Determination of Scopolamine and Atropine in Blood and Urine by LC-MS / MS
-
摘要:
目的 建立曼陀罗中毒人体血液和尿液中东莨菪碱和阿托品的LC-MS/MS检测方法。 方法 采用Shim-pack GISR-HP C18色谱柱,以乙腈-甲酸(0.1%)水溶液为流动相进行梯度洗脱,电喷雾离子源正离子多反应监测模式质谱分析,采用2个特征离子对和外标标准曲线法对曼陀罗中毒人体血液和尿液中东莨菪碱和阿托品进行定性定量分析。 结果 东莨菪碱和阿托品的定量离子对分别为m/z 304.25 [M+H]+→138.15和m/z 290.2 [M+H]+→124.15。东莨菪碱和阿托品在质量浓度1~100 ng/mL范围内线性良好(R≥0.999),检出限(LOD)分别为:血液0.45 ng/mL和0.19 ng/mL,尿液0.38 ng/mL和0.16 ng/mL;定量限(LOQ)分别为:血液1.01 ng/mL和0.63 ng/mL,尿液1.07 ng/mL和0.38 ng/mL;提取回收率分别为:血液94.38%和94.49%,尿液94.96%和96.52%;基质效应为-3.51%~0.84%。2种目标物的准确度为89.38%~102.86%,日内和日间精密度均小于6%。 结论 建立的LC-MS/MS检测方法能快速、准确的测定生物检材中东莨菪碱和阿托品的含量。 Abstract:Objective To develop a LC-MS/MS method for the determination of scopolamine and atropine in human blood and urine after Datura stramonium poisoning. Methods Shim-pack GISR-HP C18 column was used for gradient elution with acetonitrile formic acid (0.1%) as the mobile phase. The electrospray ionization ion source multiple reaction monitoring mode mass spectrometry was used to analyze the scopolamine and atropine by two characteristic ion pairs and the external standard curve method. Results The quantitative ion pairs of scopolamine and atropine were m/z 304.25 [M+H]+→138.15 and m/z 290.2 [M+H]+→124.15, respectively. The linear range of scopolamine and atropine were 1~100 ng/mL (R≥0.999). The limits of detection (LOD) were 0.45 ng/ml and 0.19 ng/ml in blood, 0.38 ng/ml and 0.16 ng/ml in urine; The limits of quantitation (LOQ) were 1.01 ng/ml and 0.63 ng/ml in blood, 1.07 ng/ml and 0.38 ng/ml in urine; The extraction recoveries were 94.38% and 94.49% in blood, 94.96% and 96.52% in urine; The average recoveries of the substances were 94.38% and 94.49% in matrixs. The matrix effects effect was -3.51%~0.84%. The accuracy of substances were 89.38%~102.86%, and the intra day and inter day precisions were less than 6%. Conclusions The method can be used to determine the concentration of scopolamine and atropine in biological samples quickly and accurately. -
Key words:
- LC–MS/MS /
- Blood /
- Urine /
- Scopolamine /
- Atropine
-
表 1 梯度洗脱条件
Table 1. Gradient elution conditions
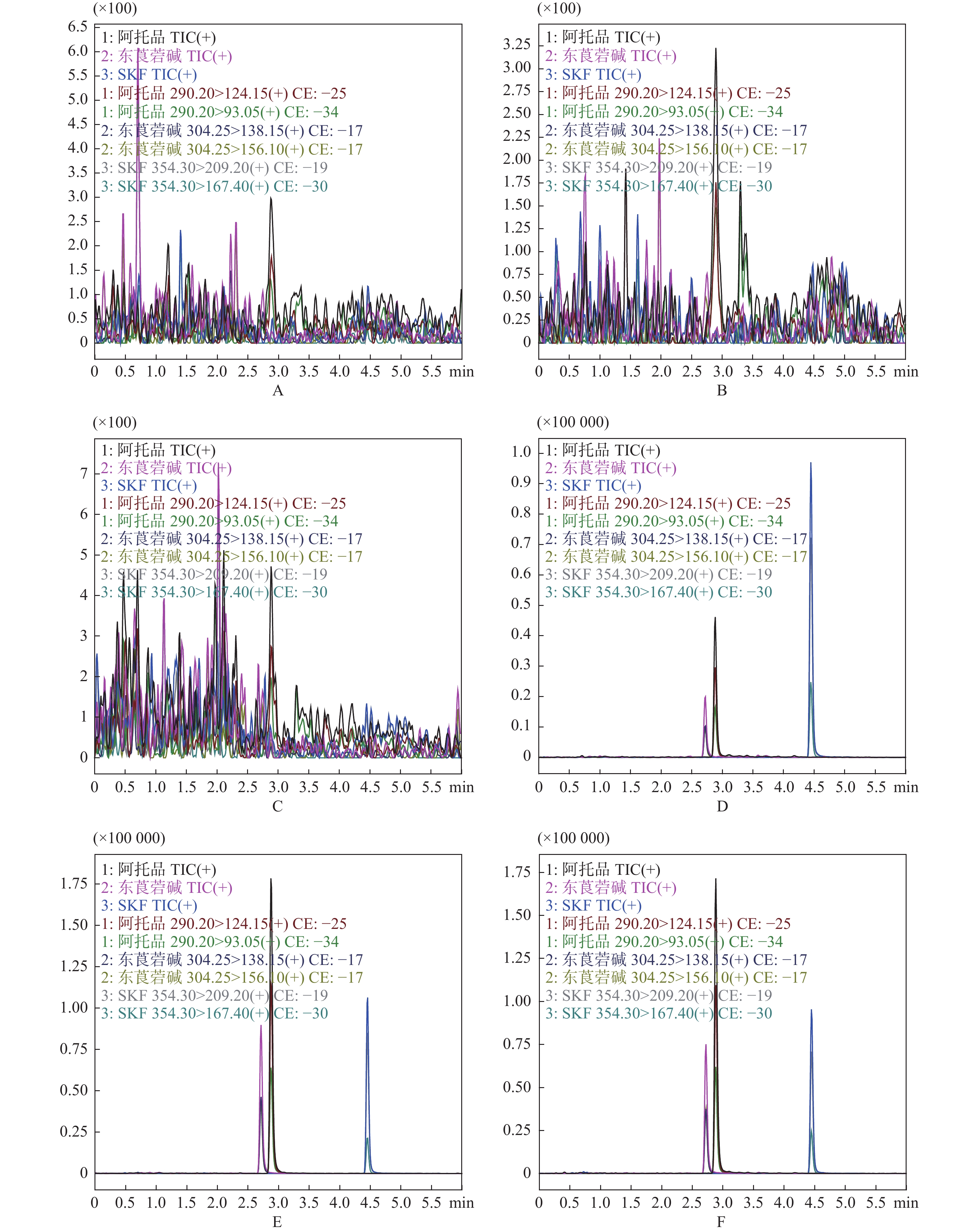
时间(min) 流动相A(%) 流动相B(%) 0.10 90 10 0.80 70 30 2.50 50 50 2.60 30 70 3.50 10 90 4.00 90 10 6.00 90 10 表 2 东莨菪碱和阿托品的检测参数
Table 2. Detection parameters of scopolamine and atropine
目标物 监测离子对 Q1 pre偏差(V) CE(V) Q3 pre偏差(V) 东莨菪碱 304.25 > 138.15 −10 −17 −29 304.25 > 156.10 −19 −17 −15 阿托品 290.20 > 124.15 −18 −25 −22 290.20 > 93.05 −19 −34 −17 东莨菪碱N-氧化物 320.15 > 94.0 −15 −35 −17 320.15 > 154.1 −15 −26 −28 表 3 3种提取方法的提取率比较(高浓度)(%)
Table 3. Comparison of extraction rate of three extraction methods (high concentration)(%)
检材 空白添加东莨菪碱(100 ng/mL) 空白添加阿托品(100 ng/mL) 乙腈直接提取 液-液萃取 固相萃取 乙腈直接提取 液-液萃取 固相萃取 血液 94.23 73.45 35.64 94.44 82.33 34.7 尿液 95.45 72.78 42.78 92.51 84.77 48.09 表 4 3种提取方法提取率比较(中浓度)(%)
Table 4. Comparison of extraction rate of three extraction methods (medium concentration)(%)
检材 空白添加东莨菪碱(50 ng/mL) 空白添加阿托品(50 ng/mL) 乙腈直接提取 液-液萃取 固相萃取 乙腈直接提取 液-液萃取 固相萃取 血液 93.66 68.12 34.23 92.52 81.33 34.58 尿液 96.75 75.79 41.04 89.97 75.38 39.19 表 5 3种提取方法提取率比较(低浓度)(%)
Table 5. Comparison of extraction rate of three extraction methods (low concentration)(%)
检材 空白添加东莨菪碱(10 ng/mL) 空白添加阿托品(10 ng/mL) 乙腈直接提取 液-液萃取 固相萃取 乙腈直接提取 液-液萃取 固相萃取 血液 96.65 70.59 44.33 88.14 79.01 36.44 尿液 93.07 78.29 50.26 96.98 86.29 43.42 表 6 人体血液和尿液中东莨菪碱和阿托品的日内精密度(RSD)
Table 6. Intra day precision of scopolamine and atropine in human blood and urine (RSD)
检材 目标物 加标浓度 10 ng/mL 40 ng/mL 80 ng/mL $\bar x $ ± SD RSD(%) $\bar x $ ± SD RSD(%) $\bar x $ ± SD RSD(%) 空白血添加 东莨菪碱 10.19 ± 0.27 2.62 35.93 ± 0.77 2.14 76.79 ± 1.75 2.28 阿托品 10.15 ± .26 2.58 37.95 ± 0.81 2.13 77.65 ± 1.33 1.71 空白尿添加 东莨菪碱 9.39 ± 0.41 4.36 35.75 ± 1.11 3.09 74.64 ± 1.65 2.21 阿托品 9.95 ± 0.32 3.25 40.45 ± 0.82 2.03 82.29 ± 2.01 2.44 表 7 人体血液和尿液中东莨菪碱和阿托品的日间精密度(RSD)
Table 7. Inter day precision of scopolamine and atropine in human blood and urine (RSD)
检材 目标物 加标浓度 10 ng/mL 40 ng/mL 80 ng/mL $\bar x $ ± SD RSD(%) $\bar x $ ± SD RSD(%) $\bar x $ ± SD RSD(%) 空白血添加 东莨菪碱 10.19 ± 0.56 5.46 35.93 ± 1.84 5.11 76.79 ± 4.52 5.88 阿托品 10.15 ± 0.41 4.06 37.95 ± 1.74 4.59 77.65 ± 3.06 3.94 空白尿添加 东莨菪碱 9.39 ± 0.54 5.77 35.75 ± 2.02 5.64 74.64 ± 3.46 4.63 阿托品 9.95 ± 0.59 5.9 40.45 ± 2.54 5.04 82.29 ± 3.18 3.87 表 8 东莨菪碱和阿托品的准确度
Table 8. Accuracy of scopolamine and atropine
检材 药物名称 加标浓度 10 ng/mL 40 ng/mL 80 ng/mL 准确度(%) 准确度(%) 准确度(%) 空白血液 东莨菪碱 101.9 89.83 95.99 阿托品 101.5 94.88 97.06 空白尿液 东莨菪碱 93.90 89.38 93.30 阿托品 99.50 101.13 102.86 表 9 室温放置36 h后人体血液和尿液中东莨菪碱和阿托品的稳定性试验
Table 9. Stability test of scopolamine and atropine in human blood and urine after 36 hours at room temperature
检材 目标物 添加浓度 10 ng/mL 40 ng/mL 80 ng/mL 偏倚值(%) 偏倚值(%) 偏倚值(%) 血液 东莨菪碱 1.50 4.28 2.34 阿托品 2.30 3.58 1.90 尿液 东莨菪碱 3.80 4.80 2.15 阿托品 3.80 4.88 1.18 表 10 4 ℃冰箱放置4周后人体血液和尿液中东莨菪碱和阿托品的稳定性试验
Table 10. Stability test of scopolamine and atropine in human blood and urine after 4 weeks in 4 ℃ refrigerator
检材 目标物 添加浓度 10 ng/mL 40 ng/mL 80 ng/mL 偏倚值(%) 偏倚值(%) 偏倚值(%) 血液 东莨菪碱 3.40 3.70 1.05 阿托品 0.10 0.68 1.18 尿液 东莨菪碱 1.70 1.45 1.08 阿托品 1.10 0.90 1.85 表 11 东莨菪碱和阿托品在人体血液和尿液中的基质效应
Table 11. Matrix effects of scopolamine and atropine in human blood and urine
检材 目标物 基质效应(%)$ \left[=\dfrac{B}{\mathrm{A}}-1\right]\times 100 $ 10 ng/mL 40 ng/mL 80 ng/mL 基质效应 RSD(%) 基质效应 RSD(%) 基质效应 RSD(%) 血液 东莨菪碱 −1.81 0.3 −2.43 0.72 0.84 1.67 阿托品 −0.12 0.81 −1.05 0.73 −0.84 0.97 尿液 东莨菪碱 −3.24 0.48 −2.47 0.57 −0.73 1.07 阿托品 −3.51 0.19 −1.14 0.59 −0.45 0.40 表 12 案例样品中2种目标物的含量(μg/mL)
Table 12. Contents of two target substances in case samples (μg/mL)
检材 东莨菪碱 阿托品 血液 1.240 0.958 尿液 1.681 83.380 -
[1] 张宏利,杨学军,刘文国,等. 曼陀罗化学成分与生物活性研究现状及展望[J]. 西北林学院学报,2004,19(2):98-102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2004.02.030 [2] Perharič L,Juvan K A,Stanovnik L. Acute effects of a low-dose atropine/ scopolamine mixture as a food contaminant inhuman volunteers[J]. Journal of Applied Toxicology,2013,33(9):980-990. doi: 10.1002/jat.2797 [3] Zhang P,Li Y,Liu G,et al. Simultaneous determination of atropine,scopolamine,and anisodamine from Hyoscyamus niger L. in rat plasmaby high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry and its application to a pharmacokinetics study[J]. Journal of Separation Science,2014,37(19):2664-2674. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201400534 [4] Kintz P,Villain M,Barguil Y,et al. Testing for atropine and scopolamine in hair by LC-MS-MS after datura inoxia abuse[J]. Journal of Analytical Toxicology,2006,30(7):454-457. doi: 10.1093/jat/30.7.454 [5] Tian F,Li C,Wang X,et al. Comparative study on pharmacokinetics of a series of anticholinergics,atropine,anisodamine,anisodine,scopolamine and tiotropium in rats[J]. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet,2015,40(3):245-253. doi: 10.1007/s13318-014-0192-y [6] Lakstygal A M,Kolesnikova T O,Khatsko S L,et al. DARK classics in chemical neuroscience:Atropine,scopolamine,and other anticholinergic deliriant hallucinogens[J]. ACS Chemical Neuroscience,2018,10(5):2144-2159. [7] Juliet N Olayinka,Anthony Eduviere,Olusegun Adeoluwa,et al. Quercetin mitigates scopolamine-induced memory dysfunction:Impact on oxidative stress and cholinergic mechanisms[J]. Metab Brain Dis,2022,37(1):265-277. [8] 侯士果,谷学新,王书妍,等. HPLC测定洋金花中东莨菪碱和阿托品的含量[J]. 中国中药杂志,2006,31(13):1065-1067. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-5302.2006.13.008 [9] 佘彩蒙,杜鸿雁,王芳琳,等. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法检测全血中的东莨菪碱和阿托品[J]. 刑事技术,2017,42(2):133-136. doi: 10.16467/j.1008-3650.2017.02.011 [10] 蒋运斌,苟琰,马逾英,等. 野生山莨菪根的生物碱类成分分析[J]. 时珍国医国药,2015,26(5):1243-1245. [11] 任小娜,马永钧,周敏,等. 毛细管电泳-电致化学发光检测法分离测定中药马尿泡中的托烷类生物碱成分[J]. 色谱,2008,26(2):223-227. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8713.2008.02.016 -






 下载:
下载: