Analysis of Vitamin D Level in Pregnant Women and Infants in Kunming and Study on the Relationship between Fasting Blood Glucose Level and Vitamin D Level during Pregnancy
-
摘要:
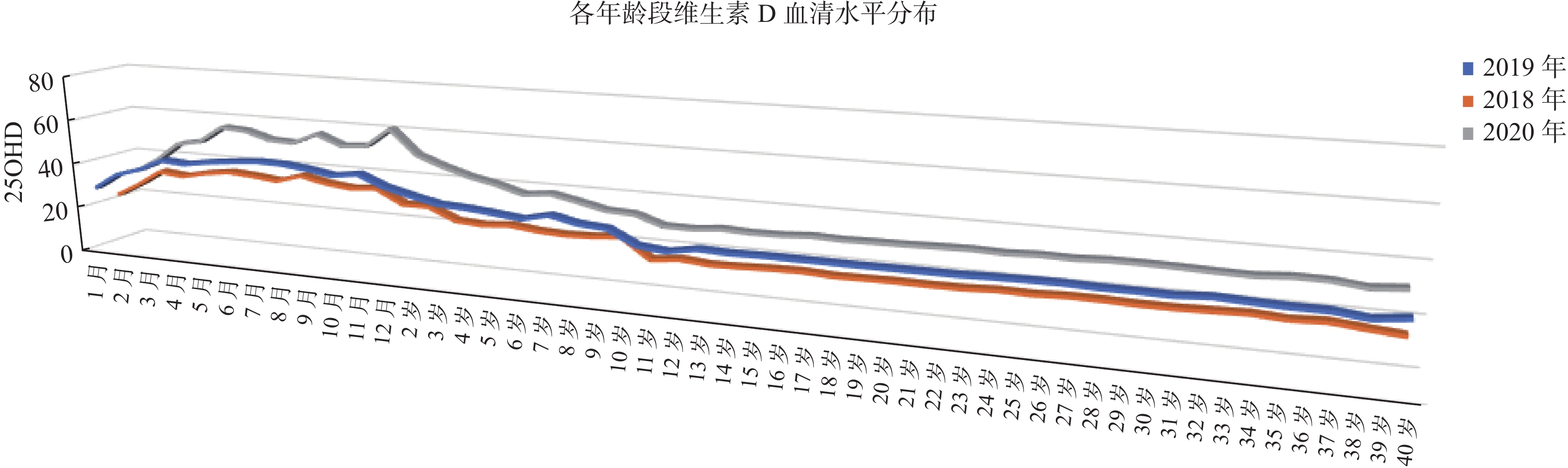
目的 通过分析昆明地区妊娠期妇女和婴幼儿血清25羟维生素D(25OHD)群体水平,了解当地此类人群维生素D营养状况,同时探究维生素D与妊娠期糖尿病发生风险,为补充维生素D提供合理性建议。 方法 采集正常孕妇婴幼儿血清25OHD检测结果和血糖水平等数据,通过SPSS19.0进行数据分析。 结果 昆明地区妊娠期妇女与婴幼儿血清25OHD的 3a整体水平为(20.41±8.08)ng/mL、(29.14±8.89)ng/mL、(31.67±9.77)ng/mL。2018年至2020年血清25OHD缺乏比例由7.31%减少至0.09%,不足比例由66.7%减少至7.95%。孕妇血清25OHD与其血糖水平存在负相关性。 结论 昆明地区妊娠期妇女与婴幼儿血清25OHD整体水平逐年上升,各年龄段的血清25OHD水平呈现出婴幼儿略高,维生素D水平一定程度上对血糖水平存在影响,孕妇适当补维生素D,以食物和适当光照为主,维生素D制剂为辅,不仅有利于防治缺钙等相关疾病,而且有助于稳定妊娠期妇女血糖水平。 Abstract:Objective To understand the vitamin D nutritional status of pregnant women and infants in Kunming by analyzing the serum level of 25 hydroxyvitamin D(25OHD), and to explore the relationship between vitamin D and the risk of gestational diabetes so as to provide reasonable suggestions for vitamin D supplementation. Methods The serum 25OHD and blood glucose levels of normal pregnant women and infants were collected and analyzed by SPSS19.0. Results The overall levels of serum 25OHD in pregnant women and infants in Kunming were (20.41±8.08)ng/mL, (29.14±8.89)ng/mL and (31.67±9.77)ng/mL. From 2018 to 2020, the deficiency rate of serum 25OHD decreased from 7.31% to 0.09%, and the deficiency rate decreased from 66.7% to 7.95%. There was a negative correlation between serum 25OHD and blood glucose level in pregnant women. Conclusion The overall level of serum 25OHD in pregnant women and infants in Kunming has been increasing year by year, and the level of serum 25OHD in all ages shows a slightly higher level in infants. Vitamin D level has an impact on blood glucose level to some extent. Pregnant women should take vitamin D supplements, mainly with food and sunshine, appropriate light, supplemented by vitamin D preparation.It is not only beneficial to the prevention and treatment of which can not only prevent the calcium deficiency and other related diseases, but also helps to stabilize the blood sugar level of women during pregnancy. -
Key words:
- Vitamin D /
- Pregnant woman /
- Infants and young children /
- Blood sugar
-
表 1 2018年至2020年孕妇和婴幼儿血清25羟维生素D水平分布情况[n(%)]
Table 1. Distribution of serum 25 hydroxyvitamin D levels in pregnant women and infants from 2018 to 2020 [n(%)]
年份 分组 n 41~80
(ng/mL)31~40
(ng/mL)21~30
(ng/mL)11~20
(ng/mL)0~10
(ng/mL)2018年 孕妇 16755 47(0.28) 732(4.37) 5677(33.88) 9251(55.21) 1048(6.25) 婴幼儿 2646 469(17.72) 852(32.20) 993(37.53) 304(11.49) 28(1.06) 2019年 孕妇 19014 757(3.98) 5518(29.02) 10537(55.42) 2112(11.11) 90(0.47) 婴幼儿 2954 1281(43.36) 1029(34.83) 517(17.50) 124(4.20) 3(0.10) 2020年 孕妇 12905 1097(8.50) 4938(38.26) 6105(47.31) 762(5.90) 3(0.02) 婴幼儿 1460 892(61.10) 397(27.19) 140(9.59) 30(2.05) 1(0.07) 表 2 孕妇25OHD血清水平与血糖水平的相关性分析结果
Table 2. Correlation analysis results of serum 25OHD level and blood glucose level in pregnant women
检测年限 n 25OHD (ng/mL) 空腹血糖 (mmol/L) r P 2018 14 620 18.12 ± 5.88 4.59 ± 0.52 −0.043 < 0.01 2019 16 437 25.54 ± 6.77 4.57 ± 0.41 −0.341 < 0.01 2020 11 252 29.56 ± 6.76 4.65 ± 0.46 −0.046 < 0.01 表 3 不同25OHD水平孕妇空腹血糖高于正常值比例[n(%)]
Table 3. Proportion of pregnant women with different 25OHD levels with higher than normal fasting blood glucose [n(%)]
25OHD水平(ng/mL) 孕妇(n) 空腹血糖> 5.1 mmol/L χ2 P 0~10 1 133 215(18.98) 832.182 0.000 11~20 12 222 2166(17.72) 21~30 19 738 1740(8.82) > 30 9 216 677(7.35) -
[1] 王汐蕊,余晓丹,张丽珊,等. 健康学龄前351名儿童25-羟维生素D水平及影响因素[J]. 中国儿童保健杂志,2020,28(10):1101-1105. [2] 张玉,武常倩,马晓英,等. 妇女孕前和孕期维生素D水平及影响因素[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志,2020,24(1):41-45. [3] 陈莉莉,区肇真,夏伟桃. 婴幼儿血清25-羟维生素D3影响因素分析及药物联合行为干预的效果[J]. 中国卫生标准管理,2020,11(14):98-100. [4] 陈寒,刘海艳,宋慧颖,等. 妊娠早期血清维生素D水平与妊娠期糖尿病发病率和严重程度的关系[J]. 中国生育健康杂志,2020,31(2):123-126. [5] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会. 维生素D及其类似物临床应用共识[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2018,11(1):1-19. [6] 程红,李海波,侯冬青,等. 学龄儿童维生素D营养状况与身体肌肉量关系的研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志,2021,42(3):455-461. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20201130-01360 [7] 郑倩,唐哲,彭葆坤,等. 甲状腺癌患者1,25-(OH)2D3水平变化及临床价值[J]. 云南医药,2020,41(5):425-428. [8] 谢忠建,程群,丁悦. 维生素D代谢和作用[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂质,2018,11(1):26-33. [9] 李艳红,张娴,张俊涛,等. 昆明市呼吸道感染儿童维生素D营养状况[J]. 昆明医科大学学报,2018,39(11):67-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4706.2018.11.016 [10] 尹万军, 张梦笑, 张英, 等 . 妊娠中期维生素D水平与GDM发生风险的相关性[J]. 中华妇产科杂志, 2019, 54(11): 763-769. [11] 付林,陈远华,于震. 母体孕期维生素D缺乏诱发胎儿生长受限[J]. 中国药理学通报,2021,37(4):591-592. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2021.04.026 [12] 魏占超,李光辉. 孕期维生素D水平与母儿结局的相关研究进展[J]. 中华全科医师杂志,2021,20(2):239-243. [13] 杨玲蓉,李桦,张彤. 维生素 D 缺乏与早产儿坏死性小肠结肠炎的相关性[J]. 中国当代儿科杂志,2018,20(3):178-183. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2018.03.003 [14] 杨敏. 妊娠期糖尿病患者血清25-羟维生素D水平及胰岛素抵抗的关系[J]. 中国妇幼保健,2013,28(28):4639-4641. doi: 10.7620/zgfybj.j.issn.1001-4411.2013.28.16 [15] 中国老年学学会骨质疏松委员会维生素D学科组专家委员会. 维生素D与成年人骨骼健康应用指南(2014年标准版)[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,20(9):1011-1030. -






 下载:
下载: