Effects of Willed Movement on the Expression of GLUA2 and N-cadherin in Rats with Focal Cerebral Ischemia
-
摘要:
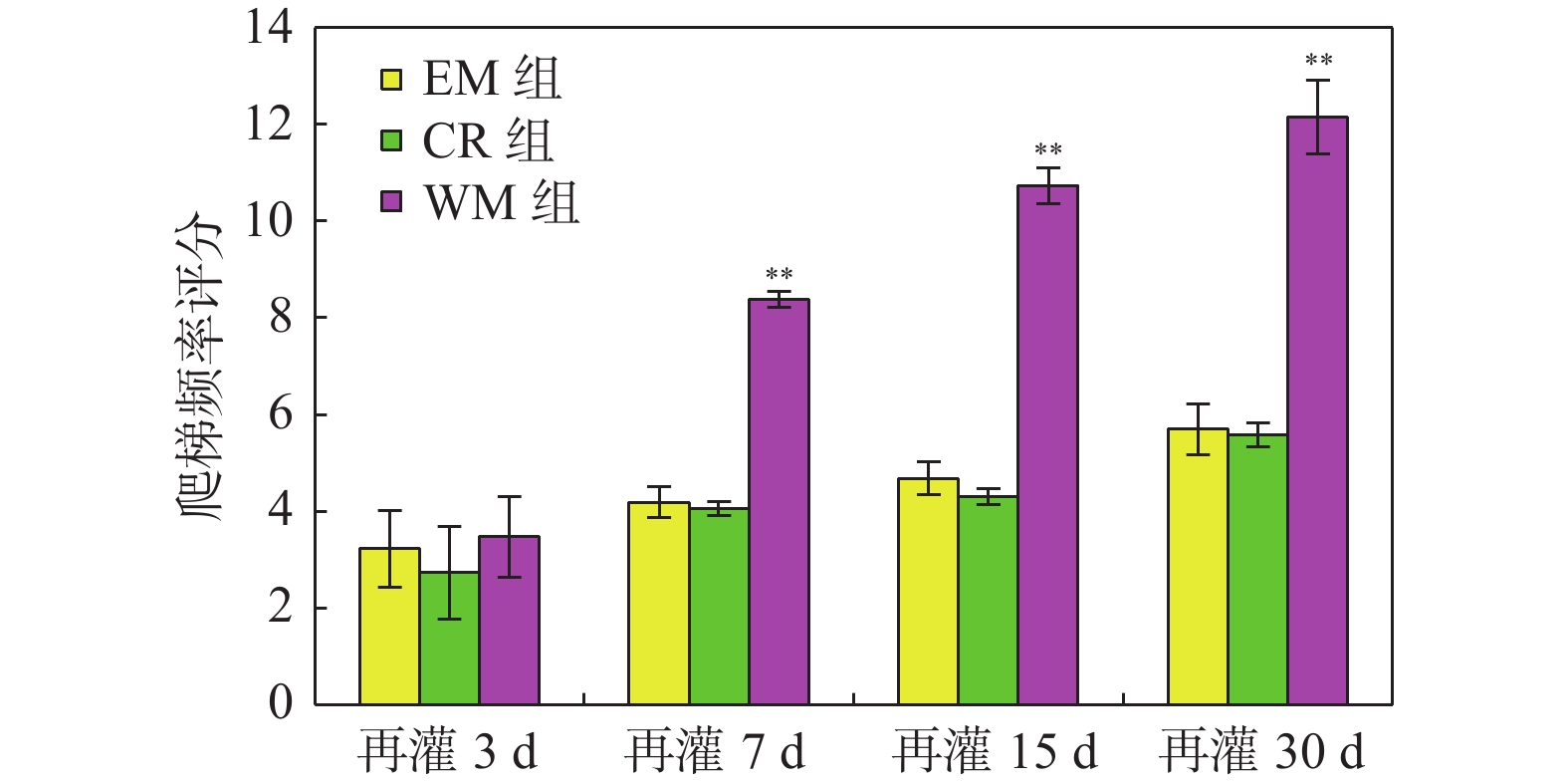
目的 研究意向性运动干预治疗对大脑局部缺血大鼠行为学及梗死灶周围组织中GluA2和N-cadherin表达的影响。 方法 利用鱼线栓堵法将大鼠制成大脑中动脉栓塞(middle cerebral artery occlusion,MCAO)模型共144只,随机分成模型(MCAO)组、生活环境变化(environment modification,EM)组、普通康复训练(control rehabilitstion, CR)组和意向性运动干预(willed movement,WM)组,每组根据术后时间划分为7 d、15 d、30 d 3个亚组。对各组研究对象的行为变化进行观察分析,通过免疫组化技术研究脑梗死灶周围组织中GluA2和N-cadherin蛋白水平。 结果 再灌7 d、15 d、30 d,意向性运动干预组的攀爬频率显著高于EM及CR组(P < 0.01);再灌30 d,和MCAO组相比,意向性运动干预组的神经功能缺损评分更低(P < 0.05 );而其缺血半暗带区域GLUA2、N-cadherin蛋白表达量都更高(P < 0.05)。 结论 对于大脑局部缺血所导致的神经功能障碍,意向性运动干预治疗可促进其恢复,这可能是因为该运动可激活缺血半暗带中GLUA2和N-cadherin的表达,提高突触可塑性。 -
关键词:
- 局灶性脑缺血 /
- 意向性运动 /
- 突触可塑性 /
- GLUA2 /
- N-cadherin
Abstract:Objective To explore effect of the Willed movement on behaviours of rats with focal cerebral ischemia and the expression of GluA2 and N-cadherin in the brain tissue around ischemia. Methods We selected clean-level healthy male SD rats, and prepared 144 middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) models by thread occlusion method, and randomly divided them into model (MCAO) group, environment modification (EM) group, control rehabilitstion (CR) group and Willed movement (WM) group, each group was divided into four subgroups of 7, 15, and 30 days according to the postoperative time. The behavioral changes of rats in each group were dynamically observed, and the expression changes of GluA2 and N-cadherin protein in the brain tissue around the ischemic area were observed by immunohistochemical staining. Results On 7, 15, and 30 days after reperfusion, the climbing frequency of rats which were treated by willed movement was obviously higher than EM and CR group (P < 0.01). After 30 days of reperfusion, the neurological deficits score of the intentional exercise intervention group was lower than MCAO rats (P < 0.05). Compare with MCAO rats, the expression levels of GLUA2 and N-cadherin were higher in ischemic penumbra (P < 0.05). Conclusions Willed movement can promote the recovery of damaged nerve function after focal cerebral ischemia, which may be related to up-regulating the expression of GLUA2 and N-cadherin in the brain tissue around the ischemic focus and enhancing synaptic plasticity. -
Key words:
- Focal cerebral ischemia /
- Willed movement /
- Synaptic plasticity /
- GLUA2 /
- N-cadherin
-
表 1 4组大鼠各时间点神经功能缺损评分比较 [n = 12,(
$\bar x \pm s $ )]Table 1. The comparison of neurologic impairment scores in four groups at different timing [n = 12,(
$\bar x \pm s $ )]组别 时间 再灌24 h 再灌3 d 再灌7 d 再灌15 d 再灌30 d MCAO组 2.15 ± 0.61 1.92 ± 0.19 1.75 ± 0.45 1.50 ± 0.52 1.33 ± 0.49 EM组 2.21 ± 0.45 1.83 ± 0.38 1.58 ± 0.51 1.33 ± 0.49 1.08 ± 0.79a CR组 2.15 ± 0.72 1.83 ± 0.38 1.67 ± 0.49 1.41 ± 0.51 1.17 ± 0.72a WM组 2.23 ± 0.45 1.75 ± 0.45 1.50 ± 0.52 1.25 ± 0.45 0.75 ± 0.62abc F 1.894 1.887 1.789 1.488 3.102 P 0.164 0.152 0.170 0.109 0.037* *P < 0.05;与MCAO组同时间点比较,aP < 0.05;与EM组同时间点比较,bP < 0.05;与CR组同时间点比较,cP < 0.05。 -
[1] Maigeng Zhou,Haidong Wang,Xinying,et al. Mortality,morbidity,and risk factors in China and its provinces,1990–2017:A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017[J]. Lancet,2019,394(17):102-104. [2] Jingjing Nie,Xiaosu Yang,Qingping Tang,et al. Willed-movement trainingreduces brain damage and enhances synaptic plasticity related proteins synt-hesisafter focal ischemia[J]. Brain Res Bull,2016,120(11):90-96. [3] Zhiwen Zhou,Qidong Yang,Qingping Tang,et al. Effect of willed movement training on neurorehabilitation after focal cerebral ischemia and on the neural plasticity-associated signaling pathway[J]. Mol Med Rep,2018,17(1):1173-1181. [4] Qingping Tang,Qidong Yang,Zhongyang Hu,et a1. The effects of willed movement therapy on AMPA receptor properties for adult rat following focal cerebral ischemia[J]. Behav Brain Res,2007,181(2):254-261. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2007.04.013 [5] Parkinson Gabrielle T,Hanley Jonathan G. Mechanisms of AMPA ReceptorEndosomal Sorting[J]. Front Mol Neurosci,2018,11(2):440-441. [6] Surya P,Pandey,Rakesh Rai,Pankaj Gaur,et al. Development- and age-related alterations in the expression of AMPA receptor subunit GluR2 and its trafficking proteins in the hippocampus of male mouse brain[J]. Biogerontology,2015,16(3):17-28. [7] Parkinson Gabrielle T,Chamberlain Sophie E L,Jaafari Nadia,et al. Cortactin regulates endo-lysosomal sorting of AMPARs via direct interaction with GluA2 subunit[J]. Sci rep,2018,8(1):15-17. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16936-8 [8] Zikai Zhou,An Liu,Shuting Xia,et al. Publisher correction:The C-terminal tails of endogenous GluA1 and GluA2 differentially contribute to hippoc-ampal synaptic plasticity and learning[J]. Nat neurosci,2018,4(10):11-15. [9] Zsombor Koszegi,Maria Fiuza,Jonathan G. Endocytosis and lysosomal de-gradation of GluA2/3 AMPARs in response to oxygen/glucose deprivation in hippocampal but not cortical neurons[J]. Sci Rep,2017,7(1):28-29. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00040-y [10] Hu Jian,Li Ce,Hua Yan,et al. Constraint-induced movement therapy imp-roves functional recovery after ischemic stroke and its impacts on synaptic-plasticity in sensorimotor cortex and hippocampus[J]. Brain Res Bull,2020,4(2):160-162. [11] Yamagata Masahito,Duan Xin,Sanes Joshua R. Cadherins interact with synaptic organizers to promote synaptic differentiation[J]. Front Mol N-eurosci,2018,4(1):11-13. [12] Cen Cheng,Luo Li-Da,Li Wen-Qi,et al. PKD1 promotes functional synapse formation coordinated with N-Cadherin in hippocampus[J]. J Neurosci,2018,38(1):28-31. [13] Elena Bacchelli,Fabiola Ceroni,Dalila Pinto,et al. A CTNNA3 compound heterozygous deletion implicates a role for αT-catenin in susceptibility to autism spectrum disorder[J]. J Neurodev Disord,2014,6(1):17. doi: 10.1186/1866-1955-6-17 [14] Tucci,Valter,Kleefstra,et al. Dominant β-catenin mutations cause intelle-ctual disability with recognizable syndromic features[J]. J Clin Invest,2014,124(4):1468-1482. doi: 10.1172/JCI70372 [15] Alejandro Uribe-Arias,Rafael Andrés Posada-Duque,Christian González‐Billault,et al. p120-catenin is necessary for neuroprotection induced by CDK5 silencing in models of Alzheimer’s disease[J]. J Neurochemistry,2016,138(4):115-118. [16] Heisler Frank F,Lee Han Kyu,Gromova Kira V,et al. GRIP1 interlinks N-cadherin and AMPA receptors at vesicles to promote combined cargo t-ransport into dendrites[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci,2014,111(13):224-226. [17] Xiaoying Wu,Shengqun Liu,Zhenhua Hu,et al. Enriched housing promo-tes post-stroke neurogenesis through calpain 1-STAT3/HIF-1α/VEGF signal-ing[J]. Brain Res Bull,2018,139(18):133-143. -






 下载:
下载: