The Effect of Bronchoscopic Alveolar Lavage on the Maintenance of Borderline Donor Lung in Brain Death
-
摘要:
目的 研究纤支镜肺泡灌洗在脑死亡边缘性供肺维护中的作用。 方法 选取昆明医科大学附属甘美医院2017年9月至2019年12月收治的符合纳入标准的脑死亡患者,按照随机分组原则,在常规维护的基础上,分为纤支镜肺泡灌洗组(实验组)及对照组,通过2组胸片、动脉血气(氧合指数)、纤支镜检查等指标的比较,进行统计学分析。 结果 2组实验后氧合指数、胸片、纤支镜镜下表现评分均低于实验前评分,差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05),且2组试验后有效率比较差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),实验组有效率大于对照组。 结论 纤支镜肺泡灌洗可以作为一种有效维护供肺的技术,是提高边缘性供肺利用的有效手段。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of bronchoscopic alveolar lavage on the maintenance of borderline donor lung in brain death. Methods The brain death patients meeting the inclusion criteria and admitted to Ganmei Hospital of Kunming Medical University from September 2017 to December 2019 were randomly divided into the fiberoptic bronchoscopy alveolar lavage group (experimental group) and the control group on the basis of routine maintenance. Statistical analysis was carried out through the comparison of chest film, arterial blood gas (oxygenation index), fiberoptic bronchoscopy and other indexes between the two groups. Result The scores of oxygenation index, chest radiograph and fiberbronchoscope performance of the two groups after the experiment were all lower than those before the experiment the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05), and there was statistically significant difference in effective rate between the two groups (P < 0.05). The effective rate of the experimental group was higher than that of the control group. Conclusion Fiberbronchoscope alveolar lavage can be used as an effective technique to maintain the donor lung and has a wide application prospect. -
表 1 2组患者一般情况比较
Table 1. Compare of general condition between two groups
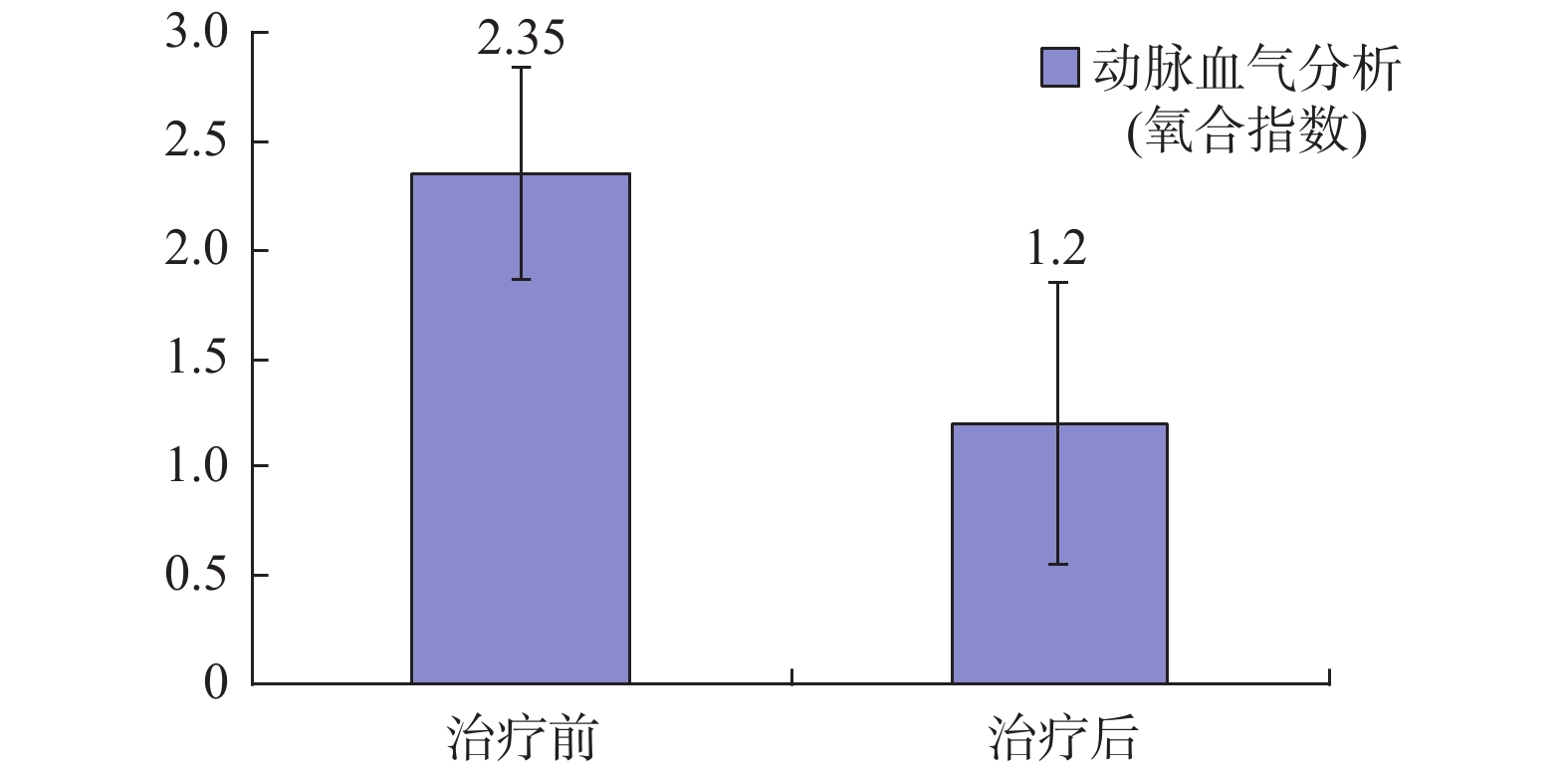
基本信息 实验组(n = 20) 对照组(n = 16) t/χ2 P 年龄(岁) 41.65 ± 15.86 42.19 ± 13.54 −0.108 0.915 性别 1.20 ± 0.65 1.99 ± 0.93 2.563 0.109 男n(%) 18 (90.00) 11 (68.75) 女n(%) 2 (10.00) 5 (31.25) 身高(cm) 165.90 ± 6.76 163.56 ± 8.95 1.454 0.155 体重(kg) 62.90 ± 9.55 61.38 ± 7.24 0.839 0.407 胸围(cm) 88.40 ± 4.13 88.94 ± 3.13 −0.430 0.670 带机时间(d) 5.35 ± 2.37 5.88 ± 2.94 −0.594 0.557 表 2 2组患者治疗前后的氧合指数评分比较(分)
Table 2. Comparison of oxygenation index scores before and after treatment between two groups (scores)
氧合指数 实验组
(n = 20)对照组
(n = 16)t P 治疗前 2.35 ± 0.49 2.38 ± 0.60 −0.151 0.881 治疗后 1.20 ± 0.65 1.99 ± 0.93 −2.482 0.018 t 7.815 2.300 P < 0.001 0.036 表 3 2组患者治疗前后的胸片评分比较(分)
Table 3. Comparison of chest X-ray scores before and after treatment between two groups (scores)
胸片 实验组(n = 20) 对照组(n = 16) t P 治疗前 2.05 ± 0.89 1.94 ± 0.77 0.612 0.545 治疗后 1.20 ± 0.51 1.60 ± 0.62 −2.179 0.036 t 5.784 2.423 P < 0.001 0.029 表 4 2组患者治疗前后的纤支镜检查评分比较(分)
Table 4. Comparison of bronchoscopy scores before and after treatment between two groups (scores)
纤支镜检查 实验组
(n = 20)对照组
(n = 16)t P 治疗前 1.95 ± 0.75 1.88 ± 0.85 0.195 0.847 治疗后 0.75 ± 0.51 0.80 ± 0.56 −2.520 0.017 t 6.294 2.423 P < 0.001 0.039 表 5 2组患者治疗的临床有效性比较 n(%)
Table 5. Comparison of the clinical effectiveness of treatment between two groups n(%)
临床效果 实验组(n = 20) 对照组(n = 16) χ2 P 有效性 4.425 0.035 无效 11 (55.00) 14 (87.50) 有效 9 (45.00) 2 (12.50) -
[1] 陈静瑜,毛文君,马千里,等. 中国肺移植供体标准及获取转运指南[J]. 器官移植,2018,9(5):325-333. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2018.05.001 [2] 徐龙明,左云霞,林一丹. 肺移植研究现状及移植期的规范化管理[J]. 中国胸心血管外科临床杂志,2020,27(2):209-213. [3] 郭明晓,李幼生. 脑死亡供体器官研究进展[J]. 中国普外基础与临床杂志,2013,20(10):1183-1187. [4] 高彤彤,田慧. 公民逝世后器官捐献供体评估、维护及护理[J]. 实用器官移植电子杂志,2017,5(1):31-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-5332.2017.01.011 [5] Kotloff R M,Blosser S,Fulda G J,et al. Management of the potential organ donor in the ICU:Society of critical care medicine/American college of chest physicians/association of organ procurement organizations consensus statement[J]. Critical Care Medicine,2015,43(6):1291-1325. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000958 [6] Bittner H B,Kendall S W,Campbell K A,et al. A valid experimental brain death donor model[J]. J Heart Lung Transplant,1995,14(2):308-317. [7] Viemann D,Strey A,Janning A,et al. Myeloid-related proteins 8 and 14 induce a specific inflammatory response in human microvascular endothelial cells[J]. Blood,2005,105(7):2955-2962. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-07-2520 [8] Apostolakis E,Parissis H,Dougenis D. Brain death and donor heart dysfunction:Implications in cardiac transplantation[J]. J Card Surg,2010,25(1):98-106. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8191.2008.00790.x [9] Zweers N,Petersen A H,van der Hoeven J A,et al. Donor brain death aggravates chronic rejection after lung transplantation in rats[J]. Transplantation,2004,78(9):1251-1258. doi: 10.1097/01.TP.0000142679.45418.96 [10] Murray J F,Matthay M A,Luce J M,et al. An expanded definition of the adult respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Am Rev Respir Dis,1988,138(3):720-723. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.3.720 [11] Oto T,Levvey B J,Whitford H,et al. Feasibility and utility of a lung donor score:Correlation with early post-transplant outcomes[J]. Ann Thorac Surg,2007,83(1):257-63. [12] 蔡兴俊,黄奕江,付姣,等. 急性肺损伤患者肺损伤评分与AGEs在预后评价中的作用[J]. 海南医学院学报,2013,19(2):186-188. [13] Dimopoulou I,Tsagarakis S,Anthi A,et al. High prevalence of decreased cortisol reserve in brain-dead potential organ donors[J]. Crit Care Med,2003,31(4):1113-1117. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000059644.54819.67 [14] 孙振涛,韩雪萍,苗丽君,等. 脑死亡状态巴马小型猪肺水含量及肺超微结构变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,8(9):1428-1430. [15] 窦晓婧,王清平. 炎性反应对脑死亡供体器官影响的研究进展[J]. 实用器官移植电子杂志,2016,4(5):315-318. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-5332.2016.05.013 [16] Mascia L,Pasero D,Slutsky A S,et al. Effect of a lung protective strategy for organ donors on eligibility and availability of lungs for transplantation:A randomized controlled trial[J]. JAMA,2010,304(23):2620-2627. doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.1796 [17] 吴波,冯靖,张静,等. 诊断性介入肺脏病学取材联合病原微生物宏基因组测序在肺部感染应用的原则[J]. 天津医药,2019,47(4):368-370. doi: 10.11958/20190835 [18] 钟南山, 刘又宁. 呼吸病学[M]第2版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2017: 857-859. [19] 李建辉,乔银标,贾俊君,等. 推动体外器官灌注技术发展,提高捐献器官利用率及质量[J]. 中华移植杂志(电子版),2020,14(2):83-86. doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-3903.2020.02.005 [20] Timek T,Vahl C F,Bonz A,et al. Triiodothyronine reverses depressed contractile performance after excessive catecholamine stimulation[J]. Ann Thorac Surg,1998,66(5):1618-1625. doi: 10.1016/S0003-4975(98)00764-4 [21] 邓兴,吴生坚,胡金金,等. 纤维支气管镜ICU治疗严重肺部感染中的应用意义探析[J]. 中外医疗,2016,35(29):103-105. [22] 刘东,毛文君,叶书高,等. 中国肺移植供肺获取与保护技术规范(2019版)[J]. 中华移植杂志(电子版),2019,13(2):87-90. doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-3903.2019.02.002 -






 下载:
下载: