Effect of Repairing Patellar Cartilage Fracture with Suture Anchor
-
摘要:
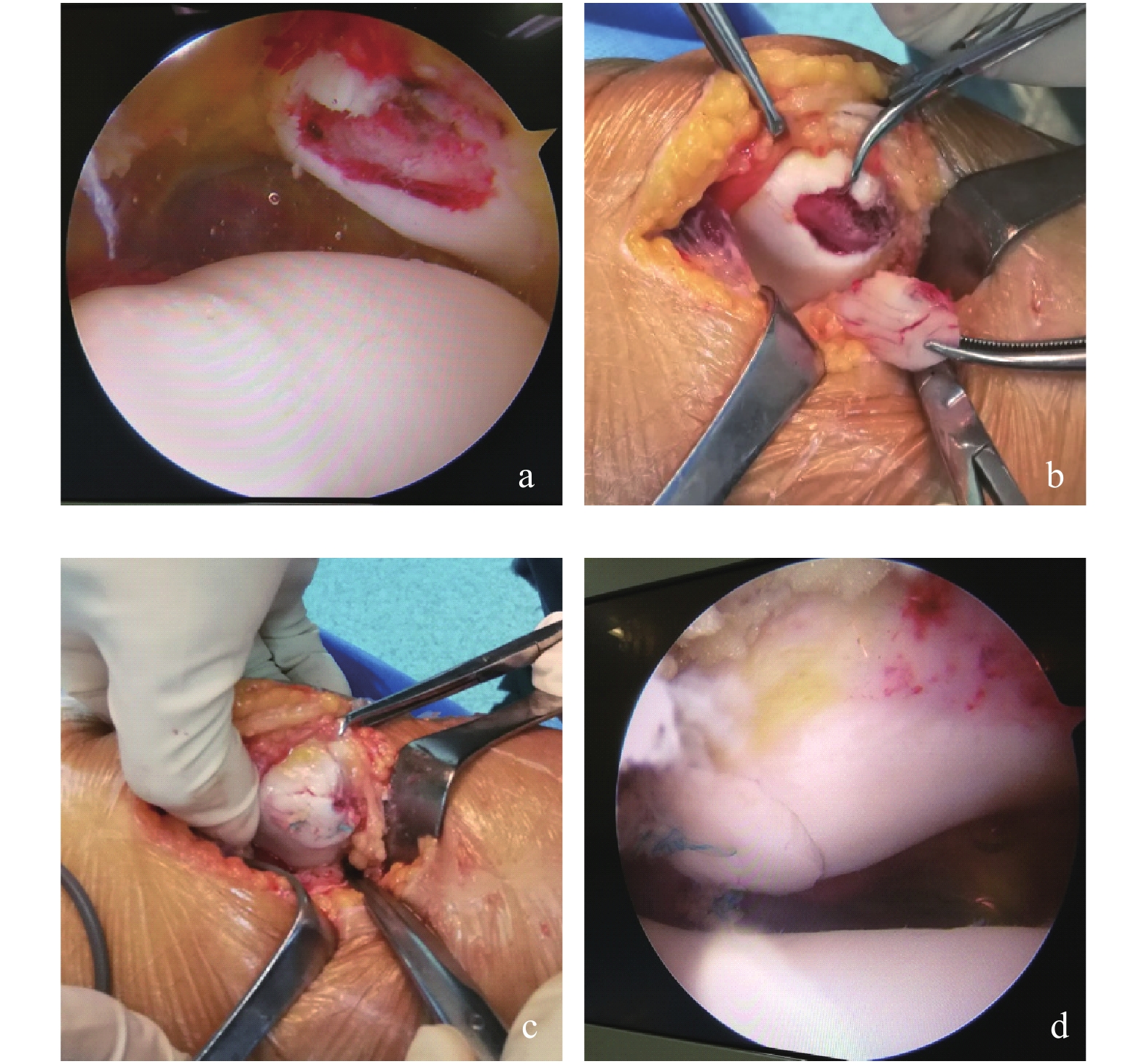
目的 研究带线锚钉固定修复髌骨软骨骨折的临床效果。 方法 选取2016年7月至2018年6月髌骨软骨骨折病例50例,其中男18例,女32例,年龄17~28岁,均为外伤致急性髌骨外侧脱位伴髌骨软骨骨折,术前Lysholm评分为(63.8±7.2),VAS评分为(8±1.7)。均采取带线锚钉缝合固定方法修复髌骨软骨骨折。 结果 术后所有患者伤口愈合良好,无膝关节肿胀及积液,髌骨软骨愈合良好,锚钉无松动、脱出,软骨块无移位。除3例患者术后6周时股四头肌轻度萎缩,肌肉力量恢复欠佳,其他患者下肢肌肉力量均恢复良好。Lysholm评分(87.3±4.1),VAS评分(2±2.3 ),均较术前明显改善(P < 0.05)。 结论 采取带线锚钉缝合固定髌骨软骨骨折,手术操作简单,能有效固定软骨骨折,避免刺激髌前滑囊,有其独特优势。 Abstract:Objective To study the effect of repairing patellar cartilage fracture with the suture anchor. Methods Between July 2016 and June 2018, 50 patients with patellar cartilage fracture were chosen, 18 male and 32 female, age 17 to 28. All of them were acute lateral dislocation of patella with fracture of patellar cartilage caused by trauma. Lysholm score is (63.8±7.2), VAS score is ( 8±1.7). All of the patellar cartilage fracture was repaired by suture anchor. Results All patients’wound healed well after operation, no swelling and effusion of knee joint, patellar cartilage healed well, no loosening of anchor, no displacement of cartilage fragments. Except for 3 patients with mild atrophy of quadriceps and poor recovery of muscle strength at 6 weeks after operation, the other patients’muscle strength recovered well. Lysholm score is (87.3±4.1), VAS score is ( 2±2.3), which were significantly improved compared with those before operation. Conclusion The operation technique which is fixation of patellar cartilage fracture with suture anchor is simple, can effectively fix cartilage fracture and avoid stimulating anterior patellar bursa, which has its unique advantages. -
Key words:
- Patellar cartilage /
- Fracture /
- Suture anchor
-
表 1 术前及术后Lysholm评分及VAS评分[(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),分]Table 1. Preoperative and postoperative Lysholm score and VAS score [(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),score]组别 Lysholm评分 VAS评分 术前 63.8 ± 6.2 8 ± 1.7 术后 87.3 ± 4.5 2 ± 2.1 P 0.01 0.03 -
[1] Franzone J M,Vitale M A,Stein B E S,et al. Is there an association between chronicity of patellar instability and patellofemoral cartilage lesions. An arthroscopic assessment of chondral injury[J]. J Knee Surg,2012,25(5):411-416. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1313747 [2] Stanitski C L,Paletta G A Jr. Articular cartilage injury with acute patellar dislocations in adolescents:arthroscopic and radiologic correlation[J]. Am J Sports Med,1998,26(1):52-55. doi: 10.1177/03635465980260012501 [3] Callewier A,Monsaert A,Lamraski G. Lateral femoral condyleostechondral fracture combined to patellar dislocation:a case report[J]. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res,2009,95(1):85-88. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2008.07.001 [4] Morris J K,Weber A E,Morris M S. Adolescent femoral chondral fragment fixation with poly-l-lactic acid chondral darts[J]. Orthopedics,2016,39(2):362-366. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20160129-05 [5] Beran M C,Samora W P,Klingele K E. Weight-bearing osteochondral lesions of the lateral femoral condyle following patellar dislocation in adolescent athletes[J]. Orthopedics,2012,35(7):1033-1037. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20120621-16 [6] Nomura E,Inoue M,Kurimura M. Chondral and osteochondral injuries associated with acute patella dislocation[J]. Arthroscopy,2003,19(7):717-721. doi: 10.1016/s0749-8063(03)00401-8 [7] Lubis A M,Sandhow L,Lubis V K A,et al. Susanto. Isolation and cultivation of mesenchymal stem cells form iliac crest bone marrow for further cartilage defect management[J]. Acta Med Indones,2011,43(3):178-184. [8] Shah M R,Kaplan K M,Meislin R J,et al. Articular cartilage restoration of the knee[J]. Bull,NYU Hosp Jt Dis,2007,65(1):51-60. [9] Hawkins R J,Bell R H,Anisette G. Acute patellar dislocations:the natural history[J]. Am J Sports Med,1986,14(2):117-120. doi: 10.1177/036354658601400204 [10] Cash J D,Hughston J C. Treatment of acute patellar dislocation[J]. Am J Sports Med,1988,16(3):244-249. doi: 10.1177/036354658801600308 [11] Salonen E E,Magga T,Sillanpää P J,et al. Traumatic patellar dislocation and cartilage injury:A follow-up study of long-term cartilage deterioration[J]. Am J Sports Med,2017,45(6):1376-1382. doi: 10.1177/0363546516687549 [12] Gesslein M,Merkl C,Bail H J,et al. Refixation of Large Osteochondral Fractures After Patella Dislocation Shows Better Mid to Long Term Outcome Compared With Debridement[J]. Cartilage,2019,13:1-8. doi: 10.1177/1947603519886637 [13] Bauer K L. Osteochondral injuries of the knee in pediatric patients[J]. J Knee Surg,2018,31(5):382-391. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1625956 [14] Lidder S,Thomas M,Desai A,et al. Osteochondral fractures of the knee in skeletally immature patients:short term results of operative fixation using omnitech screws[J]. Acta Orthop Belg,2016,82(4):762-767. [15] Kang H,Li J,Chen X X,et al. Fixation versus excision of osteochondral fractures after patellar dislocations in adolescent patients:A retrospective cohort study[J]. Chin Med J (Engl),2018,131(11):1296-1301. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.232800 [16] Fu F H,Zurakowski D,Browne J E,et al. Autologous chondrocyte implantation versus debridement for treatment of full thickness chondral defects of the knee:an observational cohort study with 3-year follow-up[J]. Am J Sports Med,2005,33(11):1658-1666. doi: 10.1177/0363546505275148 [17] Kruez P C,Steinwachs M R,Erggelet C,et al. Results after microfracture of full-thickness chondral defects in different compartments of the knee[J]. Osteoarthritis Cartilage,2006,14(11):1119-1125. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2006.05.003 [18] Gillogly S D,Arnold R M. Autologous chondrocyte implantation and anteromedialization for isolated patellar articular cartilage lesions:5- to 11-year follow-up[J]. Am J Sports Med,2014,42(4):912-920. doi: 10.1177/0363546513519077 [19] Gomoll A H,Gillogly S D,Cole B J,et al. Autologous chondrocyte implantation in the patella:a multicenter experience[J]. Am J Sports Med,2014,42(5):1074-1081. doi: 10.1177/0363546514523927 [20] Lubis A M T,Panjaitan T,Hoo C. Autologous mesenchymal stem cell application for cartilage defect in recurrent patellar dislocation:A case report[J]. Int J Surg Case Rep,2019,55:183-186. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2019.01.031 [21] Moseley J B Jr,Anderson A F,Browne J E,et al. Long term durability of autologous chondrocyte implantation:a multicenter,observational study in US patients[J]. Am J Sports Med,2010,38(2):238-246. doi: 10.1177/0363546509348000 [22] Peterson L,Vasiliadis H S,Brittberg M,et al. Autologous chondrocyte implantation:a long-term follow-up[J]. Am J Sports Med,2010,38(6):1117-1124. doi: 10.1177/0363546509357915 [23] Argawala S,Mohrir G S,Mahajan B S. Osteochondral fracture lateral femoral condyle treated with ORIF using Z-Plasty:a modification of Coonse and Adams approach[J]. Case Rep Orthop,2011,95:191-196. doi: 10.1155/2011/957196 [24] Song K S,Min B W,Bae K C,et al. Chondral fracture of the lateral femoral condyle in children with different treatment methods[J]. J Pediatr Orthop B,2016,25(1):43-47. doi: 10.1097/BPB.0000000000000222 [25] Chan C M,King J 3rd,Farmer K W. Fixation of chondral fracture of the weight-bearing area of the lateral femoral condyle in an adolescent[J]. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc,2014,22(6):1284-1287. doi: 10.1007/s00167-013-2833-0 [26] Arendt E A,Dejour D,Farr J. Patellofemoral instability[J]. Sports Med Arthrosc,2012,20(3):127. doi: 10.1097/JSA.0b013e318262a0ce [27] Millington K L,Shah J P,Dahm D L,et al. Bioabsorbable fixation of unstable osteochondritis dissecans lesions[J]. Am J Sports Med,2010,38(10):2065-2070. doi: 10.1177/0363546510371369 [28] Paša L,Veselý R,Kočiš J,et al. Treatment of Extensive Chondral Defects of the Patella after Patellar Dislocation[J]. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech,2017,84(6):441-447. -






 下载:
下载: