Correlation between Neutrophil-lymphocyte Ratio and Disease Activity in 536 Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
-
摘要:
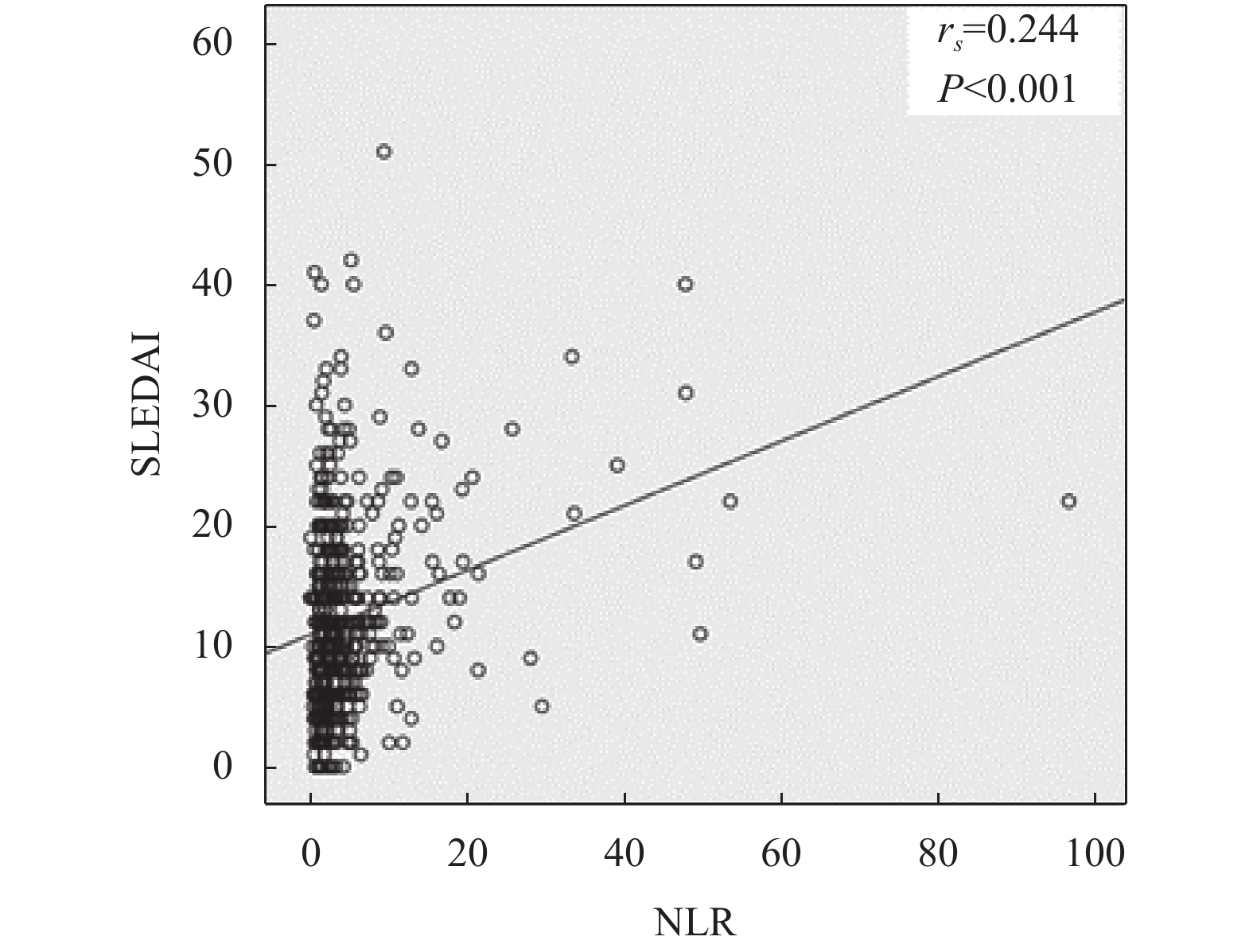
目的 评估系统性红斑狼疮(systemic lupus erythematosus,SLE)患者中性粒细胞/淋巴细胞比值(neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio,NLR)与疾病活动度的关联性。 方法 选取昆明医科大学第一附属医院风湿免疫科确诊的SLE患者共536 例。根据SLE疾病活动指数(SLEDAI)评分,将患者分为疾病无活动组,轻度活动组,中度活动组,重度活动组。比较4组间NLR的差异,并通过Spearman相关性分析,分析NLR与SLE患者疾病活动度的相关性。 结果 4组间NLR水平有差异,进一步两两比较,结果显示疾病中度活动组NLR水平高于无活动组(调整后P < 0.001);重度活动组NLR水平高于无活动组(调整后P < 0.001);重度活动组NLR水平高于轻度活动组(调整后P = 0.011)SLE患者的NLR与SLEDAI评分呈正相关 (P < 0.05)。 结论 NLR可作为评价SLE患者疾病活动度的一项参考指标。 -
关键词:
- 系统性红斑狼疮 /
- 中性粒细胞/淋巴细胞比值 /
- 疾病活动度
Abstract:Objective To assess the correlation between neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and the disease activity of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Methods A total of 536 patients with SLE from the Department of Rheumatology and Immunology of the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University were selected. According to the SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) score, patients with SLE were divided into inactive group, lightly active group, moderately active group, and severely active group. The differences in NLR among the four groups were compared, and the correlation between NLR and SLEDAI score was analyzed through Spearman correlation analysis. Results There were differences in NLR levels among the four groups. The results of pairwise comparison showed that the NLR level of the moderately active group was higher than that of the inactive group (adjusted P < 0.001); the NLR level of the severely active group was higher than that of the inactive group (adjusted P < 0.001); the NLR level of the severely active group was higher than that of the lightly active group (P = 0.011 after adjustment). The NLR of SLE patients were positively correlated with SLEDAI scores (P < 0.05). Conclusion NLR can be used as a reference index to evaluate the disease activity of SLE patients. -
表 1 研究对象的一般资料[n(%)]
Table 1. General information of the research object[n(%)]
疾病活动度 无活动(n = 81) 轻度活动(n = 141) 中度活动(n = 150) 重度活动(n = 164) H P 性别 0.362 0.948 男 7(8.64) 14(9.93) 13(8.67) 17(10.37) 女 74(91.36) 127(90.07) 137(91.33) 147(89.63) 年龄(岁) 37(26,47.5) 36(26,49) 34(25,46.25) 11.356 0.01 NLR 1.97(1.43,3.2) 2.7(1.72,4.54) 3.27(2.16,5.78) 33.465 < 0.001 表 2 4组SLE患者NLR的两两比较
Table 2. Pairwise comparison of NLR in four groups of SLE patients
两两比较 无活动与
轻度活动无活动与
中度活动无活动与
重度活动轻度活动与
中度活动轻度活动与
重度活动中度活动与
重度活动检验统计量 −55.69 −98.44 −111.02 −42.75 −55.33 −12.58 P值 0.01 < 0.001 < 0.001 0.019 0.002 0.472 调整后P值 0.059 < 0.001 < 0.001 0.112 0.011 1 -
[1] Carroll M. Innate immunity in the etiopathology of autoimmunity[J]. Nature Immunology,2001,2(12):1089-1090. doi: 10.1038/ni1201-1089 [2] Muñoz L E,Janko C,Schulze C,et al. Autoimmunity and chronic inflammation -two clearance-related steps in the etiopathogenesis of SLE[J]. Autoimmunity Reviews,2010,10(1):38-42. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2010.08.015 [3] Tsokos G C,Lo M S,Reis P C,et al. New insights into the immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Nature Reviews Rheumatology,2016,12(12):716-730. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2016.186 [4] Ohmura K. Which is the best SLE activity index for clinical trials?[J]. Modern Rheumatology,2021,31(1):20-28. doi: 10.1080/14397595.2020.1775928 [5] Seyit M,Avci E,Nar R,et al. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio,lymphocyte to monocyte ratio and platelet to lymphocyte ratio to predict the severity of COVID-19[J]. The American Journal of Emergency Medicine,2021,40(2):110-114. [6] Zhang A,Ning L,Han J,et al. Neutrophil-To-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Potential Biomarker of Neovascular Glaucoma[J]. Ocular Immunology and Inflammation,2021,29(2):417-424. doi: 10.1080/09273948.2019.1677916 [7] Menon G,Johnson S E,Hegde A,et al. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio - A novel prognostic marker following spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage[J]. Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery,2021,200(1):106339. [8] Ma L,Zeng A,Chen B,et al. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and platelet to lymphocyte ratio in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and their correlation with activity:A meta-analysis[J]. International Immunopharmacology,2019,76(1):e105949. [9] Qin B,Ma N,Tang Q,et al. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) were useful markers in assessment of inflammatory response and disease activity in SLE patients[J]. Modern Rheumatology,2016,26(3):372-376. doi: 10.3109/14397595.2015.1091136 [10] Hochberg M C. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Arthritis and Rheumatism,1997,40(9):1725. [11] Ghang B,Kwon O,Hong S,et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is a reliable marker of treatment response in rheumatoid arthritis patients during tocilizumab therapy[J]. Modern Rheumatology,2017,27(3):405-410. doi: 10.1080/14397595.2016.1214340 [12] Yolbas S,Yildirim A,Gozel N,et al. Hematological Indices May Be Useful in the Diagnosis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and in Determining Disease Activity in Behçet’s Disease[J]. Medical Principles and Practice:International Journal of the Kuwait University,Health Science Centre,2016,25(6):510-516. doi: 10.1159/000447948 [13] Seo J Y,Suh C H,Jung J Y,et al. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio could be a good diagnostic marker and predictor of relapse in patients with adult-onset Still's disease:A STROBE-compliant retrospective observational analysis[J]. Medicine,2017,96(29):7546. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007546 -






 下载:
下载: