Iodine-125 Seed Inhibits the Proliferation and Invasion of Gastric Cancer Cells by Regulating MicroRNA-193b-5p Expression
-
摘要:
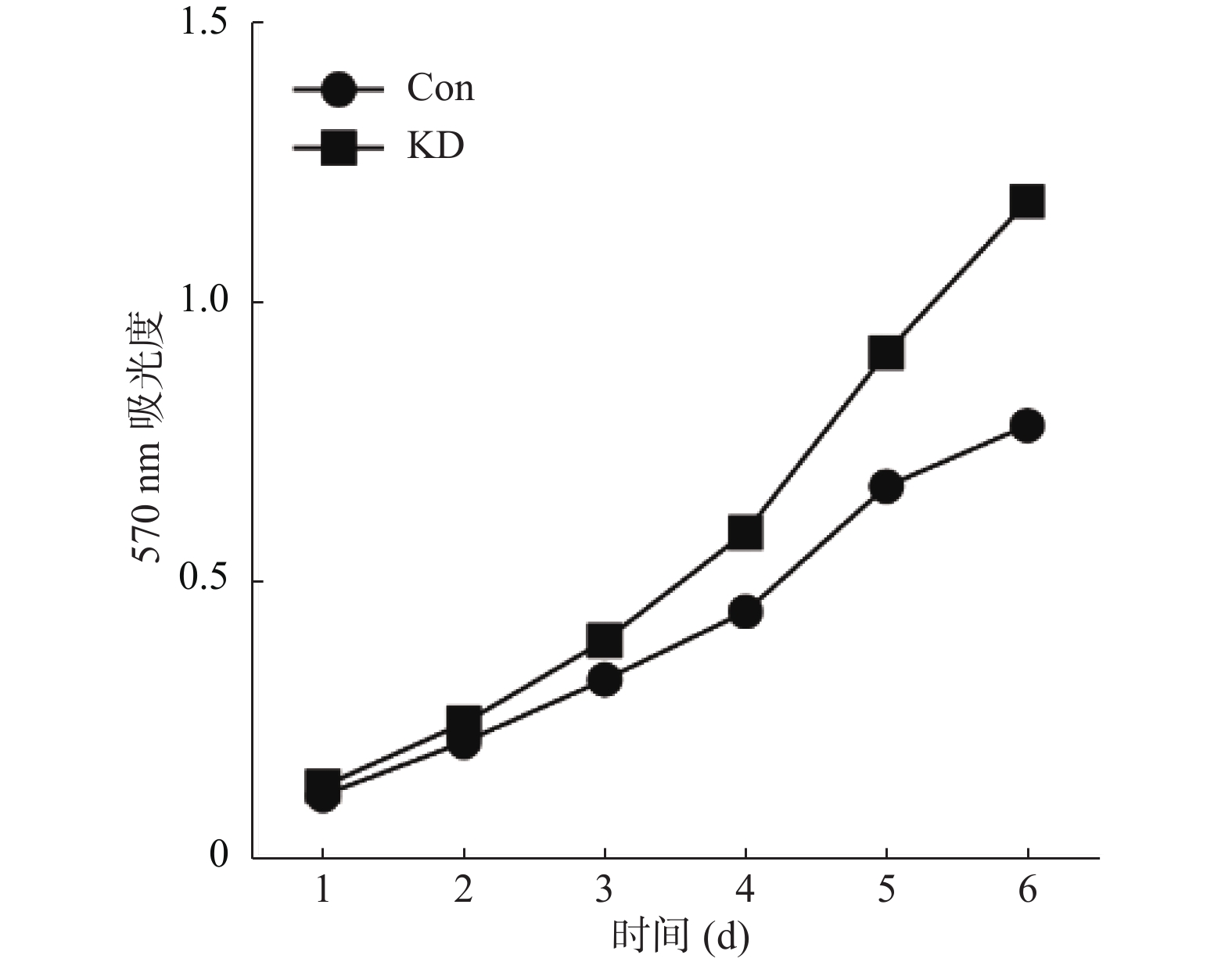
目的 探究碘-125粒子放疗胃癌过程中微小RNA(miR)-193b-5p的作用。 方法 以胃癌细胞系BGC-823作为对象,建立碘-125粒子体外照射模型,采用小分子RNA测序技术检测miRNA的表达谱。通过实时定量PCR检测碘-125辐照组和非辐照组细胞中miR-193b-5p的表达水平,使用hsa-miR-193b-5p抑制物和相应阴性抑制物转染胃癌细胞系BGC-823建立miR-193b-5p敲减细胞和对照细胞(miR-193b-5p敲减组和对照组),采用噻唑蓝(MTT)检测2组细胞增殖情况,采用Transwell分析2组细胞的侵袭情况。 结果 碘-125辐照组细胞miR-193b-5p表达水平(0.853±0.180)显著高于非辐照组(0.173±0.045),差异有统计学意义(t = 6.371,P < 0.05);敲减组细胞miR-193b-5p表达水平(1.264±0.311)明显低于对照组(12.219±2.464),差异有统计学意义(t = -7.640,P < 0.05);miR-193b-5p敲减组细胞的增殖能力(0.574±0.382)明显高于对照组细胞(0.424±0.246),差异有统计学意义(t=3.927,P < 0.05);miR-193b-5p敲减组细胞侵袭数量(222±23)明显高于对照组细胞侵袭数(40±7),差异有统计学意义(t = -13.293,P < 0.05)。 结论 碘-125放疗胃癌过程中,能通过调控miR-193b-5p的表达抑制胃癌细胞的增殖和侵袭。 -
关键词:
- 碘-125粒子 /
- 胃癌 /
- 微小RNA-193b-5p /
- 细胞增殖 /
- 细胞侵袭
Abstract:Objective To investigate the role of microRNA (miRNA, miR)-193b-5p in the process of iodine-125 particle radiotherapy for gastric cancer. Methods Gastric cancer cell line BGC-823 was used as the research object and iodine-125 seed in vitro irradiation model was established, and the expression profile of miRNA was detected by small molecule RNA sequencing. The expression of miR-193b-5p was analyzed by quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). MiR-193b-5p knockdown cell and control cell lines (knockdown group and control group) were established in gastric cancer cell line BGC-823 by hsa-miR-193b-5p inhibitor and NC inhibitor. Cell proliferation was analyzed by methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium (MTT) assay in the two groups. Cell invasion was analyzed by Transwell. Result Compared with the expression level of miR-193b-5p in the non-irradiated group (0.173±0.045), the expression of miR-193b-5p in the iodine-125 irradiated group (0.853±0.180) was significantly increased (t = 6.371, P < 0.05). Compared with the expression of miR-193b-5p in the control group (12.219±2.464), the expression of miR-193b-5p in the knockdown group (1.264±0.311) was significantly decreased (t = -7.640, P < 0.05). Compared with the control group (0.424±0.246), the proliferation of knockdown group (0.574±0.382)was significantly increased (t = 3.927, P < 0.05). Compared with the control group (40±7), the number of cell invasion in the knockdown group (222+23) was significantly increased (t = -13.293, P < 0.05). Conclusion Iodine-125 seed suppresses the proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating the expression of miR-193b-5p in the process of radiotherapy for gastric cancer. -
Key words:
- Iodine-125 seed /
- Gastric cancer /
- microRNA-193b-5p /
- Cell proliferation /
- Cell invasion
-
表 1 小分子RNA测序差异表达microRNAs结果
Table 1. Differentially expressed microRNAs identified by next generation sequencing
成熟的miRNA miRNA前体 成熟的RNA序列 差异倍数 P FDR 调节 hsa-miR-17-5p hsa-mir-17 CAAAGUGCUUACAGUGCAGGUAG 2.074 0.029 0.630 up hsa-miR-193b-5p hsa-mir-193b CGGGGUUUUGAGGGCGAGAUGA 7.000 0.049 0.630 up hsa-miR-23b-5p hsa-mir-23b UGGGUUCCUGGCAUGCUGAUUU 1.750 0.000 0.000 up hsa-miR-483-5p hsa-mir-483 AAGACGGGAGGAAAGAAGGGAG 3.569 0.033 0.630 up hsa-miR-92a-1-5p hsa-mir-92a-1 AGGUUGGGAUCGGUUGCAAUGCU 5.600 0.007 0.630 up hsa-miR-127-3p hsa-mir-127 UCGGAUCCGUCUGAGCUUGGCU −2.033 0.036 0.630 down hsa-miR-1285-3p hsa-mir-1285-1 UCUGGGCAACAAAGUGAGACCU −2.000 0.000 0.000 down hsa-miR-1285-3p hsa-mir-1285-2 UCUGGGCAACAAAGUGAGACCU −2.000 0.000 0.000 down hsa-miR-296-5p hsa-mir-296 AGGGCCCCCCCUCAAUCCUGU −2.667 0.038 0.630 down hsa-miR-421 hsa-mir-421 AUCAACAGACAUUAAUUGGGCGC −1.750 0.000 0.000 down hsa-miR-495-3p hsa-mir-495 AAACAAACAUGGUGCACUUCUU −7.714 0.034 0.630 down hsa-miR-548am-3p hsa-mir-548am CAAAAACUGCAGUUACUUUUGU −3.333 0.020 0.630 down -
[1] Sung H,Ferlay J,Siegel R L,et al. Global cancer statistics 2020:GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin,2021,71(3):209-249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660 [2] Song Z,Wu Y,Yang J,et al. Progress in the treatment of advanced gastric cancer[J]. Tumour Biol,2017,39(7):1-7. [3] Marin J J,Al-Abdulla R,Lozano E,et al. Mechanisms of resistance to chemotherapy in gastric cancer[J]. Anticancer Agents Med Chem,2016,16(3):318-334. doi: 10.2174/1871520615666150803125121 [4] Kang M,Youn H G,An J Y,et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy vs surgery alone for pT3N0M0 gastric cancer[J]. Ann Surg Oncol,2021,28(3):1437-1444. [5] 孙晋虎,李梦. 125I放射性粒子植入在口腔颌面部恶性肿瘤治疗中的应用[J]. 口腔医学研究,2019,35(5):415-418. [6] 罗东,唐能,刘国栋,等. 碘125放射性粒子植入近距离治疗不可切除胰腺癌的现状与进展[J]. 中国普通外科杂志,2017,26(9):1193-1201. [7] Ma Z. H,Yang Y,Zou L,et al. 125I seed irradiation induces up-regulation of the genes associated with apoptosis and cell cycle arrest and inhibits growth of gastric cancer xenografts[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res,2012,31(1):61. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-31-61 [8] Khordadmehr M,Shahbazi R,Sadreddini S,et al. miR-193:A new weapon against cancer[J]. J Cell Physiol,2019,234(10):16861-16872. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28368 [9] Takabayashi K,Kashiwagi K,Kawata T,et al. Continuous low-dose irradiation by I-125 seeds induces apoptosis of gastric cancer cells regardless of histological origin[J]. Cancer Biol Ther,2014,15(1):81-88. doi: 10.4161/cbt.26610 [10] Li C. G,Zhou Z. P,Jia Y. Z,et al. Radioactive (125)I seed implantation for locally advanced pancreatic cancer:A retrospective analysis of 50 cases[J]. World J Clin Cases,2020,8(17):3743-3750. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i17.3743 [11] Yang D Y,Lin Y P,Xue C,et al. CT-guided percutaneous implantation of (125)I particles in treatment of early lung cancer[J]. J Thorac Dis,2020,12(10):5996-6009. doi: 10.21037/jtd-20-2666 [12] Luo M,Chen J,Zhong Z,et al. CT-guided 125I brachytherapy combined with chemotherapy for the treatment of unresectable or locally advanced pancreatic carcinoma[J]. Diagn Interv Radiol,2021,27(1):50-58. doi: 10.5152/dir.2020.19371 [13] Xue Gang,Feng Yao,Li Jia-Bin. Significance of 125I radioactive seed implantation on growth differentiation factor and programmed death receptor-1 during treatment of oral cancer[J]. World Journal of Clinical Cases,2020,8(5):874-886. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i5.874 [14] Ji Z,Jiang Y,Tian S,et al. The effectiveness and prognostic factors of CT-guided radioactive I-125 seed implantation for the treatment of recurrent head and neck cancer after external beam radiation therapy[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys,2019,103(3):638-645. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.10.034 [15] Xia L,Li F,Qiu J,et al. Oncogenic miR-20b-5p contributes to malignant behaviors of breast cancer stem cells by bidirectionally regulating CCND1 and E2F1[J]. BMC Cancer,2020,20(1):949. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07395-y [16] Jiang F,Zhang L,Liu Y,et al. Overexpression of miR-331 indicates poor prognosis and promotes progression of breast cancer[J]. Oncol Res Treat,2020,43(9):441-448. doi: 10.1159/000508792 [17] Feliciano A,Garcia-Mayea Y,Jubierre L,et al. miR-99a reveals two novel oncogenic proteins E2F2 and EMR2 and represses stemness in lung cancer[J]. Cell Death Dis,2017,8(10):e3141. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.544 [18] Xu K,Shi J,Mo D,Y et al. miR-219a-1 inhibits colon cancer cells proliferation and invasion by targeting MEMO1[J]. Cancer Biol Ther,2020,21(12):1163-1170. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2020.1843897 [19] Yang Y,Ma Z H,Li X G,et al. Iodine-125 irradiation inhibits invasion of gastric cancer cells by reactivating microRNA-181c expression[J]. Oncol Lett,2016,12(4):2789-2795. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.5033 [20] Wang L,Zhang Y,Zhao L,et al. MicroRNA-193b inhibits the proliferation,migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells via targeting cyclin D1[J]. Acta Histochem,2016,118(4):323-330. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2016.02.001 -






 下载:
下载: