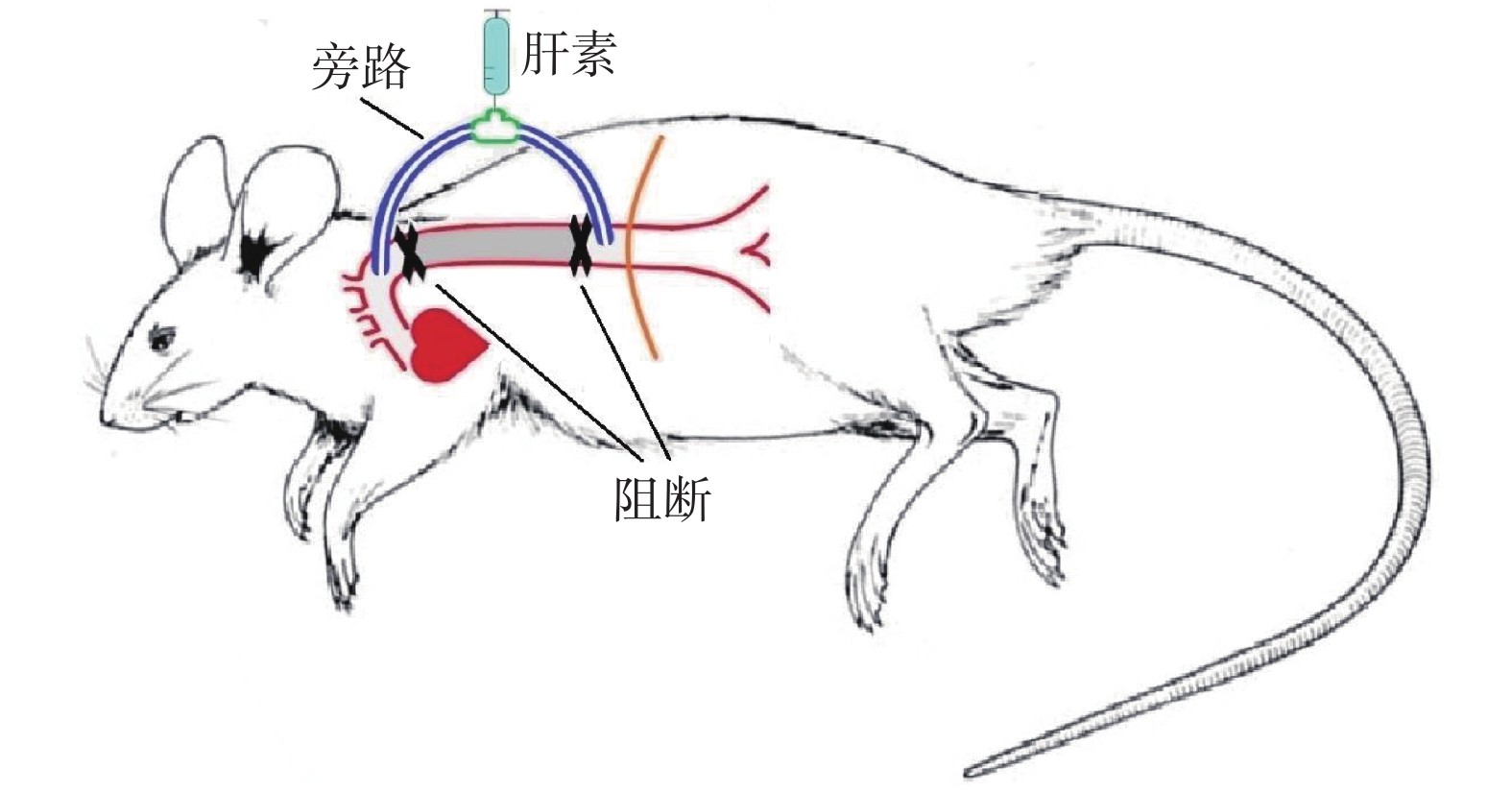
|
[1]
|
Sharif-Alhoseini M,Khormali M,Rezaei M,et al. Animal models of spinal cord injury:a systematic review[J]. Spinal Cord.,2017,55(8):714-721. doi: 10.1038/sc.2016.187
|
|
[2]
|
Ryu J H,Park J W,Hwang J Y,et al. The attenuation of neurological injury from the use of simvastatin after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats[J]. BMC Anesthesiol,2018,27,18(1):31.
|
|
[3]
|
Dong Q,Sun L,Peng L,et al. PMX53 protects spinal cord from ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats in the short term[J]. Spinal Cord,2016,54(4):254-258. doi: 10.1038/sc.2015.146
|
|
[4]
|
Tamaki T, Kubota S. History of the development of intraoperative spinal cord monitoring[J]. Eur Spine J, 2007 , 16 (Suppl 2): S140-146.
|
|
[5]
|
Basso D M,Beattie M S,Bresnahan J C. A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats[J]. J Neurotrauma.,1995,12(1):1-21. doi: 10.1089/neu.1995.12.1
|
|
[6]
|
Chen F,Wang D,Jiang Y,et al. Dexmedetomidine Postconditioning alleviates Spinal Cord Ischemia-reperfusion Injury in Rats via Inhibiting Neutrophil Infiltration,Microglia Activation,Reactive Gliosis and CXCL13/CXCR5 Axis Activation[J]. Int J Neurosci,2021,27:1-20.
|
|
[7]
|
Mazensky D,Flesarova S,Sulla I. Arterial blood supply to the spinal cord in animal models of spinal cord injury. A review[J]. Anat Rec (Hoboken),2017,300(12):2091-2106. doi: 10.1002/ar.23694
|
|
[8]
|
Bell M T,Reece T B,Smith P D,et al. Reproducable paraplegia by thoracic aortic occlusion in a murine model of spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion[J]. J Vis Exp,2014,85:50910.
|
|
[9]
|
Marsala M,Yaksh T L. Transient spinal ischemia in the rat:characterization of behavioral and histopathological consequences as a function of the duration of aortic occlusion[J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab,1994,14(3):526-535. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1994.65
|
|
[10]
|
Aydemir S,Dogan D,Kocak A,et al. The effect of melatonin on spinal cord after ischemia in rats[J]. Spinal Cord,2016,54(5):360-363. doi: 10.1038/sc.2015.204
|
|
[11]
|
Gong S,Seng Z,Wang W,et al. Bosentan protects the spinal cord from ischemia reperfusion injury in rats through vascular endothelial growth factor receptors[J]. Spinal Cord,2015,53(1):19-23. doi: 10.1038/sc.2014.147
|
|
[12]
|
Carrillo S E,Guimarães S B,Vasconcelos P R,et al. Is subdiaphragmatic aortic cross-clamping a suitable model for spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury study in rats?[J]. Acta Cir Bras,2006,21(4):219-222.
|






 下载:
下载: