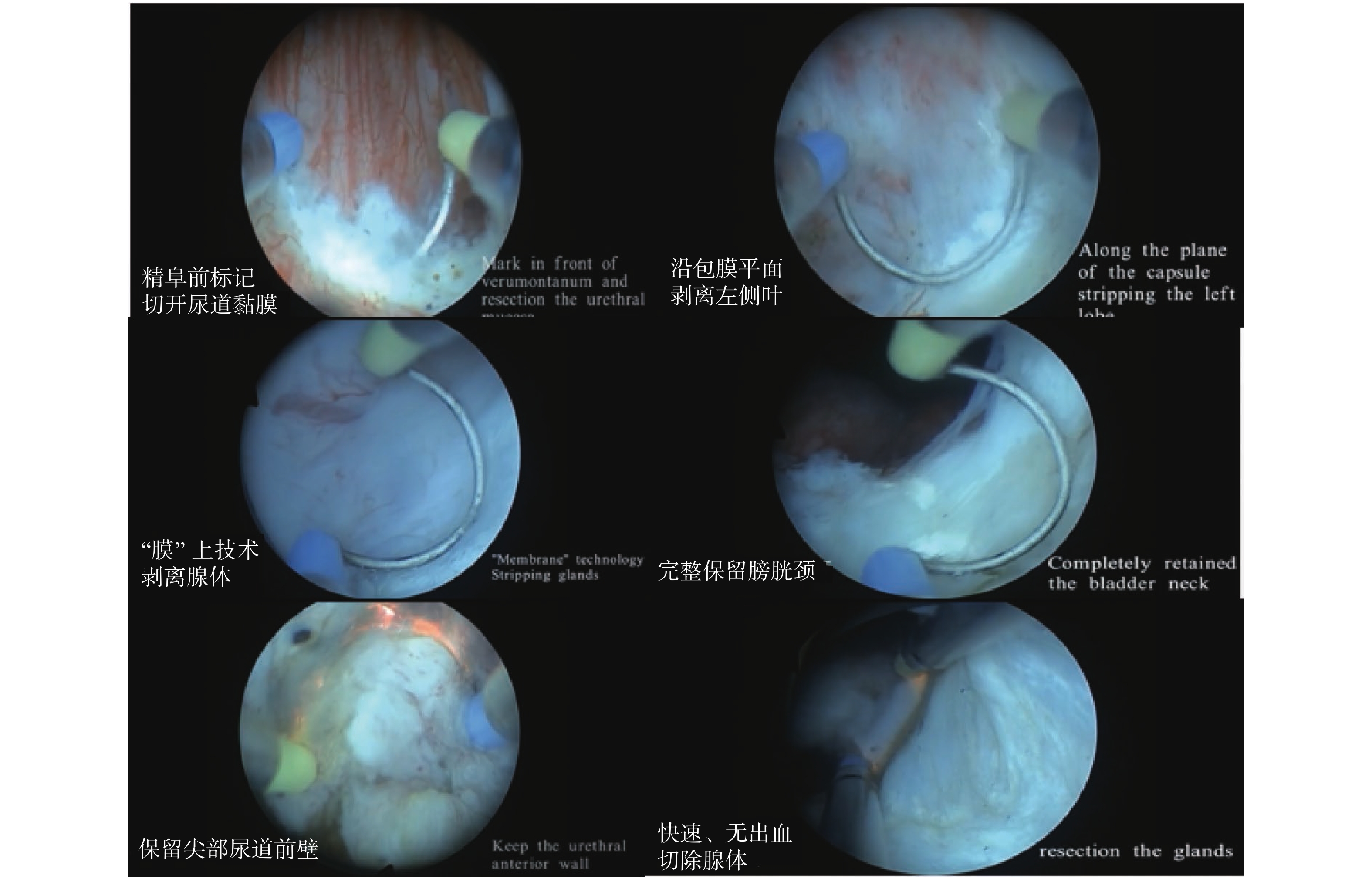
Feasibility Analysis of Short-term Indwelling Urete after PKEP
-
摘要:
目的 探讨经尿道双极等离子前列腺剜除术(transurethral plasmamakinetic enucleation surgery,PKEP)术后患者短期留置尿管的可行性。 方法 回顾性分析2019年2月至2019年12月昆明医科大学附属延安医院收治且采用PKEP治疗良性前列腺增生(benign prostatic hyperplasia,BPH)的89例患者的临床资料,将其分为对照组和观察组,其中对照组PKEP术后留置尿管,观察组行PKEP术后短期留置尿管,对比2组的手术时间、术中出血量、切除腺体重量等相关指标。 结果 对照组与观察组的手术时间[(58.40±23.10 ) min vs (67.40±29.80) min]、切除腺体重量[(54.90±16.60 ) g vs ( 61.20±21.50 ) g]、术中出血量[(31.70±13.60 ) mL vs (35.50±19.20) mL]相比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。但观察组住院时间[(10.80±3.90 ) d vs (13.70±4.60 ) d]、住院费用[(1.06±0.49) d vs (1.38±0.53) d]显著低于对照组(P < 0.05)。在术后1周尿潴留、尿路感染、尿失禁等并发症的发生率上,2组之间的差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。 结论 术者严格遵守PKEP操作规范后,术后短期留置尿管在不增加术后并发症发生率的前提下,还能缩短患者住院时间、降低住院费用。既达到了良好的治疗效果,且减轻了患者的经济负担,具有一定的可行性。 Abstract:Objective To explore the feasibility of short-term indwelling urete in patients aftert PKEP (transurethral plasmamakinetic enucleation surgery). Methods We performed a retrospective analysis of the clinical data of 89 patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and treated with PKEP in Yan'an Hospital Affiliated to Kunming Medical University from February 2019 to December 2019. These patients was divided into control group and observation group. The control group was given indwelling with the urine after PKEP, and the observation group left the urete after PKEP short-termly. Compared to the operation time, intraoperative blood volume, resection of gland weight, and other related indicators. Results The surgical time of the control group and the observation group was [(58.40 ± 29.80) min vs (67.40 ± 29.80) min], the weight of the gland was [(54.90 ± 16.60) g vs (61.20 ± 21.50) g], the volume of intraoperative bleeding was [(35.50 ± 13.20) mL vs (35.50 ± 19.20) mL], the difference was not statistically significant (P > 0.05). However, the observation group was hospitalized [(10.80 ± 3.90) D], hospitalization cost [(1.06 ± 0.49) D VS. (1.38 ± 0.53) d] was significantly lower than that in the control group (P < 0.05) . There was no significant difference between the two groups (P > 0.05) in the incidence of urinary retention, urinary tract infection, urinary incontinence complications. Conclusions After the operator strictly abides by the PKEP operating standard, postoperative short-term indwelling urete can shorten the hospitalization time and reduce the hospitalization cost without increasing the incidence of postoperative complications. It not only achieves a good therapeutic effect, but also reduces the economic burden of patients. These findings verifies the feasibility of this method. -
表 1 患者术前的的一般资料(
$\bar x \pm s $ )Table 1. General clinical data of patients before operation (
$\bar x \pm s $ )组别 n 年龄
(岁)术前前列腺
重量(g)Qmax
(mL/s)PVR
(mL/s)PSA
(ng/mL)IPSS
(分)QOL
(分)并发症(n) 心血管
疾病呼吸系统
疾病观察组 38 72.260 ± 5.780 63.400 ± 23.100 7.400 ± 2.500 173.800 ± 36.200 3.400 ± 1.200 26.300 ± 5.900 3.800 ± 0.900 18 21 对照组 51 72.550 ± 6.130 70.300 ± 20.800 8.300 ± 3.900 181.900 ± 43.600 3.800 ± 1.500 24.800 ± 6.100 4.200 ± 1.500 28 36 t/ x² 1.349 1.476 1.244 0.931 1.352 1.164 1.459 0.495 2.221 P 0.090 0.072 0.108 0.177 0.090 0.124 0.074 0.182 0.136 PSA = 前列腺特异性抗原; Qmax = 最大尿流率;PVR = 残余尿量; IPSS = 国际前列腺症状评分;QOL = 生活质量评分。 表 2 2组手术情况对比(
$\bar x \pm s $ )Table 2. Comparison of the operation information of the 2 groups (
$\bar x \pm s $ )组别 n 术中出血量(mL) 手术时间(min) 前列腺切除重量(g) 住院时间(d) 住院费用/(万元) 观察组 38 31.700 ± 13.600 58.400 ± 23.100 54.900 ± 16.600 10.800 ± 3.900 1.060 ± 0.490 对照组 51 35.500 ± 19.200 67.400 ± 29.800 61.200 ± 21.500 13.700 ± 4.600 1.380 ± 0.530 t 1.040 1.083 1.503 3.135 2.909 P 0.151 0.141 0.068 0.001* 0.002* *P < 0.05。 表 3 术后2组尿潴留的情况[n(%)]
Table 3. Comparison of the postoperative urinary retention of the 2 groups [n(%)]
组别 n 3 d 观察组 38 2(5) 对照组 51 0 χ2 - 0.873 P - 0.350 表 4 术后2组尿失禁的情况[n(%)]
Table 4. Comparison of the postoperative urinary incontinence of the 2 groups [n(%)]
组别 n 1周 2周 3周 观察组 38 3(7) 1(2.6)) 0 对照组 51 6(11.8) 4(7.8) 1(1.9) χ2 - 0.059 0.349 0.022 P - 0.081 0.554 0.882 表 5 术后2组泌尿系统感染的情况[n(%)]
Table 5. Comparison of the postoperative urinary system infection of the 2 groups [n(%)]
组别 n 3 d 1周 观察组 38 1(2.6) 0 对照组 51 11(21.5) 2(3.9) χ2 - 5.169 0.262 P - 0.003* 0.609 *P < 0.05。 -
[1] Das A K,Teplitsky Seth,Humphreys M R. Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP):A review and update[J]. Can J Urol,2019,26(4 Suppl 1):13-19. [2] Khorrami MH,Tadaion F,Ghanaat I,et al. The efficacy of fibrin glue injection in the prostatic fossa on decreasing postoperative bleeding following transurethral resection of prostate[J]. Adv Biomed Res,2016,5(1):161. doi: 10.4103/2277-9175.192733 [3] Alradhi M,Lun L K,Safi M,et al. Can bipolar transurethral enucleation of the prostate be a better alternative to the bipolar transurethral resection of the prostate?:A prospective comparative study[J]. Medicine (Baltimore),2021,100(20):e25745. [4] 李一夫,李晓琳,张岩,等. 国际前列腺症状评分的汉化与评价[J]. 全科医学临床与教育,2019,17(4):305-307. [5] 陈赵,熊晶,杜国伟,等. 良性前列腺增生患者储尿症状改善对生活质量评分的影响[J]. 现代泌尿外科杂志,2020,25(6):487-490. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8291.2020.06.005 [6] 彭毅,杜恒彬. 前列腺等离子剜除术联合钬激光碎石术治疗良性前列腺增生合并膀胱结石的疗效分析[J]. 实用医院临床杂志,2020,17(1):106-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6170.2020.01.031 [7] D Wu,Z E Shi,D Xu,et al. Serum interleukin 6 and acute urinary retention in elderly men with benign prostatic hyperplasia in China:A cross-sectional study[J]. Transl Androl Urol,2021,10(1):455-465. doi: 10.21037/tau-20-914 [8] Jiang Y,Bai X,Zhang X,et al. Comparative study of the effectiveness and safety of transurethral bipolar plasmakinetic enucleation of the prostate and transurethral bipolar plasmakinetic resection of the prostate for massive benign prostate hyperplasia (>80 ml)[J]. Med Sci Monit,2020,26(undefined):e921272. [9] Sagen E,Javid R,Liivrand L,et al. Patient related factors affecting in-hospital costs of a TURP procedure[J]. Scand J Urol,2021,55(4):1-7. [10] Zhao Z,Zeng G,Zhong W,et al. A prospective,randomised trial comparing plasmakinetic enucleation to standard transurethral resection of the prostate for symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia:three-year follow-up results[J]. Eur Urol,2010,58(5):752-758. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2010.08.026 [11] Zhang J,Wang Y,Li S,et al. Efficacy and safety evaluation of transurethral resection of the prostate versus plasmakinetic enucleation of the prostate in the treatment of massive benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Urol Int,2021,105(9-10):1-8. [12] Kranz J,Schmidt S,Wagenlehner F,et al. Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections in Adult Patients[J]. Dtsch Arztebl Int,2020,10(1):83-88. [13] Yu S,Marshall AP,Li J,et al. Interventions and strategies to prevent catheter-associated urinary tract infections with short-term indwelling urinary catheters in hospitalized patients:An integrative review[J]. Int J Nurs Pract,2020,26(3):e12834. [14] 李思恒,宋真,丁萍,等. 术后留置尿管时间对前列腺电切术后暂时性尿失禁影响[J]. 临床护理杂志,2016,15(1):26-28. [15] 杨计原. 前列腺增生术后再次尿潴留的原因分析[J]. 临床研究,2017,25(9):103-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8650.2017.09.053 [16] Trotsenko P,Wetterauer C,Grimsehl P,et al. Efficacy,safety,and perioperative outcomes of holmium laser enucleation of the prostate-a comparison of patients with lower urinary tract symptoms and urinary retention[J]. Lasers Med Sci,2021,36(7):1397-1402. [17] Ray A F,Powell J,Speakman M,J et al. Efficacy and safety of prostate artery embolization for benign prostatic hyperplasia:an observational study and propensity-matched comparison with transurethral resection of the prostate (the UK-ROPE study)[J]. BJU Int,2018,122(2):270-282. doi: 10.1111/bju.14249 -






 下载:
下载: