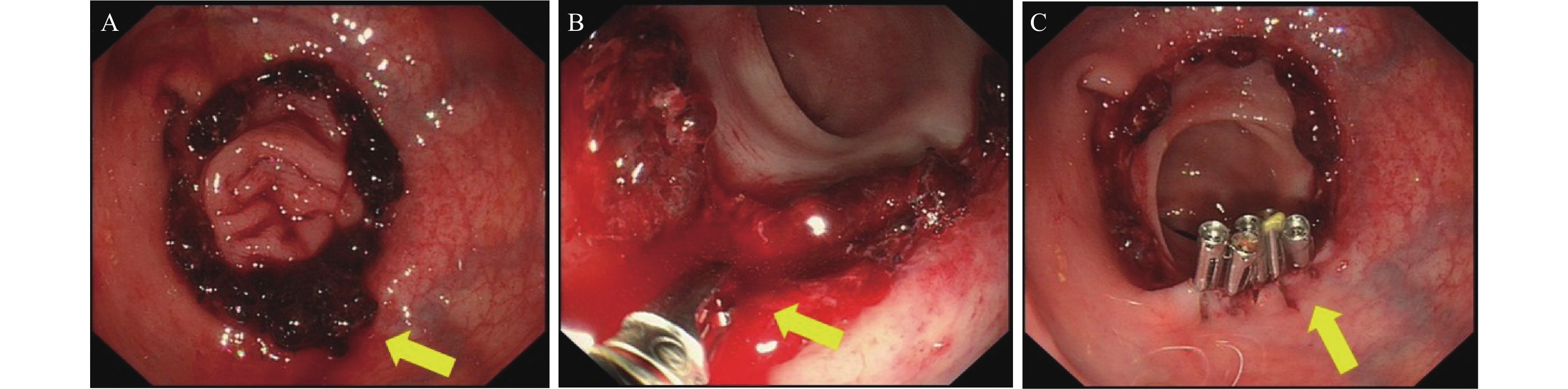
Effect Analysis of Emergency Endoscopic Treatment for Anastomotic Hemorrhage after Colorectal Cancer Resection
-
摘要:
目的 分析结直肠癌外科切除术后吻合口出血患者急诊内镜下止血的疗效。 方法 收集2005年1月至2021年12月解放军联勤保障部队第908医院结直肠肿瘤外科切除术后吻合口出血,进行急诊内镜止血治疗患者的临床资料。分析患者的人口学资料、肿瘤部位、肿瘤分期及病理类型资料,重点分析吻合口出血的时间、内镜下治疗的方法、效果及并发症,并且对未能成功内镜下止血的原因进行总结。 结果 在1 058名结直肠癌手术患者中,吻合口出血患者36名,出血率为3.4%。出血患者以左半结肠及直肠居多(83.3%)。在肿瘤分期和分化方面,以Ⅰ到Ⅲ期为主,占总人数的82.1%,病理以高分化和中分化癌为主(86.1%)。术后72 h内出血患者26例(72.2%),是出血的高发时间段。在36例患者中,内镜下成功止血32例(88.9%),钛夹机械夹闭、电凝止血联合钛夹夹闭是主要的方式(88.9%)。未能止血4例,均伴有漏口,无法明确确切的出血位点,经外科手术治疗后均成功止血。所有36例患者最终均未出现吻合口漏、腹腔脓肿及死亡等严重并发症。 结论 结直肠癌术后72 h内是吻合口出血的高峰时期,急诊内镜下止血是安全有效的治疗手段。 Abstract:Objective To analyze the efficacy of emergency endoscopic hemostasis in patients with anastomotic hemorrhage after surgical resection of colorectal cancer. Methods The clinical data of patients with anastomotic hemorrhage after surgical resection of colorectal tumor and emergency endoscopic hemostasis were collected from January 2005 to December 2021 in 908th hospital of The People's Liberation Army Joint Logistic Support Force. The demographic data, tumor site, tumor stage and pathological type were analyzed. Of which, the time of anastomotic hemorrhage, hemostasis methods, effects and complications of endoscopic treatment, and the reasons for the failure of endoscopic hemostasis were analyzed selectively. Results Among 1 058 patients undergoing colorectal cancer surgery, 36 patients had anastomotic bleeding (3.4%). The left colon and rectum cancer were the most patients with hemorrhage (83.3%). In terms of tumor staging and differentiation, most of the patients were from stage Ⅰ to stage Ⅲ (82.1%). The pathology was dominated by highly and moderately differentiated cancers (86.1%). Anastomotic hemorrhage occurred within 72 hours after surgical resection in 26 patients (72.2%), which was the time of high incidence of hemorrhage. Among the 36 patients, endoscopic hemostasis was successful in 32 cases (88.9%), in which titanium clip and electrocoagulation combined with titanium clip were the main hemostasis methods (88.9%). Beside, 4 patients failed to hemostasis by endoscopy, all of them had anastomotic leakage and could not identify the exact bleeding site, and all successfully hemostasis by surgical treatment. No serious complications such as anastomotic leakage, abdominal abscess or death occurred in all 36 patients. Conclusion The peak period of anastomotic hemorrhage is within 72 hours after surgical resection for colorectal cancer. Emergency endoscopic hemostasis is a safe and effective treatment for anastomotic hemorrhage. -
Key words:
- Colorectal cancer /
- Anastomotic hemorrhage /
- Endoscopic hemostasis /
- Effect analysis
-
表 1 吻合口出血患者资料[n(%)]
Table 1. The clinical data of patients with anastomotic hemorrhage [n (%)]
项目 [n(%)] 性别(男/女) 24/12 年龄(岁) 32~86(60.4±12.7) 肿瘤部位 右半结肠 5(13.9) 横结肠 1(2.8) 左半结肠 12(33.3) 直肠 18(50) 肿瘤分期 0 2(5.6) Ⅰ 10(27.8) Ⅱ 11(30.5) Ⅲ 10(27.8) Ⅳ 3(8.3) 肿瘤病理类型 高级别上皮内瘤变 3(8.3%) 高分化腺癌 17(47.2) 中分化腺癌 14(38.9) 低分化腺癌 2(5.6) 表 2 吻合口出血时间、止血方式、成功率及并发症[n(%)]
Table 2. The time of anastomotic hemorrhage,hemostasis methods,effects and complications of endoscopic hemostasis [n (%)]
项目 [n(%)] 出血时间(h) 2~192(61.8±63.4) 时间节段(h) < 24 8(22.2) 24~72 18(50) > 72 10(27.8) 止血方式 去甲肾上腺素稀释液 3(8.3) 电凝止血 1(2.8) 钛夹夹闭 16(44.4) 联合应用 16(44.4) 成功止血 32(88.9) 未成功止血 4(11.1) 出血伴有漏口 4(11.1) 并发症 0(0.0) -
[1] Wu Y,Li Y,Giovannucci E. Potential impact of time trend of lifestyle risk factors on burden of major gastrointestinal cancers in china[J]. Gastroenterology,2021,161(6):1830-1841. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.08.006 [2] Sung H,Ferlay J,Siegel R L,et al. Global cancer statistics 2020:GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin,2021,71(3):209-249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660 [3] Zheng R,Zhang S,Zeng H,et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in china,2016[J]. Journal of the National Cancer Center,2022,2(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jncc.2022.02.002 [4] Shi J F,Wang L,Ran J C,et al. Clinical characteristics,medical service utilization,and expenditure for colorectal cancer in China,2005 to 2014:Overall design and results from a multicenter retrospective epidemiologic survey[J]. Cancer,2021,127(11):1880-1893. doi: 10.1002/cncr.33445 [5] Davis B,Rivadeneira D E. Complications of colorectal anastomoses:leaks,strictures,and bleeding[J]. Surg Clin North Am,2013,93(1):61-87. doi: 10.1016/j.suc.2012.09.014 [6] Hébert J,Eltonsy S,Gaudet J,et al. Incidence and risk factors for anastomotic bleeding in lower gastrointestinal surgery[J]. BMC Res Notes,2019,12(1):378. doi: 10.1186/s13104-019-4403-0 [7] 崔英姿,杨东辉,王晓凤. 吻合口溃疡出血的内镜下特点及治疗[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志,2010,09(15):1125-1127. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2010.15.003 [8] Steger J,Jell A,Ficht S,et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis on colorectal anastomotic techniques[J]. Ther Clin Risk Manag,2022,18:523-539. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S335102 [9] 沈伯明,俞伟君,王永锋. 结直肠癌术后吻合口早期出血的原因及预防措施[J]. 临床医学,2018,38(10):33-34. doi: 10.19528/j.issn.1003-3548.2018.10.011 [10] Fakas S,Elias M,Lim D,et al. Comparison of gastrojejunostomy techniques and anastomotic complications:a systematic literature review[J]. Surg Endosc,2021,35(12):6489-6496. doi: 10.1007/s00464-020-08142-x [11] Perez R O,Sousa A Jr,Bresciani C,et al. Endoscopic management of postoperative stapled colorectal anastomosis hemorrhage[J]. Tech Coloproctol,2007,11(1):64-66. doi: 10.1007/s10151-007-0330-5 [12] 吴轲,古俊楠,曹英豪,等. 急诊内镜诊疗在结直肠癌根治术后吻合口出血中的应用[J]. 腹部外科,2021,34(1):40-43. [13] Malik A H,East J E,Buchanan G N,et al. Endoscopic hemostasis of staple-line hemorrhage following colorectal resection[J]. Colorectal Disease,2010,10(6):616-618. [14] Gralnek I M,Stanley A J,Morris A J,et al. Endoscopic diagnosis and management of nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage (NVUGIH):European society of gastrointestinal endoscopy (ESGE) guideline - update 2021[J]. Endoscopy,2021,53(3):300-332. doi: 10.1055/a-1369-5274 [15] Wichmann D,Fusco S,Werner C R,et al. Endoscopic management for post-surgical complications after resection of esophageal cancer[J]. Cancers (Basel),2022,14(4):980. doi: 10.3390/cancers14040980 -






 下载:
下载: