Protective Effect of Interleukin-4 in Lipopolysaccharide-induced Acute Lung Injury Models
-
摘要:
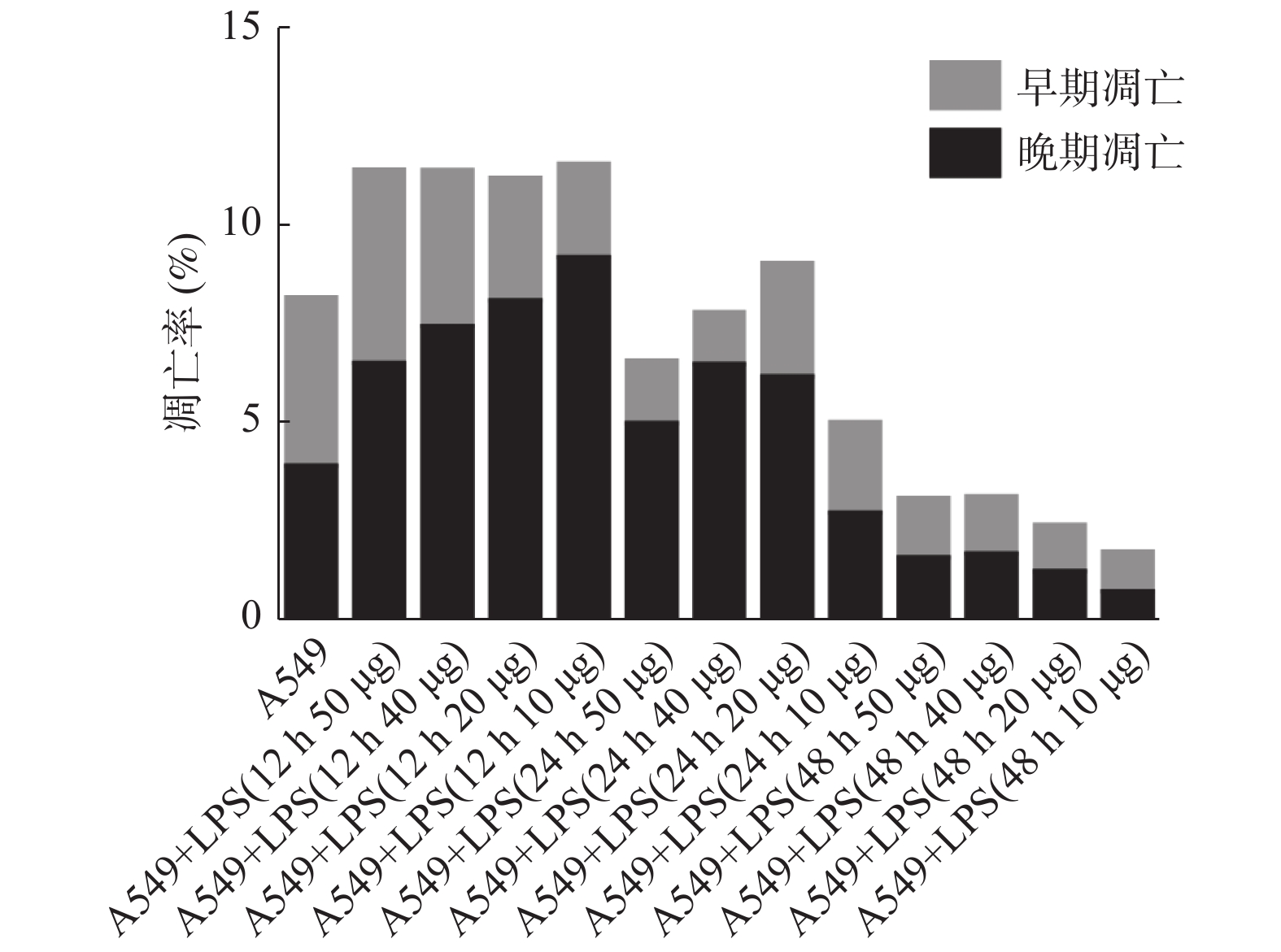
目的 探讨白细胞介素-4(IL-4)在急性肺损伤(acute lung injury,ALI)中的保护作用。 方法 脂多糖(lipopolysaccharide,LPS)诱导A549细胞形成ALI细胞模型。使用不同浓度的IL-4(0.1 μg/mL、1 μg/mL、10 μg/mL)在不同时长下干预该模型,通过流式细胞术检测A549细胞凋亡率,ELISA法测定A549细胞分泌IL-1、IL-6、IL-10、TNF-α、TNF-γ情况。 结果 IL-4可降低ALI模型中A549细胞凋亡率、抑制Caspase3表达(P < 0.05),其效果随IL-4浓度增加及干预时长延长而加强;同时促进Bcl-2表达(P < 0.05),IL-4浓度1 μg/mL干预12 h时效果最佳。上述条件下,IL-4可降低ALI模型中A549细胞的IL-1、IL-6、TNF-α、TNF-γ,并增加IL-10(P < 0.05)。 结论 IL-4可以通过改善ALI体外模型中细胞因子分泌情况,在急性肺损伤中发挥正向调节作用。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the protective effect of interleukin-4 (IL-4) on acute lung injury (ALI). Methods ALI cell models were developed using lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to induce A549 cells. The model was treated with different concentrations of IL-4 (0.1 μg/mL, 1 μg/mL, 10 μg/mL) for different durations. Then the apoptosis rate of A549 cells was detected by flow cytometry, and the secretion of IL-1, IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α, TNF-γ of A549 cells was determined by ELISA. Results IL-4 reduced the apoptosis rate of A549 cells and inhibited the expression of Caspase3 in ALI model (P < 0.05). The effect was enhanced with the increase of IL-4 concentration and the extension of intervention time. IL-4 promoted the expression of Bcl-2 (P < 0.05), and the best effect was achieved when the concentration of IL-4 was 1 μg/mL for 12 h. Under the above conditions, IL-4 decreased IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, TNF-γ and increased IL-10 in A549 cells in ALI model (P < 0.05). Conclusion IL-4 can positively regulate acute lung injury by improving cytokine secretion in ALI in vitro model. -
Key words:
- Acute lung injury /
- Interleukin-4 /
- Lipopolysaccharide /
- Regulatory T cells /
- Cytokines
-
表 1 各组细胞因子分泌情况 (pg/mL)
Table 1. Secretion of cytokines in each group (pg/mL)
分组 IL-1 IL-6 IL-10 TNF-α TNF-γ A549 2.62 43.93 0.91 10.94 74.60 ALI 5.17 62.58 0.31 16.78 89.17 ALI + IL-4 2.34 38.75 0.51 8.35 62.87 -
[1] Luo S,Ding X,Zhao S,et al. Long non-coding RNA CHRF accelerates LPS-induced acute lung injury through microRNA-146a/Notch1 axis[J]. Ann Transl Med,2021,9(16):1299. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-3064 [2] Peukert K,Fox M,Schulz S,et al. Inhibition of caspase-1 with tetracycline ameliorates acute lung injury[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2021,204(1):53-63. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202005-1916OC [3] Garibaldi B T,D’Alessio F R,Mock J R,et al. Regulatory T cells reduce acute lung injury fibroproliferation by decreasing fibrocyte recruitment[J]. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology,2013,48(1):35-43. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0198OC [4] Singer B D,Mock J R,Aggarwal N R,et al. Regulatory T cell DNA methyltransferase inhibition accelerates resolution of lung inflammation[J]. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology,2015,52(5):641-652. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2014-0327OC [5] Kawalkowska J Z,Hemmerle T,Pretto F,et al. Targeted IL-4 therapy synergizes with dexamethasone to induce a state of tolerance by promoting Treg cells and macrophages in mice with arthritis[J]. European Journal of Immunology,2016,46(5):1246-1257. doi: 10.1002/eji.201546221 [6] 赵亚杰,曹江北,米卫东. 肺保护性通气策略在围手术期的应用进展[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志,2016,32(12):1229-1232. [7] Standiford T J,Ward P A. Therapeutic targeting of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distresssyndrome[J]. Translational Research,2016,167(1):183-191. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2015.04.015 [8] 莫磊,朱黎明,戴爱国. 中性粒细胞迁移与肺部疾病的研究进展[J]. 临床与病理杂志,2016,36(4):481-485. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2095-6959.2016.04.026 [9] Gouda M M,Shaikh S B,Bhandary Y P. Inflammatory and fibrinolytic system in acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Lung,2018,196(5):609-616. doi: 10.1007/s00408-018-0150-6 [10] Lin S,Wu H,Wang C,et al. Regulatory T cells and acute lung injury:Cytokines,uncontrolled inflammation,and therapeutic implications[J]. Front Immunol,2018,9(9):1545. [11] 罗超, 曾佐静, 彭顺林. 调节性T细胞在变应性鼻炎免疫应答中的作用[J/OL]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2022, 19(06): 1-15 . [12] 黄洁媛,刘文明. 白细胞介素-4负调控NF-κB通路抑制炎症反应的机制研究[J]. 天津医药,2019,47(10):1025-1029. doi: 10.11958/20191391 [13] Yang W C,Yih-Shiou H,Chen Y Y,et al. Interleukin-4 supports the suppressive immune responses elicited by regulatory T cells[J]. Frontiers in Immunology,2017,8(1):1508. [14] Huaux F,Liu T,McGarry B,et al. Dual roles of IL-4 in lung injury and fibrosis[J]. The Journal of Immunology,2003,170(4):2083-2092. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.4.2083 [15] Wehrmann F,Lavelle J C,Collins C B,et al. γδ T cells protect against LPS-induced lung injury[J]. J Leukoc Biol,2016,99(2):373-386. doi: 10.1189/jlb.4A0115-017RR [16] Farivar A S,Krishnadasan B,Naidu B V,et al. Endogenous interleukin-4 and interleukin-10 regulate experimental lung ischemia reperfusion injury[J]. Ann Thorac Surg,2003,76(1):253-259. doi: 10.1016/S0003-4975(03)00335-7 [17] Witzenrath M,Kuebler W M. The lung-brain axis in ventilator-induced brain injury:Enter IL-6[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol,2021,65(4):339-340. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2021-0233ED [18] Pace L,Pioli C,Doria G. IL-4 modulation of CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cell-mediated suppression[J]. Journal of Immunology,2005,174(12):7645. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.12.7645 [19] Prochazkova J,Fric J,Pokorna K,et al. Distinct regulatory roles of transforming growth factor-β and interleukin-4 in the development and maintenance of natural and induced CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells[J]. Immunology,2009,128(1pt2):670-678. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03060.x [20] 赵磊,冯学斌,王跃嗣,等. 抗ICOS抗体体外对哮喘大鼠血液和淋巴液CD4+CD25+Foxp3+调节性T细胞数量及其功能影响[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2012,28(10):1029-1032,1036. -






 下载:
下载: