Value of VI-RADS Scoring System in Precision Treatment of Bladder Cancer
-
摘要:
目的 探讨VI-RADS评分在术前对膀胱癌侵袭性预测的价值。 方法 采用VI-RADS评分对320例膀胱癌MRI资料进行回顾性分析,对病灶的T2WI、DWI和DCE-MRI进行单独评分,最后获得VI-RADS评分,根据病理结果将样本分为NMIBC组和MIBC组,将VI-RADS评分与病理分期、VI-RADS评分与不同分组间进行相关性分析。 结果 肌层浸润性膀胱癌187例,非肌层浸润性膀胱癌133例,VI-RADS评分与病理结果存在正相关(r = 0.841,P < 0.001)。VI-RADS评分 > 3.5分对判断膀胱癌肌层浸润的敏感性、特异性分别为88.4%、97.1%。 结论 VI-RADS评分在术前对膀胱癌侵袭性的预测具有较好的敏感性和特异性,对指导临床治疗具有较好的价值。 -
关键词:
- 膀胱癌 /
- MRI /
- VI-RADS评分系统 /
- 临床分期
Abstract:Objective To explore the value of VI-RADS scoring system in predicting preoperative for invasive bladder cancer. Methods The MRI data of 320 cases of bladder cancer were retrospectively analyzed by the VI-RADS scoring system, T2WI, DWI and DCE-MRI were scored separately, and finally VI-RADS score was obtained, the samples were divided into NMIBC group and MIBC group according to the pathological results, and the VI-RADS scores were analyzed for correlation with pathological stages and different groups. Results There were 187 cases of muscular invasive bladder cancer and 133 cases of invasive bladder cancer. There was a positive correlation between VI-RADS score and pathological results(r = 0.841, P < 0.001). The sensitivity and specificity of VI-RADS > 3.5 for muscle invasion of bladder cancer were 88.4% and 97.1%, respectively. Conclusion The VI-RADS scoring system has better sensitivity and specificity in predicting the degree of bladder cancer invasion, and has a good value in guiding clinical treatment. -
Key words:
- Bladder cancer /
- Magnetic resonance imaging /
- VI-RADS scoring system /
- Clinical staging
-
表 1 VI-RADS具体评分标准
Table 1. VI-RADS scoring criteria.
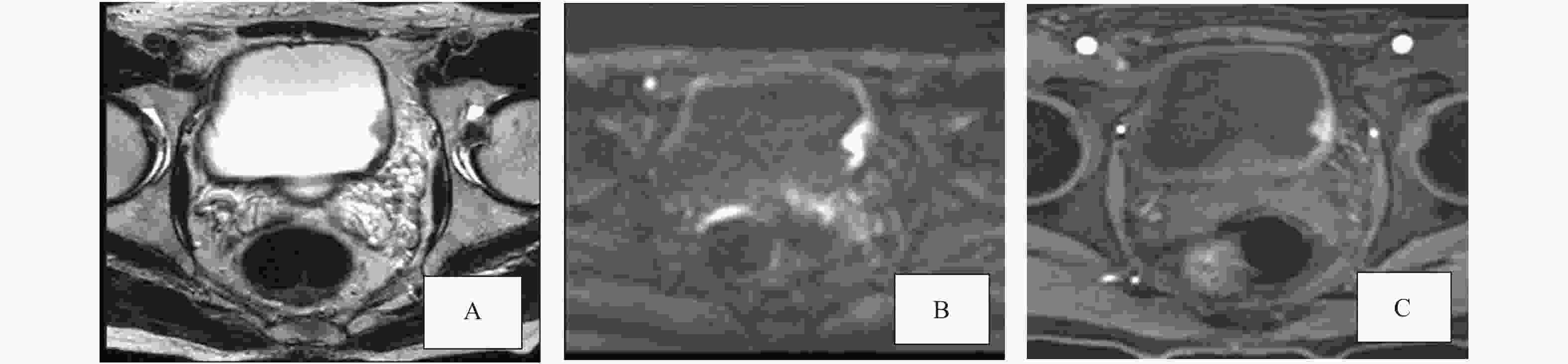
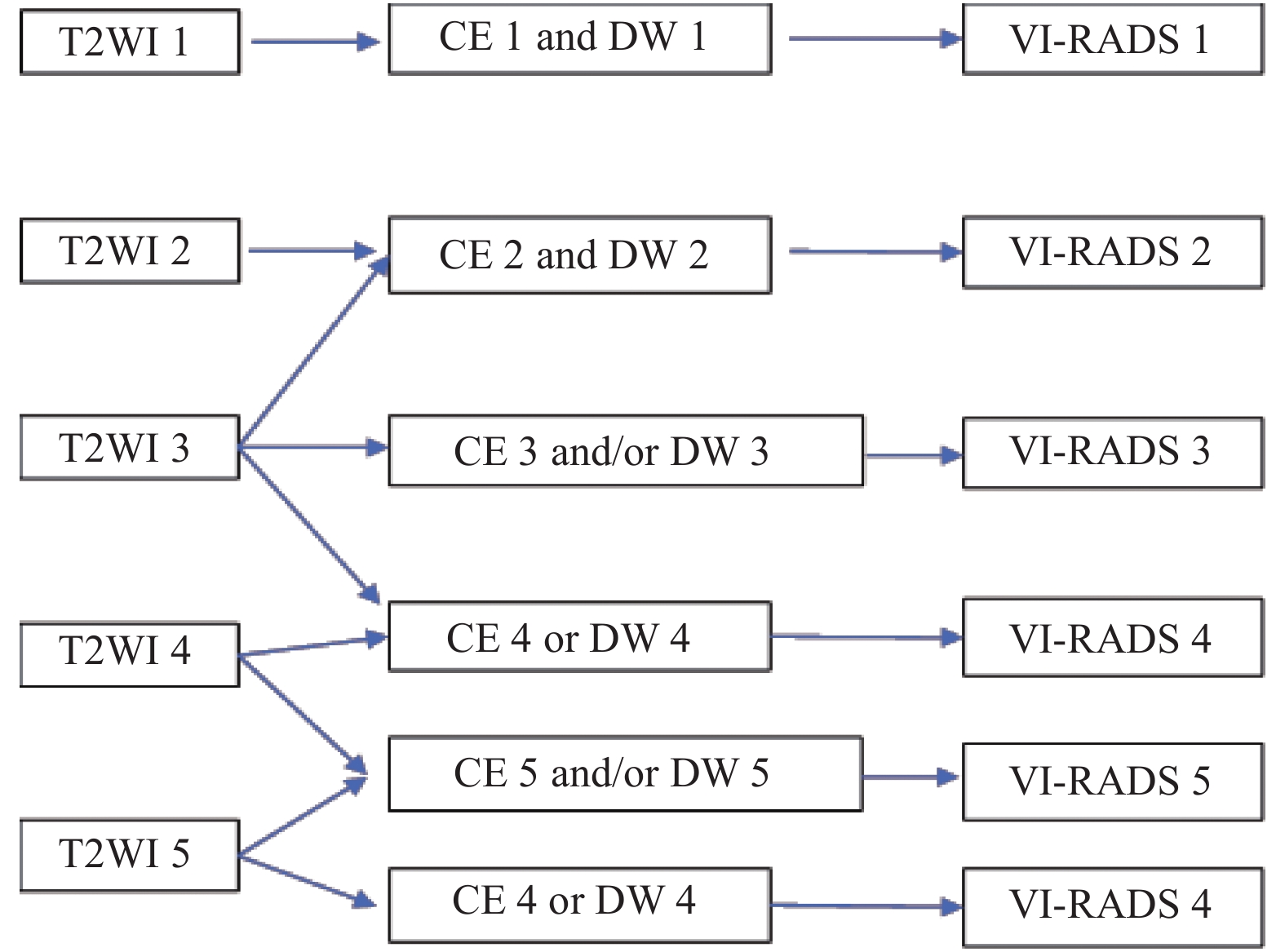
VI-RADS评分 影像学表现 T2WI 1分 固有肌层连续不间断低信号线(病灶< 1cm;有蒂或无蒂的肿瘤,有或无内层增厚) 2分 固有肌层连续不间断低信号线(病灶>1 cm,有蒂的肿瘤,有或无内层增厚;无柄/宽基底的肿瘤伴内层增厚) 3分 非2分表现,伴无蒂的外生肿瘤或无高信号的内膜增厚;无柄/宽基底的肿瘤但无明显低信号固有肌层破坏 4分 固有肌层低信号线中断,肿瘤侵犯固有肌层 5分 肿瘤向膀胱脂肪的侵犯,表现为整个膀胱壁和膀胱外组织的浸润 DWI 1分 DWI固有肌层连续性中等信号(病变< 1cm, DWI高信号,ADC值降低,DWI有/无蒂和/或内层增厚呈低信号) 2分 DWI固有肌层连续性中等信号(病变>1 cm,DWI高信号,ADC值降低,DWI有蒂低信号,
和/或增厚内层低信号;或无柄/扁平的肿瘤合并低/中等信号增厚内层)3分 未见DWI2分表现(类似T2WI的 3类表现),但未见固有肌层低信号的中断 4分 DWI高信号,ADC值降低,局部延伸至固有肌层 5分 DWI高信号,ADC值降低,延伸至膀胱全壁及膀胱外脂肪 DCE 1分 固有肌层未见早期强化 2分 固有肌层未见早期强化,内层早期强化 3分 未见2分表现,但固有肌层低信号无中断 4分 肿瘤早期强化,局灶性延伸至固有肌层 5分 肿瘤早期强化,延伸至整个膀胱壁和壁外脂肪 表 2 T2WI、DWI和DCE评分的病理结果(n)
Table 2. Pathological results of T2WI,DWI,DCEand VI-RADS scoring(n)
评分 NMIBC组 MIBC组 n Ta T1 n T2 T3 T4 T2WI评分 1(n = 37) 37 2 35 0 0 0 0 2(n = 78) 66 8 58 12 12 0 0 3(n = 74) 32 3 29 42 42 0 0 4(n = 45) 45 0 0 45 35 8 2 5(n = 86) 0 0 0 86 23 59 4 DCE-MRI评分 1(n = 37) 37 2 35 0 0 0 0 2(n = 81) 29 8 21 52 52 0 0 3(n = 62) 32 0 32 30 30 0 0 4(n = 45) 0 0 2 43 33 8 2 5(n = 95) 0 0 0 95 16 75 4 DWI评分 1(n = 37) 37 12 25 0 0 0 0 2(n = 89) 76 10 66 13 13 0 0 3(n = 52) 27 0 27 25 25 0 0 4(n = 52) 7 0 7 45 40 3 2 5(n = 90) 0 0 0 90 8 76 6 VI-RADS评分 1(n = 37) 37 12 25 0 0 0 0 2(n = 89) 76 10 66 13 13 0 0 3(n = 52) 27 0 27 25 25 0 0 4(n = 52) 7 0 7 45 40 3 2 5(n=90) 0 0 0 90 8 76 6 表 3 VI-RADS评分与肿瘤肌层浸润情况的Spearman相关性分析
Table 3. VI-RADS score and tumor muscular infiltration of Spearman analysis
组别 VI-RADS NMIBC/MIBC VI-RADS r 1.000 0.841 P . < 0.001* NMIBC/MIBC r 0.841 1.000 P < 0.001* . *P < 0.05。 -
[1] 中华医学会泌尿外科学分会,中国膀胱癌联盟. 非肌层浸润性膀胱癌二次电切中国专家共识[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志,2017,38(8):561-563. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6702.2017.08.001 [2] Barchetti G,Simone G,Ceravolo I,et al. Multiparametric MRI of the bladder:inter-observer agreement and accuracy with the Vesical Imaging-Reporting and Data System (VI-RADS) at a single reference center[J]. Eur Radiol,2019,29(10):5498-5506. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06117-8 [3] Antoni S,Ferlay J,Soerjomataram I,et al. Bladder cancer incidence and mortality:A global overview and recent trends[J]. Eur Urol,2017,71(1):96-108. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.06.010 [4] Siegel R L,Miller K D,Jemal A. Cancer statistics,2019[J]. CA Cancer J Clin,2019,69(1):7-34. doi: 10.3322/caac.21551 [5] Chang S S,Bochner B H,Chou R,et al. Treatment of non-metastatic muscle-invasive bladder cancer:AUA/ASCO/ASTRO/SUO guideline[J]. J Urol,2017,198(3):552-559. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2017.04.086 [6] Alfred Witjes J,Lebret T,Comperat E M,et al. Updated 2016 EAU guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer[J]. Eur Urol,2017,71(3):462-475. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.06.020 [7] Martingano P,Stacul F,Cavallaro M,et al. 64-Slice CT urography:30 months of clinical experience[J]. Radiol Med,2010,115(6):920-935. doi: 10.1007/s11547-010-0567-3 [8] Paik M L,Scolieri M J,Brown S L,et al. Limitations of computerized tomography in staging invasive bladder cancer before radical cystectomy[J]. J Urol,2000,163(6):1693-1696. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)67522-2 [9] Lin W C,Chen J H. Pitfalls and limitations of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of urinary bladder cancer[J]. Transl Oncol,2015,8(3):217-230. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2015.04.003 [10] Tekes A,Kamel I,Imam K,et al. Dynamic MRI of bladder cancer:evaluation of staging accuracy[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol,2005,184(1):121-127. doi: 10.2214/ajr.184.1.01840121 [11] Ark J T,Keegan K A,Barocas D A,et al. Incidence and predictors of understaging in patients with clinical T1 urothelial carcinoma undergoing radical cystectomy[J]. BJU Int,2014,113(6):894-899. doi: 10.1111/bju.12245 [12] Panebianco V,Narumi Y,Altun E,et al. Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for bladder cancer:Development of VI-RADS (Vesical Imaging-Reporting And Data System)[J]. Eur Urol,2018,74(3):294-306. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.04.029 [13] Wang H,Luo C,Zhang F,et al. Multiparametric MRI for bladder cancer:Validation of VI-RADS for the detection of detrusor muscle invasion[J]. Radiology,2019,291(3):668-674. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2019182506 [14] Huang L,Kong Q,Liu Z,et al. The diagnostic value of MR imaging in differentiating T staging of bladder cancer:A Meta-Analysis[J]. Radiology,2018,286(2):502-511. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2017171028 [15] Takeuchi M,Sasaki S,Ito M,et al. Urinary bladder cancer:diffusion-weighted MR imaging-accuracy for diagnosing T stage and estimating histologic grade[J]. Radiology,2009,251(1):112-121. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2511080873 [16] Watanabe H,Kanematsu M,Kondo H,et al. Preoperative T staging of urinary bladder cancer:Does diffusion-weighted MRI have supplementary value?[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol,2009,192(5):1361-1356. doi: 10.2214/AJR.08.1430 -





 下载:
下载: