Comparison of the Efficacy of Double Plates and Locking Plates in the Treatment of Complex Proximal Humerus Fractures
-
摘要:
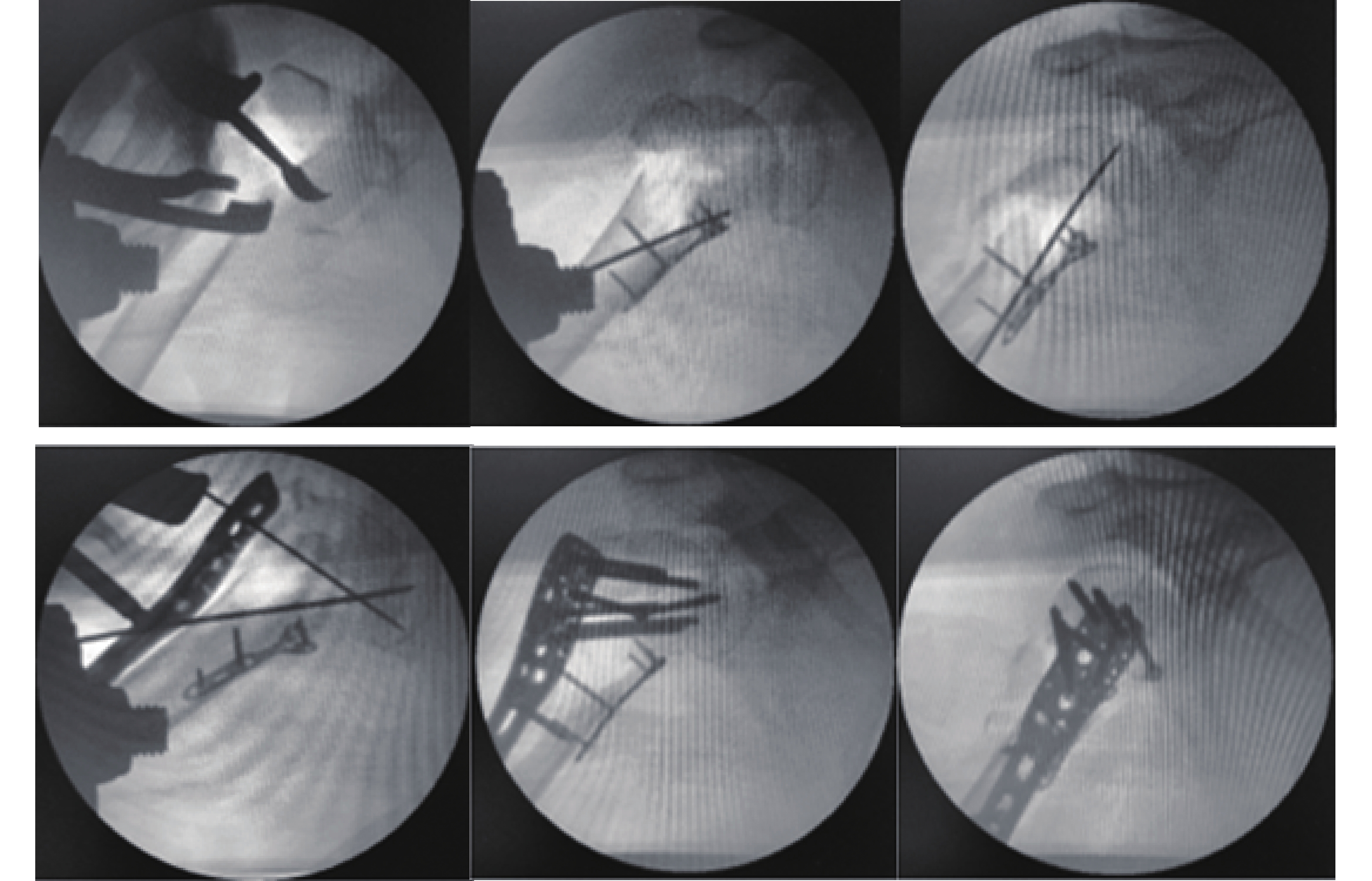
目的 比较双钢板与锁定钢板治疗复杂肱骨近端骨折的临床疗效。 方法 选取2015年01月至2020年01月昆明医科大学第四附属医院骨与创伤外科收治的57例接受手术切开复位内固定治疗并符合纳入标准的肱骨近端骨折患者。按固定方式的不同,分为双钢板组(A组,28例)和锁定钢板组(B组,29例),比较2组患者手术情况、治疗效果、术后功能恢复情况及并发症发生情况等指标综合评估其临床疗效。 结果 手术时间、术中出血量、术中透视时间、术后切口引流量比较A组均差于B组(P < 0.05),但术后颈干角丢失量、肱骨头内翻角度、肱骨高度丢失量、Constant功能评分、VAS评分比较A组则均优于B组(P < 0.05);术后总并发症发生率比较无显著性差异(P > 0.05)。 结论 双钢板及锁定钢板均可有效治疗复杂肱骨近端骨折,但双钢板在固定稳定性及功能恢复方面效果更佳,更适用于治疗骨折类型复杂、粉碎严重、内侧柱支撑不完整的患者。 Abstract:Objective To compare the clinical efficacy of double plates and locking plates in the treatment of complex proximal humerus fractures. Methods Fifty-seven patients admitted to the Department of Bone and Trauma Surgery of the Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from 01 2015 to 01 2020 who underwent surgical incisional reduction and internal fixation treatment and met the inclusion criteria for proximal humerus fractures were selected. According to the different fixation methods, they were divided into the double plate group (group A, 28 cases) and the locked plate group (group B, 29 cases), and the clinical efficacy of the 2 groups was comprehensively evaluated by comparing the indices of surgery, treatment effect, postoperative functional recovery and the occurrence of complications. Results The operating time, intraoperative bleeding, intraoperative fluoroscopy time, and postoperative incisional drainage were worse in group A than in group B (P < 0.05), but the postoperative loss of neck stem angle, humeral head inversion angle, loss of humeral height, Constant function score, and VAS score were better in group A than in group B (P < 0.05); there was no significant difference in the overall postoperative complication rate (P > 0.05 ). Conclusion Both double plates and locking plates can effectively treat complex proximal humerus fractures, but double plates are more effective in terms of fixation stability and functional recovery, and are more suitable for treating patients with complex fracture types, severe comminution, and incomplete medial column support. -
Key words:
- Proximal humerus fracture /
- Locking plate /
- Double plate /
- ORIF.
-
表 1 2组纳入患者基线资料比较[(
$\bar x \pm s $ )/n]Table 1. Comparison of baseline information of patients included in the 2 groups [(
$\bar x \pm s $ )/n]组别 A组 B组 χ2/t P 例数 28 29 − − 性别(男/女) 11/16 13/16 0.095 0.757 平均年龄(岁) 56.12 ± 8.02 57.08 ± 9.34 −0.416 0.679 受伤部位(左/右) 16/12 18/11 0.144 0.705 致伤原因(高坠伤/跌倒伤/车祸伤) 3/12/13 1/15/12 1.373 0.503 受伤至手术时间(d) 5.21 ± 0.91 5.34 ± 1.17 −0.357 0.721 骨折类型(Neer三部分/四部分) 17/11 21/8 0.877 0.349 表 2 2组患者手术情况比较(
$\bar x \pm s $ )Table 2. Comparison of surgical conditions between the 2 groups of patients (
$\bar x \pm s $ )组别 n 手术时间(min) 术中出血量(mL) 术中透视时间(min) 术后切口引流量(mL) A组 28 126.14 ± 19.14 265.17 ± 29.45 41.35 ± 6.12 176.25 ± 25.98 B组 29 95.51 ± 18.67 225.51 ± 20.67 30.68 ± 6.77 164.65 ± 26.45 T − 5.901 6.114 6.228 1.669 P − < 0.001* < 0.001* < 0.001* 0.101 *P < 0.05。 表 3 2组患者术后临床疗效比较(
$\bar x \pm s $ )Table 3. Comparison of postoperative clinical outcomes between the 2 groups of patients (
$\bar x \pm s $ )组别 n 骨折愈合
时间(月)术后颈干角
丢失量(度)肱骨头内翻
角度(度)肱骨高度
丢失量(mm)Constant功能
评分(分)VAS评分
(分)A组 28 4.52 ± 0.53 7.32 ± 1.03 3.48 ± 0.89 1.40 ± 0.10 79.62 ± 0.99 1.45 ± 0.11 B组 29 3.99 ± 0.67 9.51 ± 1.70 3.97 ± 0.92 1.70 ± 0.18 69.85 ± 0.80 2.45 ± 0.12 t − −3.611 −12.735 −2.253 −8.079 −6.634 −6.636 P − 0.001* < 0.001* 0.028* < 0.001* < 0.001* < 0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 4 2组患者术后各种并发症发生率比较[n(%)]
Table 4. Comparison of the incidence of various postoperative complications between the 2 groups of patients [n(%)]
组别 n 螺钉切除关节面 肱骨头坏死 肩峰下撞击症 骨不连 总体并发症发生率 二次手术率 A组 28 0(0) 3(10.71) 1(3.57) 1(3.57) 5(17.85) 4(14.28) B组 29 2(6.89) 1(3.44) 1(3.44) 0(0) 4(13.79) 3(10.34) χ2 − 2.001 1.153 0.001 1.054 0.231 0.205 P − 0.157 0.283 0.980 0.305 0.630 0.650 -
[1] 戴峰,王青,王江,等. 3D打印模拟手术方法在肱骨近端Neer四部分骨折中的优势及对术后功能恢复的影响[J]. 中国医药导报,2020,17(36):95-98+104. [2] Hardeman F,Bollars P,Donnelly M,et al. Predictive factors for functional outcome and failure in angular stable osteosynthesis of the proximal humerus[J]. Injury,2012,43(2):153-158. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2011.04.003 [3] Lanting B,MacDermid J,Drosdowech D,et al. Proximal humeral fractures:a systematic review of treatment modalities[J]. J Shoulder Elbow Surg,2008,17(1):42-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2007.03.016 [4] Euler S A,Petri M,Venderley M B,et al. Biomechanical evaluation of straight antegrade nailing in proximal humeral fractures:the rationale of the “proximal anchoring point”[J]. Int Orthop,2017,41(9):1715-1721. doi: 10.1007/s00264-017-3498-y [5] Gardner M J,Weil Y,Barker J U,et al. The importance of medial support in locked plating of proximal humerus fractures[J]. J Orthop Trauma,2007,21(3):185-191. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0b013e3180333094 [6] Ockert B,Siebenbürger G,Kettler M,et al. Long-term functional outcomes (median 10 years) after locked plating for displaced fractures of the proximal humerus[J]. J Shoulder Elbow Surg,2014,23(8):1223-1231. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2013.11.009 [7] Sproul R C,Iyengar J J,Devcic Z,et al. A systematic review of locking plate fixation of proximal humerus fractures[J]. Injury,2011,42(4):408-413. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2010.11.058 [8] Laux C J,Grubhofer F,Werner C M L,et al. Current concepts in locking plate fixation of proximal humerus fractures[J]. J Orthop Surg Res,2017,12(1):137. doi: 10.1186/s13018-017-0639-3 [9] 马福元,杨铁毅,姜锐,等. 肱骨近端锁定加压钢板置入内固定治疗复杂肱骨近端骨折的并发症[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(48):8381-8387. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.48.014 [10] Rangan A,Handoll H,Brealey S,et al. Surgical vs nonsurgical treatment of adults with displaced fractures of the proximal humerus:the PROFHER randomized clinical trial[J]. Jama,2015,313(10):1037-1047. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.1629 [11] Handoll H H,Brorson S. Interventions for treating proximal humeral fractures in adults[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev,2015(11):Cd000434. [12] Oppebøen S,Wikerøy A K B,Fuglesang H F S,et al. Calcar screws and adequate reduction reduced the risk of fixation failure in proximal humeral fractures treated with a locking plate:190 patients followed for a mean of 3 years[J]. J Orthop Surg Res,2018,13(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s13018-018-0906-y [13] Bai L,Fu Z G,Wang T B,et al. Radiological evaluation of reduction loss in unstable proximal humeral fractures treated with locking plates[J]. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res,2014,100(3):271-274. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2013.12.024 [14] Padegimas E M,Zmistowski B,Lawrence C,et al. Defining optimal calcar screw positioning in proximal humerus fracture fixation[J]. J Shoulder Elbow Surg,2017,26(11):1931-1937. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2017.05.003 [15] 周文峰,周雄清,李显辉. PHILOS自锁系统在治疗中老年肱骨近端骨折患者中的优势[J]. 实用医学杂志,2019,35(10):1621-1624. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2019.10.020 [16] 钟华,陈劲,李建炜,等. 3D打印技术在PHILOS内固定肱骨近端骨折内侧距支撑重建中的应用[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018,33(7):757-759. [17] Thanasas C,Kontakis G,Angoules A,et al. Treatment of proximal humerus fractures with locking plates:a systematic review[J]. J Shoulder Elbow Surg,2009,18(6):837-844. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2009.06.004 [18] Jost B,Spross C,Grehn H,et al. Locking plate fixation of fractures of the proximal humerus:analysis of complications,revision strategies and outcome[J]. J Shoulder Elbow Surg,2013,22(4):542-549. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2012.06.008 [19] Osterhoff G,Baumgartner D,Favre P,et al. Medial support by fibula bone graft in angular stable plate fixation of proximal humeral fractures:an in vitro study with synthetic bone[J]. J Shoulder Elbow Surg,2011,20(5):740-746. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2010.10.040 [20] Theopold J,Schleifenbaum S,Müller M,et al. Biomechanical evaluation of hybrid double plate osteosynthesis using a locking plate and an inverted third tubular plate for the treatment of proximal humeral fractures[J]. PLoS One,2018,13(10):e0206349. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206349 -






 下载:
下载: