Comparison of Six Methods of Ultrasound-guided Fine-needle Aspiration Biopsy of Thyroid Nodules
-
摘要:
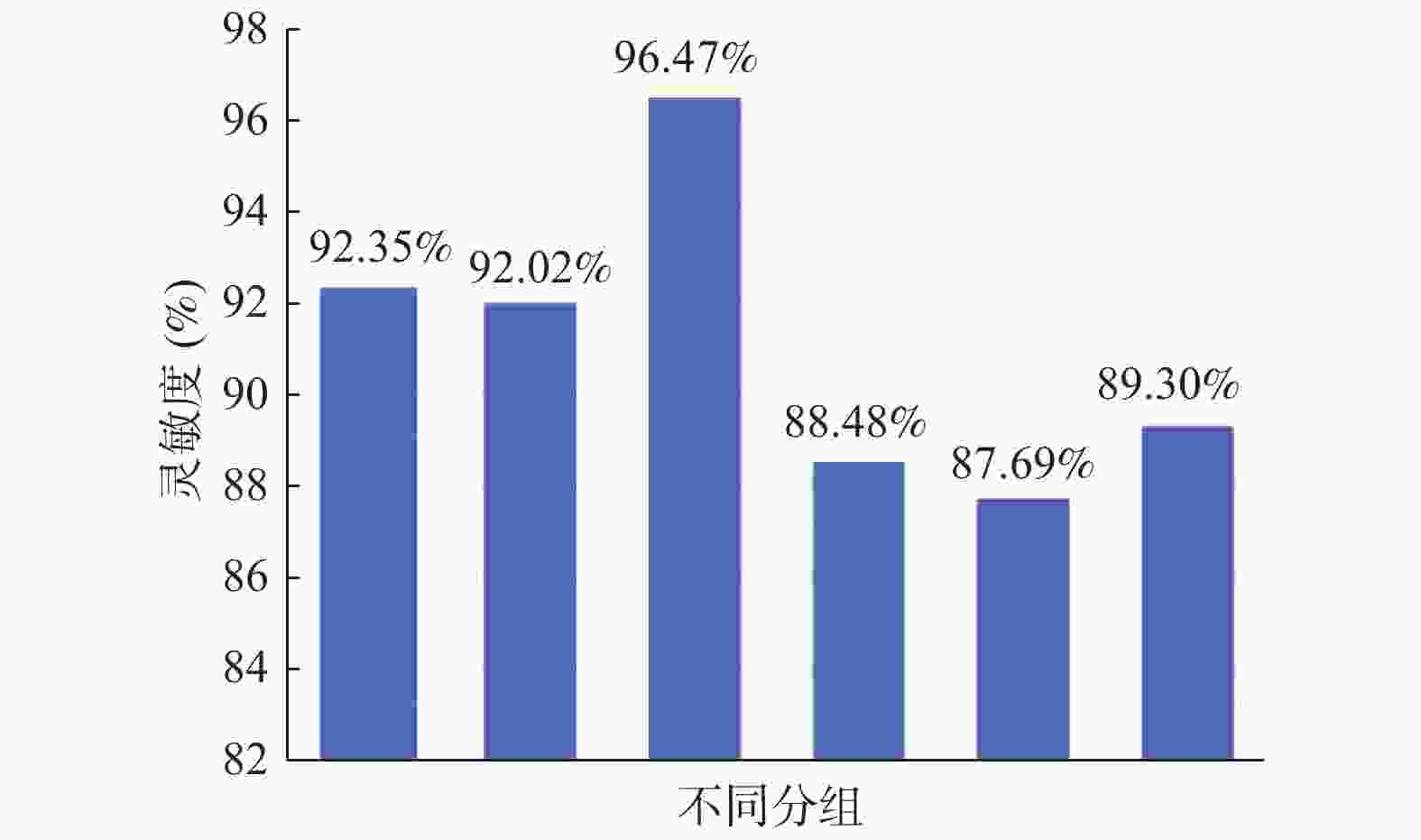
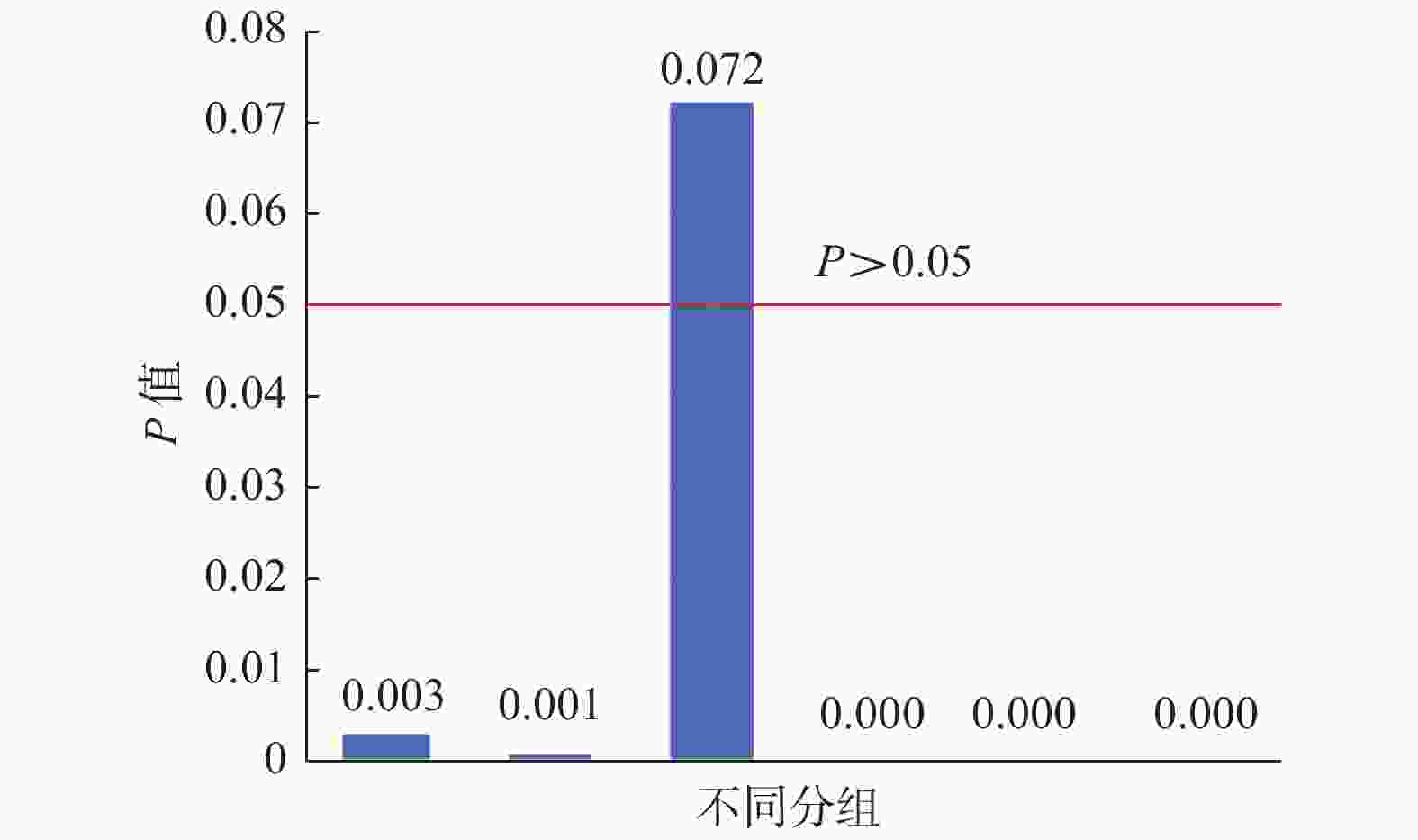
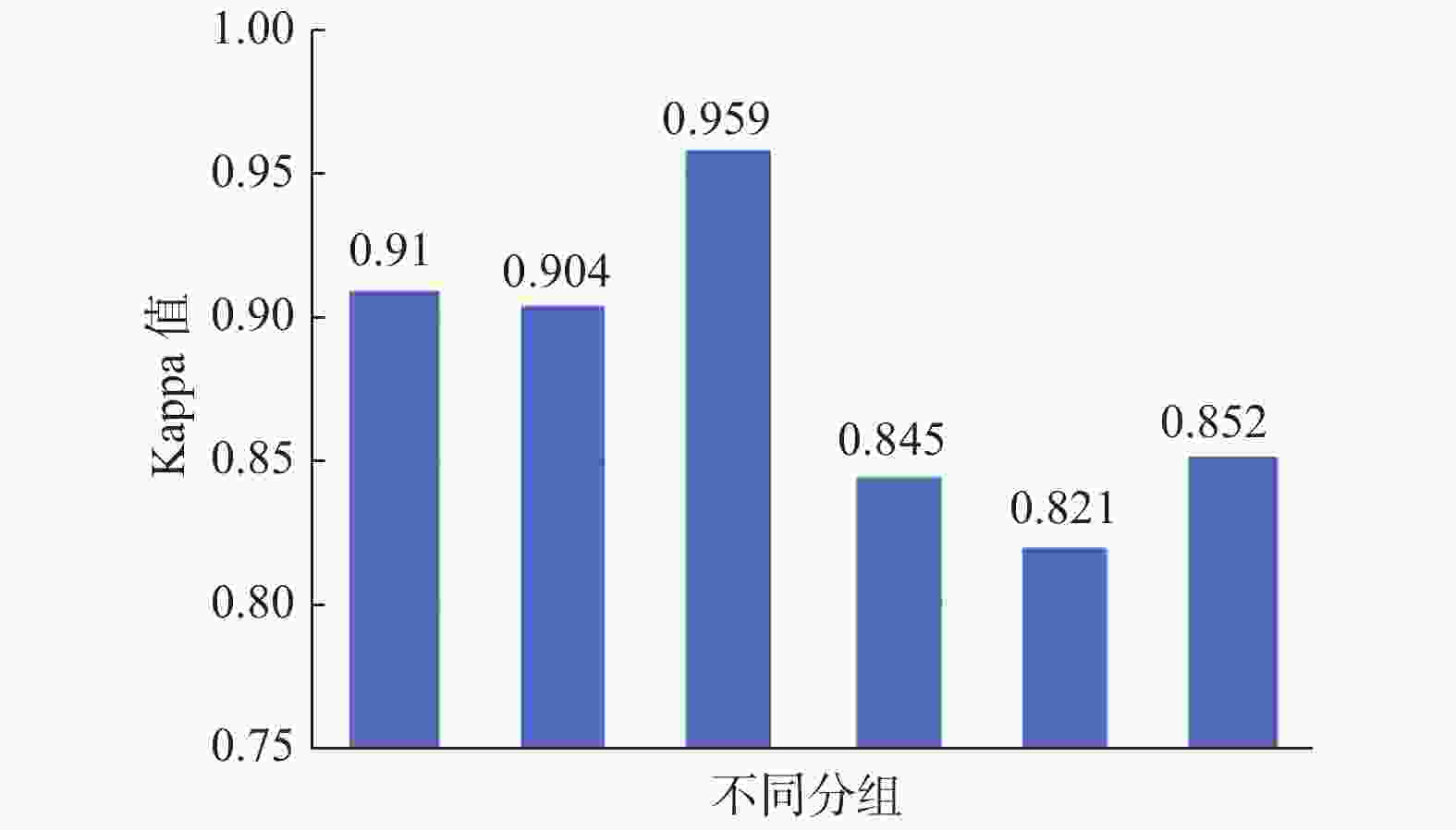
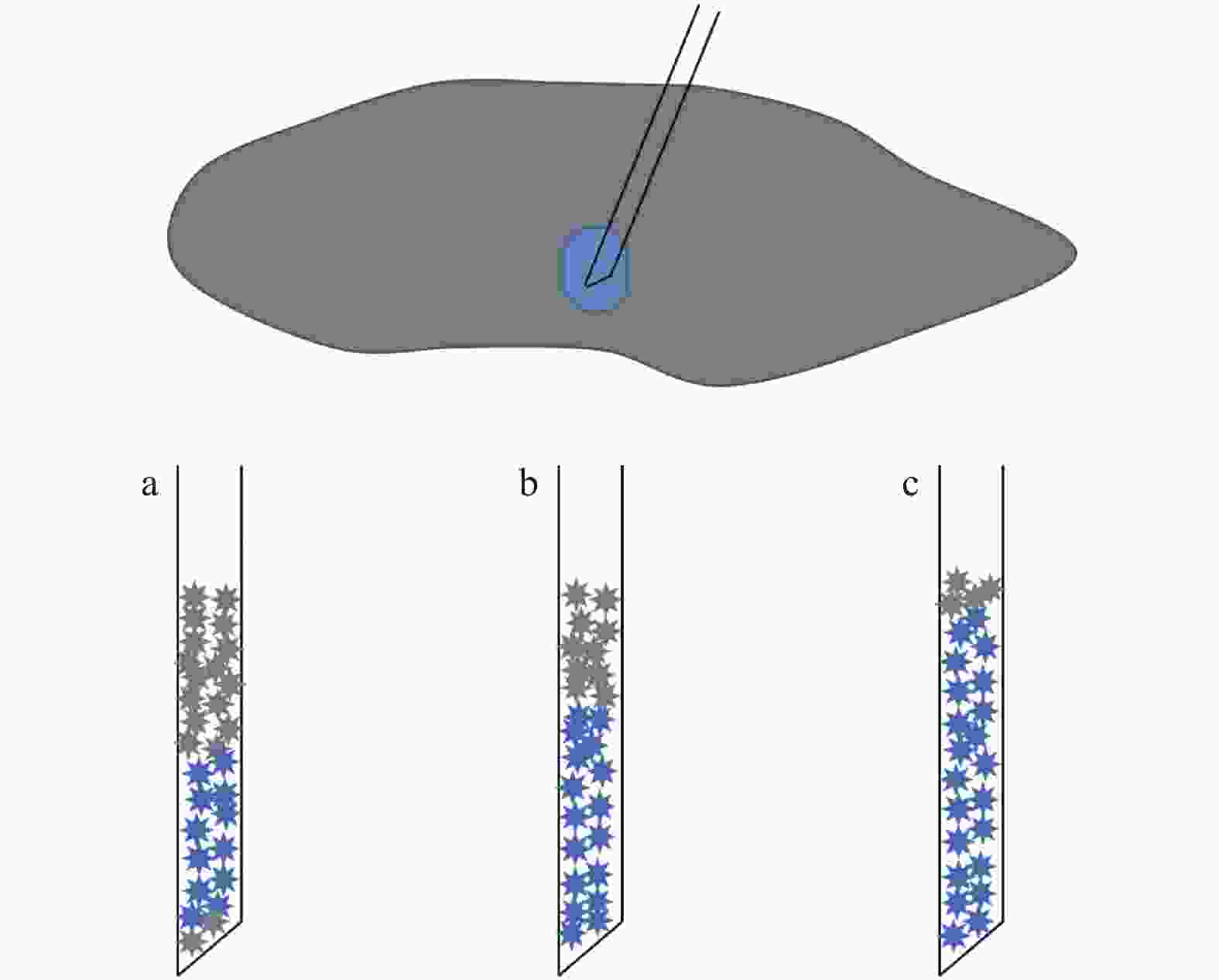
目的 比较超声引导下甲状腺结节细针穿刺活检6种操作方法的检验准确性并分享穿刺经验。 方法 纳入1903例行甲状腺结节细针穿刺活检,并经甲状腺外科手术证实,且手术前后都有明确病理结果的患者资料。按照FNA进针角度及取材手法将上述患者资料共分6组:A1~A3,B1~B3组,A类为端侧式,B类为边侧式;1类为负压抽吸法,2类为常压抽吸法,3类为闭压进出法。在传统的评价指标基础上,采用Bowker加权检验对比其差异性, Kappa线性加权检验其一致性。最终评价6种不同操作方法的优缺点。 结果 灵敏度:A类高于B类,A3组最高,为96.47%,最低为B2组87.69%;特异度:均为100%;准确度:A类高于B类,A3组最高,为97.69%,最低为B2组 91.20%;阳性预测率:均为100%;阴性预测率:A类高于B类,最高为A3组95.65%,最低为B2组78.57%;约登指数:A类高于B类,最高为A3组96.47%,最低为B2组87.69%;Bowker加权检验结果:P值由高至低排列为:A3 > A1 > A2 > B3 = B1 = B2;A1、A2、B1、B2、B3组P < 0.01,与术后组织病理学结果有显著统计学差异;A3组P值最高,为0.072,P > 0.05,与术后组织病理学结果无统计学差异;Kappa一致性检验(线性加权)结果:A3 > A1 > A2 > B3 > B1 > B2;A3组最高,为0.959,最低为B2组为0.821。 结论 基于传统评价指标、配对卡方及Kappa检验结果,端侧式入路配合闭压进出取材法(A3组)的细胞学病理结果与术后组织学病理结果最为接近,是取材质量非常高的FNA方式。 -
关键词:
- 超声引导 /
- 细针穿刺活检 /
- Bowker加权检验 /
- Kappa线性加权检验
Abstract:Objective To compare the accuracy of six operative methods of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy of thyroid nodules and to share the experience of the operation. Methods The data of 1903 patients who underwent thyroid surgery, preoperative fine-needle biopsy (FNA) and definite pathological findings after surgery were included. The data of the above patients were divided into 6 groups: A1-A3, B1-B3 according to the angle of FNA needle insertion and sampling technique. category A for end-lateral and category B for side-lateral; category 1 for negative pressure aspiration, category 2 for normal pressure aspiration, and category 3 for closed pressure entry and exit. Based on the traditional evaluation indexes, the Bowker weighted test was used to compare their differences and the Kappa linear weighted test for consistency. The advantages and disadvantages of the six different operation methods were finally evaluated. Results Sensitivity: Category A was higher than category B. Highest in group A3; 96.47% and lowest in group B2; 87.69%; Specificity: all were 100%; Accuracy: category A was higher than category B subgroups, highest in group A3; 97.69%, and lowest in group B2; 91.20%;Positive prediction rate: all were 100%; Negative prediction rate: category A was higher than class B subgroups. The highest A3 was 95.65% in group A3, and the lowest was 78.57% in group B2;Yordon index: higher in category A than in category B. The highest was 96.47% in group A3 and the lowest was 87.69% in group B2. Bowker’ s weighted test results: the P -values were: A3 > A1 > A2 > B3 = B1 = B2.The P of A1, A2, B1, B2, and B3 < 0.01, statistically significantly different from postoperative histopathological results. The P -value of A3 was 0.072, P > 0.05. There was no statistical difference with the postoperative histopathological result in A3; Kappa consistency test (linear weighted) results: A3 > A1 > A2 > B3 > B1 > B2; The highest value was 0.959 for the A3 group, and the lowest was 0.821 for the B2 group. Conclusions Based on the traditional evaluation index, paired chi-square and Kappa test results, the end-lateral approach with closed-pressure entry and exit sampling method (A3 group) have the closest cytologic pathology results to postoperative histologic pathology and is the best FNA approach with high sampling quality. -
表 1 6个组的FNA与病理学结果符合度及对应的kappa一致性检验和常规的评价指标数值(n)(1)
Table 1. Consistency for FNA and pathology of six groups and values of corresponding Kappa Consistency Tests (Linear Weighted) and conventional evaluation indicators (n)(1)
组别 FNA结果 病理结果(n) 总计 Kappa值 良性 非典型病变 恶性/可疑恶性 A1 良性 117 0 13 130 0.91
P = 0.000**非典型病变 0 19 1 20 恶性/可疑恶性 0 0 157 157 总计 117 19 171 307 A2 良性 128 1 15 144 0.904
P = 0.000**非典型病变 0 23 1 24 恶性/可疑恶性 0 0 173 173 总计 128 24 189 341 A3 良性 132 1 6 139 0.959
P = 0.000**非典型病变 0 17 0 17 恶性/可疑恶性 0 0 164 164 总计 132 18 170 320 B1 良性 98 1 22 121 0.845
P = 0.000**非典型病变 0 29 2 31 恶性/可疑恶性 0 0 169 169 总计 98 30 193 321 B2 良性 88 1 24 113 0.821
P = 0.000**非典型病变 0 21 2 23 恶性/可疑恶性 0 0 171 171 总计 88 22 197 307 B3 良性 87 1 20 108 0.852
P = 0.000**非典型病变 0 31 1 32 恶性/可疑恶性 0 0 167 167 总计 87 32 188 307 **P < 0.01。 表 1 6个组的FNA与病理学结果符合度及对应的kappa一致性检验和常规的评价指标数值(%)(2)
Table 1. Consistency for FNA and pathology of six groups and values of corresponding Kappa Consistency Tests (Linear Weighted) and conventional evaluation indicators (%)(2)
灵敏度 特异度 准确度 阳性预测值 阴性预测值 约登指数 92.35 100.00 95.47 100.00 90.00 92.35 92.02 100.00 94.95 100.00 89.51 92.02 96.47 100.00 97.69 100.00 95.65 96.47 88.48 100.00 92.07 100.00 81.67 88.48 87.69 100.00 91.20 100.00 78.57 87.69 89.30 100.00 92.36 100.00 81.31 89.30 表 2 6个组的FNA与病理学结果符合度及配对卡方检验(Bowker加权检验)结果(n)
Table 2. Consistency for FNA and pathology of six groups and values of corresponding Chi-Square Test (Bowker Weighted Test)(n)
组别 FNA结果 病理结果 总计 χ P 良性 非典型病变 恶性/可疑恶性 A1 良性 117 0 13 130 14 0.003** 非典型病变 0 19 1 20 恶性/可疑恶性 0 0 157 157 总计 117 19 171 307 A2 良性 128 1 15 144 17 0.001** 非典型病变 0 23 1 24 恶性/可疑恶性 0 0 173 173 总计 128 24 189 341 A3 良性 132 1 6 139 7 0.072** 非典型病变 0 17 0 17 恶性/可疑恶性 0 0 164 164 总计 132 18 170 320 B1 良性 98 1 22 121 25 0.000** 非典型病变 0 29 2 31 恶性/可疑恶性 0 0 169 169 总计 98 30 193 321 B2 良性 88 1 24 113 27 0.000** 非典型病变 0 21 2 23 恶性/可疑恶性 0 0 171 171 总计 88 22 197 307 B3 良性 87 1 20 108 22 0.000** 非典型病变 0 31 1 32 恶性/可疑恶性 0 0 167 167 总计 87 32 188 307 **P < 0.01。 -
[1] 霍立双,刘丰雨,高琛,等. 我国地区甲状腺结节患病率Meta分析[J]. 河北医科大学学报,2017,38(2):138-141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3205.2017.02.004 [2] 陈万青,李贺,孙可欣,等. 2014年中国恶性肿瘤发病和死亡分析[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志,2018,40(1):5-13. [3] Orloff L A,Wiseman S M,Bernet V J,et al. American Thyroid Association Statement on Postoperative Hypoparathyroidism:Diagnosis,Prevention,and Management in Adults[J]. Thyroid,2018,28(7):830-841. doi: 10.1089/thy.2017.0309 [4] Haugen B R,Alexander E K,Bible K C,et al. 2015 American Thyroid Association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer:the American Thyroid Association guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer[J]. Thyroid,2016,26(1):1-33. doi: 10.1089/thy.2015.0020 [5] Filetti S,Durante C,Hartl D,et al. Thyroid cancer:ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis,treatment and follow-up[J]. Ann Oncol,2019,30(12):1856-1883. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz400 [6] Dorothy A, Shead M S, Erin Vidic M A, et al. National comprehensive Cancer Netwrok(NCCN) Guidelines For Patients: Thyroid Cancer Version. Online-Web, 2020.02. [7] 上海市医学会超声医学分会介入学组,上海市社会医疗机构协会超声医学分会介入与重症超声专业委员会. 超声引导下甲状腺结节细针穿刺细胞学检查实践指南(2019版)[J]. 中华超声影像学杂志,2020,29(5):369-383. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn131148-20191107-00678 [8] Ha E J,Na D G,Baek J H,et al. US fine-needle aspiration biopsy for thyroid malignancy:diagnostic performance of seven society guidelines applied to 2000 thyroid nodules[J]. Radiology,2018,287(3):893-900. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2018171074 [9] Ha S M,Baek J H,Na D G,et al. Diagnostic performance of practice guidelines for thyroid nodules:thyroid nodule size versus biopsy rates[J]. Radiology,2019,291(1):92-99. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2019181723 [10] Nguyen X V,Roy Choudhury K,Tessler F N,et al. Effect of tumor size on risk of metastatic disease and survival for thyroid cancer:implications for biopsy guidelines[J]. Thyroid,2018,28(3):295-300. doi: 10.1089/thy.2017.0526 [11] Khatami F,Tavangar S M. Liquid biopsy in thyroid cancer:new insight[J]. International Journal of Hematology-oncology and Stem Cell Research,2018,12(3):235. [12] 颜虹, 徐勇勇. 医学统计学[M]. 第3版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2017: 16-19. [13] Fleiss J L,Cohen J. The Equivalence of Weighted Kappa and the Intraclass Correlation Coefficient As Measures of Reliability[J]. Educational & Psychological Measurement,2016,33(3):613-619. -






 下载:
下载: