Detection Rate and Determinants of Hypertension among Seniors in Anning City
-
摘要:
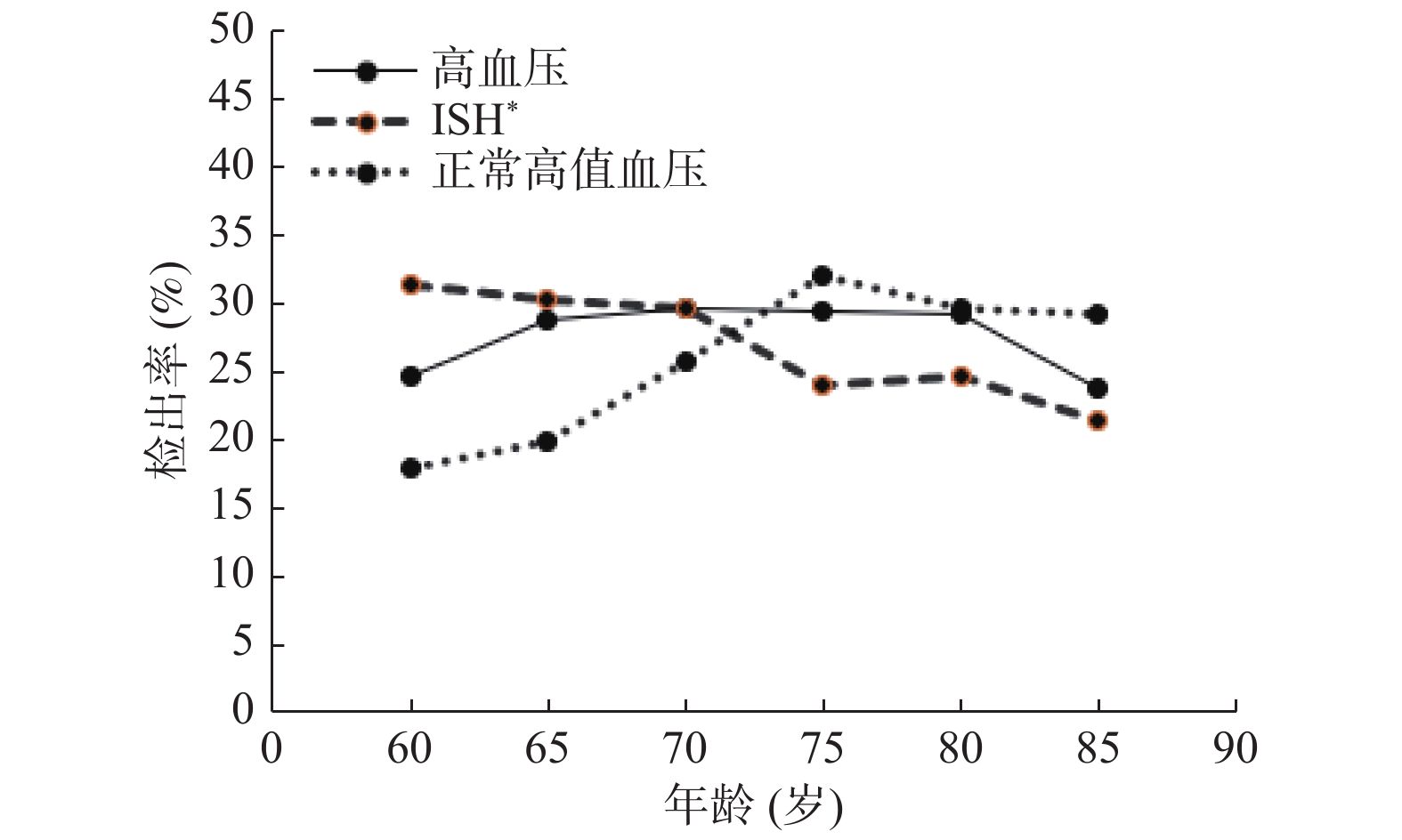
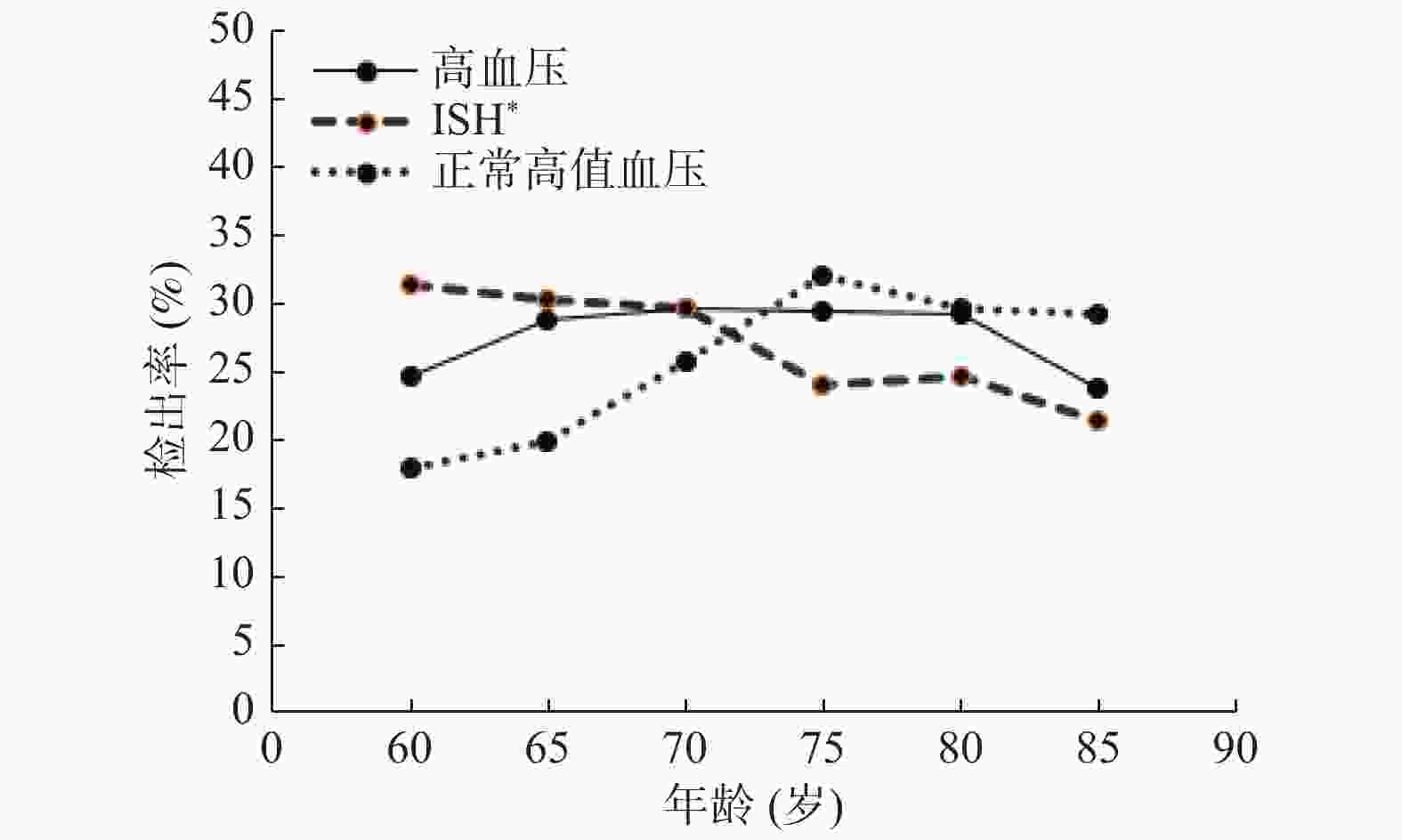
目的 了解安宁市老年人高血压的流行现状,并分析其影响因素。 方法 用多阶段比例分层随机抽样法于2019年9月至2020年1月,抽取安宁市 ≥ 60岁老年人9 709人,用问卷、体格及实验室检测的方法进行调查研究。 结果 共调查了老年人9 709例,年龄60~100岁,高血压检出率为28.82%(95%CI:27.92%~29.72%),低于全国 ≥ 60岁老年人高血压患病率(49%,P < 0.05)。女性人群高血压检出率高于男性人群,但正常高值和单纯性收缩期高血压(ISH)的检出率均低于男性;不同地区高血压检出率,差异有统计学意义( P < 0.05)。Logistic回归分析表明,糖尿病( OR = 1.338)、超重(OR = 1.481)、肥胖(OR = 2.032)、甘油三酯异常(OR = 1.177)、总胆固醇异常(OR = 1.361)的老年人患高血压的可能性较高(P < 0.05)。 结论 安宁市老年人高血压检出率低于全国水平,糖尿病、超重、肥胖、甘油三酯异常、总胆固醇异常为主要危险因素。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the prevalence and determinants of hypertension in seniors in Anning city. Methods From September 2019 to January 2020, 9 709 people over 60 years old in Anning city were selected by multi-stage proportional stratified random sampling method. Questionnaires, physical and laboratory tests were used. Results A total of 9709 people aged 60-100 years (72.07±6.17) were investigated. The detection rate of hypertension was 28.82% (95%CI: 27.92%~29.72%), which was lower than the hypertension prevalence in people over 60 in China (49%, P < 0.05). The detection rate of hypertension in female was higher than that in male, but the detection rate of high normal and simple systolic hypertension (ISH) was lower than that in male population. The detection rate of hypertension varies in different areas ( P < 0.05). Logistic regression results showed that the senior with diabetes ( OR = 1.338), overweight (OR = 1.481), obesity (OR = 2.032), abnormal triglyceride (OR = 1.177), abnormal total cholesterol (OR = 1.361) were more likely to develop hypertension (P < 0.05). Conclusion The detection rate of hypertension in seniors in Anning city is lower than the national level. Diabetes, overweight, obesity, abnormal triglyceride and abnormal total cholesterol are the main risk factors. -
Key words:
- Seniors /
- Hypertension /
- Detection rate /
- Determinants
-
表 1 安宁市不同人群特征老年人高血压和正常高值的检出情况[n(%)]
Table 1. Detection of hypertension and normal high value in different population in Anning City [n (%)]
项目 n 高血压
(n=2 798)正常高值
(n=2 733)性别 男 4 332 1180(27.2) 1307(30.2) 女 5 377 1618(30.1)* 1426 (26.5)* χ2 9.513 15.807 P 0.002 < 0.0001 民族 汉族 9 091 2610(28.7) 2552(28.1) 少数民族 618 188(30.4) 181(29.3) χ2 0.826 0.423 P 0.364 0.515 与男性比较,*P < 0.05。 表 2 安宁市不同地区老年人高血压和正常高值的检出情况[n(%)]
Table 2. Detection of hypertension and high normal value in the elderly in different areas of Anning city [n(%)]
项目 n 高血压
(n = 2 798)正常高值
(n = 2 733)乡镇 连然 3 422 910(26.6) 1044(30.5) 草铺 702 227(32.3)* 132(18.8)* 县街 1 794 652(36.3)*▲ 480(26.8)*# 青龙 583 128(22.0)# 161(27.6)# 八街 3 208 881(27.5)△ 916(28.6)# χ2 78.281 41.797 P < 0.0001 < 0.0001 与连然比较,*P < 0.005;与草铺比较, #P < 0.005;与青龙比较, ▲P < 0.005;与县街比较, △P < 0.005。 表 3 高血压患者与正常人的一般临床资料比较[
$ \bar x \pm s $ /M(P25,P75)Table 3. Comparison of general clinical data between hypertensive patients and normal controls[
$ \bar x \pm s $ /M(P25,P75)指标 高血压(n = 2 798) 正常高值(n = 2 733) 正常血压(n = 4 178) F/H P 年龄(岁) 72.02 ± 5.96# 71.48 ± 5.90* 72.49 ± 6.45 35.95 < 0.001 BMI (kg/m2) 23.96 ± 3.69*# 23.35 ± 3.39* 22.49 ± 3.46 150.23 < 0.001 收缩压(mm Hg) 150.95 ± 20.59*# 140.81 ± 14.93* 127.25 ± 17.84 2393.76 < 0.001 舒张压(mm Hg) 88.11 ± 12.57*# 84.05 ± 4.10* 70.27 ± 7.36 5397.13 < 0.001 脉压(mm Hg) 62.84 ± 16.11*# 56.76 ± 15.19 56.98 ± 17.47 271.33 < 0.001 心率(次/min) 77.52 ± 12.05*# 75.82 ± 10.49* 74.04 ± 10.77 156.60 < 0.001 谷草转氨酶(U/L) 24(20,29) 24(21,29) 24(20,29) 5.28 0.072 谷丙转氨酶(U/L) 1.1(0.9,1.4)* 1.1(0.9,1.4)* 1.2(0.8,1.5) 58.83 < 0.001 尿酸(μmol/L) 352.29 ± 93.47* 245.20 ± 88.17* 337.76 ± 89.82 40.73 < 0.001 总胆红素(mmol/L) 14.60 ± 5.6 14.82 ± 5.55 14.57 ± 5.93 1.58 0.207 甘油三脂(mmol/L) 1.49(1.07,2.13)*# 1.41(1.01,2.02)* 1.27(0.95,1.82) 140.65 < 0.001 总胆固醇(mmol/L) 5.37 ± 1.10*# 5.29 ± 1.03* 5.17 ± 1.00 59.90 < 0.001 高密度脂蛋白(mmol/L) 1.67 ± 0.41 1.68 ± 0.41 1.68 ± 0.40 0.34 0.710 低密度脂蛋白(mmol/L) 3.36 ± 0.86*# 3.31 ± 0.84* 3.22 ± 0.81 50.65 < 0.001 尿素(mmol/L) 5.88 ± 1.83 5.83 ± 1.90* 5.98 ± 2.08 4.66 0.009 静脉空腹血糖(mmol/L) 6.15 ± 2.21*# 5.99 ± 2.03 6.01 ± 2.21 4.87 0.008 肌酐(μmol/L) 78.99 ± 28.38* 77.41 ± 20.63 76.75 ± 24.33 6.95 0.001 与正常组比较,*P < 0.05;与正常高值组比较, #P < 0.05。 表 4 拟选高血压检出率影响因素及其数量化
Table 4. To choose hypertension detection rate with determinants and its quantification
因素 数量化 性别 男 = 1,女 = 2 民族 汉族 = 1,少数民族 = 2 年龄组 60~< 65岁 = 1,65~< 70岁 = 2,70~< 75岁 = 3,75~< 80岁 = 4,85~岁 = 5 BMI 偏瘦 = 1,正常 = 2,超重 = 3,肥胖 = 4 甘油三酯 否 = 0,是 = 1 总胆固醇 否 = 0,是 = 1 低密度脂蛋白 否 = 0,是 = 1 高密度脂蛋白 否 = 0,是 = 1 糖尿病 否 = 0,是 = 1 高尿酸血症 否 = 0,是 = 1 表 5 高血压的多因素Logistic回归分析结果(n = 9709)
Table 5. Multivariate Logistic regression analysis results of hypertension (n = 9709)
变量 b SEb Waldχ2 P OR(95%CI) 常数项 −1.226 0.033 1375.454 < 0.0001 —— 糖尿病 0.291 0.059 24.618 < 0.0001 1.338(1.193,1.501) 超重 0.393 0.050 60.886 <0 .0001 1.481(1.342,1.634) 肥胖 0.709 0.080 78.818 < 0.0001 2.032(1.737,2.376) 甘油三酯 0.163 0.059 7.538 0.0060 1.177(1.048,1.322) 总胆固醇 0.308 0.060 26.257 < 0.0001 1.361(1.210,1.531) -
[1] 胡丽华,黄晓,蔡华秀,等. 江西省城乡居民高血压患病现状调查及影响因素分析[J]. 中华高血压杂志,2017,25(2):169-175. [2] Marwick T H,Gillebert T C,Aurigemma G,et al. Recommendations on the use of echocardiography in adult hypertension:A report from the european association of cardiovascular imaging (EACVI) and the american society of echocardiography (ASE)[J]. Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography,2015,28(7):727-754. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2015.05.002 [3] Lackland D T,Weber M A. Global burden of cardiovascular disease and stroke:Hypertension at the core[J]. The Canadian Journal of Cardiology,2015,31(5):569-571. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2015.01.009 [4] Roth G A,Johnson C,Abajobir A,et al. Global,Regional,and national burden of cardiovascular diseases for 10 causes,1990 to 2015[J]. Journal of the American College of Cardiology,2017,70(1):1-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.04.052 [5] 中国高血压防治指南修订委员会.中国高血压防治指南(2018年修订版)[J]. 中国心血管杂志, 2019, 24(1): 24-56. [6] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会.中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2017年版)[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2018, 38(4): 292-344. [7] 国际生命科学学会中国办事处中国肥胖问题工作组联合数据汇总分析协作组. 中国成人体质指数分类的推荐意见简介[J]. 中华预防医学杂志,2001,35(5):62-63. [8] 诸骏仁,高润霖,赵水平,等. 中国成人血脂异常防治指南(2016年修订版)[J]. 中华心血管病杂志,2016,44(10):833-853. [9] 葛均波, 徐永健, 王辰. 内科学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2017: 754-783. [10] 罗晓佳,吕政兵,洪必荧,等. 成都地区中老年人群高血压前期合并糖尿病前期患病率及影响因素分析[J]. 中国循环杂志,2015,30(10):984-988. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2015.10.014 [11] 刘晨越,邱琳,飒日娜,等. 血压测量次数对成人高血压检出率的影响分析[J]. 现代预防医学,2021,48(14):2603-2607. [12] 尹淑英,杨灵华,张晓丽,等. 山东省不同性别老年人肥胖与高血压的关系[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2020,40(3):648-651. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2020.03.060 [13] 张涛,乔毅娟,李卫芹,等. 天津市年龄5~6岁儿童偶测高血压检出率及其与超重和肥胖的关系[J]. 中华高血压杂志,2021,29(7):656-660. [14] 李雪,龚开凤,丁森华,等. 心血管病高危人群的隐匿性 高血压检出率及相关筛查指标研究[J]. 心脑血管病防治,2020,20(6):561-565. [15] Katzmarzyk P T,Mason C. Prevalence of class I,II and III obesity in canada[J]. CMAJ,2006,174(2):156-157. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.050806 [16] 张靳冬,付强. 中国农村人群高血压危险因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国卫生统计,2015,32(2):298-300. [17] 彭强,苏海. 血脂异常与高血压的关联[J]. 中华高血压杂志,2007,15(10):874-877. [18] 王天宇,窦倩,郭子坤,等. 1947例体检人群高血压与高血糖和高尿酸血症及血脂异常关系分析[J]. 社区医学杂志,2020,18(22):1509-1511. [19] 王莉丽. 河西区柳林街老年人群血脂异常现状及影响因素分析[J]. 继续医学教育,2021,35(9):67-68. [20] 周茜,汪晓洲,白洁. 青海地区65岁以上老年群体高血压多病共存患者治疗现状调查[J]. 公共卫生与预防医学,2021,32(5):153-156. [21] 刘美玲,赵天易,陆萍. 上海市嘉定区马陆镇辖区14 483名老年人血脂异常筛查及影响因素分析[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2021,19(17):2978-2981. [22] 李志刚,黄晓波,刘剑雄,等. 成都地区老年人群高血压患病状况及血压与血糖的关系研究[J]. 实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2017,25(12):30-34. -





 下载:
下载: