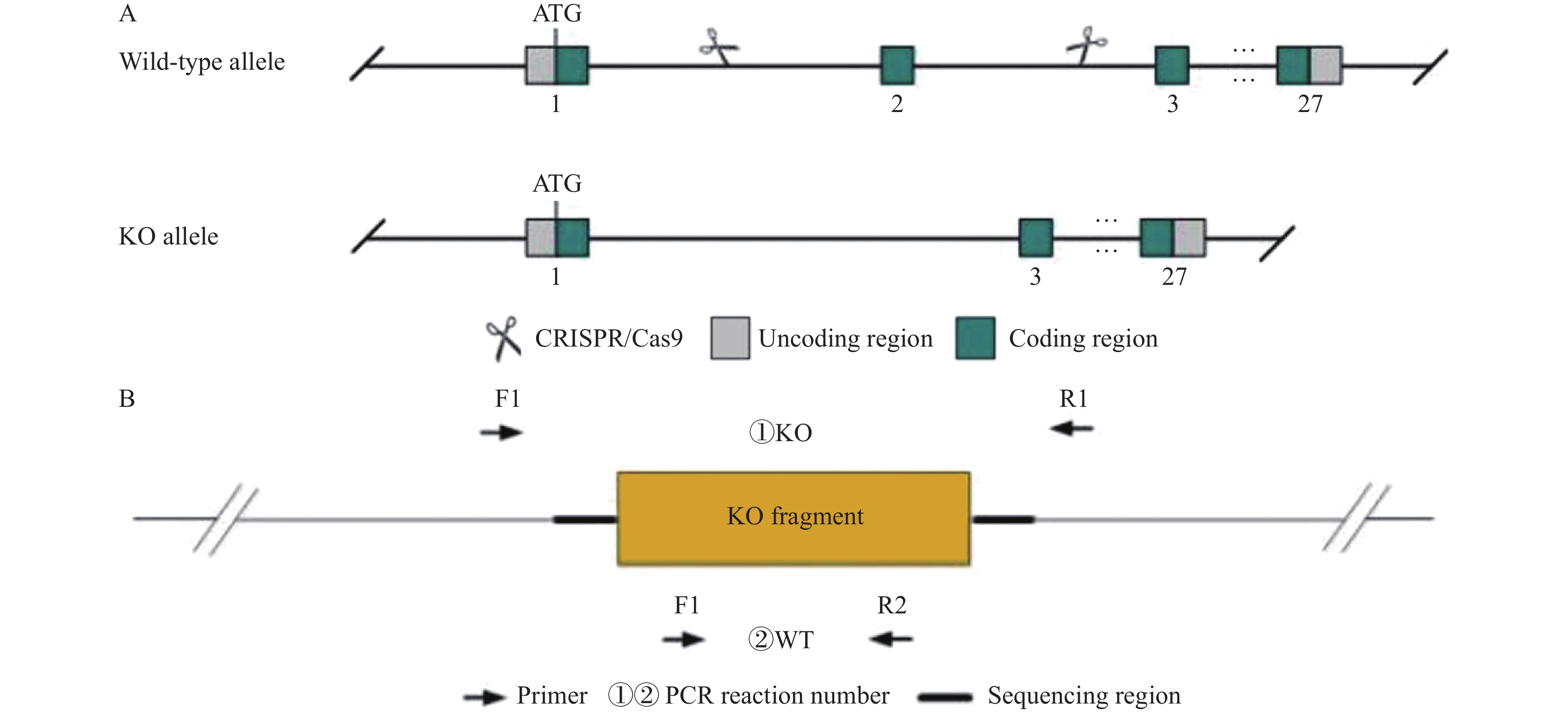
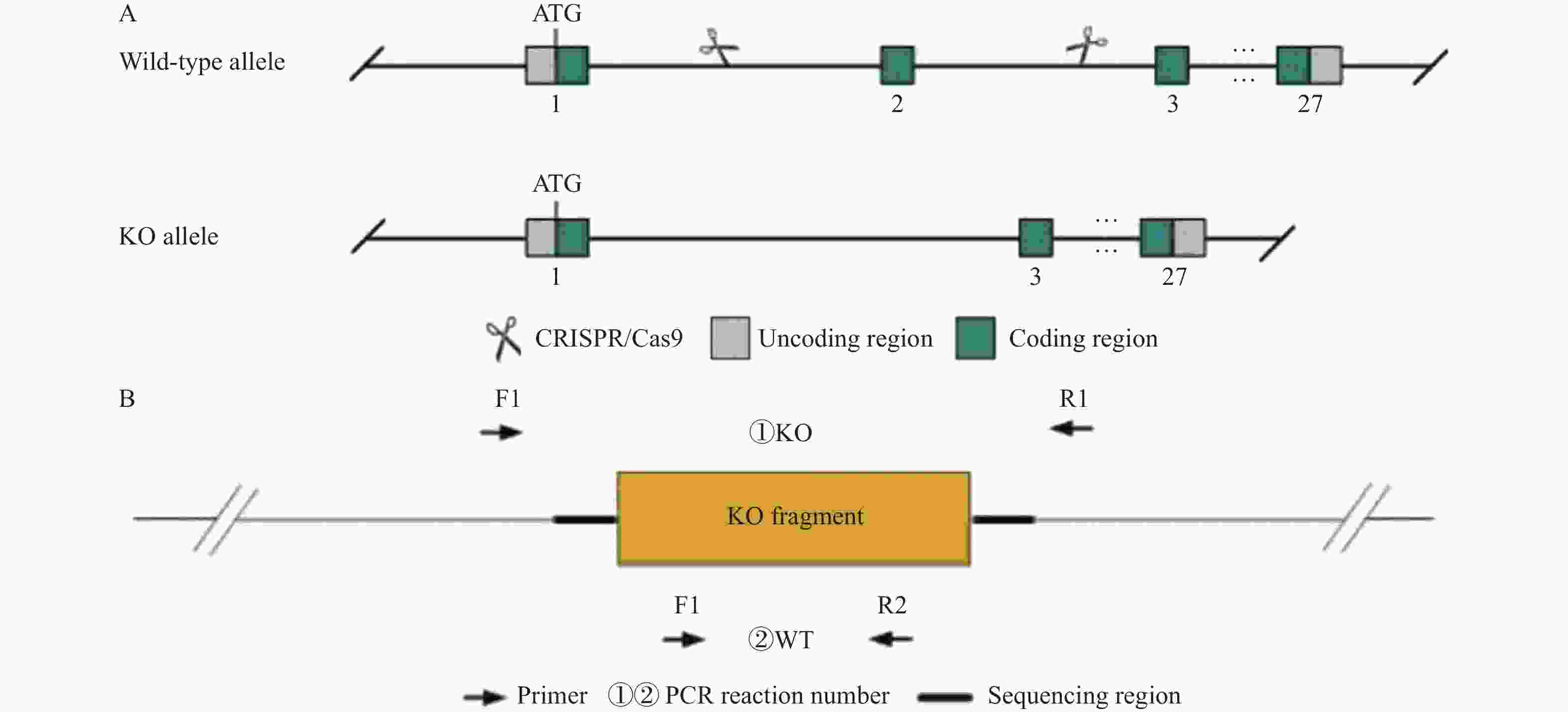
Changes of Intestinal Inflammatory Injury Induced by DSS in GC-C-/- Mice
-
摘要:
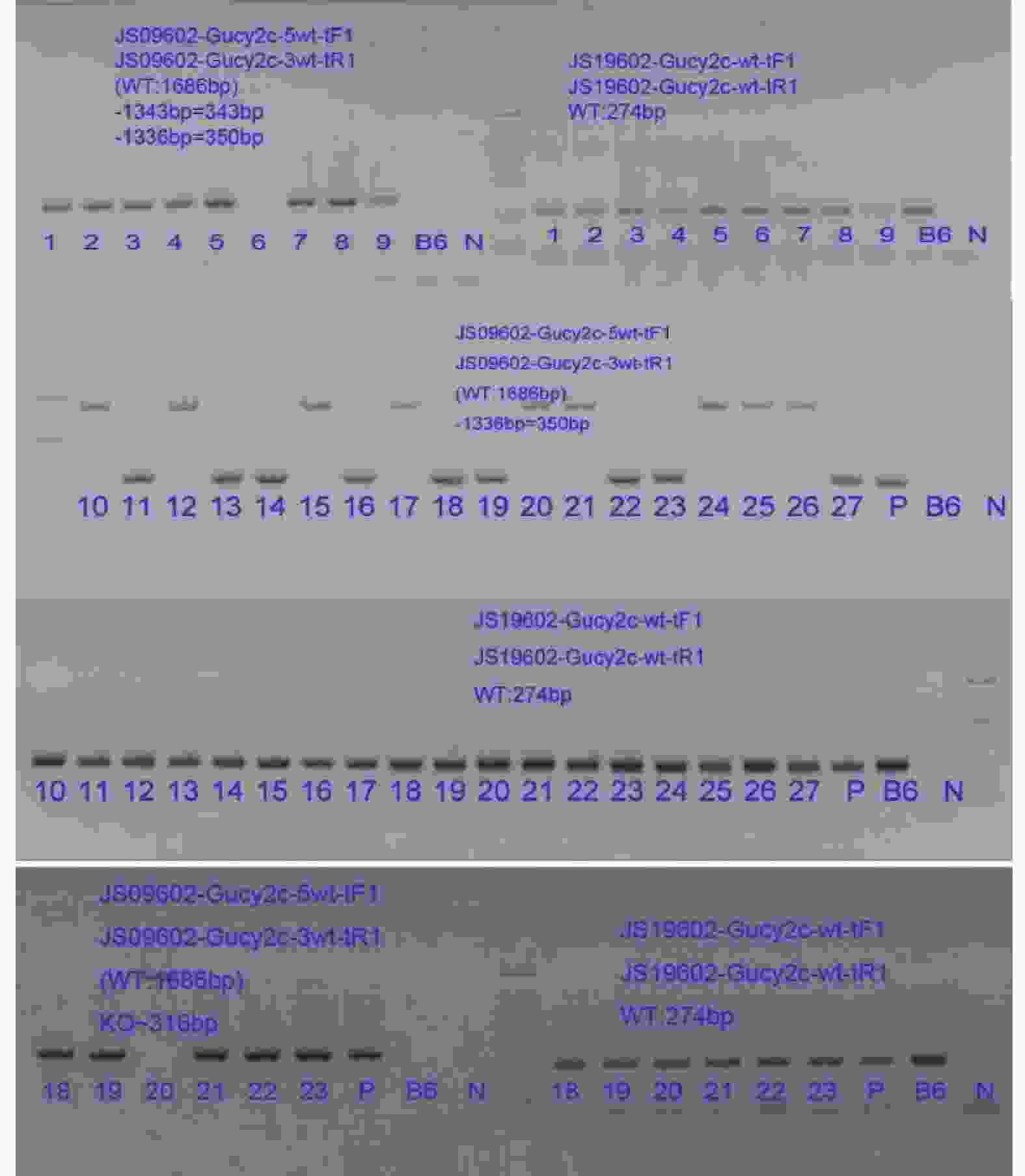
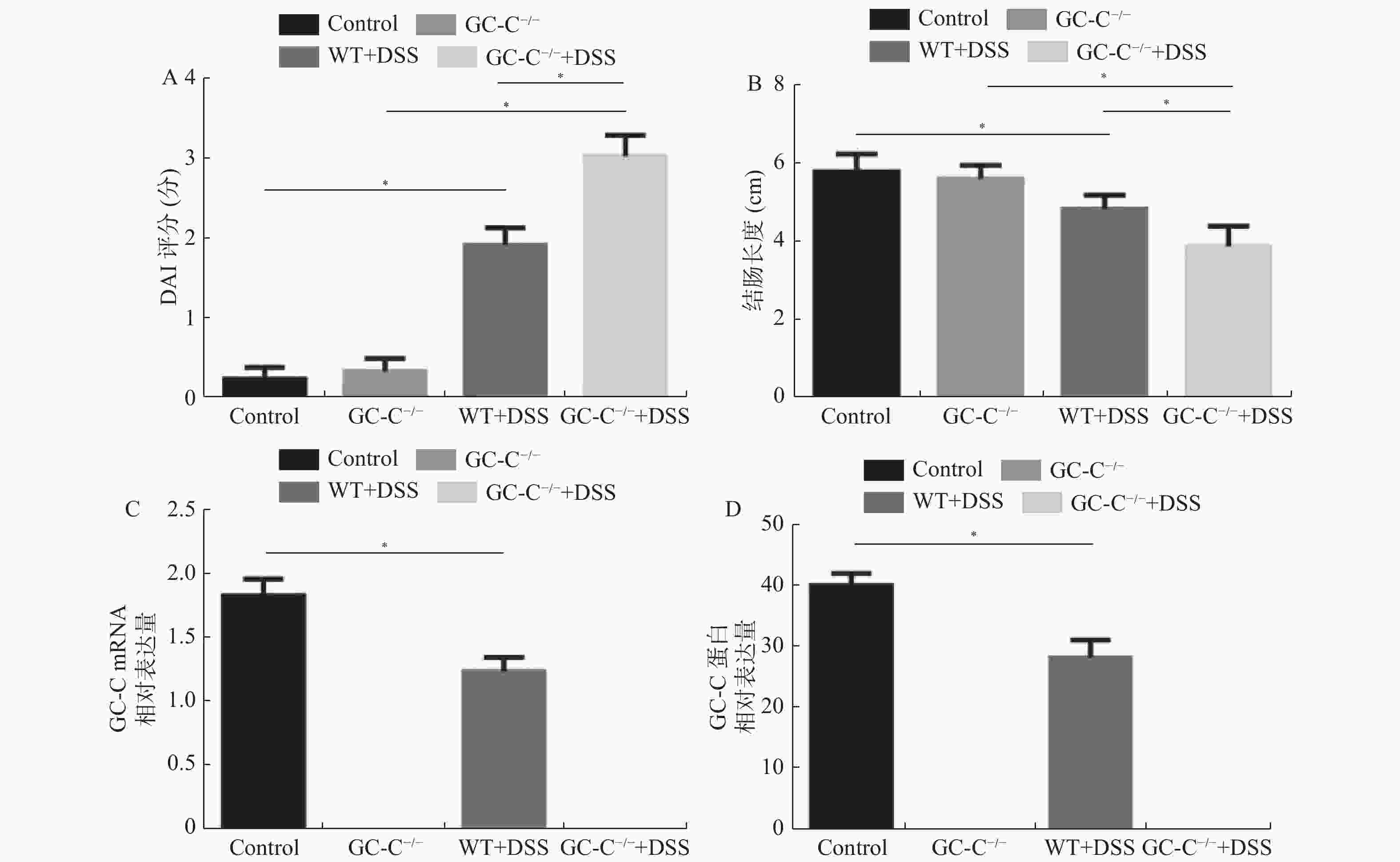
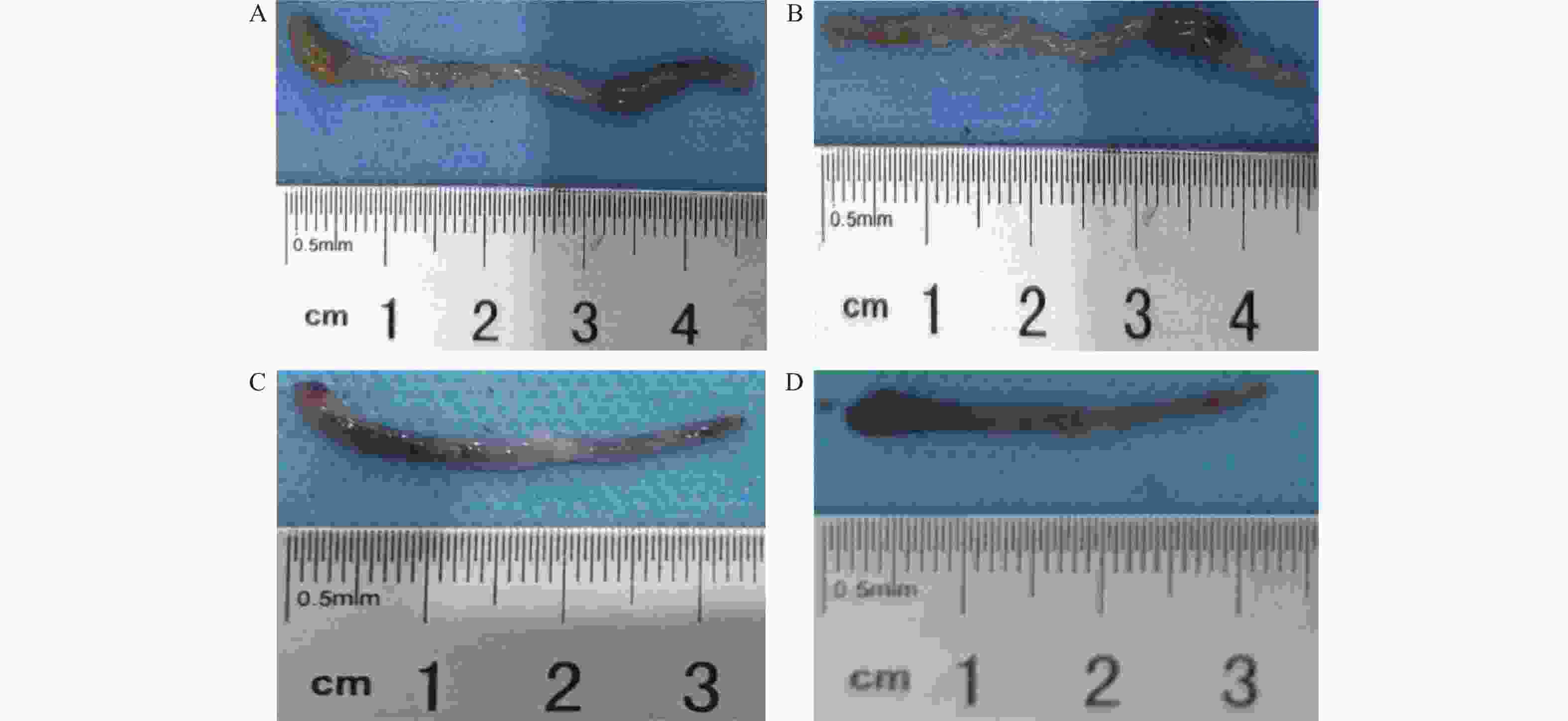
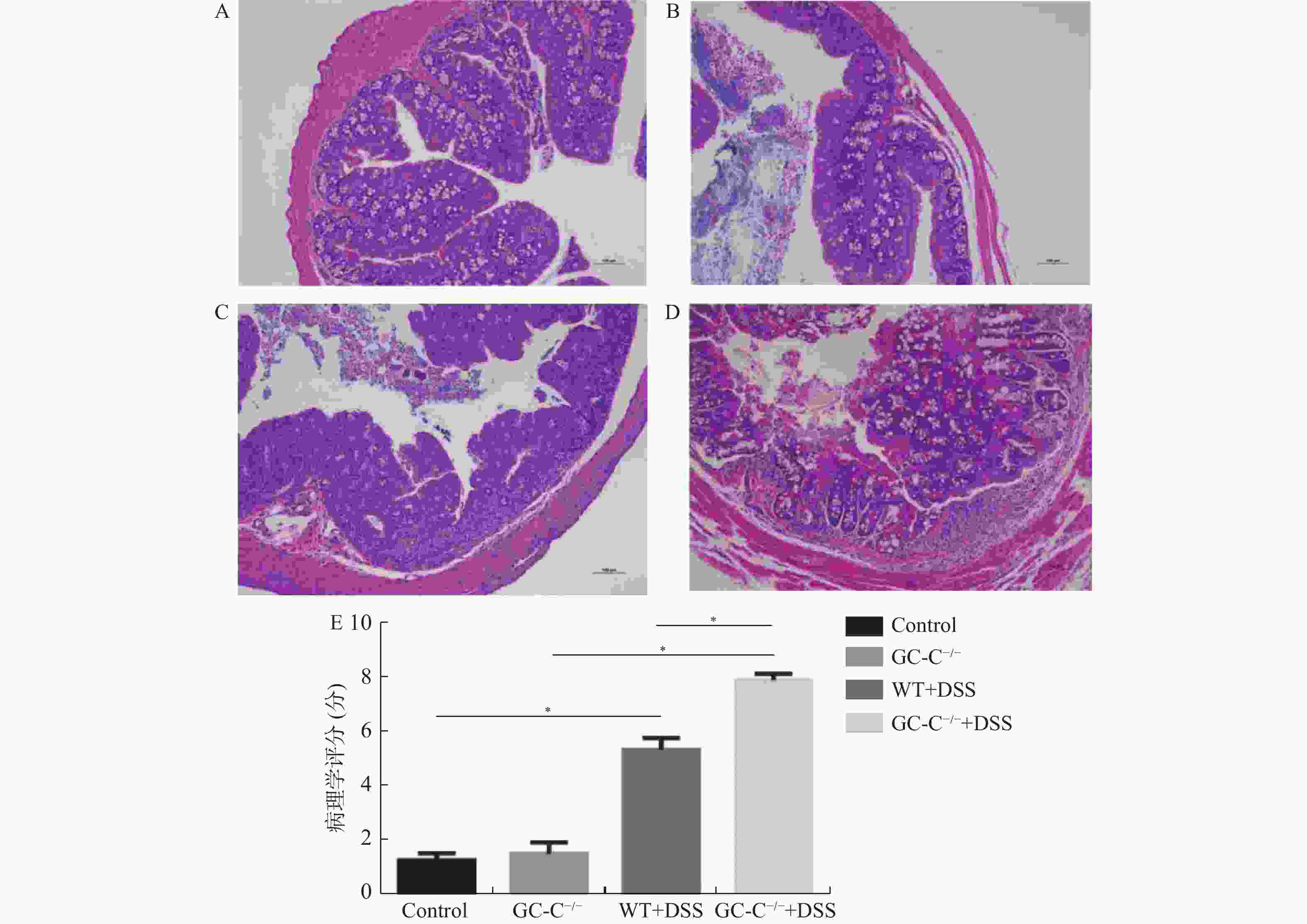
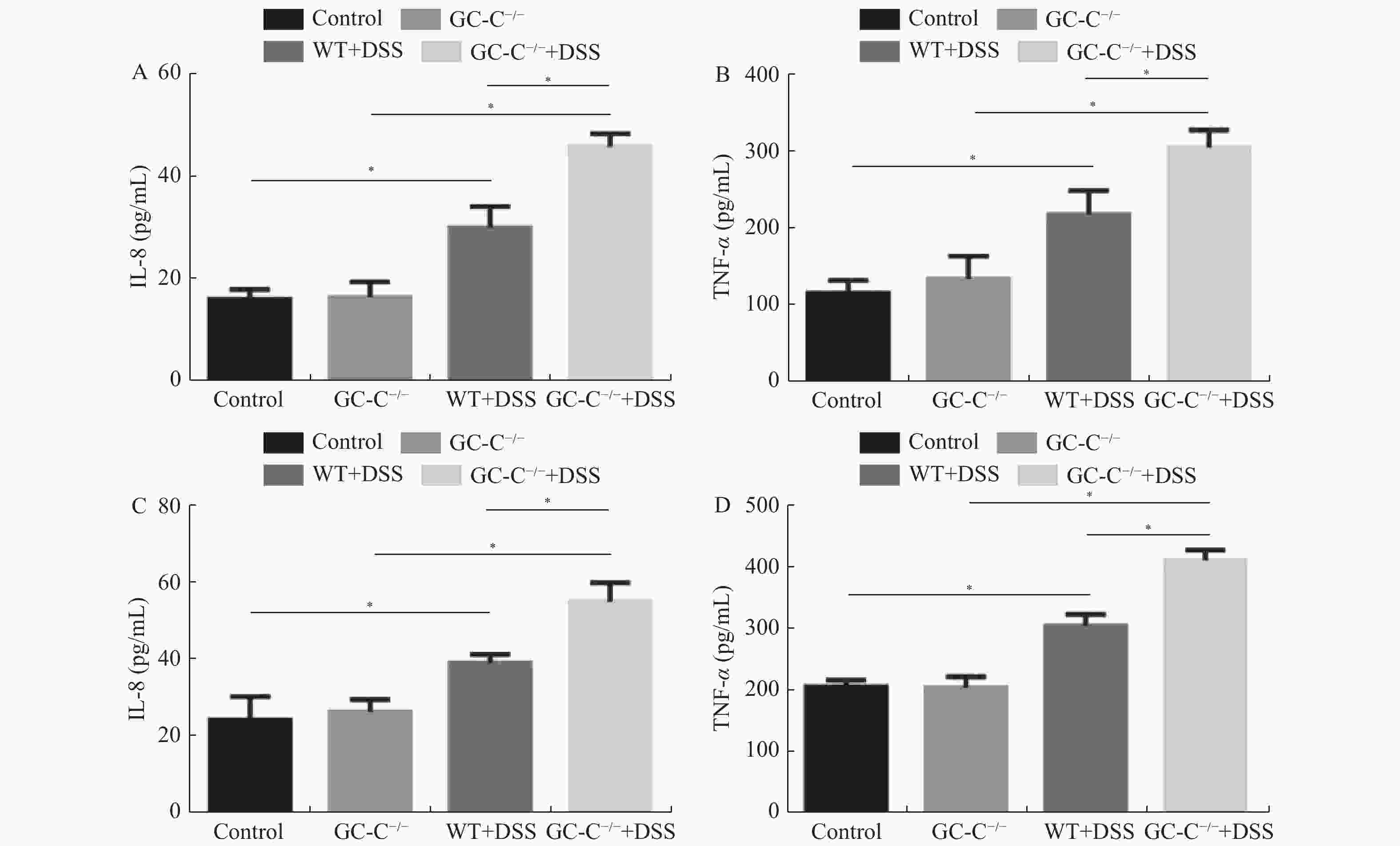
目的 了解鸟苷酸环化酶C(GC-C)信号通路在右旋糖酐硫酸酯钠(DSS)诱导小鼠肠道炎症性损伤发生中的作用。 方法 运用DSS构建GC-C基因敲除(GC-C-/-)小鼠和野生型(WT)小鼠结肠炎模型,将小鼠分为炎症组和对照组,前者给予3%的DSS溶液自由饮用1周,后者给予正常饮食。运用qRT-PCR和Westernblot方法检测结肠组织GC-C mRNA和蛋白的表达,在光学显微镜下观察经HE染色后结肠组织的炎症损伤情况并进行组织病理学评分。运用ELISA方法检测小鼠外周血与肠黏液中炎症因子(IL-8和TNF-α)的水平。 结果 (1)与WT小鼠相比,GC-C-/-小鼠在DSS作用下疾病活动指数(DAI)评分明显升高(P < 0.05), 结肠缩短、肠管增粗、充血水肿更明显;(2)显微镜下观察到GC-C-/-+DSS组小鼠结肠组织炎症损伤更为严重,组织病理学评分较WT+DSS组小鼠明显升高(P < 0.05);(3)GC-C-/-小鼠在DSS诱导下外周血和肠粘液中IL-8和TNF-α水平较WT+DSS组明显升高(P < 0.05)。 结论 GC-C-/-小鼠在化学物质诱导下肠道炎症性损伤加重,GC-C信号通路可能参与了溃疡性结肠炎(UC)的发生与发展。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the role of guanylate cyclase C (GC-C) signaling pathway in the intestinal inflammatory injury of mice induced by sodium dextran sulfate (DSS). Methods The colitis models were constructed using DSS in the GC-C gene knockout (GC-C-/-) mice and wild-type (WT) mice. The mice were divided into the colitis groups which were given drinking 3% DSS solution for one week, and the control groups which were given normal diet. The expressions of GC-C mRNA and protein in colon tissues were detected by the methods of qRT-PCR and western blot. The inflammatory damage of colon tissues was observed by the HE staining and the histopathological score was performed by the light microscope. The levels of inflammatory factors (IL-8 and TNF-α) in the peripheral blood as well as intestinal mucus of mice were determined by ELISA. Results 1. Compared with the WT mice, the disease activity index (DAI) scores of the GC-C-/- mice induced by DSS increased significantly (P < 0.05), and the shortening of colon, intestinal thickening, hyperemia and edema were more obvious; 2. The inflammatory damage of colon tissues was more serious and the histopathological score was higher in the GC-C-/-+DSS group than that of the WT+DSS group significantly (P < 0.05); 3. The levels of IL-8 and TNF-αin the peripheral blood and intestinal mucus were higher in the GC-C-/-+DSS group than that of the WT+DSS group significantly (P < 0.05, respectively). Conclusions The intestinal inflammatory injury is more serious in the GC-C-/- mice induced by chemical substances. GC-C signaling pathway may be involved in the occurrence and development of ulcerative colitis (UC). -
Key words:
- Guanylate cyclase C /
- Gene knockout /
- Intestinal inflammation /
- Ulcerative colitis
-
表 1 DAI 评分标准
Table 1. DAI scoring criteria
计分 体重下降(%) 大便性状 大便潜血 0 0 正常 正常 1 1~5 介于两者中间 介于两者中间 2 5~10 松散 潜血阳性 3 10~15 介于两者中间 介于两者中间 4 >15 稀便 肉眼血便 表 2 组织病理学评分标准
Table 2. Histopathological scoring criteria
评分 上皮损伤和溃疡形成 溃疡深度 水肿 炎细胞浸润 浸润深度 0 无 无 无 无 无 1 糜烂 粘膜下层 轻度 轻度 粘膜下层 2 溃疡 肌层 中度 中度 肌层 3 浆膜层 重度 重度 浆膜层 -
[1] Shah S C,Itzkowitz S H. Colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease:mechanisms and management[J]. Gastroenterology,2022,162(3):715-730. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.10.035 [2] Ng S C,Shi H Y,Hamidi N,et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century:a systematic review of population-based studies[J]. Lancet,2018,390(10114):2769-2778. [3] Benchimol E I,Bernstein C N,Bitton A,et al. Trends in epidemiology of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease in Canada:distributed network analysis of multiple population-based provincial health administrative databases[J]. Am J Gastroenterol,2017,112(7):1120-1134. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2017.97 [4] Uranga J A,Castro M,Abalo R. Guanylate cyclase C:A current hot target,from physiology to pathology[J]. Curr Med Chem,2018,25(16):1879-1908. [5] Rappaport J A,Waldman S A. The guanylate cyclase C-cGMP signaling axis opposes intestinal epithelial injury and neoplasia[J]. Front Oncol,2018,8:299. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00299 [6] Xing C,Zhang T,Liu X,et al. Guanylin ligand protects the intestinal immune barrier by activating the guanylate cyclase-C signaling pathway[J]. Acta Histochem,2022,124(1):151811. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2021.151811 [7] Lan D,Wen Y,Dong X,et al. The endogenous ligand for guanylate cyclase-C activation reliefs intestinal inflammation in the DSS colitis model[J]. Acta Biochim Pol,2020,67(3):333-340. [8] 苗政,钱家鸣,李景南,等. 两种溃疡性结肠炎小鼠模型的构建及其炎症反应机制比较[J]. 协和医学杂志,2010,1(2):145-149. [9] Baumgart D C,Le Berre C. Newer Biologic and Small-Molecule Therapies for Inflammatory Bowel Disease[J]. N Engl J Med,2020,385(14):1302-1315. [10] Su H J,Chiu Y T,Chiu C T,et al. Inflammatory bowel disease and its treatment in 2018:Global and Taiwan residents status updates[J]. J Formos Med Assoc,2019,118(7):1083-1092. [11] Sasson A N,Ananthakrishnan A N,Raman M. Diet in Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol,2021,19(3):425-435. [12] Camilleri M. Guanylate cyclase C agonists:emerging gastrointestinal therapies and actions[J]. Gastroenterology,2015,148(3):483-487. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.01.003 [13] Lan D,Niu J,Miao J,et al. Expression of guanylate cyclase-C,guanylin,and uroguanylin is downregulated proportionally to the ulcerative colitis disease activity index[J]. Sci Rep,2016,6:25034. doi: 10.1038/srep25034 [14] Wang Y J,Lan D F,Niu J K,et al. Guanylate cyclase-C signaling pathway regulates intestinal inflammatory injury and epithelial barrier function in Caco-2 cells[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol,2016,9(9):8858-8868. [15] Harmel-Laws E,Mann E A,Cohen M B,et al. Guanylate cyclase C deficiency causes severe inflammation in a murine model of spontaneous colitis[J]. PLoS One,2013,8(11):e79180. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079180 [16] Fiskerstrand T,Arshad N,Haukanes B I,et al. Familial diarrhea syndrome caused by an activating GUCY2C mutation[J]. N Engl J Med,2012,366(17):1586-1595. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1110132 [17] Mishra V,Bose A,Kiran S,et al. Gut-associated cGMP mediates colitis and dysbiosis in a mouse model of an activating mutation in GUCY2C[J]. J Exp Med,2021,218(11):e20210479c. doi: 10.1084/jem.20210479 [18] Steinbrecher K A,Harmel-Laws E,Garin-Laflam M P,et al. Murine guanylate cyclase C regulates colonic injury and inflammation[J]. J Immunol,2011,186(12):7205-7214. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002469 [19] Lin J E,Snook A E,Li P,et al. GUCY2C opposes systemic genotoxic tumorigenesis by regulating AKT-dependent intestinal barrier integrity[J]. PLoS One,2012,7(2):e31686. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031686 [20] Han X,Mann E,Gilbert S,et al. Loss of guanylyl cyclase C (GCC) signaling leads to dysfunctional intestinal barrier[J]. PLoS One,2011,6(1):e16139. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016139 [21] Li P, Lin J E, Chervoneva I, et al. Homeostatic control of the crypt-villus axis by the bacterial enterotoxin receptor guanylyl cyclase C restricts the proliferating compartment in intestine. Am J Pathol, 2007, 171(6): 1847-1858. -





 下载:
下载: