Effects of miR-208a on Myocardial Ischemia-reperfusion Injury by Regulating the Expression of QKI5 in Rats
-
摘要:
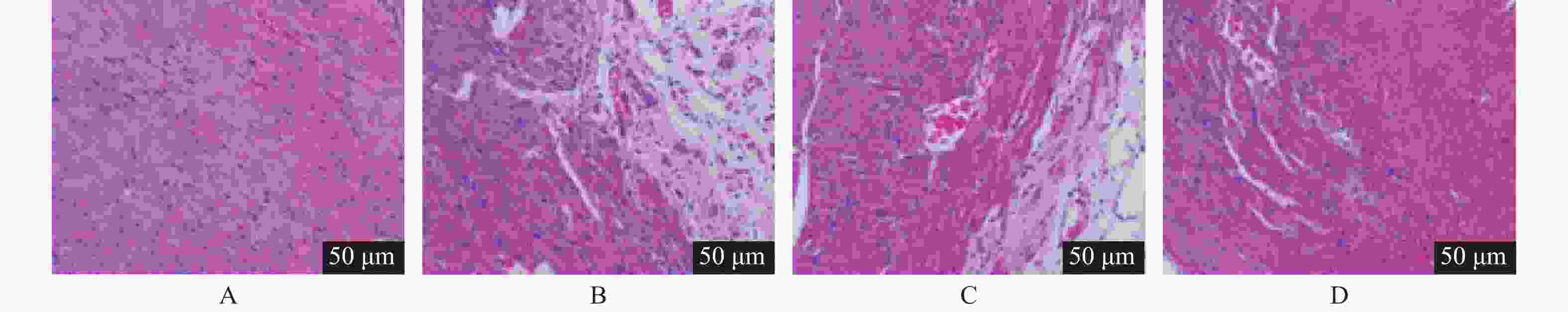
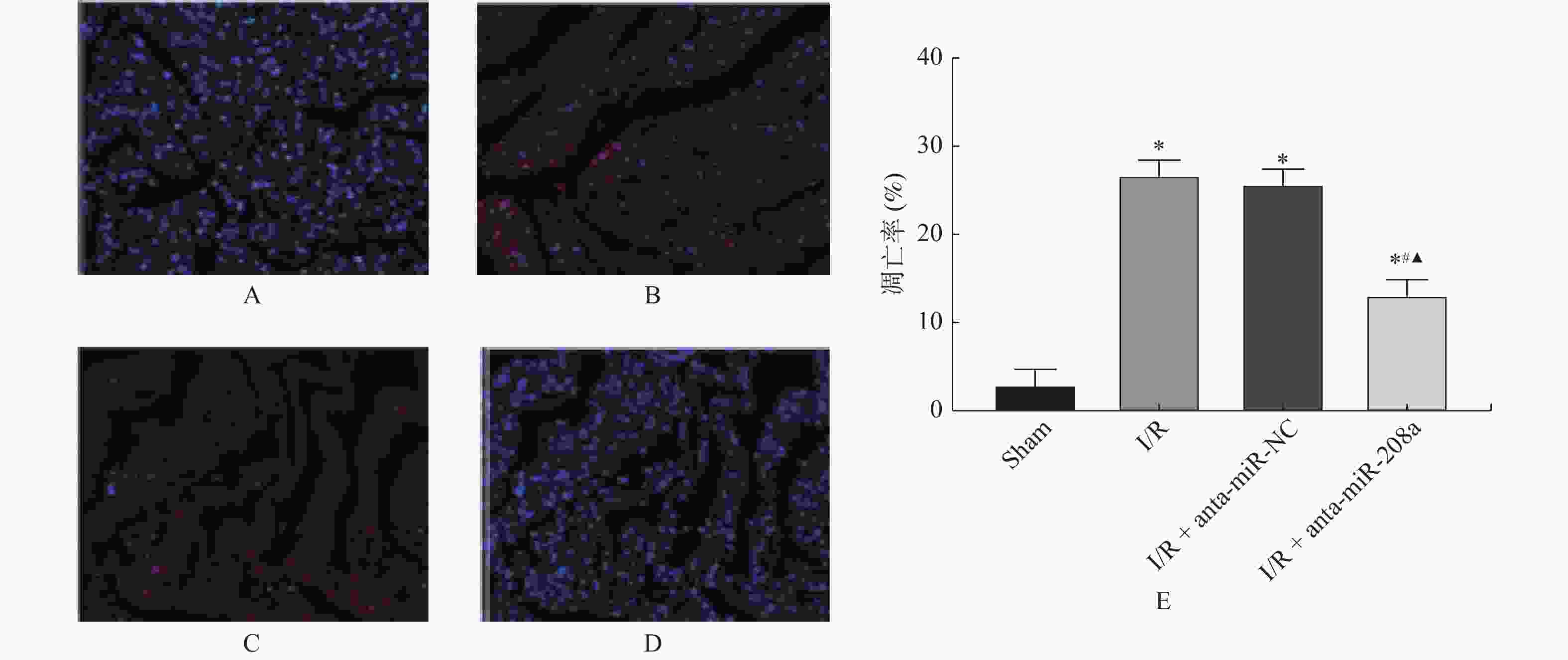
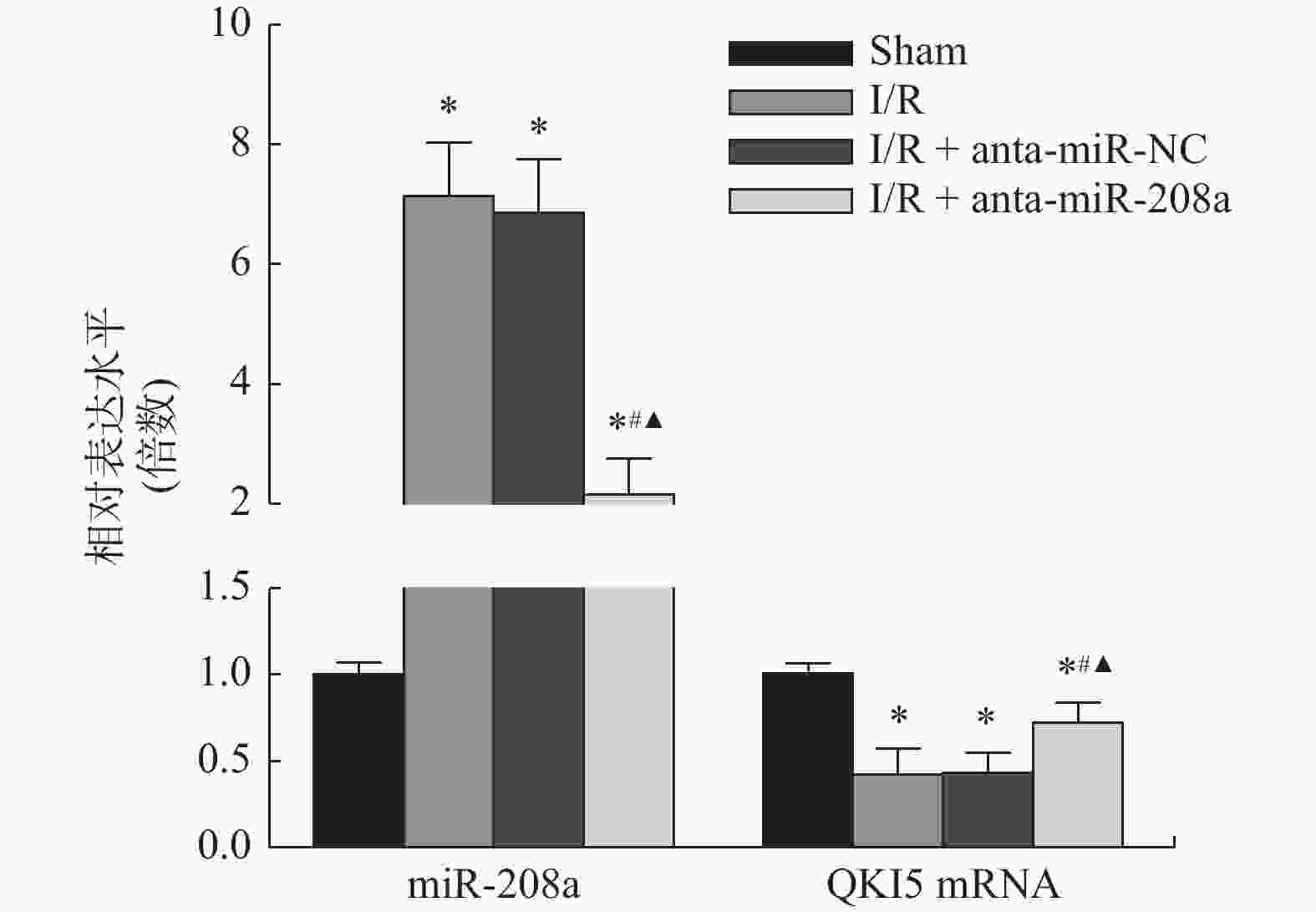
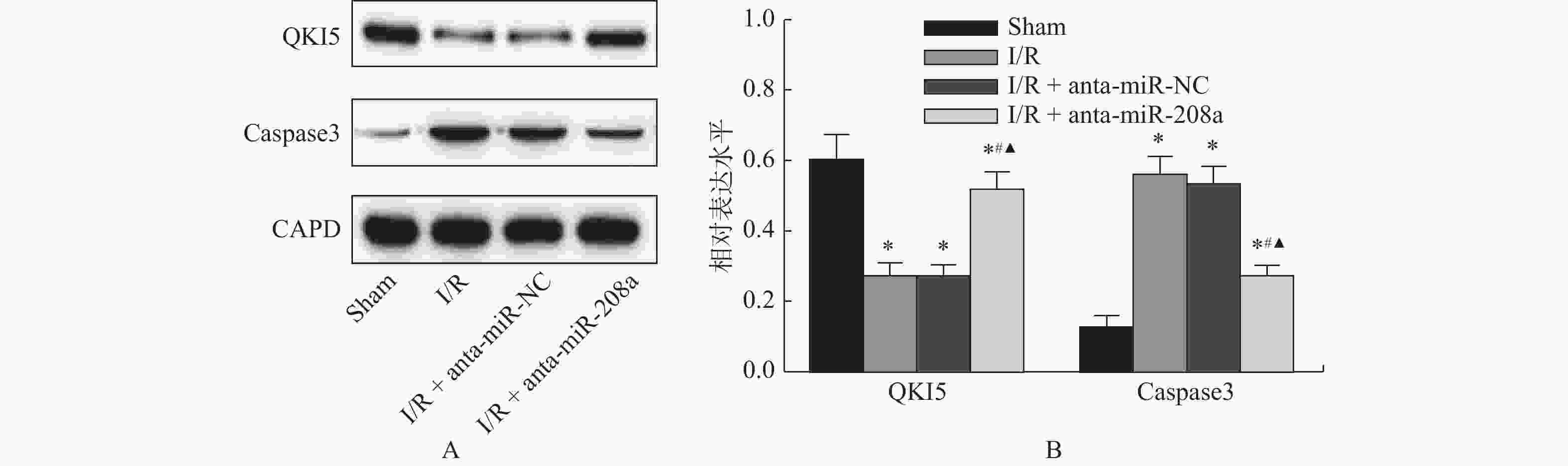
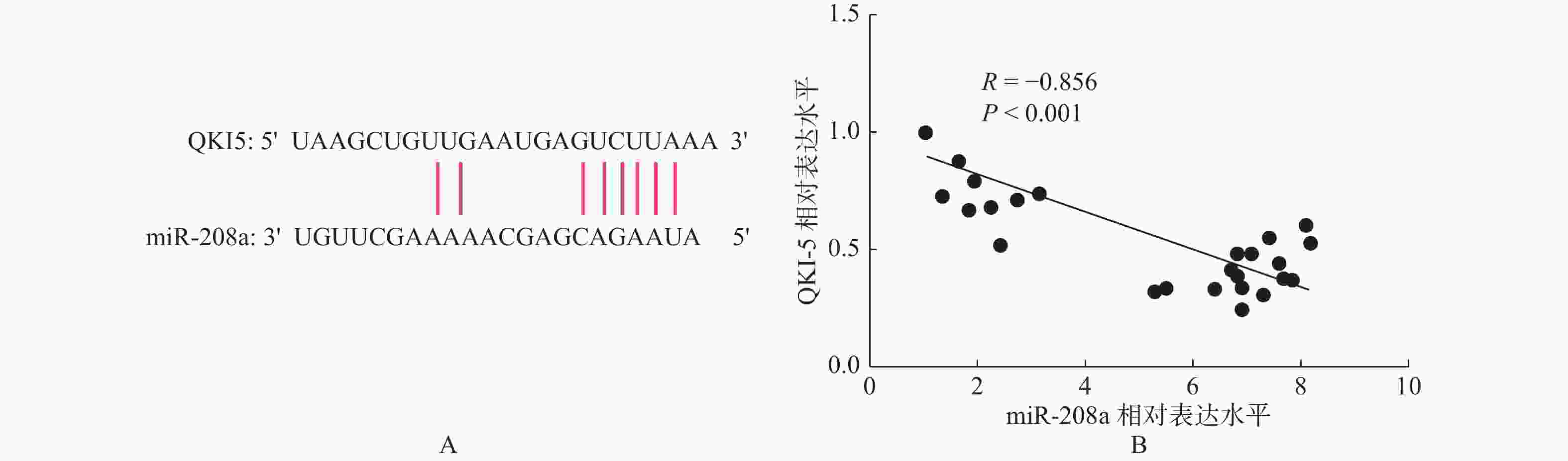
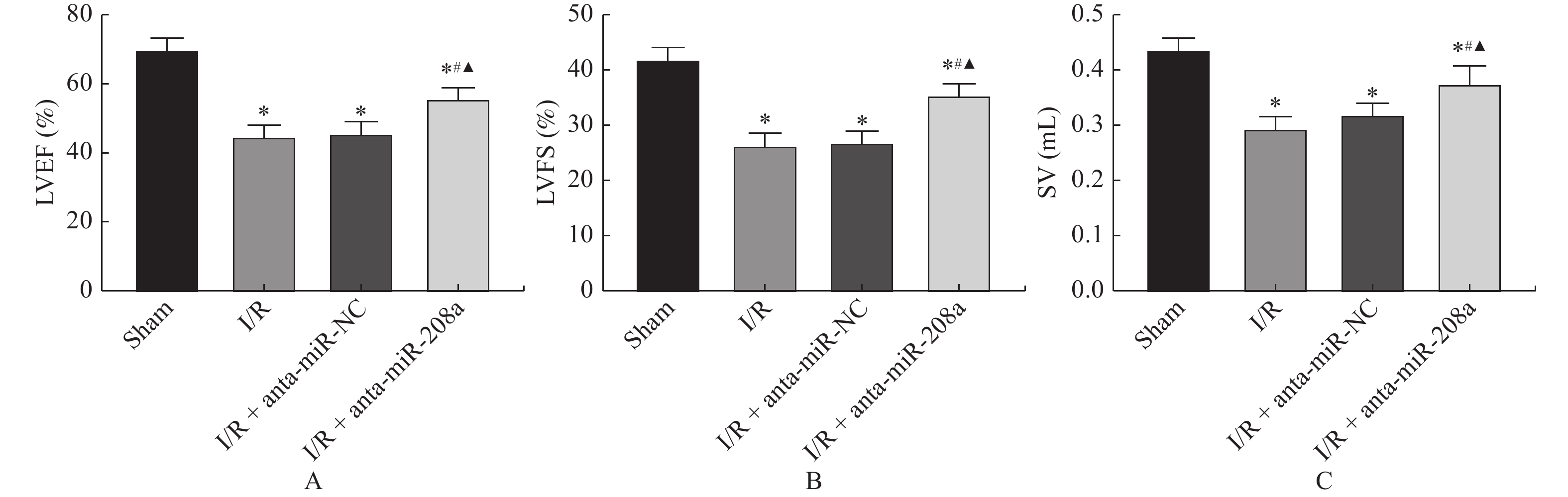
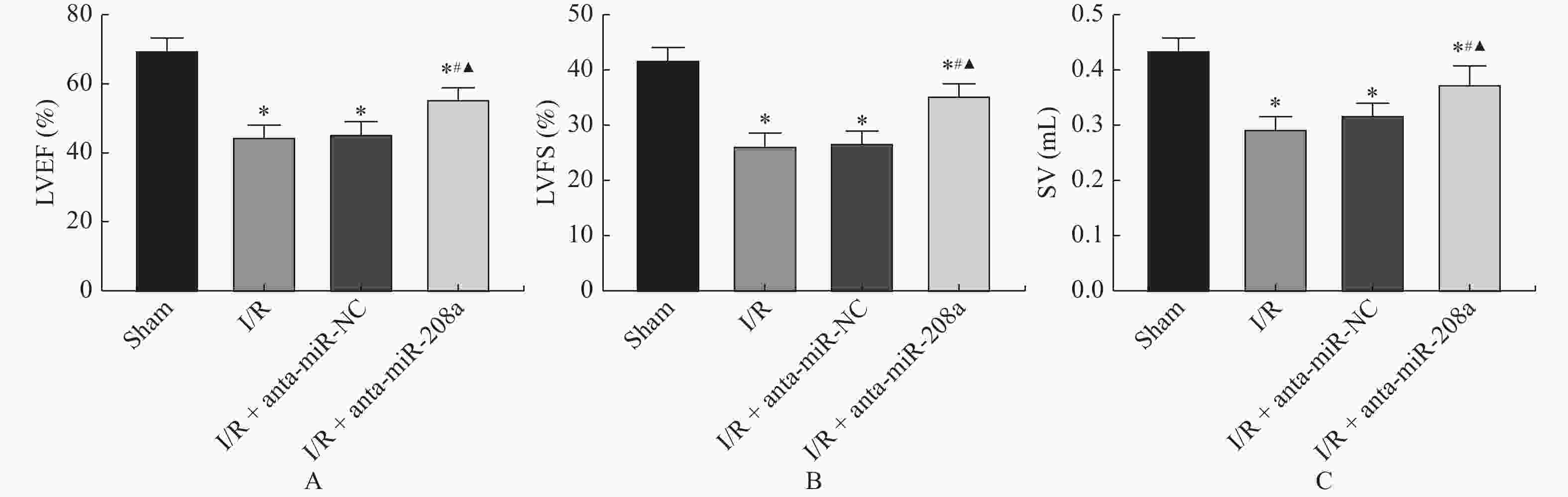
目的 研究miR-208a调控QKI5表达对大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤的影响及作用机制。 方法 将雄性SD大鼠32只随机选择分为假手术组(Sham组)、缺血再灌注组(I/R组)、I/R+antagomir阴性对照组(I/R+anta-miR-NC组)和I/R+miR-208a antagomir 组 (I/R+anta-miR-208a组),构建大鼠心肌I/R模型后检测各组大鼠心脏左室射血分数(LVEF)、左室短轴缩短率(LVFS)和左室每搏量(SV);ELISA法检测血清肌酐激酶同工酶(CK-MB)和心肌肌钙蛋白(cTnI)以及IL-1β、IL-6和肿瘤坏死因子(TNF-α)水平;采用HE染色观察各组心肌组织病理变化,采用TUNEL染色检测心肌组织细胞凋亡;RT-PCR检测心肌组织miR-208a和QKI5 mRNA表达,Western blot检测心肌组织QKI5蛋白和凋亡蛋白Caspase-3的相对表达水平。 结果 与Sham组比较,I/R组中LVEF、LVFS、SV值降低,心肌细胞凋亡率升高,血清中CK-MB、cTnI和IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α水平及心肌组织中miR-208a和Caspase-3表达升高,而QKI5表达水平降低(P < 0.05);与I/R+anta-miR-NC组比较,I/R+anta-miR-208a组中LVEF、LVFS、SV值升高,心肌细胞凋亡率降低,血清中CK-MB、cTnI和IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α及心肌组织中miR-208a和Caspase-3表达水平降低,而QKI5表达升高(P < 0.05)。相关性分析发现miR-208a与QKI5表达呈负相关。 结论 抑制miR-208a可能通过调控QKI5表达减轻心肌缺血再灌注损伤中炎症反应,发挥心肌保护作用。 -
关键词:
- 心肌缺血再灌注损伤 /
- 微小RNA-208a /
- QKI5蛋白 /
- 相关性
Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect and mechanism of miR-208a on myocardial injury induced by myocardial ischemia reperfusion by regulating the expression of QKI5 in rats. Methods Thirty-two male SD rats were randomly divided into sham group, I/R group, I/R+anta-miR-NC group and I/R+anta-miR-208a group. The rat model of myocardial I/R was established, and the LVEF, LVFS and SV were detected in each group. The levels of CK-MB, cTnI, IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-αwere measured by ELISA. HE staining was used to observe the pathological changes of myocardial tissue in each group, and TUNEL staining was used to detect myocardial cell apoptosis.RT-PCR was used to detect the expression of miR-208a and QKI5 mRNA in myocardial tissue, and Western blot was used to detect the realative expression levels of QKI5 protein and Caspase-3 in myocardial tissue. Results Compared with the Sham group, the levels of LVEF, LVFS, SV in the I/R group were decreased, while the apoptosis rate of cardiomyocytes was increased, and the levels of CK-MB, cTnI, IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α in serum and the expressions of miR-208a and Caspase-3 in the myocardial tissue were increased, and the expressions of QKI5 were decreased (P < 0.05). Compared with the I/R+anta-miR-NC group, the levels of LVEF, LVFS, SV in the I/R+anta-miR-208a group were increased, while the apoptosis rate of cardiomyocytes was decreased, and the levels of CK-MB, cTnI, IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α in serum and the expressions of miR-208a and Caspase-3 in the myocardial tissue were decreased, and the expressions of QKI5 were increased (P < 0.05). Correlation analysis found that the expression of miR-208a and QKI5 had negative correlation in the I/R rats. Conclusion Inhibition of miR-208a may alleviate the inflammatory response to exert myocardial protective function in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating the expression of QKI5. -
Key words:
- Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury /
- miR-208a /
- QKI5 protein /
- Correlation
-
-
[1] Mokhtari-Zaer A,Marefati N,Atkin S L,et al. The protective role of curcumin in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Journal of Cellular Physiology,2018,234(1):214-222. [2] Russo I,Penna C,Musso T,et al. Platelets,diabetes and myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury[J]. Cardiovascular Diabetology,2017,16(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12933-017-0550-6 [3] 常国楫,顾金松,孙林. MicroRNA在心肌再灌注损伤应用的研究进展[J]. 昆明医科大学学报,2017,38(5):138-143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4706.2017.05.031 [4] Tony H,Yu K,Qiutang Z. MicroRNA-208a silencing attenuates doxorubicin induced myocyte apoptosis and cardiac dysfunction[J]. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity,2015,6(2015):597032. [5] Guo W,Shi X,Liu A,et al. RNA binding protein QKI inhibits the ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis in neonatal cardiomyocytes[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem,2011,28(4):593-602. doi: 10.1159/000335755 [6] Kunecki M,Płazak W,Podolec P,et al. Effects of endogenous cardioprotective mechanisms on ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online),2017,71(10):20-31. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0010.3786 [7] 陈耽,李骊华. miR-208a在大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤及缺血后处理中的表达及其作用[J]. 重庆医科大学学报,2015,4(40):501-505. doi: 10.13406/j.cnki.cyxb.000494 [8] Kura B,Szeiffova Bacova B,Kalocayova B,et al. Oxidative Stress-Responsive MicroRNAs in Heart Injury[J]. Int J Mol Sci.,2020,21(1):358. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010358 [9] Wang F,Yuan Y,Yang P,et al. Extracellular vesicles-mediated transfer of miR-208a/b exaggerate hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in cardiomyocytes by reducing QKI expression[J]. Mol Cell Biochem,2017,431(1-2):187-195. doi: 10.1007/s11010-017-2990-4 [10] Yan F,Liu R,Zhuang X,et al. Salidroside attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiac dysfunction partially through activation of QKI/FoxO1 pathway[J]. J Cardiovasc Transl Res,2021,14(2):355-364. doi: 10.1007/s12265-020-10056-x [11] Guo W,Jiang T,Lian C,et al. QKI deficiency promotes FoxO1 mediated nitrosative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress contributing to increased vulnerability to ischemic injury in diabetic heart[J]. J Mol Cell Cardiol,2014,75(10):131-140. [12] Al-Salam S,Hashmi S. Myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury:Apoptotic,inflammatory and oxidative stress role of galectin-3[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem,2018,50(3):1123-1139. doi: 10.1159/000494539 [13] Taki J,Wakabayashi H,Inaki A,et al. 14C-Methionine uptake as a potential marker of inflammatory processes after myocardial ischemia and reperfusion[J]. J Nucl Med,2013,54(3):431-436. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.112.112060 [14] Li Y,Li Z,Liu J,et al. miR-190-5p alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by targeting PHLPP1[J]. Disease Markers,2021,2021:8709298. -






 下载:
下载: