MRI Diagnosis of Nodular Breast Lesions
-
摘要:
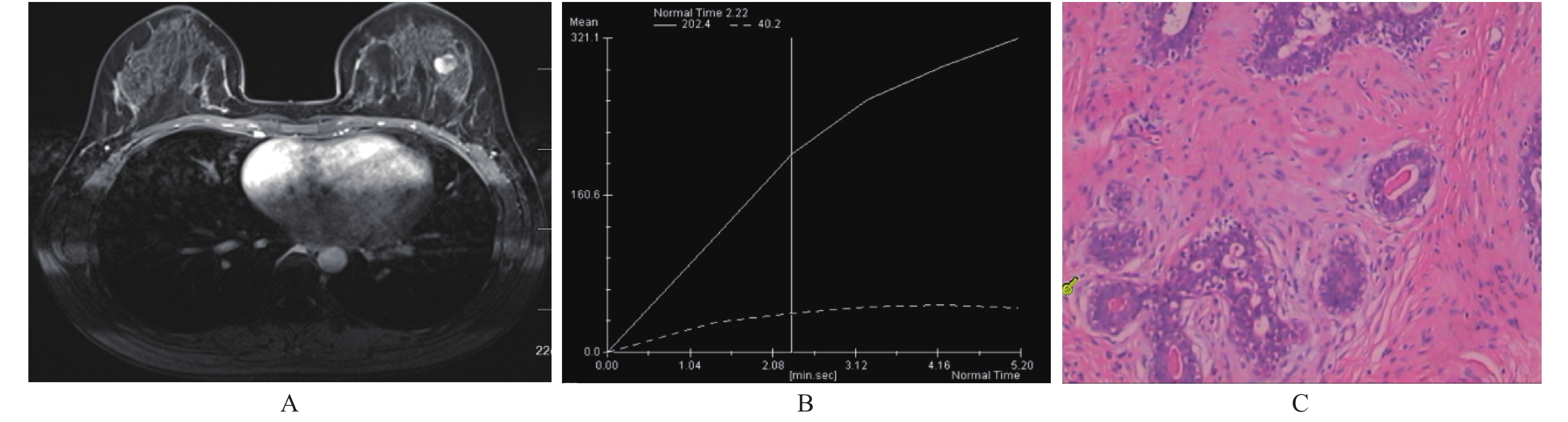
目的 探讨乳腺良、恶性结节病变的MRI诊断价值。 方法 回顾性分析来芜湖市第一人民医院就诊的乳腺疾病患者71例,均经过病理证实结节状病灶,术前均进行MRI多参数成像,选取动态增强(DCE-MRI)和DWI数据进行分析,经处理得到:时间-信号曲线(TIC),达峰时间(Tpeak),峰值强化率(PER),峰值(SImax)及表观扩散系数(ADC),结合形态学特征:边缘毛糙、环形强化、边缘毛刺征及分叶征进行分析。 结果 恶性病灶43例,良性病灶 28例。TIC时间-信号曲线Ⅰ型22个,以良性为主17例,恶性5例;Ⅱ型35例,恶性为主24例,良性11例;Ⅲ型14个,均为恶性;良、恶性病灶TIC曲线类型有差异,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);良、恶性病变的峰时(Tpeak),峰值强化率(PER),峰值(SImax)及ADC有显著差异,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。边缘毛糙33例,均为恶性;环形强化24例,良性5例,恶性19例;毛刺征29例,均为恶性;有分叶征42例,良性7例,恶性35例。良恶性病灶形态学,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。 结论 磁共振动态增强扫描血流动力学参数、ADC结合形态学特征对乳腺结节状良、恶性疾病的诊断具有重要价值。 Abstract:objective To investigate the value of MRI diagnosis of nodular breast benign and malignant lesions. Methods Retrospective analysis of 71 patients with nodular breast disease confirmed by pathology in our hospital, Perform MRI multi-parameter imaging before surgery, Select DCE-MRI and DWI for analysis, After processing: TIC time-signal curve, peak time, peak enhancement rate, SImax peak and ADC apparent diffusion coefficient, Combined with morphological characteristics: rough edges, ring strengthening, edge burr sign and leaf leaf sign for analysis. Results 43 malignant lesions, 28 benign lesions.There were 22 TIC time-signal curves of type I, with 17 cases of benign lesions and 5 cases of malignant lesions.There were 35 cases of type Ⅱ, of which 24 were malignant and 11 were benign.14 of type Ⅲ are all malignant lesions.The TIC time-signal curve types of benign and malignant lesions are different, and the difference is statistically significant (P < 0.05); The peak time, peak enhancement rate, SImax peak and ADC apparent diffusion coefficient of benign and malignant lesions were significantly different, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion MRI dynamic enhanced scanning hemodynamic parameters, ADC combined with morphological features are of great value in the diagnosis of breast nodular benign and malignant diseases. -
Key words:
- Breast nodules /
- Malignant lesions /
- Benign lesions /
- MRI /
- DCE-MRI
-
表 1 良恶性病灶TIC曲线类型比较[n(%)]
Table 1. Comparison of TIC curve types forbenign and malignant lesions [n(%)]
组别 Ⅰ型 Ⅱ型 Ⅲ型 例数 良性 17(23.94) 11(15.49) 0(0.0) 28(39.43) 恶性 5(7.04) 24(33.80) 14(19.72) 43(60.56) 组间比较χ2 = 23.242,P < 0.05。 表 2 乳腺良恶性结节MRI征象比较(n)
Table 2. Comparison of MRI signs of benign and malignant breast nodules (n)
组别 恶性结节 良性结节 例数 环形强化 19 5 24 边缘毛糙 33 0 33 毛刺征 29 0 29 分叶征 35 7 42 组间比较χ2 = 12.751,P < 0.05。 表 3 良恶性病灶动态增强参数及ADC比较
Table 3. Comparison of dynamic enhancement parametersand ADC of benign and malignant lesion
组别 Tpeak(s) SImax PER(% ) ADC(mm2/s) 良性 300.6 557.8 93.60 1.49 恶性 190.2 637.3 76.70 0.94 t 6.928 2.320 13.37 5.95 P 0.01* 0.023* 0.037* 0.028* 组间比较,*P < 0.05。 表 4 良恶性病灶动态增强参数及ADC效能比较(%)
Table 4. Comparison of dynamic enhancement parameters of Benignand malignant lesions and ADC efficiency (%)
参数 阈值 灵敏度 特异性 ADC(mm2/s) 1.21 83.7(36/43) 75.9(22/29) Tpeak(s) 210 72.1(12/43) 69.2(27/39) SImax 540 74.4(32/43) 60.7(17/28) PER/(%) 90.0% 93.0(40/43) 88.0(22/25) -
[1] Cheng Ziliang,Wu Zhou,Shi Guangzi,et al. Discrimination between benign and malignant breast lesions using volumetric quantitative dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging[J]. Eur Radiol,2018,28(3):982-991. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5050-2 [2] Natsuko Onishi,Meredith Sadinski,Peter Gibbs,et al. Differentiation between subcentimeter carcinomas and benign lesions using kinetic parameters derived from ultrafast dynamic contrast-enhanced breast MRI[J]. Eur Radiol,2020,30(2):756-766. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06392-5 [3] Fan WeiXiong,Chen XiaoFeng,Cheng FengYan,et al. Retrospective analysis of the utility of multiparametric MRI for differentiating between benign and malignant breast lesions in women in China[J]. Medicine (Baltimore),2018,97(4):e9666. [4] Ioannis Tsougos,Michael Bakosis,Dimitra Tsivaka,et al. Diagnostic performance of quantitative diffusion tensor imaging for the differentiation of breast lesions at 3T MRI[J]. Clinical Imaging,2019,53:25-31. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2018.10.002 [5] Vivian Youngjean Park,Sungheon G. Kim,Eun-Kyung Kim,et al. Diffff -usional kurtosis imaging for difffferentiation of additional suspicious lesions on preoperative breast MRI of patients with known breast cancer[J]. Magn Reson Imaging,2019,62:199-208. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2019.07.011 [6] Lei Song,Liang Li,Bin Liu,et al. Diagnostic evaluations of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in mammary duct ectasia and breast cancer[J]. Oncology Letters,2018,15(2):1698-1706. [7] 罗艺,余建群,陈冬冬,等. 扩散加权成像及动态增强MRI在鉴别诊断乳腺肿瘤中的价值[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志,2013,30(6):1219-1223. [8] Liu F,Kornecki A,Shmuilovich O,et al. Optimization of time-to-peakanalysis for differentiating malignant and benign breast lesions withdynamiccontrast-enhanced MRI[J]. Acad Radiol,2011,18(6):694-704. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2011.01.005 [9] 靳雅楠,张焱,程敬亮,等. DCE-MRI及DWI在鉴别乳腺良、恶性病变中的价值[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版),2016,51(4):530-533. [10] 徐丽娜,唐竹晓,李双标,等. 乳腺癌3.0T MRI影像学表现及临床病理特征研究[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志,2021,19(5):43-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5131.2021.05.015 [11] 王洁,唐文伟,田忠甫,等. 乳腺癌 DCE-MRI 参数及ADC与病理分子预后标记物的相关性分析[J]. 磁共振成像,2021,12(3):76-79. doi: 10.12015/issn.1674-8034.2021.03.017 [12] 臧慧,朱丽钰,王晓,等. 乳腺非肿块样强化病变MRI影像特征分析及诊断模型构建[J]. 临床放射学杂志,2021,4(3):436-441. -






 下载:
下载: