Effects of Scutellarin on Expressions of PKC and TNF-α in OX-LDL Injured RAW264.7 Cells in vitro
-
摘要:
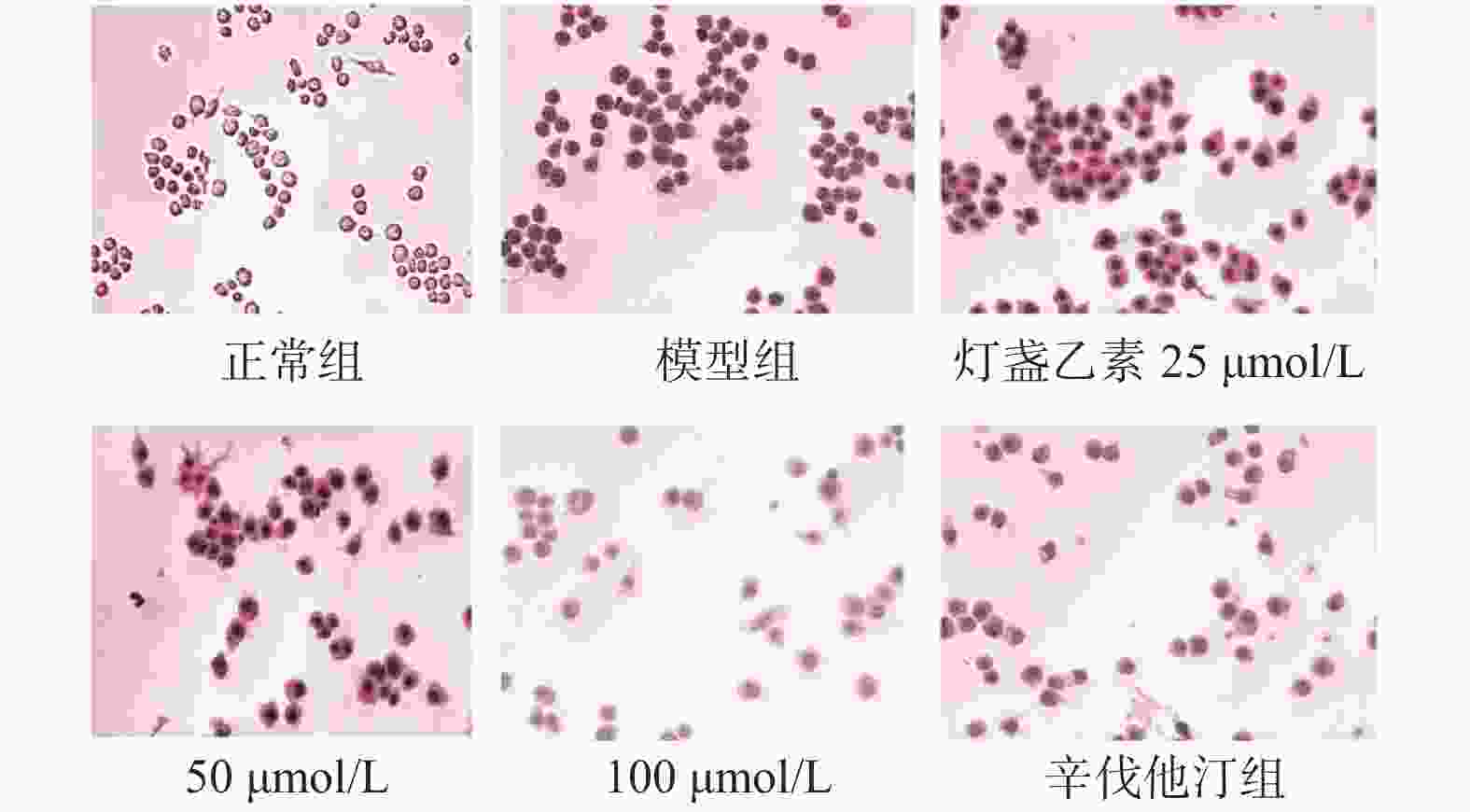
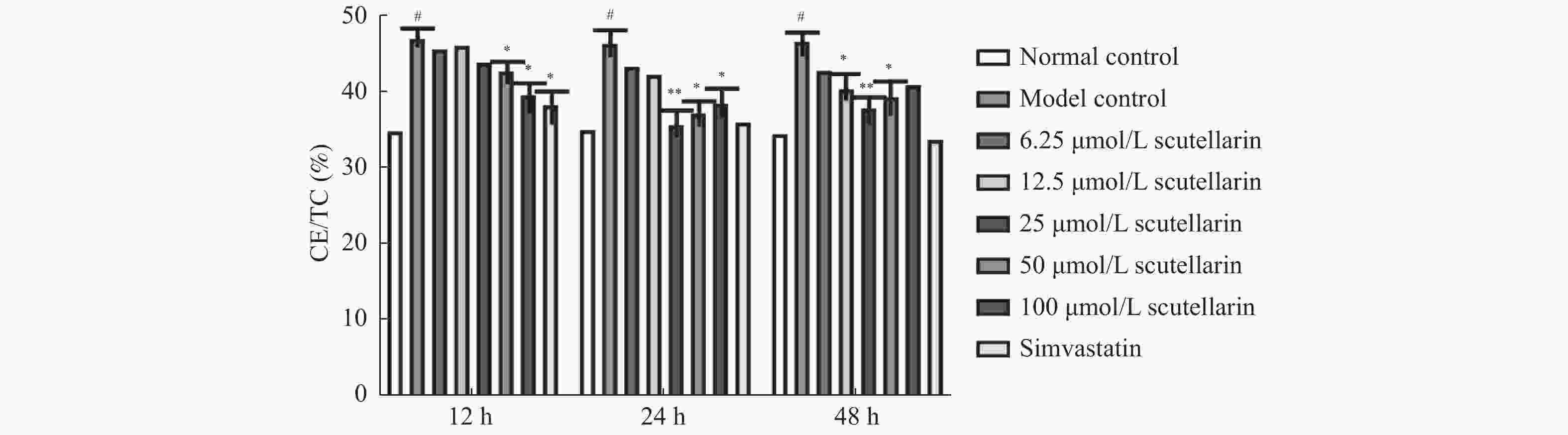
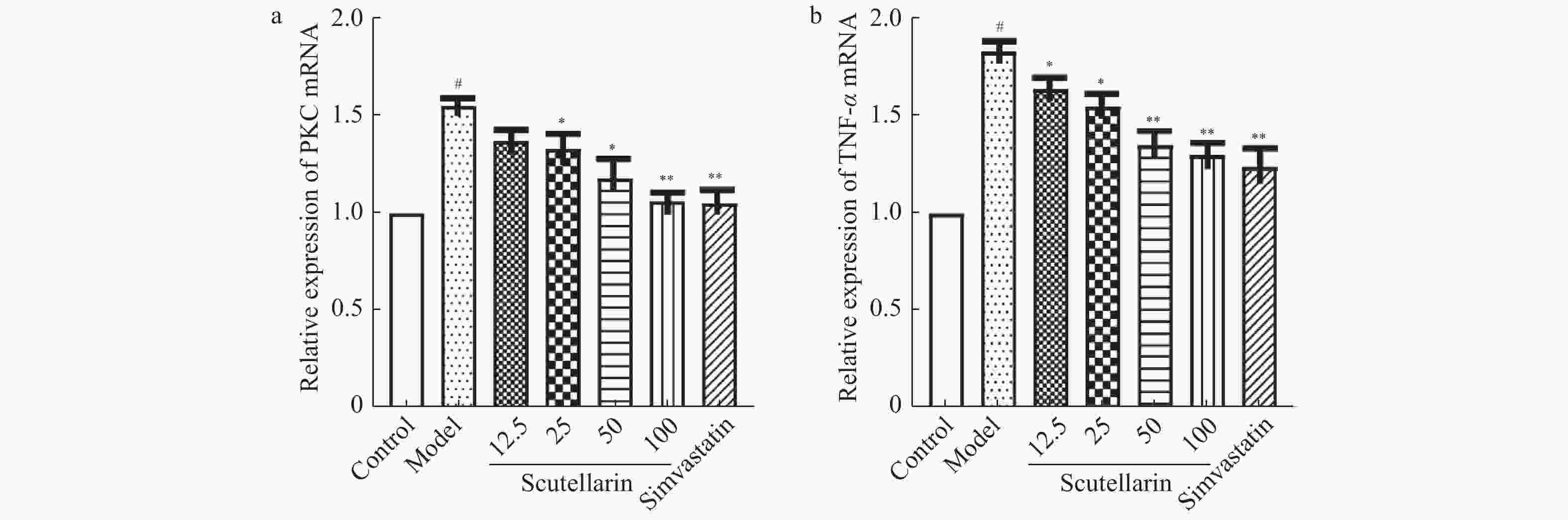
目的 研究灯盏乙素(scutellarin)对OX-LDL诱导损伤的巨噬细胞RAW264.7脂质吞噬能力及对PKC和TNF-α的蛋白和mRNA表达调控的影响。 方法 体外培养小鼠单核巨噬细胞RAW264.7,复制OX-LDL诱导损伤模型,通过油红O染色检测脂质吞噬及试剂盒检测细胞损伤模型胆固醇酯的含量。Western blot和RT-PCR方法检测RAW264.7细胞中PKC和TNF-α表达变化。 结果( 1) 油红O结果显示:与正常对照组比较,模型组细胞红染程度明显高于正常对照组;与模型组比较,辛伐他汀组、灯盏乙素50和100 μmol /L组细胞红染程度均低于模型组;( 2)胆固醇酯含量检测显示:与正常对照组比较,各时间点模型组细胞CE/TC值均明显升高;与模型组比较,各时间点用药组细胞CE/TC值均降低。( 3) WB和RT-PCR结果显示:与正常对照组比较,模型组PKC和TNF-α的蛋白和mRNA表达升高;与模型组比较,辛伐他汀组(simvastatin) PKC和TNF-α的蛋白和mRNA表达降低,且灯盏乙素组呈浓度依赖性下调PKC和TNF-α的蛋白和mRNA表达。 结论 (1)灯盏乙素能明显抑制OX-LDL诱导损伤的RAW264.7细胞脂质吞噬能力。( 2) 灯盏乙素能够明显下调OX-LDL诱导损伤的RAW264.7中PKC和TNF-α的蛋白和mRNA表达水平。 -
关键词:
- 灯盏乙素 /
- 巨噬细胞RAW264.7 /
- 氧化型低密度脂蛋白 /
- 蛋白激酶C /
- 肿瘤坏死因子-α
Abstract:Objectives To investigate the effects of scutellarin on lipid phagocytosis and the regulation of PKC, and TNF-α expressions in low density lipoprotein (OX-LDL) injured RAW264.7 cells. Methods Murine RAW264.7 macrophages was cultured in vitro. Then, the OX-LDL-induced injury model was replicated. Combined with oil red O staining, cellular cholesteryl ester content was also detected in OX-LDL-induced injury model. Furthermore, Western blot and RT-PCR methods were used to detect changes in PKC and TNF-α protein as well as mRNA expression in RAW264.7 cells. Results (1) The results of oil red O showed that the degree of cell red staining in model group was significantly higher than that in normal control group; compared with model group, the degree of cell red staining in simvastatin group, scutellarin 50 and 100 μmol/L group were lower than that in the model group; (2) The cholesteryl ester content assay showed that: compared with the normal control group, the CE/TC values of the model group cells were significantly increased at each time point; compared with model group, and cellular CE/TC values were significantly decreased in the dosing group at each time point. (3) WB and RT-PCR results showed that compared with normal control group, protein and mRNA expressions of PKC and TNF-α were increased in the model group; compared with the model group, protein and mRNA expression of PKC and TNF-α were decreased in simvastatin group, and scutellarin group showed a concentration-dependent downregulation of PKC and TNF-α expression. Conclusions (1) Scutellarin can significantly inhibit the levels of cholesterol in OX-LDL injuried RAW264.7 cells. (2) Scutellarin can down-regulated the protein and mRNA expressions of PKC, TNF-α in OX-LDL induced RAW264.7 cells. -
Key words:
- Scutellarin /
- RAW264.7 macrophages /
- oxidized low-density lipoprotein (OX-LDL) /
- PKC /
- TNF-α
-
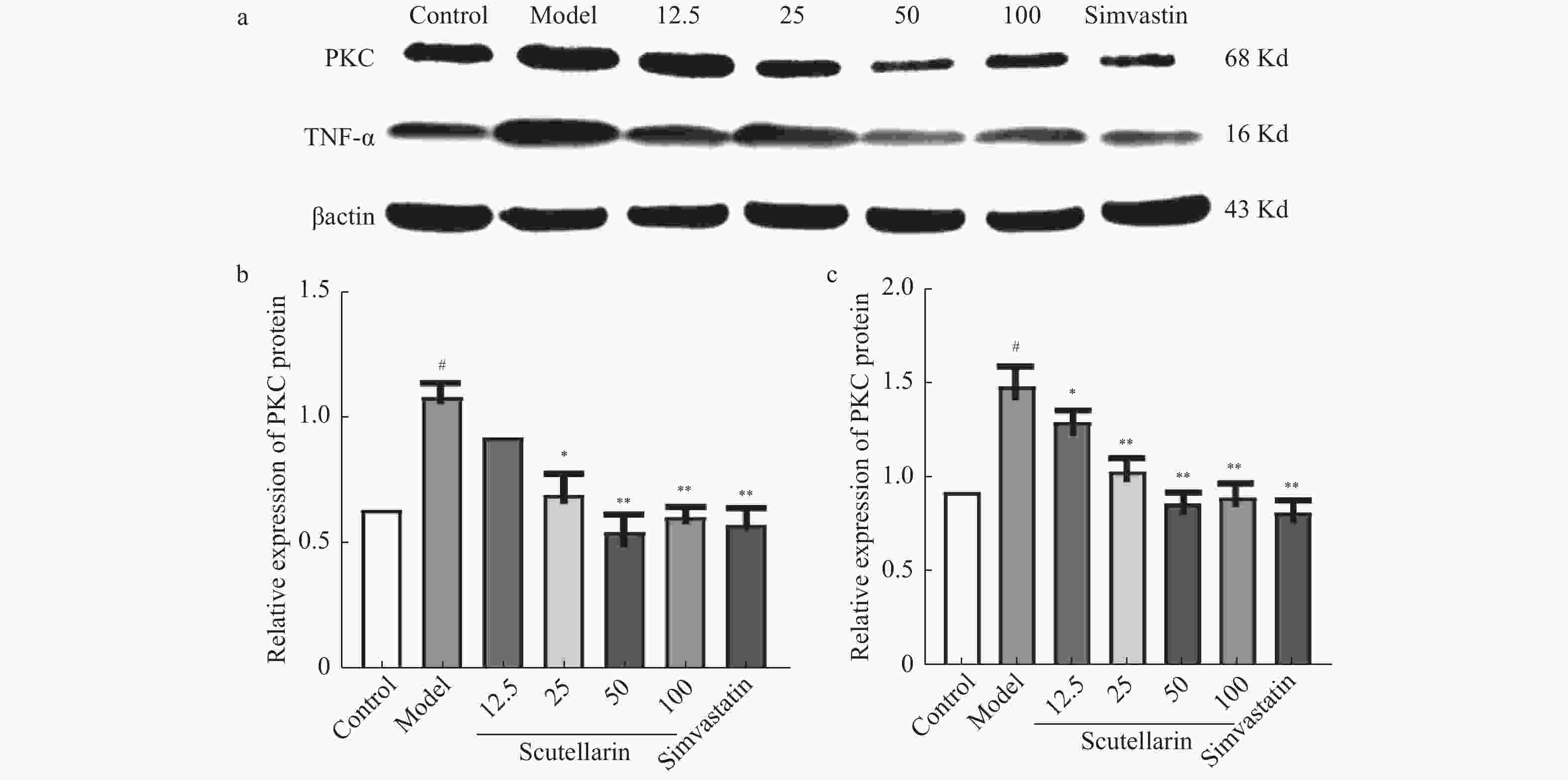
图 4 灯盏乙素对OX-LDL损伤的RAW264.7中PKC和TNF-α蛋白表达的影响[(
$ \bar x \pm s $ ),n = 6]注:a:PKC和TNF-α的蛋白表达电泳图;b,c:细胞损伤模型中PKC和TNF-α蛋白表达变化。用ImageJ 1.4.3.67对蛋白条带进行统计分析,βactin是内参。与空白对照组相比较,#P < 0.05;与模型组比较,*P < 0.05,**P < 0.01。
Figure 4. Effects of scutellarin on OX-LDL induced RAW264.7 cells PKC and TNF-α protein expression [(
$ \bar x \pm s $ ),n = 6]表 1 引物序列
Table 1. Primer sequence
基因名称 双向引物序列 β-actin Forward:5′ TGAGAGGGAAATCGTGCGTGAC 3′ Reverse:5′ GCTCGTTGCCAATAGTGATGACC 3′ PKC Forward:5′ TCACCAAGGAATCCAAGGAC3′ Reverse:5′ CCAGGAGGGACCAGTTGATA3′ TNF-α Forward:5′ ACGGCATAAATCTCAAAGAC 3′ Reverse:5′ GTGGGTGAGGAGCACGTAGT 3′ -
[1] Jonas D E,Reddy S,Middleton J C,et al. Screening for cardiovascular disease risk with resting or exercise electrocardiography:evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force[J]. JAMA,2018,319(22):2315-2328. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.6897 [2] Ira Tabas,Karin E Bornfeldt. Macrophage phenotype and function in different Stages of atherosclerosis[J]. Circulation Research,2016,118(4):653-667. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306256 [3] Silverstein R L. Linking metabolic dysfunction to atherosclerosis via activation of macrophage CD36 gene transcription by retinol binding protein-4[J]. Circulation,2017,135(14):1355-1356. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.027505 [4] Kasahara K,Tanoue T,Yamashita T,et al. Commensal bacteria at the crossroad between cholesterol homeostasis and chronic inflammation in atherosclerosis[J]. Journal of Lipid Research,2017,58(3):519-528. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M072165 [5] Fan H C,Fernandez-Hernando C,Lai J H. Protein kinase C isoforms in atherosclerosis:Pro or anti-inflammatory[J]. Biochemical Pharmacology,2014,88(2):139-149. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2014.01.006 [6] Lien C F,Chen S J,Tsai M C,Lin C S. Potential Role of Protein Kinase C in the Pathophysiology of Diabetes-Associated Atherosclerosis[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2021,12:716332. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.716332 [7] Oberoi R,Vlacil AK,Schuett J,Schösser F,Schuett H,Tietge UJF,Schieffer B,Grote K. Anti-tumor necrosis factor-α therapy increases plaque burden in a mouse model of experimental atherosclerosis[J]. Atherosclerosis,2018,277:80-89. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.08.030 [8] M F Linton,J J Moslehi,V R Babaev,et al. Akt signaling in macrophage polarization,survival,and atherosclerosis[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2019,20(11):2703. [9] 张安邦,高杰,李令根,李义. 相关炎症因子与动脉粥样硬化的关系[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志,2014,10(5):563-566. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6948.2014.05.042 [10] 张卫东,陈万生,王永红,等. 灯盏花黄酮苷化学成分的研究[J]. 中草药,2000,31(8):565-566. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2670.2000.08.002 [11] 张小超,沈志强,杨仁华,等. 灯盏乙素对大鼠动脉粥样硬化的防治作用[J]. 中药药理与临床,2017(2):59-63. [12] 曹慧敏,宋囡,张妮,等. 丹参酮ⅡA通过P13K/Akt/mTOR信号通路调控自噬抗内皮细胞氧化应激损伤研究[J]. 北京中医药大学学报,2017,40(11):933-940. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2157.2017.11.011 [13] Malekmohammad K,Bezsonov E E,Rafieian-Kopaei M. Role of lipid accumulation and inflammation in atherosclerosis:Focus on molecular and cellular mechanisms[J]. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine,2021,8:707529. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.707529 [14] Xu H,Jiang J,Chen W,Li W,Chen Z. Vascular Macrophages in Atherosclerosis[J]. Journal of Immunology Research,2019,2019:4354786. [15] Hussain S,Assender J W,Bond M,et al. Activation of protein kinase C zeta is essential for cytokine induced metallo-proteinase-1,-3,and -9 secretion from rabbit smooth muscle cells and inhibits proliferation[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,2002,277(30):27345-27352. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111890200 [16] Chih-Tung Chiu,Sheng-Nan Kuo,Shao-Wen Hung,et al. Combined treatment with hyaluronic acid and mesalamine protects rats from inflammatory bowel disease induced by intracolonic administration of trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid[J]. Molecules,2017,22(6):904-912. doi: 10.3390/molecules22060904 [17] Hong Jin,Daniel Y. Li,Ekaterina,et al. Local Delivery of miR-21 Stabilizes Fibrous Caps in Vulnerable Atherosclerotic Lesions.[J]. Molecular Therapy,2018,26(4):1040-1055. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.01.011 -





 下载:
下载: