Evaluation of Red Blood Cell Fragment Parameter Detection of Automatic Hematology Analyzer
-
摘要:
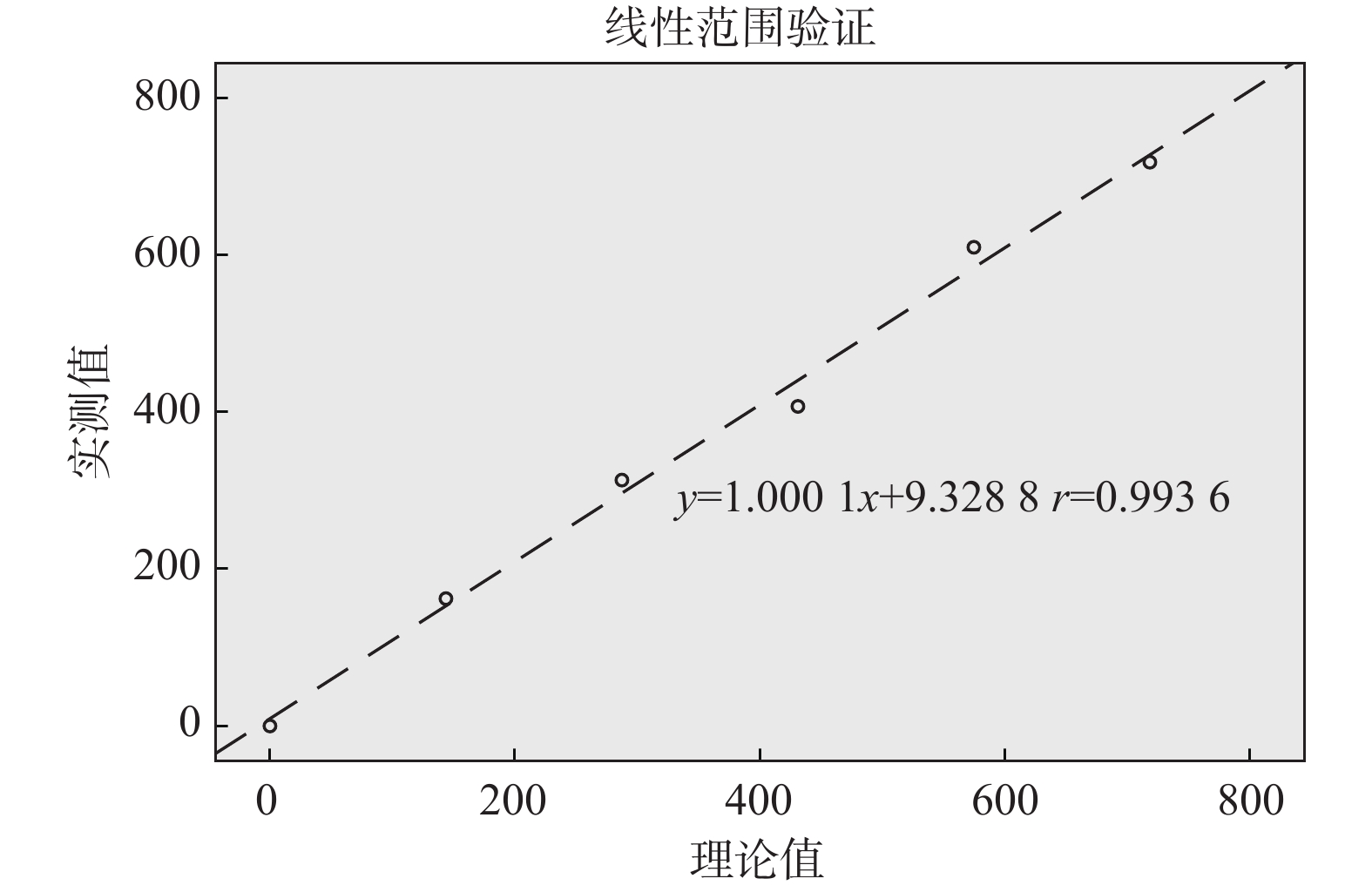
目的 红细胞碎片(fragmented red cells,FRC)是全自动血液细胞分析仪提供的一项新的检测参数,其与血栓性微血管病等多种疾病密切相关,因此对血液细胞分析仪红细胞碎片的检测性能进行评价。 方法 通过携带污染率、精密度、线性、正确度、灵敏度、特异度等指标,对SYSMEX XN系列全自动血液细胞分析仪红细胞碎片的检测性能进行评价。所有数据采用 SPSS 19.0软件进行分析整理。 结果 SYSMEX XN系列全自动血细胞分析仪检测红细胞碎片的携带污染率为0.11%;批内精密度:各实验浓度下其变异系数(coefficient of variation,CV)分别为8.75%(FRC:42.15×109/L)、6.38%(FRC:83.42×109/L )、4.57%(FRC:228.74×109/L)、5.31%(FRC:796.89×109/L);线性验证:线性回归方程为Y = 1.0001X + 9.3288,相关系数为r = 0.9936;正确度验证:以人工镜检为标准,仪器法与其比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),其相关系数为r = 0.82,灵敏度为92%,特异度为82%。 结论 SYSMEX XN系列全自动血液细胞分析仪检测红细胞碎片快速、简便,携带污染率低,精密度尚佳,线性范围满足要求,与人工镜检法相比具有较好的相关性,特异度和敏感度也较高。血液细胞分析仪可作为外周血红细胞碎片的快速筛查手段,但其检测的精密度仍需进一步提高,且由于方法的局限性,阳性标本需要在显微镜下进行确认。 Abstract:Objective Fragmented red blood cells (FRC) is a new detection parameter provided by the automatic blood cell analyzer, which is closely related to thrombotic microangiopaemia and other diseases. This study is aimed at evaluating the detection performance of automatic hematology analyzer for RBC fragments. Methods The performance of SYSMEX XN series automatic blood cell analyzer was evaluated by carrying contamination rate, precision, linearity, accuracy, sensitivity, specificity and other indicators. All data were analyzed by SPSS 19.0 software. Results The contamination rate of red blood cell fragments detected by SYSMEX XN series automatic hematology analyzer was 0.11%. Intra-batch precision: coefficient of variation (CV) at each experimental concentration were 8.75% (42.15×109/L), 6.38% (83.42×109/L), 4.57% (228.74×109/L), 5.31% (796.89×109/L). Linear verification: the linear regression equation was Y = 1.0001X + 9.3288, and the correlation coefficient is r = 0.9936., and the correlation coefficient is R =0.9936; Correctness verification: compared with manual microscopy, the was no statistically significant difference(P>0.05), the correlation coefficient, sensitivity and specificity were r = 0.82, 92% and 82% respectively. Conclusion SYSMEX XN series automatic blood cell analyzer is quick and easy to operate in detecting red blood cell fragments, with low contamination rate, fair precision and satisfactory linear range. Compared with manual microscopy, it has better correlation, higher specificity and sensitivity. Blood cell analyzer can be used as a rapid screening method for fragments of peripheral blood red blood cells, but the precision of its detection still needs to be further improved, and due to the limitations of the method, positive specimens need to be confirmed under a microscope. -
Key words:
- Erythrocyte fragments /
- Hematology analyzer /
- Performance evaluation
-
表 1 标本稳定性实验结果(%)
Table 1. Results of specimen stability (%)
静置
时间浓度1
(CV)浓度2
(CV)浓度3
(CV)浓度4
(CV)30 min 2.8 2.1 2.2 2.4 60 min 3.9 3.8 3.0 4.2 90 min 6.3 6.1 6.0 7.4 120 min 18.4 10.2 14.1 15.2 表 2 携带污染率值
Table 2. Results of carrying contamination rate
项目 H1 H2 H3 L1 L2 L3 携带污染率(%) FRC绝对值(×109/L) 726.7 801 836.2 17.7 19.3 18.6 0.11 表 3 重复性测定结果[(
$ \bar x \pm s $ ),(%)]Table 3. Results of repeatability test[(
$ \bar x \pm s $ ),(%)]组别 FRC绝对值(×109/L) 变异系数CV 浓度1 42.15 ± 3.69 8.75 浓度2 83.42 ± 5.32 6.38 浓度3 228.74 ± 10.45 4.57 浓度4 796.89 ± 58.28 5.31 表 4 仪器法与人工法的FRC%检测结果
Table 4. FRC% counting results of instrumental method and manual method
方法 人工显微镜镜检法 合计(n) 阳性(n) 阴性(n) 仪器法 阳性(n) 12 7 19 阴性(n) 1 30 31 合计(n) 13 37 50 -
[1] 鲁伟. 国际血液学标准委员会关于裂红细胞的标准化及临床应用建议[J]. 临床检验杂志,2014,32(6):478-479. [2] Agarwal Pooja,Khan Rafiullah,Brannock Kristina. Standardization of schistocyte identification and quantitation for the diagnosis of thrombotic microangiopathic anemia at university of cincinnati medical center[J]. Blood,2019,134(S1):4796-4796. [3] Schapkaitz E,Baiden A. The automated schistocyte count requires microscopic confirmation[J]. The Journal of Medical Laboratory Science and Technology of South Africa,2019,1(1):20-28. [4] 王礼法. Sysmex XN-9000全自动血液分析仪性能评价[J]. 中国医学装备,2014,11(12):38-41. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1672-8270.2014.12.013 [5] 纪玥玥,冯家维,柏玉,等. BC-6800plus型全自动血细胞分析仪性能评价[J]. 中国医学装备,2021,18(2):20-24. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1672-8270.2021.02.006 [6] 中华人民共和国卫生部. WS/T 406-2012, 临床血液学检验常规项目分析质量要求[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2013. [7] Hantaweepant C,Sasijareonrat N,Chutvanichkul B,et al. Comparison between optical microscopy and the Sysmex XN-3000 for schistocyte determination in patients suspected of having schistocytosis[J]. Health Science Reports,2020,3(1):138. [8] Zini G,D'Onofrio G,Erber W N,et al. International Council for Standardization in Hematology (ICSH). 2021 update of the 2012 ICSH Recommendations for identification,diagnostic value,and quantitation of schistocytes:Impact and revisions[J]. Int J Lab Hematol,2021,43(6):1264-1271. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.13682 [9] Zini G. ICSH recommendations for identification,diagnostic value,and quantitation of schistocytes[J]. International Journal of Laboratory Hematology,2012,34(2):107-116. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-553X.2011.01380.x [10] Bain B J. Schistocytes in megaloblastic anemia[J]. Am J Hematol,2010,85(8):599. doi: 10.1002/ajh.21657 [11] 贺艺璇,李斯丹,吴润晖,等. 移植相关性血栓性微血管病诊治进展[J]. 中国实验血液学杂志,2018,26(6):1831-1835. [12] 王文,何杨. 血栓性血小板减少性紫癜治疗的研究进展[J]. 中国实验血液学杂志,2022,30(01):314-318. [13] Lesesve J F,Asnafi V,Braun F,et al. Fragmented red blood cells automated measurement is a useful parameter to exclude schistocytes on the blood film[J]. International Journal of Laboratory Hematology,2012,34(6):566-576. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-553X.2012.01434.x [14] 崔婵娟,张捷,乔蕊. 破碎红细胞检测研究进展[J]. 现代检验医学杂志,2016,31(2):1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7414.2016.02.001 [15] Hervent A S,Godefroid M,Cauwelier B,et al. Evaluation of schistocyte analysis by a novel automated digital cell morphology application[J]. Blood,2014,124(21):4878-4878. doi: 10.1182/blood.V124.21.4878.4878 [16] Noutsos T,Laidman A Y,Survela L,et al. An evaluation of existing manual blood film schistocyte quantitation guidelines and a new proposed method[J]. Pathology,2021,53(6):746-752. doi: 10.1016/j.pathol.2021.01.008 [17] Bahr T M,Judkins A J,Christensen R D,et al. Neonates with suspected microangiopathic disorders:performance of standard manual schistocyte enumeration vs. the automated fragmented red cell count[J]. Journal of Perinatology,2019,39(3):1555-1561. [18] Maenhout T M,Marcelis L. Automated microscopy could decrease intra- and interobserver variation in microscopic schistocyte quantitation[J]. International Journal of Laboratory Hematology,2014,36(6):91-93. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.12217 [19] Lesesve J F,Speyer E,Perol J P. Fragmented red cells reference range for the sysmex XN‐series of automated blood cell counters[J]. International Journal of Laboratory Hematology,2015,37(5):583-587. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.12364 [20] Huh H J,Chung J W,Chae S L. Microscopic schistocyte determination according to international council for standardization in hematology recommendations in various diseases[J]. International Journal of Laboratory Hematology,2013,35(5):542-547. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.12059 [21] Abe Y,Wada H,Yamada E,et al. The effectiveness of measuring for fragmented red cells using an automated hematology analyzer in patients with thrombotic microangiopathy[J]. Clinical & Applied Thrombosis/hemostasis,2009,15(3):257-262. [22] El Gamal R A,Mekawy M A,Elkader A A,et al. Combined immature platelet fraction and schistocyte count to differentiate pregnancy-associated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura from severe preeclampsia/haemolysis,elevated liver enzymes,and low platelet syndrome (SPE/HELLP)[J]. Indian Journal of Hematology and Blood Transfusion,2020,36(2):316-323. doi: 10.1007/s12288-019-01200-y [23] Jekarl D W,Kim Y,Lim J,et al. Fragmented red cell as a possible favorable prognostic marker of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation associated thrombotic microangiopathy[J]. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis,2016,29(6):444-450. [24] Judkins A J,Macqueen B C,Christensen R D,et al. Automated quantification of fragmented red blood cells:Neonatal reference intervals and clinical disorders of neonatal intensive care unit patients with high values[J]. Neonatology,2019,115(1):5-12. doi: 10.1159/000491626 [25] 刘继,童辉纯,黄道连. 外周血涂片裂红细胞计数联合MCV/RBC比值对珠蛋白生成障碍性贫血的诊断价值[J]. 检验医学与临床,2020,17(16):2403-2404. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9455.2020.16.045 -






 下载:
下载: