Potential Value of G6PD Activity Detection in the Peripheral Blood for the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Cervical Cancer Patients with High Risk Human Papillomavirus Infection
-
摘要:
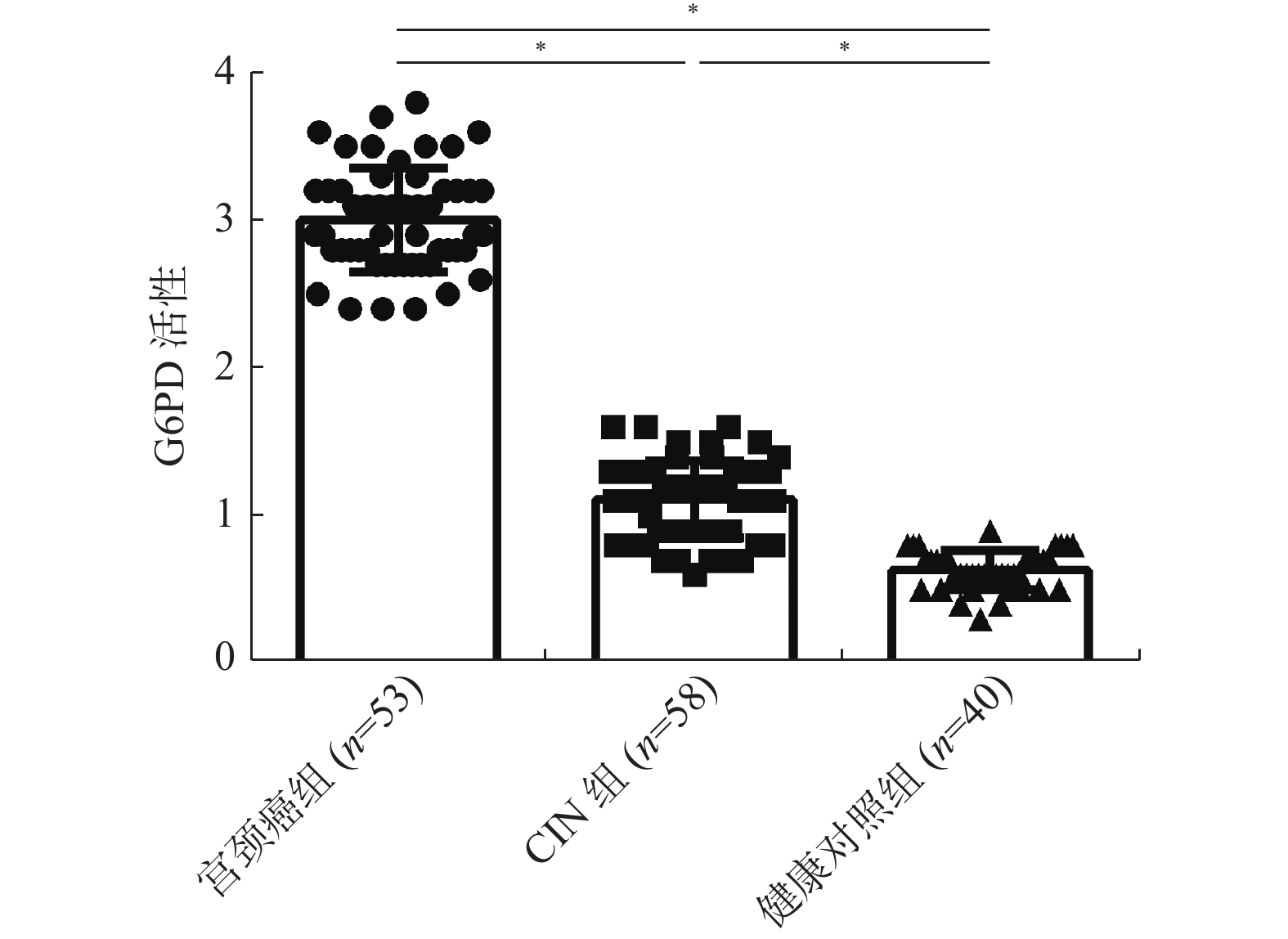
目的 探讨外周血葡萄糖-6-磷酸脱氢酶(Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase,G6PD)活性检测对于感染高危型人乳头瘤病毒(high-risk Human papilloma virus,HR-HPV)宫颈癌患者的诊断预后价值。 方法 选取2014年6月至2015年12月间确诊的宫颈癌患者53例、宫颈上皮内瘤病变(cervicalintraepithelial neoplasia,CIN)患者58 例、健康体检者40例为研究对象,采用HPV检测试剂盒对各组人群HPV感染进行检测与基因分型;宫颈癌患者手术切除标本进行病理学评估及分型;同时取各组人群血清标本,运用免疫荧光法检测G6PD的活性;结合临床资料及G6PD活性检测结果进行相关分析;并对检测结果进行循证分析。 结果 宫颈癌组中外周血G6PD的活性最高,与CIN组、健康对照组相比有统计学差异(P < 0.01),CIN组与健康对照组相比,差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05);CIN患者外周血中G6PD的活性改变与患者的疾病病程恶化密切相关;宫颈癌组与CIN组外周血中G6PD的活性都与患者HPV16/18型感染的状态契合;HPV 16/18感染宫颈癌患者OS曲线与外周血G6PD活性的关联性分析结果显示,外周血G6PD活性高的患者5 a生存率显著下降(P < 0.05)。HPV 16/18感染检测与外周血G6PD活性检测在CIN 及宫颈癌的循证实验诊断中价值较高,其中G6PD活性检测对于CIN的诊断价值优于HPV16/18检测。 结论 G6PD活性与宫颈癌患者病程进展相关,外周血G6PD活性检测可作为高危型HPV尤其是HPV 16/18型感染宫颈癌的早期诊断及预后指标之一。 Abstract:Objective To explore the value of detecting G6PD activity in the peripheral blood for the diagnosis and prognosis of cervical cancer patients with high-risk human papillomavirus (HR-HPV) infection. Methods A total of 53 cervical cancer (CC) patients, 58 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) patients and 40 health cohorts (HC), visiting and attending the clinic of Yunnan Third People’s Hospital during June 2014 to December 2015, were employed in this study. HPV Gene Chip Test Kit was used to detect and screen the genotype HPV infection in each group of population. Pathological evaluation and genotyping were performed on surgical specimens of cervical cancer patients. Serum samples were taken from each group of population, the activity of G6PD was detected by immunofluorescence assay, and the correlation analysis was carried out according to the clinical data and the results of G6PD activity. The results were then analyzed based on evidence. Results The activity of G6PD in peripheral blood was the highest in CC group, and there was significant difference to CIN Group and HC Group (P < 0.01) , and CIN Group to HC Group (P < 0.05). The change of G6PD activity in peripheral blood of CC patients is closely related to the progression of cervical cancer, and the change of G6PD activity in peripheral blood of CIN patients is closely related to the progression of cervical cancer. In CC group and CIN Group, the activity of G6PD in peripheral blood was consistent with HPV16/18 infection, and the relationship between the OS curve and the activity of G6PD in peripheral blood of CC patients infected with HPV 16/18 was analyzed, the 5-year survival rate decreased significantly in patients with high G6PD activity in peripheral blood (P <0.05) . The validity and reliability of G6PD activity detection and / or HPV16/18 infection test are valuable in evidence-based diagnosis for CIN or cervical cancer. Conclusions The activity of G6PD is related to the progression of cervical cancer. The detection of G6PD activity in peripheral blood can be used as one of the diagnostic and prognostic indicators of CIN and HR-HPV-infected cervical cancer, especially HPV 16/18. -
Key words:
- G6PD /
- High-risk human papillomavirus /
- Cervical cancer /
- Prognosis /
- Evidence-based Diagnosis
-
表 1 HPV检测与基因分型的结果[n(%)]
Table 1. HPV infection rates and HPV genotype detected in different cohorts [ n(%)]
HPV基因分型 各组HPV感染的检测结果 宫颈癌患者
(53例)CIN组
(58例)健康体检者
(40例)HPV16 28(52.8) 26(44.8) -- HPV18 17(32.1) 19(32.8) -- HPV39 3(5.7) 3(5.2) -- HPV45 3(5.7) -- -- HPV51 3(5.7) 2(3.4) -- HPV52 2(3.8) -- -- HPV59 1(1.9) -- -- HPV31 -- 4(6.9) -- HPV11 -- 3(5.2) -- HPV58 1(1.9) 2(3.4) -- HPV40 -- -- 1(2.5) HPV6 -- -- 1(2.5) HPV12 -- -- 1(2.5) 多重HPV感染 5(9.4) 10(17.2) -- HR-HPV 16/18 45(84.9) 42(72.4) 0 HPV感染率 51(96.2) 53(91.4) 3(7.5) 注:--:未检出。 表 2 高危型HPV16/18感染状态、血清G6PD活性与宫颈癌患者的临床资料关联性分析(n)
Table 2. Association analysis of high risk HPV16/18 infection status, serum G6PD activity and clinical data of cervical cancer patients (n)
临床特征
FIGO 分级HPV16/18感染状态 P 外周血G6PD活性 P HPV16/18+
(n = 45)HPV16/18-
(n = 8)校正的OR
(odds ratio)
95%CI高活性
(> median)
(n=49)低活性
(≤ median)
(n = 4)校正的OR
(odds ratio)
95%CIⅠ 3 5 1.19 (0.44~1.47) 0.652 4 2 1.32(0.51~1.86) 0.327 Ⅱ 8 2 1.32 (0.68~1.64) 0.721 6 2 1.19(0.62~1.39) 0.527 Ⅲ 15 1 13.37(10.24~18.41) < 0.05 21 0 25.69(19.54~33.5) < 0.001 Ⅳ 19 0 17.78(12.47~24.68) < 0.001 18 0 19.17(15.32~29.2) < 0.001 病理分级 高 5 6 1.23(0.74~1.68) 0.752 7 3 1.09(0.57~1.95) 0.268 中等 18 1 15.21(11.02~20.37) < 0.001 17 1 14.12(9.57~18.17) < 0.05 低 22 1 19.38(13.29~25.24) < 0.001 25 0 29.35(22.97~36.1) < 0.001 肿瘤体积 ≤ 4 cm 8 6 1.24(0.64~1.69) 0.358 9 4 1.11(0.62~1.64) 0.427 > 4 cm 37 2 32.68(29.57~38.75) < 0.001 40 0 36.71(32.71~42.1) < 0.001 表 3 高危型HPV16/18感染状态、血清G6PD活性与CIN患者的临床资料关联性分析(n)
Table 3. Correlation analysis of high-risk HPV16/18 infection status, serum G6PD activity and clinical data of CIN patients (n)
CIN分级 HPV16/18感染状态 P 外周血G6PD活性 P HPV16/18+
(n = 42)HPV16/18-
(n = 16)校正的OR
(odds ratio)
95%CI高活性
(> median)
(n = 51)低活性
(≤ median)
(n = 7)校正的OR
(odds ratio)
95%CIⅠ 4 9 1.26(0.59~1.51) 0.524 6 4 1.01(0.61~1.32) 0.398 Ⅱ 17 6 15.07(10.21~21.35) 0.006 23 3 28.11(24.19~34.8) < 0.001 Ⅲ 21 1 22.33(18.12~26.93) < 0.001 22 0 22.17(17.31~28.4) < 0.001 表 4 外周血G6PD检测实验在宫颈癌以及CIN诊断中的效能基本数据表(n)
Table 4. Efficacy of peripheral blood G6PD test in the diagnosis of cervical cancer and CIN basic data sheet (n)
外周血G6PD活性检测 宫颈癌患者 合计 外周血G6PD活性检测 CIN患者 合计 病理检测结果 病理检测结果 患者(+) 非患者(−) 患者(+) 非患者(−) 高活性(+) 49 1 50 高活性(+) 51 1 52 低活性(−) 4 39 43 低活性(−) 7 39 46 合计 53 40 93 合计 58 40 98 表 5 HPV16/18检测实验在宫颈癌以及CIN诊断中的效能基本数据表(n)
Table 5. Efficacy of HPV16 / 18 test in diagnosis of cervical cancer and CIN basic data table (n)
HPV16/18检测 宫颈癌患者 合计 HPV16/18检测 CIN患者 合计 病理检测结果 病理检测结果 患者(+) 非患者(−) 患者(+) 非患者(−) 阳性(+) 45 0 45 阳性(+) 42 0 52 阴性(−) 8 40 48 阴性(−) 16 40 46 合计 53 40 93 合计 58 40 98 表 6 HPV16/18检测、外周血G6PD活性检测对宫颈癌的诊断价值评价
Table 6. Evaluation of HPV16 / 18 test and G6PD activity in peripheral blood in the diagnosis of cervical cancer
检测方法 灵敏度 特异性 准确度 阳性似然比(LR+) 阴性似然比(LR−) Youden指数 HPV16/18检测 1 1 0.914 - 0.151 1 外周血G6PD活性检测 0.849 0.975 0.903 33.96 0.155 0.824 串联实验 0.811 1 0.892 - 0.189 0.811 并联实验 0.925 0.975 0.946 37 0.077 0.9 表 7 HPV16/18检测、外周血G6PD活性检测对CIN的诊断价值评价
Table 7. Evaluation of diagnostic value of HPV16 / 18 test and peripheral blood G6PD activity test for CIN
检测方法 灵敏度 特异性 准确度 阳性似然比(LR+) 阴性似然比(LR−) Youden指数 HPV16/18检测 0.724 1 0.837 - 0.276 0.724 外周血G6PD活性检测 0.879 0.975 0.918 35.16 0.124 0.854 串联实验 0.689 1 0.889 - 0.310 0.689 并联实验 0.793 0.975 0.867 31.72 0.212 0.842 -
[1] Berman T A,Schiller J T. Human papillomavirus in cervical cancer and oropharyngeal cancer:One cause,two diseases[J]. Cancer,2017,123(12):2219-2229. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30588 [2] Joseph A N,Bhatla N. Population-based human papillomavirus testing:The new paradigm for cervical cancer screening[J]. Natl Med J India,2021,34:36-37. doi: 10.4103/0970-258X.323447 [3] Mammas I N,Sourvinos G,Spandidos D A. Human papilloma virus (HPV) infection in children and adolescents[J]. European Journal of Pediatrics,2009,168(3):267-273. doi: 10.1007/s00431-008-0882-z [4] Margaret,E,Cruickshank. The role of human papillomavirus in risk management[J]. Reviews in Gynaecological Practice,2003,3(4):229-233. doi: 10.1016/S1471-7697(03)00057-1 [5] Munoz N,Bosch F X,De-Sanjose S,et al. Epidemiologic classification of human papillomavirus types associated with cervical cancer[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine,2003,348(6):518-527. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa021641 [6] Hu T , Li Y S , Chen B , et al. Elevated glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase expression in the cervical cancer cases is associated with the cancerigenic event of high-risk human papillomaviruses[J]. Experimental Biology & Medicine, 2015, 1287-1297. [7] Luo Z,Du D,Liu Y,et al. Discovery and characterization of a novel glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) inhibitor via high-throughput screening[J]. Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2021,40:127905. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2021.127905 [8] Hu,T. ,Zhang,C.,Tang,Q.,et al. Variant G6PD levels promote tumor cell proliferation or apoptosis via the STAT3/5 pathway in the human melanoma xenograft mouse model[J]. Bio Med Central,2013,13(1):251. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-13-251 [9] 苏琼,黄成双,吴柳松,等. G6PD活性在急性白血病患儿中的变化及其临床意义[J]. 中国实验血液学杂志,2018,26(06):1649-1656. [10] 樊小群,李欢,朱华雄,等. Mir-335-5p靶向G6PD对结肠癌细胞增殖、凋亡的影响[J]. 中国应用生理学杂,2021,37(04):402-406. [11] Polat M F,Taysi S,Gul M,et al. Oxidant/antioxidant status in blood of patients with malignant breast tumour and benign breast disease[J]. Cell Biochem Funct,2002,20(4):327-331. doi: 10.1002/cbf.980 [12] 蒋素贞,方艺川,卢丽娜,等. 6-磷酸葡萄糖脱氢酶在子宫内膜癌中的表达[J]. 广东医学,2016,37(22):3400-3403. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9448.2016.22.027 [13] Hu T,Chang Y,Xiao Z,et al. miR-1 inhibits progression of high-risk papillomavirus-associated human cervical cancer by targeting G6PD[J]. Oncotarget,2016,7:86103-86116. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13344 [14] 中华医学会病理学分会女性生殖系统疾病学组,中国优生科学协会阴道镜与宫颈病理学会病理学组. 宫颈癌及癌前病变病理诊断规范[J]. 中华病理学杂志,2019,48(4):265-269. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-5807.2019.04.001 [15] Jiang Z,Albanese J,Kesterson J,et al. Monoclonal Antibodies Against Human Papillomavirus E6 and E7 Oncoproteins Inhibit Tumor Growth in Experimental Cervical Cancer[J]. Translational Oncology,2019,12(10):1289-1295. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2019.06.003 [16] He Z,Xia Y,Liu B,et al. Down-regulation of miR-452 is associated with poor prognosis in the non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. J Thorac Dis,2016,8(5):894-900. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2016.03.51 [17] Goodman,A. HPV testing as a screen for cervical cancer[J]. Bmj,2015,350:2372. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h2372 [18] Kontostathi G,Zoidakis J,Anagnou N P,et al. Proteomics approaches in cervical cancer:focus on the discovery of biomarkers for diagnosis and drug treatment monitoring.[J]. Expert Rev Proteomics,2016,13:731-745. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2016.1210514 -






 下载:
下载: