Epidemiological investigation and Analysis of Pre-hospital Emergency Patients in Kunming
-
摘要:
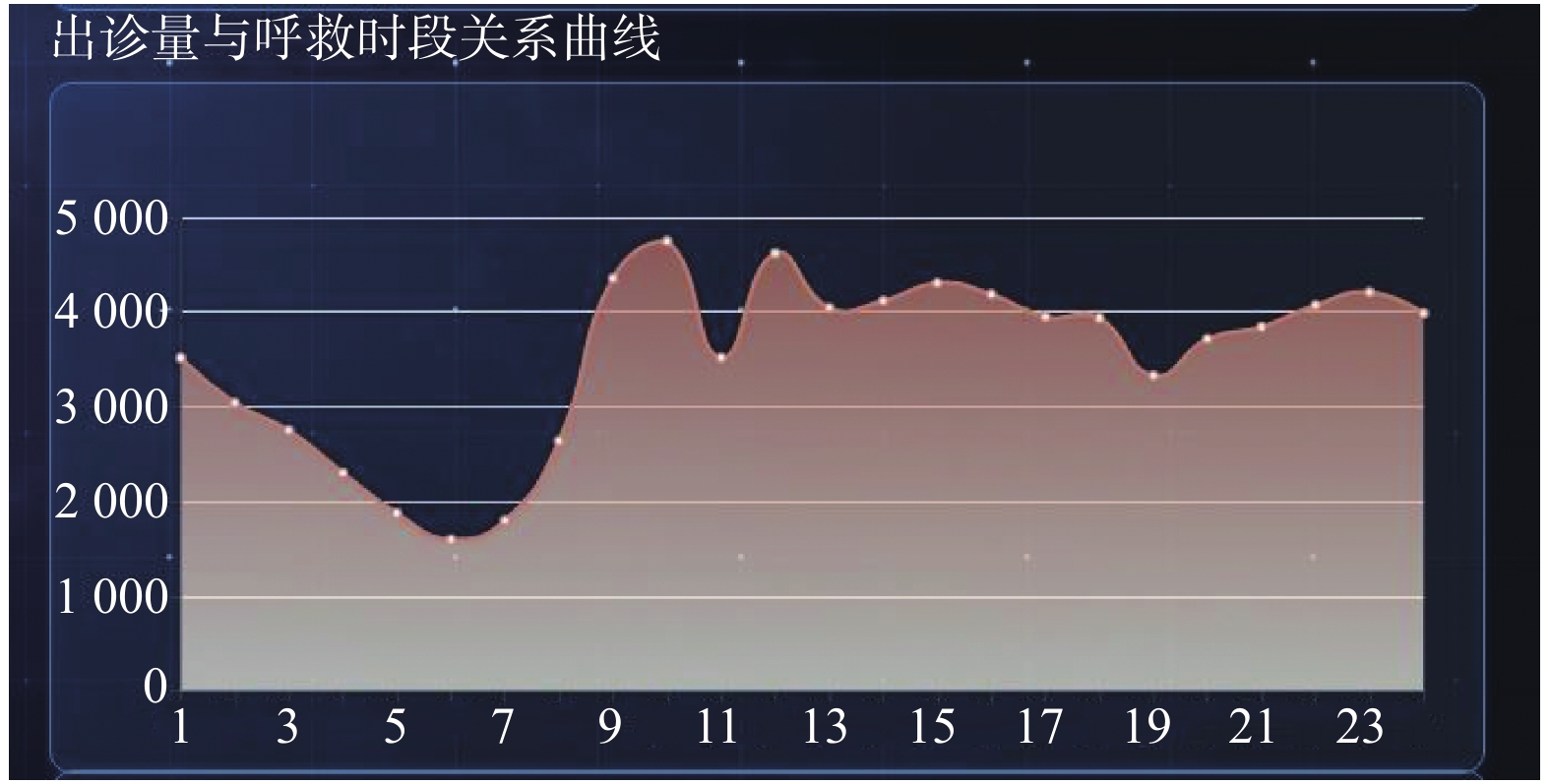
目的 了解昆明市院前急救患者流行病学特点,分析其特征,为优化院前急救资源配置提供依据。 方法 收集云南省急救中心2020年1~12月院前救治的患者资料,并进行现况调查研究。 结果 80 169例院前急救患者中,男性47 723例(59.5%),女性32 446例(40.5%);年龄分布在0.2~110岁,以14~44岁多见,28 313例(35.3%)。院前急救患者疾病谱前3位分别为:损伤和中毒类疾病28 786例(35.9%),症状和体征类疾病占25 618例(32.0%),循环系统疾病8 129例(10.1%)。对症状、体征类疾病进行亚组分析,结果显示,疾病谱前5位主要为:神经系统症状、发热和乏力等无法按系统分类为主诉的症状、死亡为主诉的症状、消化系统以及呼吸系统症状。院前急救患者以秋季最多22 571例(28.2%),其次为夏季21 129例(26.4%),春季最少17 747例(22.1%),1 d中,出诊高峰期主要集中在每日上午9:00~11:00和中午12:00~13:00,不同疾病的高发月份不同。 结论 昆明市院前急救患者男性多于女性,年龄主要集中在14~44岁,疾病谱以损伤和中毒类疾病、症状和体征类疾病以及循环系统疾病为主。秋季是出诊高峰季节,每日出诊高峰主要集中在上午9:00-11:00和中午12:00-13:00。 Abstract:Objective To understand and analyze the epidemiological characteristics of pre-hospital emergency patients in Kunming, so as to provide basis for optimizing the allocation of pre-hospital emergency resources. Methods Data of patients in Yunnan Emergency Center from January to December 2020 were collected, and an investigation was conducted. Results Among 80169 pre-hospital emergency patients, 47723 (59.5%) were male and 32446 (40.5%) were female. The age distribution ranged from 0.2 to 110 years, and most of them were 14 to 44 years, accounting for 28313 cases (35.3%). The top three disease spectrums were injury and poisoning diseases (28786 cases, 35.9%), symptoms and signs diseases (25, 618 cases, 32.0%) and circulatory system diseases (8129 cases, 10.1%). The subgroup analysis of diseases with symptoms and signs showed that the top five diseases were neurological symptoms, fever and fatigue symptoms that could not be classified, death symptoms, digestive system and respiratory system symptoms. The number of patients was 22, 571 in autumn (28.2%), followed by 21, 129 in summer (26.4%), and 17, 747 in spring (22.1%). In a day, most calls were made from 9:00 to11:00 and 12:00 to13:00, and the high incidence of different diseases was different in different months. Conclusions In Kunming, there were more males than females in pre-hospital emergency patients, and the ages of patients were mainly 14-44 years old. The disease spectrum mainly includes injury and poisoning diseases, symptoms and signs diseases and circulatory system diseases. Autumn is the peak season of outpatient visits, and the peak of daily outpatient visits mainly concentrates on 9:00-11:00 a.m. and 12:00-13:00 noon. -
Key words:
- Pre-hospital emergency /
- Epidemiology /
- Spectrum of disease
-
表 1 昆明市院前急救患者基线特征[n(%)]
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of pre-hospital emergency patients in Kunming [n(%)]
性别 n(%) 男性 47 723(59.5) 女性 32 446(40.5) 男女比例 47 723∶32 446(1.47∶1) 表 2 昆明市院前急救的疾病谱前5位疾病[n(%)]
Table 2. Top five diseases in disease spectrums of pre-hospital emergency in Kunming [n(%)]
指标 n(%) 损伤和中毒类疾病 28786(35.9) 症状、体征和临床与实验室异常
所见,不可归类其他处者25618(32.0) 循环系统疾病 8129(10.1) 消化系统疾病 2731(3.4) 呼吸系统疾病 2116(2.6) 表 3 不同年龄段院前急救的疾病谱前三位疾病[n(%)]
Table 3. The top three diseases in disease spectrums of pre-hospital emergency in different age groups [n(%)]
指标 n(%) 儿童组患者疾病谱(n) 2 125 症状、体征和临床与实验室异常
所见,不可归类其他处者907(42.7) 损伤和中毒类疾病 793(37.3) 影响健康状态和与保健机构接触的因素 67(3.2) 青壮年组患者疾病谱(n) 28 313 损伤和中毒类疾病 15 623(55.2) 症状、体征和临床与实验室异常
所见,不可归类其他处者5 584(19.7) 妊娠、分娩和产褥期情况 1 290(4.6) 中年组患者疾病谱(n) 16732 损伤和中毒类疾病 6 733(40.2) 症状、体征和临床与实验室异常
所见,不可归类其他处者4 804(28.7) 循环系统疾病 1 851(11.1) 年轻老年组患者疾病谱(n) 14 653 症状、体征和临床与实验室异常
所见,不可归类其他处者5 951(40.6) 损伤和中毒类疾病 2 810(19.2) 循环系统疾病 2 557(17.5) 老年组患者疾病谱(n) 15 708 症状、体征和临床与实验室异常
所见,不可归类其他处者7 094(45.2) 循环系统疾病 2 645(16.8) 损伤和中毒类疾病 2 427(15.5) 长寿老年组患者疾病谱(n) 2 638 症状、体征和临床与实验室异常
所见,不可归类其他处者1 278(48.4) 损伤和中毒类疾病 400(15.2) 循环系统疾病 333(12.6) 表 4 不同性别院前急救的疾病谱前3位疾病[n(%)]
Table 4. The top three disease in disease spectrums of pre-hospital emergency in different gender [n(%)]
指标 n(%) 女性(n) 32 446 症状、体征和临床与实验室异常
所见,不可归类其他处者11 208(34.5) 损伤和中毒类疾病 10 354(31.9) 循环系统疾病 3 038(9.4) 男性(n) 47 723 损伤和中毒类疾病 18 432(38.6) 症状、体征和临床与实验室异常
所见,不可归类其他处者14 410(30.2) 循环系统疾病 5 091(10.7) 表 5 院前急救不同季节的出诊频次及疾病谱情况[n(%)]
Table 5. The frequency of visits and disease spectrums in different seasons of pre-hospital emergency [n(%)]
指标 n(%) 春季 17 747(22.1) 夏季 21 129(26.4) 秋季 22 571(28.2) 冬季 18 722(23.4) 春季 17 747 损伤和中毒类疾病 6 241(35.2) 症状、体征和临床与实验室异常
所见,不可归类其他处者5 760(32.5) 循环系统疾病 1 859(10.5) 夏季 21 129 损伤和中毒类疾病 8 134(38.5) 症状、体征和临床与实验室异常
所见,不可归类其他处者6 325(29.9) 循环系统疾病 2 033(9.6) 秋季 22 571 损伤和中毒类疾病 8 596(38.1) 症状、体征和临床与实验室异常
所见,不可归类其他处者7 059(31.3) 循环系统疾病 2 153(9.5) 冬季 18 722 症状、体征和临床与实验室异常
所见,不可归类其他处者6 474(34.6) 损伤和中毒类疾病 5 815(31.1) 循环系统疾病 2 084(11.1) 表 6 昆明市院前急救的症状类疾病亚组分组前五位疾病[n(%)]
Table 6. The top five diseases in the subgroup of symptomatic diseases of pre-hospital emergency in Kunming [n(%)]
指标 n(%) 中枢神经系统 7 959(31.5) 发热、乏力等无法归类 4 552(18.0) 死亡 4 433(17.5) 消化系统 3 489(13.8) 呼吸系统 2 714(10.7) -
[1] Mackenzie R. Brief history of pre-hospital emergency medicine[J]. Emerg Med J,2018,35(3):629-631. [2] 李艳,李鹏,崔永英,等. 院前急救的历史回顾[J]. 中华医史杂志,2013,43(4):218-221. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0255-7053.2013.04.006 [3] 张在其,骆福添,陈兵,等. 我国八个大中城市院前急救流行病学调查分析[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志,2010,19(11):1130-1136. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0282.2010.11.003 [4] 赵思宇,柳芳超,刘民,等. 2013-2017年北京市120院前急救患者疾病谱特征分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志,2019,23(4):474-479. [5] 周奕男,白鸽,曹晓琳,等. 上海市区院前急救疾病谱时空分布[J]. 中国卫生资源,2020,23(2):166-171. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-953X.2020.02.017 [6] 高维玲,胡玉萍,贾应茂,等. 院前急救中不同评分系统评估颅脑损伤患者病情及预后价值比较[J]. 昆明医科大学学报,2019,40(8):88-92. [7] 杨钦娟,杨阳. 综合干预对不同年龄段2型糖尿病患者自我管理的影响[J]. 中国保健营养,2018,34(上旬刊):67. [8] Suryanto,Plimmer V,Boyle M. EMS systems in lower-middle income countries:A literature review[J]. Prehosp Disaster Med,2017,32(1):64-70. doi: 10.1017/S1049023X1600114X [9] 张海涛,王芳,张进军,等. 2015年院前急救医学进展[J]. 重庆医学,2016,45(10):1383-1385. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2016.10.029 [10] 方利, 陈敏, 王仕豪, 等, 2016—2018 年上海市奉贤区院前急救疾病谱特征及动态变化[J]. 实用临床医学, 2020, 21(2): 89-93. [11] 黄树青,满达,巴特金,等. 呼和浩特市2016年院前急救患者疾病谱分布及流行病学特点[J]. 中华危重病急救医学,2018,30(1):78-82. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2018.01.015 [12] 杨万广,李德剑,崔宗朝,等. 郑州市院前急救患者疾病谱分布与院前创伤流行病学调查[J]. 河南医学研究,2020,29(10):1736-1739. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-437X.2020.10.003 [13] 徐恩利、夏蓓茹. 2014-2016温州市院前急救患者疾病谱分析与应对措施分析[J]. 中国农村卫生事业管理,2018,38(1):27-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5916.2018.01.011 [14] Jiang B,Liang S,Peng Z R,et al. Transport and public health in China:The road to a healthy future[J]. Lancet,2017,390(10104):1781-1791. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31958-X [15] 俞瑾淳,陈 莹,黄巧云,等. 2016年至2018年昆明市石林彝族自治县居民的死因监测[J]. 昆明医科大学学报,2020,41(5):57-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4706.2020.05.011 [16] 张远军,张长风,朱建军,等. 四川资阳及川南经济区2010-2014年创伤患者院前救治流行病学特征调查研究[J]. 陕西医学杂志,2019,48(5):667-670. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7377.2019.05.035 [17] 杨旭,左道旭,郭征勋,等. 北京急救中心南区分中心院前创伤急救流行病学特点分析[J]. 北京医学,2018,40(3):271-272. -





 下载:
下载: