Comparison of the Clinical Outcome of Orbitotomy for Orbital Cavernous Hemangiomas Removal Through Transconjunctival Orbitotomy and Lateral-Medial Orbitotomy
-
摘要:
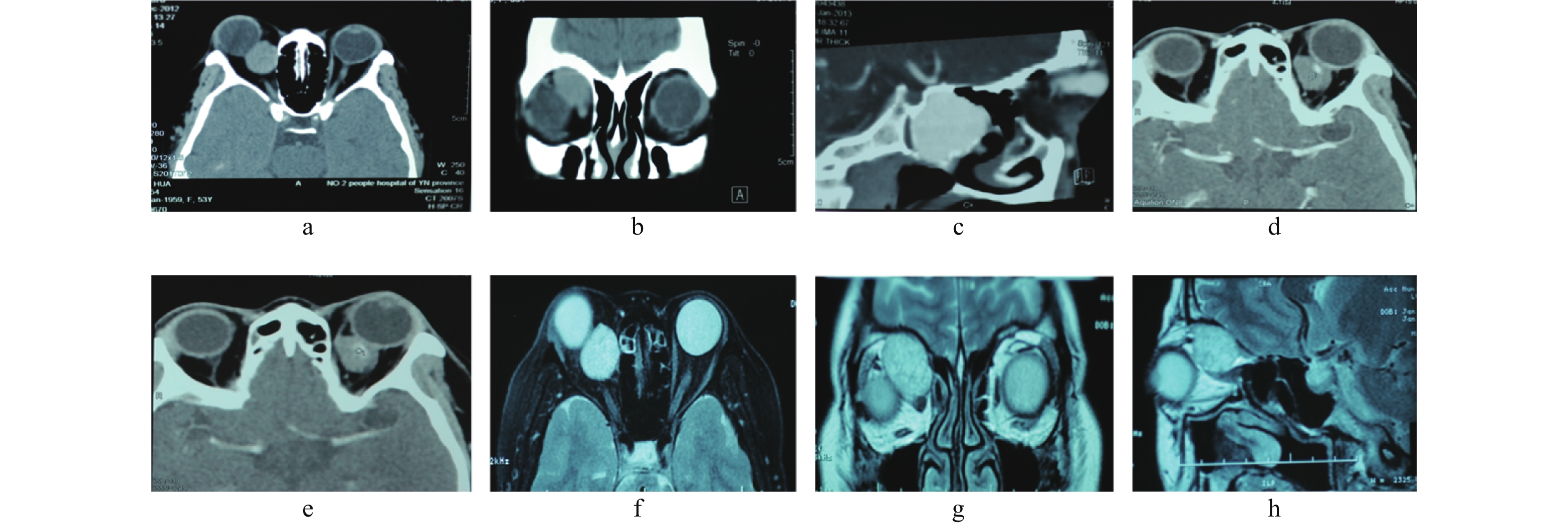
目的 评估经结膜入路前路开眶术,内外侧联合开眶术,2种不同入路手术摘除肌锥内视神经内侧眼眶海绵状血管瘤的临床效果。 方法 回顾性分析云南省第二人民医院2009 年09 月至2019年09 月收治的68例眼眶海绵状血管瘤,根据术式分为A、B 2组。A组为结膜入路前路开眶术共33例,B组为内外侧联合开眶术共35例,评估2组患者在平均住院时间、手术时间、手术操作空间、术中出血量、肿瘤完整摘、术后并发症等指标,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。 结果 A组平均住院天数为(5.03±1.63)d,B组为(8.34±2.13) d,两者相比差异有统计学意义(t = -4.926,P = 0.000)。A组平均手术时间为(55.62±5.43) min,B组为(109.21±13.72) min,两者相比差异有统计学意义(t = -16.428,P = 0.000)。手术操作空间用注水法测量,用所注水的体积表示,A组平均为(5.22±0.21) mL,B组平均为(16.501±1.22) mL,两者相比差异有统计学意义(t = -48.362,P = 0.000)。术中出血量:A组平均为(17.22±1.65)mL,B组平均为(59.29±6.42)mL,两者相比差异有统计学意义(t = -28.098,P = 0.000)。肿瘤完整摘除率:A组为90.9%(30/33),B组为97.14%(34/35);术后视力:A组患者术后视力提高和不变者占93.9%(31/33),术后视力下降占6.06%(2/33);B组术后视力提高和不变者占85.71%(30/35),术后视力下降或丧失者占14.3%(5/35)。 结论 结膜入路前路开眶术和内外侧联合开眶术在神经内侧眼眶海绵状血管瘤摘除术中各有优缺点,正确选择手术方式是完整摘除眼眶海绵状血管瘤的关键,术前应根据影像学资料准确判断肿瘤位置和大小。 -
关键词:
- 眼眶海绵状血管瘤 /
- 经结膜入路前路开眶术 /
- 内外侧联合开眶术
Abstract:Objectve To evaluate the clinical outcomes of orbitotomy for orbital cavernous hemangiomas through transconjunctival orbitotomy and lateral-medial orbitotomy. Methods A retrospective analysis was performed on 68 cases of orbital cavernous hemangioma admitted to the Second People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province from September 2009 to September 2019. All cases were divided into two groups, patients underwent transconjunctival orbitotomy were assigned in group A (33 cases)and patients underwent lateral-medial orbitotomy were assigned in group B (35 cases). Average hospital stay, operating time, operation space, bleeding volume, complete tumor removal rate, and postoperative complications were evaluated(P > 0.05). Results The average hospital stay was (5.03 ± 1.63)d in group A and (8.34 ± 2.13)d in group B, and the difference was statistically significant (t = -4.926, P = 0.000). The mean operation time was (55.62 ± 5.43)min in group A and (109.21 ± 13.72)min in group B, and the difference was statistically significant (t = -16.428, P = 0.000). The operation space was measured by water injection method, which was expressed by the volume of water injection. The average value of group A was (5.22 ± 0.21)mL, and that of group B was (16.501 ± 1.22)mL, with statistical significance (t = -48.362, P = 0.000). Blood loss was (17.22 ± 1.65)mL in group A and (59.29 ± 6.42)mL in group B, and the difference was statistically significant (t = -28.098, P = 0.000). The complete tumor removal rate was 90.9% (30/33) in group A and 97.14% (34/35)in group B. Postoperative visual acuity: 93.9% (31/33) of patients in group A had improved or unchanged postoperative visual acuity, and 6.06% (2/33) had decreased postoperative visual acuity. In group B, 85.71% (30/35) had improved or unchanged visual acuity, and 14.3% (5/35) had decreased or lost visual acuity. Conclusion Both transconjunctival orbitotomy and lateral-medial orbitotoy have advantages and disadvantages. The key of removing orbital cavernous hemangiomas completely is to select the right operation method. Preoperative imaging data should be used to accurately determine the location and size of the tumor. -
表 1 住院天数、手术时间、手术操作空间、出血量比较(
$ \bar x \pm s $ )Table 1. Comparison of days in hospital, operation time,operation room and bleeding volume (
$ \bar x \pm s $ )项目 A组 B组 t P 住院天数(d) 5.03 ± 1.63 8.34 ± 2.13 −4.926 < 0.001* 手术时间(min) 55.62 ± 5.43 109.21 ± 13.72 −16.428 < 0.001* 手术操作空间(mL) 5.22 ± 0.21 16.501 ± 1.22 −48.362 < 0.001* 术中出血量(mL) 17.22 ± 1.65 59.29 ± 6.42 −29.029 < 0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 2 肿瘤完整摘除率比较[n(%)]
Table 2. Comparison of complete tumor removal rate[n(%)]
组别 完全摘除 部分摘除 χ2 P A组 30(90.90) 3(9.10) 1.192 0.275 B组 34(97.14) 1(2.86) 表 3 术后视力比较[n(%)]
Table 3. Comparison of postoperative visual acuity [n(%)]
组别 提高和不变 下降 χ2 P A组 31(93.90) 2(6.10) 1.244 0.265 B组 30(85.71) 5(14.29) 表 4 术后上睑下垂比较(n)
Table 4. Comparison of postoperative ptosis(n)
组别 术后上睑下垂 χ2 P A组 2 = 1.286 0.257 B组 5 -
[1] Bristot R,Santoro A. Fantozzil cavemoma of the cavemous sinus:Case report[J]. Surg Neurol,1997,48(2):160-163. doi: 10.1016/S0090-3019(97)00033-5 [2] 刘家琦等主编. 实用眼科学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2010: 497-498 [3] Garrity J A, Henderson J W. Henderson’S orbital tumors[M]. 4th ed. Rochester: Lippincott Williams&Wilkins. 2007: 192-197. [4] 程金伟,魏锐利. 眼眶海绵状血管瘤的手术入路选择[J]. 中华眼视光学与视觉科学杂志,2012,14(5):264-266. [5] 鲜军舫, 王振常, 安裕志, 等, 眼眶海绵状血管瘤的影像学表现及其意义[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 1999, 33(6): 400-402. [6] 李金星,郭庆环,张林昌. CT、MRI在眼眶海绵状血管瘤与眼眶神经鞘瘤影像学鉴别诊断中的研究[J]. 中国实验诊断学,2017,21(11):1890-1893. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4287.2017.11.007 [7] Hejazi N,Classen R,Hassler W. Orbital and cerebral cavernomas:Comparison of clinical,neuroimaging,and neuropathological features[J]. Neurosurg Rev,1999,22(1):28-33. doi: 10.1007/s101430050005 [8] 王毅, 李月月, 赵海萍, 等. 经骨膜下入路摘除眼眶海绵状血管瘤的疗效观察[J]中华眼科杂志, 2013, 49(8): 679-684. [9] 唐东润, 张楠. 重视眼科影像学检查提高临床诊断率[J]中国实用眼科杂志, 2010, 28(5): 543-547. [10] Chen J W,Wei R L,Cai J P,et a1. Transcon junctivalorbitotomy for orbital cavernous hemangiomas[J]. Can JOphthalmol,2008,43(2):234-238. doi: 10.3129/i08-005 [11] 于翠杰,刘桂香. 经结膜入路摘除眼眶海绵状血管瘤临床分析[J]. 眼科新进展,2011,31(11):1068-1070,1074. [12] Kiratli H,Bulur B,Bilgiç S. Transconjunctival approach for retrobulbar intraconal orbital cavernous hemangiomas orbital surgeon’s perspective[J]. Neurol Surg,2005,64(1):71-74. doi: 10.1016/j.surneu.2004.09.046 [13] 沈亚, 高连娣, 程金伟, 等. 不同手术入路摘除眼眶海绵状血管瘤的效果[J], 上海医学, 2013, 36(1): 70-72. [14] 何彦津, 宋围祥. 血管淋巴管肿瘤和血管畸形, 眼眶病学[M]. 2版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2010: 179一187. [15] 钟一凡,吴婷. 李家,等. 结膜入路联合指法分离技术摘除眼眶肌锥内海绵状血管瘤[J]. 中国美容整形外科杂志,2017,28(6):368-370,377. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7040.2017.06.017 [16] Scheuerle A F,Steiner H H,Kolling G,et al. Treatment and long-term outcome of patients with orbital cavernomas[J]. Am J Ophthalmol.,2004,138(2):237-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2004.03.011 [17] 唐东润, 孙丰源, 吴桐, 等. 眼眶肿瘤手术的操作体会[J]中国实用眼科杂志, 2012, 30(2): 160-163. -






 下载:
下载: