Expression and Clinical Significance of Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factors 5A2 and Ki67 in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
-
摘要:
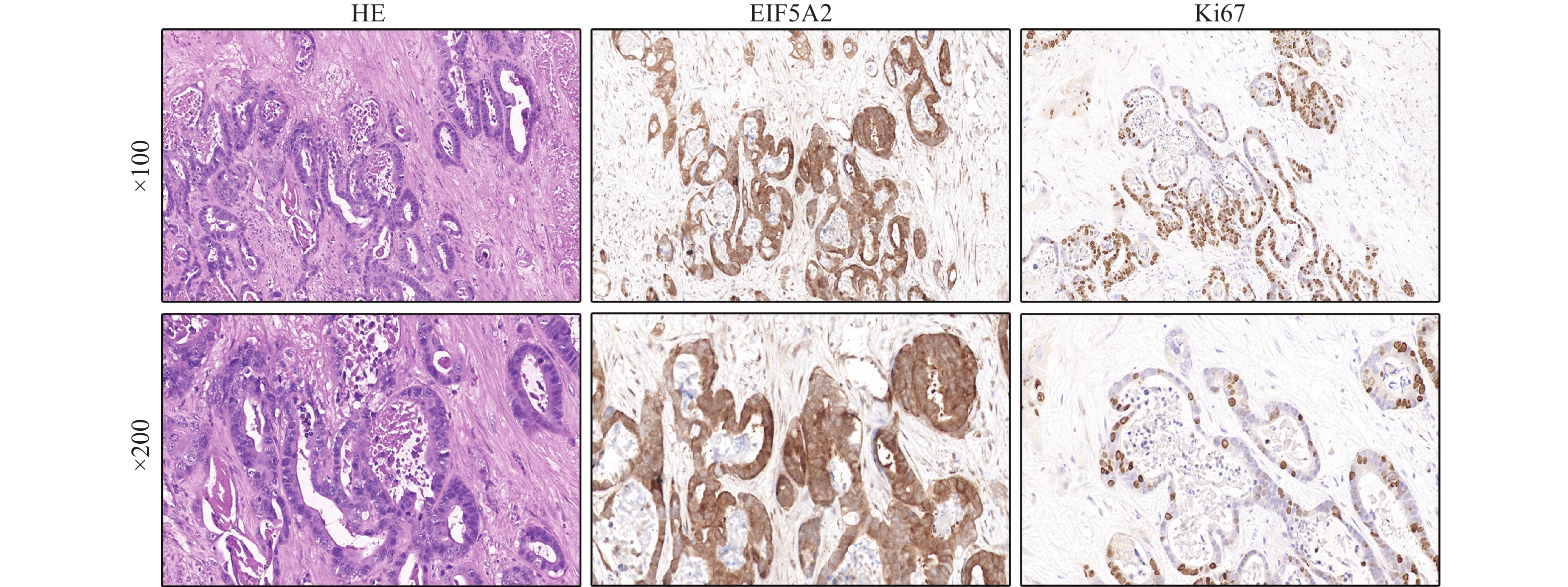
目的 分析真核翻译起始因子5A2(eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2,EIF5A2)和Ki67在肝内胆管癌组织中表达的临床意义及两者的相关性。 方法 收集成都市第七人民医院肝胆外科、昆明医科大学第二附属医院肝胆胰外科2014年9月至2021年12月118例肝内胆管癌患者术后石蜡切片,采用免疫组化的方法检测EIF5A2和Ki67表达,收集临床病理资料,分析EIF5A2、Ki67高表达与不同病理特征的关系及两者的相关性。 结果 肝内胆管癌组织中EIF5A2高表达60例(50.85%),Ki67高表达81例(68.64%),EIF5A2高表达与患者年龄、性别、肿瘤直径、肿瘤数量无关(P > 0.05),与TNM分期和淋巴转移有关(P < 0.05);肝内胆管癌组织中Ki67高表达与患者年龄、性别、肿瘤数量无关(P > 0.05),与TNM分期、淋巴转移、肿瘤直径有关(P < 0.05),EIF5A2与Ki-67的表达呈正相关(r = 0.285,P = 0.002)。 结论 肝内胆管癌中EIF5A2和Ki-67的高表达与高TNM分期和淋巴转移有关,两者表达呈正相关,有助于预判肝内胆管癌患者的临床分期及预后。 Abstract:Objective To analyze the clinical significance and correlation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 (EIF5A2) and Ki67 expression in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma tissues. Methods Paraffin sections were collected from 118 patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery of The Seventh People's Hospital of Chengdu and the Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from September 2014 to December 2021. Immunohistochemical methods were used to detect the expressions of EIF5A2 and Ki67, and clinicopathological data were collected. The positive expression of EIF5A2, Ki67 and different pathological features were analyzed. Results EIF5A2 was positively expressed in 60 cases (50.85%) and Ki67 was positively expressed in 81 cases (68.64%). EIF5A2 expression was not related to age, sex, tumor diameter and tumor number (P > 0.05), but related to TNM stage and lymphatic metastasis (P < 0.05). The expression of Ki67 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma tissues was not correlated with age, sex and tumor number (P > 0.05), but with TNM stage, lymphatic metastasis and tumor diameter (P < 0.05). EIF5A2 was positively correlated with the expression of Ki-67 (R = 0.285, P = 0.002). Conclusion The expression of EIF5A2 and KI-67 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma is positively correlated with high TNM stage and lymphatic metastasis, which is helpful to predict the clinical stage and prognosis of patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. -
表 1 EIF5A2和Ki67表达水平与肝内胆管癌临床病理特征的关系[n(%)]
Table 1. Relationship between EIF5A2 and Ki67 expression levels and clinicopathological features of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma [n (%)]
临床特征 n EIF5A2 Ki67 高表达(n = 60) 低表达(n = 58) χ2 P 高表达(n = 81) 低表达(n = 37) χ2 P 年龄(岁) ≥53 60 34(56.67) 26(43.33) 1.654 0.198 38(63.33) 22(36.67) 1.600 0.206 < 53 58 26(44.83) 32(55.17) 43(74.14) 15(25.86) 性别 男 49 29(59.18) 20(40.82) 2.330 0.127 31(63.27) 18(36.73) 1.126 0.298 女 69 31(44.93) 38(55.07) 50(72.46) 19(27.54) TNM分期 III/IV 38 27(71.05) 11(28.95) 9.156 0.002* 32(84.21) 6(15.79) 6.310 0.012* I/II 80 33(41.25) 47(58.75) 49(61.25) 31(38.75) 淋巴转移 是 35 23(65.71) 12(34.29) 4.400 0.036* 29(82.86) 6(17.14) 4.670 0.031* 否 83 37(45.58) 46(55.42) 52(62.65) 31(37.35) 肿瘤直径(cm) ≥5 87 48(55.17) 39(44.83) 2.478 0.115 65(74.71) 22(25.29) 5.666 0.017* < 5 31 12(38.71) 19(61.29) 16(51.61) 15(48.39) 肿瘤数量 多发 15 9(60.00) 6(40.00) 0.576 0.448 11(73.33) 4(26.67) 0.176 0.675 单发 103 51(49.51) 52(50.49) 70(67.96) 33(32.04) *P < 0.05。 表 2 EIF5A2和Ki67在肝内胆管癌中表达的相关性
Table 2. Correlation of EIF5A2 and Ki67 expression in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
Ki67 EIF5A2 r P 高表达
(n = 60)低表达
(n = 58)高表达(n = 81) 49 32 0.285 0.002 低表达(n = 37) 11 26 *P < 0.05。 -
[1] Bridgewater J,Galle P R,Khan S A,et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma[J]. J Hepatol,2014,60(6):1268-1289. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.01.021 [2] Bergquist A and von Seth E. Epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol,2015,29(2):221-232. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2015.02.003 [3] Bagante F,Spolverato G,Weiss M,et al. Impact of Morphological Status on Long-Term Outcome Among Patients Undergoing Liver Surgery for Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Ann Surg Oncol,2017,24(9):2491-2501. doi: 10.1245/s10434-017-5870-y [4] Esnaola N F,Meyer J E,Karachristos A,et al. Evaluation and management of intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Cancer,2016,122(9):1349-1369. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29692 [5] Kelley R K,Bridgewater J,Gores G J,et al. Systemic therapies for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma[J]. J Hepatol,2020,72(2):353-363. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.10.009 [6] Sirica A E,Gores G J,Groopman J D,et al. Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma:Continuing Challenges and Translational Advances[J]. Hepatology,2019,69(4):1803-1815. doi: 10.1002/hep.30289 [7] Rahnemai-Azar A A,Weisbrod A B,Dillhoff M,et al. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma:current management and emerging therapies[J]. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol,2017,11(5):439-449. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2017.1309290 [8] Guan X Y,Sham J S,Tang T C,et al. Isolation of a novel candidate oncogene within a frequently amplified region at 3q26 in ovarian cancer[J]. Cancer Res,2001,61(9):3806-3809. [9] Zhao G,Zhang W,Dong P,et al. EIF5A2 controls ovarian tumor growth and metastasis by promoting epithelial to mesenchymal transition via the TGFbeta pathway[J]. Cell Biosci,2021,11(1):70-81. [10] Pällmann N,Braig M,Sievert H,et al. Biological Relevance and Therapeutic Potential of the Hypusine Modification System[J]. J Biol Chem,2015,290(30):18343-18360. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.664490 [11] Ning L,Wang L,Zhang H,et al. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A in the pathogenesis of cancers[J]. Oncol Lett,2020,20(4):81. [12] Yang Q,Ye Z,Zhang Q,et al. Expression of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A-2 (eIF5A-2) associated with poor survival in gastric cancer[J]. Tumour Biol,2016,37(1):1189-1195. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3894-0 [13] Xie D,Ma N F,Pan Z Z,et al. Overexpression of EIF-5A2 is associated with metastasis of human colorectal carcinoma[J]. Hum Pathol,2008,39(1):80-86. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2007.05.011 [14] Qiang Z,Zhang W,Jin S,et al. Carcinoembryonic antigen,α-fetoprotein,and Ki67 as biomarkers and prognostic factors in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma:A retrospective cohort study[J]. Ann Hepatol,2021,20:100242. doi: 10.1016/j.aohep.2020.07.010 [15] El-Diwany R,Pawlik T M,Ejaz A. Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Surg Oncol Clin N Am,2019,28(4):587-599. [16] Yang R,Song Y,Shakoor K,et al. Insights into the role of STAT3 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (Review)[J]. Mol Med Rep,2022,25(5):171-179. [17] 陈敏山,周仲国,徐立,等. 关于ICC重新定义、分类和命名的建议[J]. 中华消化外科杂志,2021,20(12):1278-1282. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20211101-00534 [18] Wang G,Wang Q,Liang N,et al. Oncogenic driver genes and tumor microenvironment determine the type of liver cancer[J]. Cell Death Dis,2020,11(5):313-325. [19] 汤朝晖,于小鹏,童焕军,等. 从异质性角度看胆道恶性肿瘤的转化治疗[J]. 中华外科杂志,2021,59(4):260-264. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112139-20210105-00006 [20] Dong L,Lu D,Chen R,et al. Proteogenomic characterization identifies clinically relevant subgroups of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Cancer Cell,2022,40(1):70-87. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.12.006 [21] Job S,Rapoud D,Dos Santos A,et al. Identification of Four Immune Subtypes Characterized by Distinct Composition and Functions of Tumor Microenvironment in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Hepatology,2020,72(3):965-981. [22] 沈锋,谢之豪,夏勇,等. 肝内胆管癌的外科治疗进展[J]. 中华外科杂志,2019,57(4):241-246. [23] Spolverato G,Kim Y,Alexandrescu S,et al. Management and Outcomes of Patients with Recurrent Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Following Previous Curative-Intent Surgical Resection[J]. Ann Surg Oncol,2016,23(1):235-243. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4642-9 [24] Yao M,Hong Y,Liu Y,et al. N1-guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane enhances the sensitivity of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells to gemcitabine via the inhibition of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2[J]. Exp Ther Med,2017,14(3):2101-2107. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4740 [25] 杨少华,廖周俊,胡晟,等. 真核翻译起始因子-5A2在肝内胆管癌中的表达及意义[J]. 昆明医科大学学报,2021,42(5):24-28. [26] Tang D J,Dong S S,Ma N F,et al. Overexpression of eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 enhances cell motility and promotes tumor metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology,2010,51(4):1255-1263. doi: 10.1002/hep.23451 [27] Zhu W,Cai M Y,Tong Z T,et al. Overexpression of EIF5A2 promotes colorectal carcinoma cell aggressiveness by upregulating MTA1 through C-myc to induce epithelial-mesenchymaltransition[J]. Gut,2012,61(4):562-575. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300207 [28] Wan G,Liu Y,Zhu J,et al. SLFN5 suppresses cancer cell migration and invasion by inhibiting MT1-MMP expression via AKT/GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway[J]. Cell Signal,2019,59:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2019.03.004 [29] Mondal S,Adhikari N,Banerjee S,et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and its inhibitors in cancer:A minireview[J]. Eur J Med Chem,2020,194(3):112260-112278. [30] Khosravi S,Martinka M,Zhou Y,et al. Prognostic significance of the expression of nuclear eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 in human melanoma[J]. Oncol Lett,2016,12(5):3089-3100. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.5057 [31] Wang F W,Cai M Y,Mai S J,et al. Ablation of EIF5A2 induces tumor vasculature remodeling and improves tumor response to chemotherapy via regulation of matrix metalloproteinase 2 expression[J]. Oncotarget,2014,5(16):6716-6733. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2236 [32] 周浩辉,陈燕凌,黄长玉,等. Ki67抗原与P16蛋白在人肝内胆管癌中的表达及其意义[J]. 医学信息(中旬刊),2010,5(10):2739-2740. [33] 何坚男. SATB1和Ki-67在肝内胆管细胞癌中的表达及其临床意义[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学硕士论文, 2018. [34] Yang G F,Xie D,Liu J H,et al. Expression and amplification of eIF-5A2 in human epithelial ovarian tumors and overexpression of EIF-5A2 is a new independent predictor of outcome in patients with ovarian carcinoma[J]. Gynecol Oncol,2009,112(2):314-318. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.10.024 -






 下载:
下载: