Epidemic Trends and Characteristics of Hypertension among Primary and Secondary Students from 2017 to 2020 in Kunming,Yunnan
-
摘要:
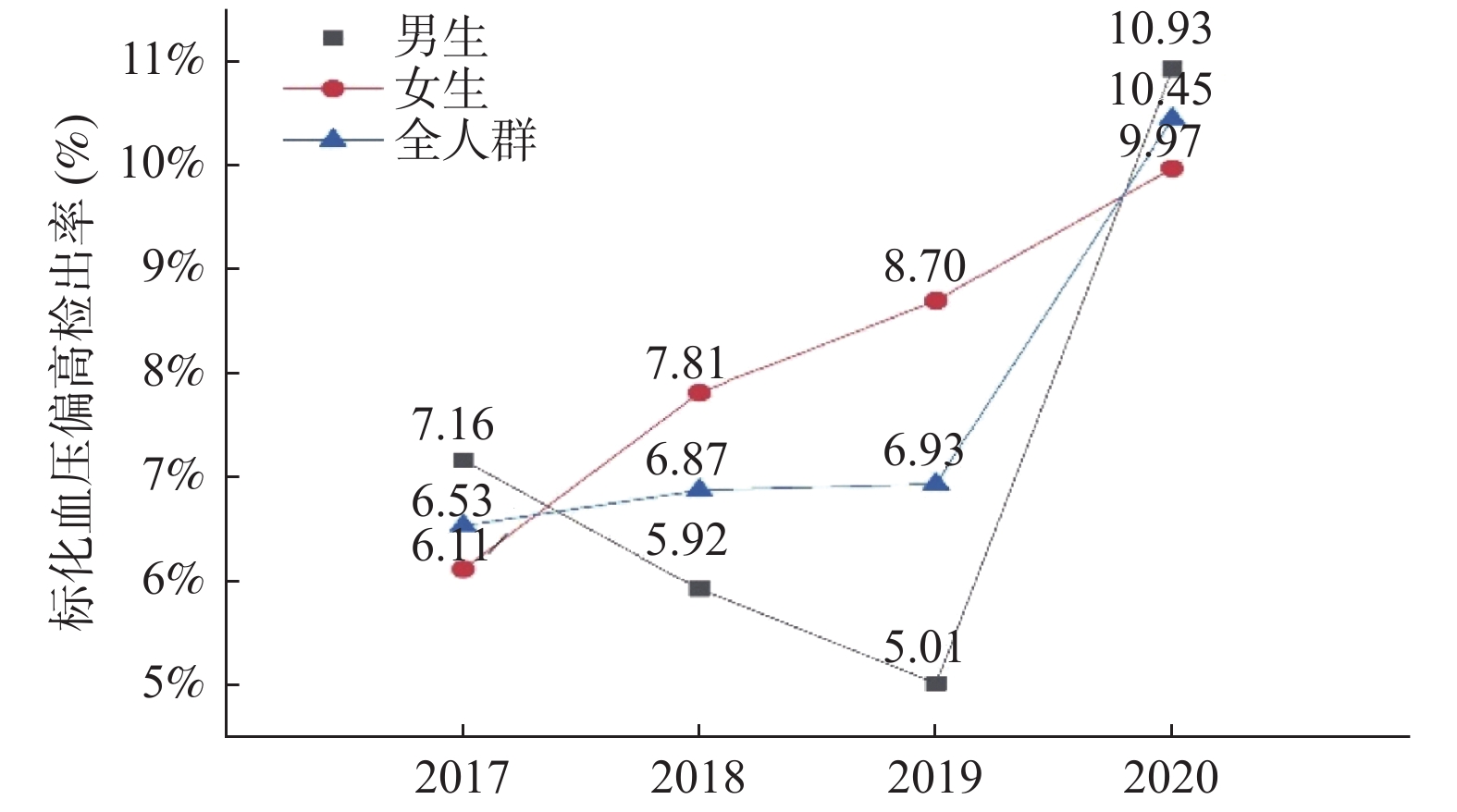
目的 分析昆明市中小学生血压偏高的流行趋势、分布特征,为制定昆明市中小学生高血压的预防干预策略提供科学依据。 方法 采用多阶段分层随机整群抽样的方法,随机抽取云南省昆明市2个县(区)11所学校9至18岁中小学生,进行现场体格测量及问卷调查。本研究共调查12 026人。 结果 昆明市中小学生血压偏高的检出率为8.15%,标化检出率为7.85%。中小学生血压偏高呈现逐年上升的趋势(P < 0.01)。流行特征为:随着年龄的增加,患血压偏高的风险也相应的增加(P < 0.01);男生高于女生(P < 0.01);汉族学生血压偏高检出水平上升较快,年平均上升1.11%(P < 0.01);城区学生高于郊/县区学生,但郊/县区学生血压偏高检出水平上升速度快于城区学生, 年平均上升2.78%(P < 0.01);超重(OR = 2.45)、肥胖(OR = 4.78)是血压偏高的高危人群(P < 0.05)。 结论 昆明市中小学生血压偏高问题不容忽视,应尽快开展昆明市中小学生高血压的危险因素探究,以降低中小学生不健康行为生活方式的发生,从而减少成人高血压、冠心病和脑卒中等慢性病的发生。 Abstract:Objectives To analyze the prevalence trend and epidemic characteristics of hypertension among primary and middle school students in Kunming, and to provide scientific basis for the formulation of prevention and intervention strategies for hypertension among children and adolescents in Kunming. Methods A multi-stage stratified random cluster sampling was used to randomly select students aged 9 to 18 from 11 primary and secondary schools in 2 counties (districts) of Kunming, Yunnan. A total of 12,026 people were surveyed. Results The detection rate of hypertension in primary and secondary school students of Kunming was 8.15% and the standardized detection rate was 7.85%. The hypertension of primary and middle school students was increasing year by year (P < 0.01). The prevalence of hypertension increased with age (P < 0.01); Boys were higher than girls (P < 0.01); The prevalence of hypertension in Han students increased faster than those of minority (P < 0.01). Urban students were higher than suburban/county students, but the elevated blood pressure level of the suburban/county students increased faster than the urban students (P < 0.01). Overweight (OR = 2.45) and obesity (OR = 4.78) were high-risk groups with hypertension (P < 0.05). Conclusions The problem of hypertension among primary and secondary school students in Kunming cannot be ignored, and the risk factors of hypertension should be explored as soon as possible. In order to reduce the occurrence of unhealthy behaviors in primary and secondary school students, so as to reduce the occurrence of chronic diseases such as adult hypertension, coronary heart disease and stroke. -
Key words:
- Students /
- Children /
- Adolescents /
- Hypertension /
- Epidemic trends /
- Characteristics
-
表 1 2017年至2020年昆明市中小学生不同分组基本情况表(n)
Table 1. The basic situation of different groups among primary and middle school students in Kunming from 2017 to 2020 (n)
变量 2017年 2018年 2019年 2020年 合计 性别 男 1246 1407 1515 1686 5854 女 1447 1458 1635 1632 6172 年龄(岁) 9~ 952 1137 1328 1331 4748 13~ 939 903 1005 1092 3939 16~18 802 825 817 895 3339 民族 汉族 2317 2437 2677 2604 10193 少数民族 376 428 473 714 1833 城乡 城区 1631 1675 1835 1915 7056 郊/县区 1062 1190 1315 1403 4970 地区 呈贡区 1631 1675 1835 2771 7912 富民县 1062 1190 1315 547 4114 营养状况 偏瘦 216 274 423 256 1169 正常 1877 1960 1136 2239 7212 超重 376 374 388 456 1594 肥胖 224 248 243 358 1073 合计 2693 2856 2190 3309 12026 表 2 2017年2020年昆明市中小学生血压偏高人群流行特征情况(n)
Table 2. The epidemic characteristics of hypertension among primary and middle school students in Kunming in 2017 and 2020 (n)
变量 2017年 2018年 2019年 2020年 χ2/F P 总人数 血压偏
高人数检出率
(%)总人数 血压偏
高人数检出率
(%)总人数 血压偏
高人数检出率
(%)总人数 血压偏
高人数检出率
(%)性别 男 1246 90 7.22 1407 89 6.33 1515 82 5.41 1686 181 10.74 37.638 < 0.001** 女 1447 94 6.50 1458 119 8.16 1635 152 9.30 1632 173 10.60 17.500 0.001** 年龄(岁) 9~ 953 40 4.20 1137 78 6.86 1328 99 7.45 1331 123 9.24 21.531 < 0.001** 13~ 939 66 7.03 903 68 7.53 1005 88 8.76 1092 133 12.18 20.362 < 0.001** 16~18 802 78 9.73 825 62 7.52 817 47 5.75 895 98 10.95 17.341 0.001** 民族 汉族 2317 147 6.34 2437 183 7.51 2677 188 7.02 2604 281 10.79 40.618 < 0.001** 少数民族 376 37 9.84 428 25 5.84 473 46 9.73 714 73 10.22 7.065 0.070 地区 呈贡区 1631 165 10.12 1675 151 9.01 1835 148 8.07 2771 285 10.29 7.572 0.056 富民县 1062 19 1.79 1190 57 4.79 1315 86 5.81 547 69 12.61 83.548 < 0.001** 城乡 城区 1631 165 10.12 1675 151 9.01 1835 148 8.07 1915 173 9.03 54.275 < 0.001** 郊/县区 1062 19 1.79 1190 57 4.79 1315 86 5.81 1403 181 12.90 30.491 < 0.001** 营养状况 偏瘦 216 9 4.17 274 16 5.84 423 18 4.26 256 14 5.47 1.328 0.723 正常 1877 97 5.17 1969 114 5.79 2096 130 6.20 2248 193 8.59 23.434 < 0.001** 超重 376 35 9.31 374 32 8.56 388 44 11.34 456 67 14.69 9.606 0.022* 肥胖 224 43 19.20 248 46 18.55 243 42 17.38 358 80 22.35 0.728 0.435 *P < 0.05,**P < 0.01。 表 3 昆明市中小学生营养状况对血压偏高的影响
Table 3. The influence of nutritional status on high blood pressure among primary and middle school students in Kunming
影响因素 β S.E χ2 P OR 95%CI 营养状况:正常 − − 232.217 < 0.001** − − 偏瘦 0.308 0.143 4.640 0.031* 1.361 1.028~1.801 超重 0.897 0.157 32.491 < 0.001** 2.452 1.801~3.338 肥胖 1.563 0.156 100.418 < 0.001** 4.775 3.517~6.484 常数 −2.971 0.136 478.554 < 0.001** 0.051 − *P < 0.05,**P < 0.01。 -
[1] 杨巧玲,晏晓颖,安康,等. 北京市海淀区9-14岁儿童营养过剩和血压偏高关系分析[J]. 中国学校卫生,2010,31(10):1273-1274. [2] 邓晓娟,晏晓颖,徐亮,等. 广州市中学生血压偏高状况及其相关因素分析[J]. 中国学校卫生,2010,31(7):816-817. [3] 陈昭,沈维高,张小刚,等. 吉林市中小学生血压分布现状分析[J]. 华北大学学报,2002,3(1):34-37. [4] 杨云娟,常利涛,陈露,等. 云南省部分少数民族儿童青少年血压分布特征[J]. 中国学校卫生,2016,37(1):16-19. [5] Yang Y J,Min J Q,Chang L T,et al. Prevalence trends of hypertension among 9-17 aged children and adolescents in Yunnan,2017-2019:a serial cross-sectional surveillance survey[J]. BMC Public Health,2021,21(1):338. [6] 杨云娟,常利涛,吕慧,等. 中国部分民族儿童青少年超重肥胖流行态势及影响因素[J]. 中国学校卫生,2016,37(8):1147-1150. [7] 陶芳标. 儿童少年卫生学(第8版)[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2017: 188-189. [8] 中国肥胖问题工作组. 中国学龄儿童青少年超重、肥胖筛查体重指数值分类标准[J]. 中华流行病学杂志,2004,25(2):97-102. doi: 10.3760/j.issn:0254-6450.2004.02.003 [9] 中国学生体质与健康研究组. 2005年中国学生体质与健康研究报告[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2008: 49-62. [10] 季成叶主编. 现代儿童少年卫生学 [M]. 第2版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2010: 798-802. [11] Rosner B,Prineas R,Daniels S R,et al. Blood pressure differences between blacks and whites in relation to body size among US children and sdolescents[J]. Am J Epidemiol,2000,151(10):1007-1019. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a010129 [12] Cheung Y B,Machin D,Karlberg J,et al. A longitudinal study of pediatric body mass index values predicted health in middle age[J]. J Clin Epidemiol,2004,57(12):1216-1322. [13] 金仲和,王晓琴. 儿童血压发育规律的研究[J]. 实用儿科临床杂志.,2005,20(3):270-271. [14] Ingelfinger J R. Pediatric antecedents of adult cardiovascular disease-awareness and intervention[J]. N Eng J Med,2004,350(21):2123-2126. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp048069 [15] 杨硕,郭红卫. 小学生肥胖及代谢异常对血压影响的病例对照研究[J]. 中国学校卫生,2014,35(10):1472-1474. [16] Chen X,Wang Y. Tracking of blood pressure from childhood to adulthood:a systematic review and met a-regression analysis[J]. Circulation,2008,117(25):3171-3180. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.730366 -






 下载:
下载: