5% ropivacaine + 4 mg DXM total 20 mL, n = 10); R + HDXM group (0.5% ropivacaine + 8 mg DXM total 20 ml, n = 10). Results Compared with other groups, the block onset time ofR + LDEX groupand R + HDEX group was significantly shorter (P < 0.05). Compared with R group, the block time of other experimental groups significantly prolonged (P < 0.01). The 12 and 24 h VAS scores and the number of postoperative patient-controlled analgesia in the 4 experimental groups were significantly lower than those in the R group (P < 0.001). The HR of the patients in the R + HDEX group was reduced after 5 minutes of blockade, and lasted for 30 minutes (P < 0.05). The SBP, DBP and MAP ofR + LDEX and R + HDEX groups increased by 5, 10, and 15 minutes later after blocked (P < 0.05). After 5 minutes injection of local anesthetics, patients in the R + LDEX and R + HDEX groups showed a decrease in BIS and continued for 30 minutes (P < 0.05), the decrease in BIS of R + HDEX group was more obvious than that of R + LDEX group. Conclusions Adding DEX and DXM to local anesthetics can significantly prolong the action time of brachial plexus block. DEX can shorten the onset time ofinterscalene brachial plexus block and cause a transient increase in blood pressure. DEX can produce central sedation in a dose-dependent manner effect. -
Key words:
- Dexmedetomidine /
- Dexamethasone /
- Brachial plexus block
-
表 1 患者特征统计表(
$\bar x \pm s $ )Table 1. Statistical table of patient characteristics (
$\bar x \pm s $ )组别 n 年龄(岁) 性别(男/女) BMI(kg/m2) ASA分级(Ⅰ/Ⅱ) 手术时间(min) R 10 42.20±6.34 7/3 24.05±2.51 7/3 49.00±11.26 R+LDEX 10 44.60±10.00 6/4 22.66±3.00 8/2 50.60±6.65 R+HDEX 10 44.90±5.13 5/5 26.07±4.21 8/2 49.60±14.81 R+LDXM 10 43.30±5.14 6/4 23.60±1.91 6/4 50.50±7.25 R+HDXM 10 42.30±8.42 4/6 25.28±3.34 9/1 51.10±5.34 P / 表 2 各组臂丛神经阻滞起效与维持时间比较(
$\bar x \pm s $ )Table 2. Comparison of onset and maintenance time of brachial plexus block in each group (
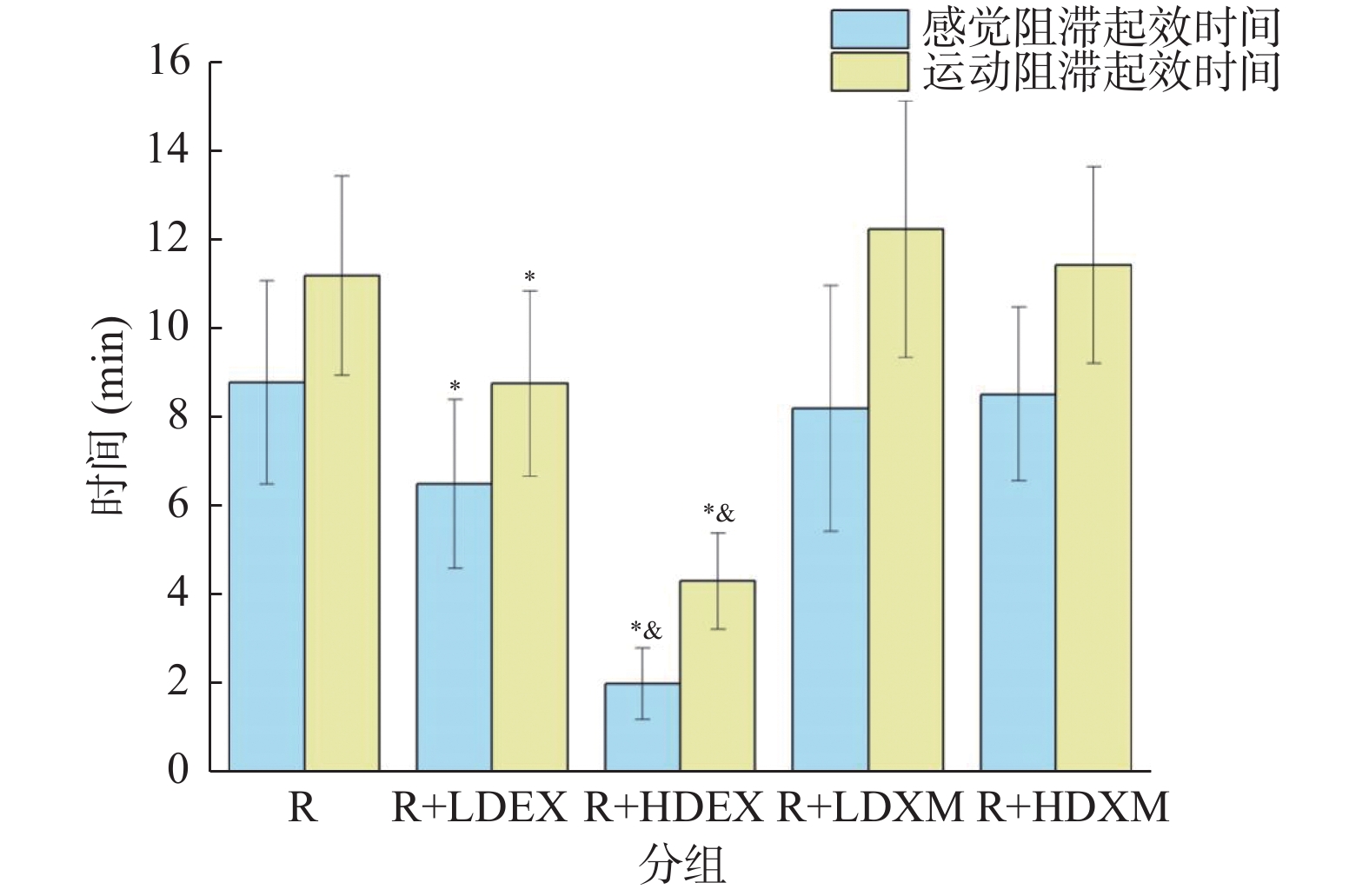
$\bar x \pm s $ )组别 感觉阻滞起效时间(min) 运动阻滞起效时间(min) 感觉阻滞维持时间(h) 运动阻滞维持时间(h) R 8.76 ± 2.28 11.17 ± 2.24 8.99 ± 2.61 9.37 ± 2.58 R+LDEX 6.48 ± 1.90* 8.74 ± 2.09* 12.45 ± 2.35#+ 16.06 ± 2.02#+ R+HDEX 1.99 ± 0.81*& 4.30 ± 1.09*& 18.81 ± 2.26# 19.17 ± 2.23# R+LDXM 8.18 ± 2.76 12.21 ± 2.89 19.32 ± 2.93# 19.66 ± 2.98# R+HDXM 8.50 ± 1.96 11.40 ± 2.21 20.09 ± 1.34# 20.53 ± 1.37# 与R组比较,R+LDEX和R+HDEX组显著缩短感觉和运动阻滞起效时间,*P < 0.05;与R+LDEX、R+LDXM和R+HDXM组比较,R+HDEX组显著缩短感觉和运动阻滞起效时间,&P < 0.01;与R组比较,R+LDEX、R+HDEX、R+LDXM和R+HDXM组显著延长感觉和运动阻滞作用时间,#P < 0.01;与R+HDEX、R+LDXM和R+HDXM组比较,R+LDEX组感觉与运动阻滞维持时间较短,+P < 0.05。 表 3 阻滞后后8、12、24 h患者VAS评分比较(
$\bar x \pm s $ )Table 3. Comparison of VAS scores at 8,12 and 24 hours after nerve block (
$\bar x \pm s $ )组别 8 h 12 h 24 h R 2.30 ± 0.68 4.20 ± 0.92 3.90 ± 0.57 R+LDEX 2.00 ± 1.05 2.00 ± 0.82* 2.10 ± 0.74* R+HDEX 2.10 ± 0.57 1.90 ± 0.57* 2.00 ± 0.67* R+LDXM 1.90 ± 0.74 1.80 ± 0.63* 2.10 ± 0.74* R+HDXM 2.20 ± 0.92 2.10 ± 0.74* 2.10 ± 0.57* 与R组比较,R+LDEX、R+HDEX、R+LDXM和R+HDXM组在12、24 hVAS评分显著降低,*P < 0.001。 表 4 各组患者不同时间点HR比较[(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),次/min]Table 4. Comparison of HR at different time points in each group [(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),次/min]组别 麻醉前 5 min 10 min 15 min 20 min 25 min 30 min R 81.40 ± 11.01 82.40 ± 10.96 84.30 ± 11.11 83.90 ± 11.83 83.90 ± 10.28 82.80 ± 10.70 84.00 ± 10.54 R+LDEX 81.70 ± 8.60 78.40 ± 8.22 75.00 ± 8.17* 73.90 ± 8.06* 73.50 ± 8.18* 73.90 ± 8.72* 74.20 ± 8.69* R+HDEX 80.80 ± 7.41 73.50 ± 10.03 72.90 ± 6.27* 71.20 ± 6.71* 71.00 ± 7.26* 70.50 ± 6.64* 70.30 ± 6.62* R+LDXM 81.80 ± 9.26 82.30 ± 9.30 84.10 ± 9.20 84.20 ± 9.69 83.70 ± 9.30 84.10 ± 9.78 84.60 ± 9.81 R+HDXM 83.10 ± 10.63 83.10 ± 11.65 83.80 ± 11.61 83.90 ± 11.70 83.90 ± 11.63 81.30 ± 12.92 82.50 ± 12.40 与其余各组比较,R+LDEX和R+HDEX组心率显著下降,*P < 0.05。 表 5 各组患者不同时间点SBP比较[(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),mmHg)]Table 5. Comparison of SBP at different time points in each group [(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),mmHg]组别 麻醉前 5 min 10 min 15 min 20 min 25 min 30 min R 111.40 ± 6.08 112.10 ± 6.14 112.20 ± 5.75 112.50 ± 5.80 112.00 ± 5.68 111.80 ± 5.81 112.20 ± 6.20 R+LDEX 111.90 ± 8.46 122.90 ± 5.43* 122.60 ± 5.34* 119.80 ± 6.16* 112.00 ± 8.74 111.60 ± 9.36 111.70 ± 9.09 R+HDEX 111.40 ± 7.00 124.90 ± 6.15* 124.30 ± 6.73* 120.90 ± 6.21* 112.50 ± 8.38 112.30 ± 6.34 112.10 ± 6.76 R+LDXM 108.20 ± 6.84 108.70 ± 6.63 109.20 ± 6.61 108.70 ± 6.27 108.80 ± 6.65 109.42 ± 8.04 109.20 ± 7.07 R+HDXM 114.10 ± 4.84 114.50 ± 4.81 114.30 ± 4.95 114.00 ± 5.03 113.60 ± 4.97 115.20 ± 4.49 115.72 ± 5.87 与其余各组比较,*P < 0.05。 表 6 各组患者不同时间点DBP比较[(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),mmHg]Table 6. Comparison of DBP at different time points in each group [(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),mmHg]组别 麻醉前 5 min 10 min 15 min 20 min 25 min 30 min R 70.10 ± 6.12 70.10 ± 6.84 70.70 ± 6.60 70.30 ± 7.15 70.10 ± 5.76 71.80 ± 6.02 71.50 ± 7.00 R+LDEX 68.36 ± 10.03 78.62 ± 10.86* 79.60 ± 10.31* 79.10 ± 10.07* 68.68 ± 8.57 68.60 ± 8.25 66.00 ± 10.23 R+HDEX 74.20 ± 8.90 81.90 ± 6.64* 83.00 ± 6.27* 78.80 ± 7.12* 75.50 ± 7.99 73.50 ± 8.26 74.80 ± 9.18 R+LDXM 70.40 ± 9.92 70.70 ± 10.39 70.70 ± 10.85 71.20 ± 10.61 71.20 ± 9.40 71.50 ± 8.87 71.70 ± 9.57 R+HDXM 65.90 ± 6.47 66.90 ± 6.17 66.18 ± 6.49 66.10 ± 6.57 65.80 ± 6.27 66.30 ± 6.95 66.50 ± 6.98 与其余各组比较,*P < 0.05。 表 7 各组患者不同时间点MAP比较[(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),mmHg]Table 7. Comparison of MAP at different time points in each group [(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),mmHg]组别 麻醉前 5 min 10 min 15 min 20 min 25 min 30 min R 83.87 ± 3.06 84.10 ± 3.42 84.53 ± 3.51 84.37 ± 3.54 84.07 ± 2.78 85.13 ± 3.47 85.07 ± 3.27 R+LDEX 82.83 ± 7.59 93.37 ± 7.83* 93.93 ± 7.45* 92.67 ± 7.26* 83.20 ± 6.90 82.93 ± 6.58 81.23 ± 7.52 R+HDEX 86.60 ± 6.05 96.23 ± 4.71* 96.77 ± 4.63* 92.83 ± 5.07* 87.83 ± 5.86 86.43 ± 5.68 87.23 ± 6.07 R+LDXM 83.00 ± 7.75 83.37 ± 8.04 83.53 ± 8.34 83.70 ± 8.01 83.73 ± 7.34 84.20 ± 7.25 84.20 ± 7.54 R+HDXM 81.97 ± 4.56 82.77 ± 4.22 82.17 ± 4.67 82.07 ± 4.44 81.73 ± 4.65 82.60 ± 4.51 82.80 ± 4.90 与其余各组比较,*P < 0.05。 表 8 各组患者阻滞前后BIS比较(
$\bar x \pm s $ )Table 8. Comparison of BIS before and after nerve block in all groups (
$\bar x \pm s $ )组别 麻醉前 5 min 10 min 15 min 20 min 25 min 30 min R 99.20 ± 0.79 99.50 ± 0.71 99.50 ± 0.71 99.60 ± 0.52 99.50 ± 0.53 99.50 ± 0.53 99.60 ± 0.52 R+LDEX 99.90 ± 0.32 83.10 ± 2.51*# 74.20 ± 2.15*# 72.70 ± 2.41*# 71.00 ± 2.16*# 70.40 ± 1.84*# 70.20 ± 1.69*# R+HDEX 99.80 ± 0.42 72.50 ± 3.87*# 63.70 ± 3.77*# 56.90 ± 3.84*# 56.00 ± 3.83*# 54.80 ± 3.91*# 54.50 ± 3.75*# R+LDXM 99.70 ± 0.68 99.80 ± 0.42 99.90 ± 0.32 99.90 ± 0.32 99.90 ± 0.32 99.80 ± 0.42 99.70 ± 0.68 R+HDXM 99.80 ± 0.42 99.70 ± 0.48 99.50 ± 0.71 99.50 ± 0.71 99.50 ± 0.71 99.50 ± 0.71 99.50 ± 0.71 与其余各组比较,*P < 0.001。与R+LDEX组比较,#P < 0.001。 -
[1] Koraki E,Stachtari C,Kapsokalyvas I,et al. Dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant to 0.5% ropivacaine in ultrasound-guided axillary brachial plexus bloc k[J]. J Clin Pharm Ther,2018,43(3):348-352. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12657 [2] Morita S,Oizumi N,Suenaga N,et al. Dexamethasone added to levobupivacaine prolongs the duration of interscalene brachial plexus block an d decreases rebound pain after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair[J]. J Shoulder Elbow Surg,2020,29(9):1751-1757. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2020.04.019 [3] Weerink M A S,Struys M,Hannivoort L N,et al. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of dexmedetomidine[J]. Clin Pharmacokinet,2017,56(8):893-913. doi: 10.1007/s40262-017-0507-7 [4] Kosugi T,Mizuta K,Fujita T,et al. High concentrations of dexmedetomidine inhibit compound action potentials in frog sciatic nerves with out alpha(2) adrenoceptor activation[J]. Br J Pharmacol,2010,160(7):1662-1676. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00833.x [5] 安丽,高鸿,段宏伟,等. 右美托咪定引起心动过缓的心脏电生理机制及其与钾通道的关系[J]. 实用医学杂志,2015,31(21):3496-3498. [6] Aliste J,Leurcharusmee P,Engsusophon P,et al. A randomized comparison between intravenous and perineural dexamethasone for ultrasound-guided axilla ry block[J]. Can J Anaesth,2017,64(1):29-36. doi: 10.1007/s12630-016-0741-8 [7] Xie W,Luo S,Xuan H,et al. Betamethasone affects cerebral expressions of NF-kappaB and cytokines that correlate with pain behavi or in a rat model of neuropathy[J]. Ann Clin Lab Sci,2006,36(1):39-46. [8] Zhang S,Song M,An W,et al. Effects of different doses of dexamethasone as local anesthetic adjuvant on brachial plexus block:A protocol for systematic review and meta analysis[J]. Medicine (Baltimore),2021,100(17):e25651. [9] Ferré F,Krin A,Sanchez M,et al. Perineural dexamethasone attenuates liposomal bupivacaine-induced delayed neural inflammation in mice in vivo[J]. Br J Anaesth,2020,125(2):175-183. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2020.04.091 [10] Sun Z,Liu H,Guo Q,et al. In vivo and in vitro evidence of the neurotoxic effects of ropivacaine:the role of the Akt signaling pathway[J]. Mol Med Rep,2012,6(6):1455-1459. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2012.1115 [11] Yang S,Abrahams M S,Hurn P D,et al. Local anesthetic Schwann cell toxicity is time and concentration dependent[J]. Reg Anesth Pain Med,2011,36(5):444-451. doi: 10.1097/AAP.0b013e318228c835 [12] Xue X,Fan J,Ma X,et al. Effects of local dexmedetomidine administration on the neurotoxicity of ropivacaine for sciatic nerve block in rats[J]. Mol Med Rep,2020,22(5):4360-4366. [13] Zheng L N,Guo F Q,Li Z S,et al. Dexmedetomidine protects against lidocaine-induced neurotoxicity through SIRT1 downregulation-mediate d activation of FOXO3a[J]. Hum Exp Toxicol,2020,39(9):1213-1223. doi: 10.1177/0960327120914971 [14] Memari E,Hosseinian M A,Mirkheshti A,et al. Comparison of histopathological effects of perineural administration of bupivacaine and bupivacaine-d exmedetomidine in rat sciatic nerve[J]. Exp Toxicol Pathol,2016,68(10):559-564. doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2016.09.001 [15] Benzon H T,Chew T L,McCarthy R J,et al. Comparison of the particle sizes of different steroids and the effect of dilution:a review of the re lative neurotoxicities of the steroids[J]. Anesthesiology,2007,106(2):331-338. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200702000-00022 -






 下载:
下载: