Effects of Puerarin on Th17/Treg Cell Immune Homeostasis and the Expression of Related Transcription Factors in Rats with Periodontitis
-
摘要:
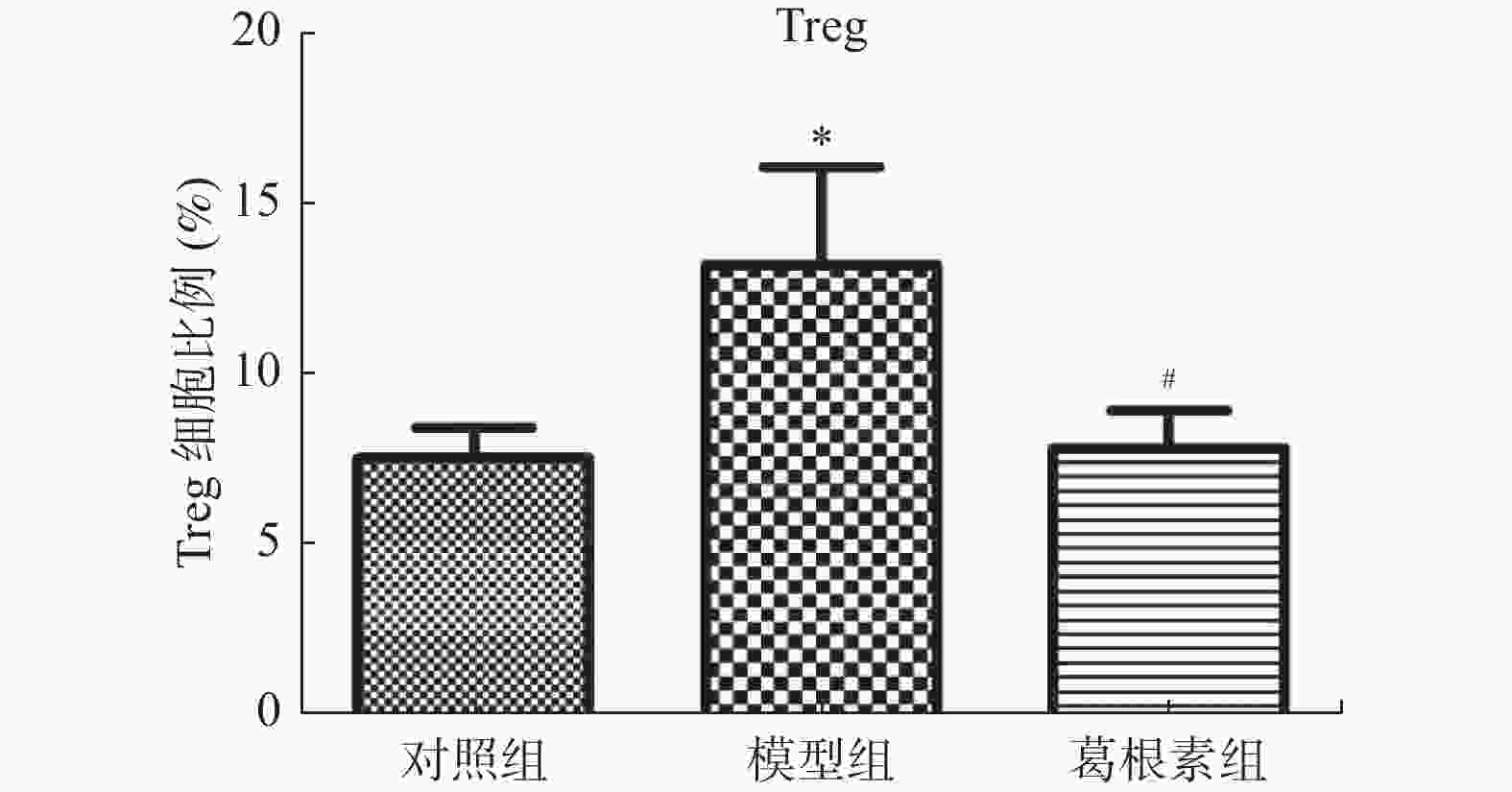
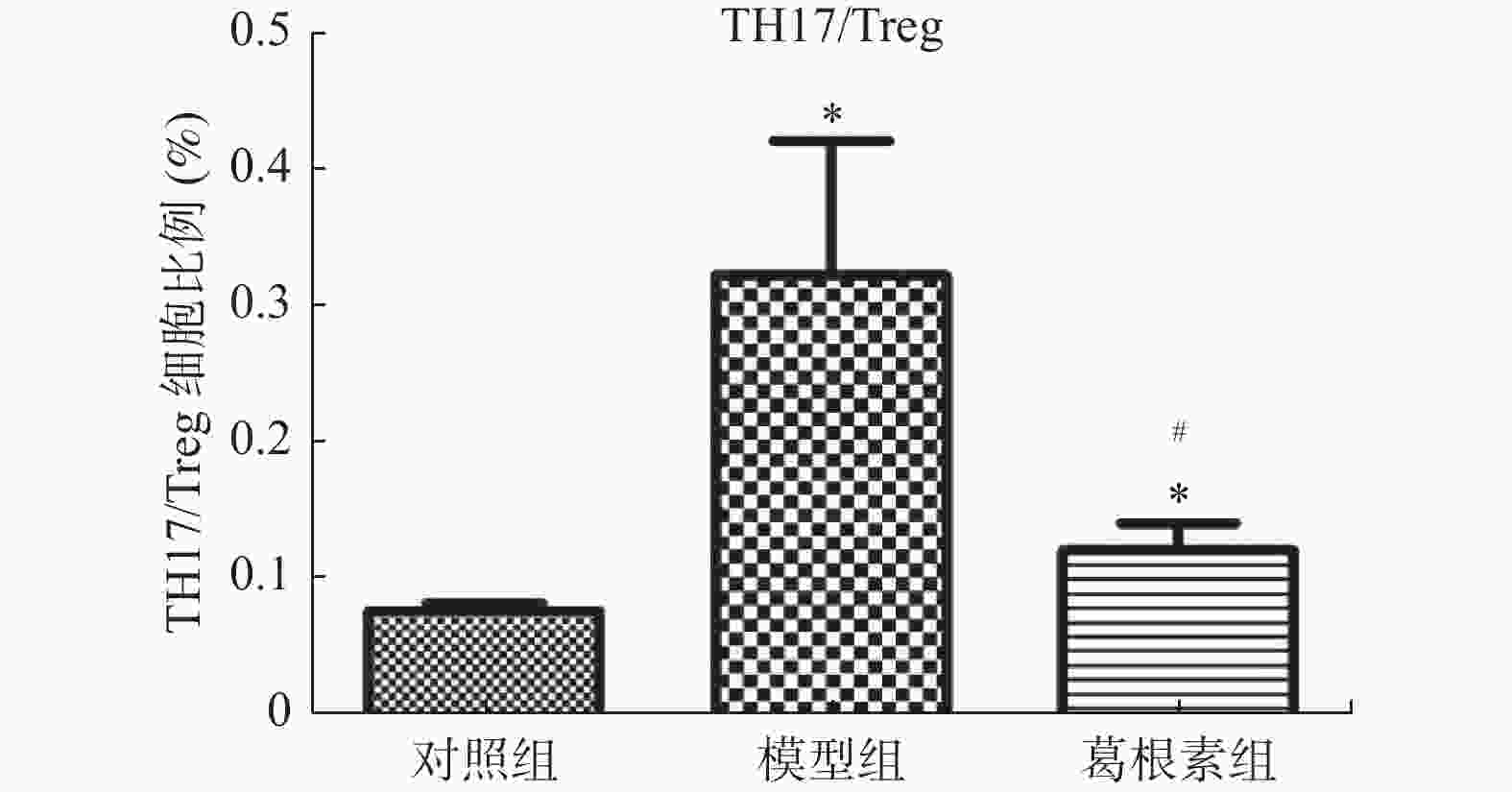
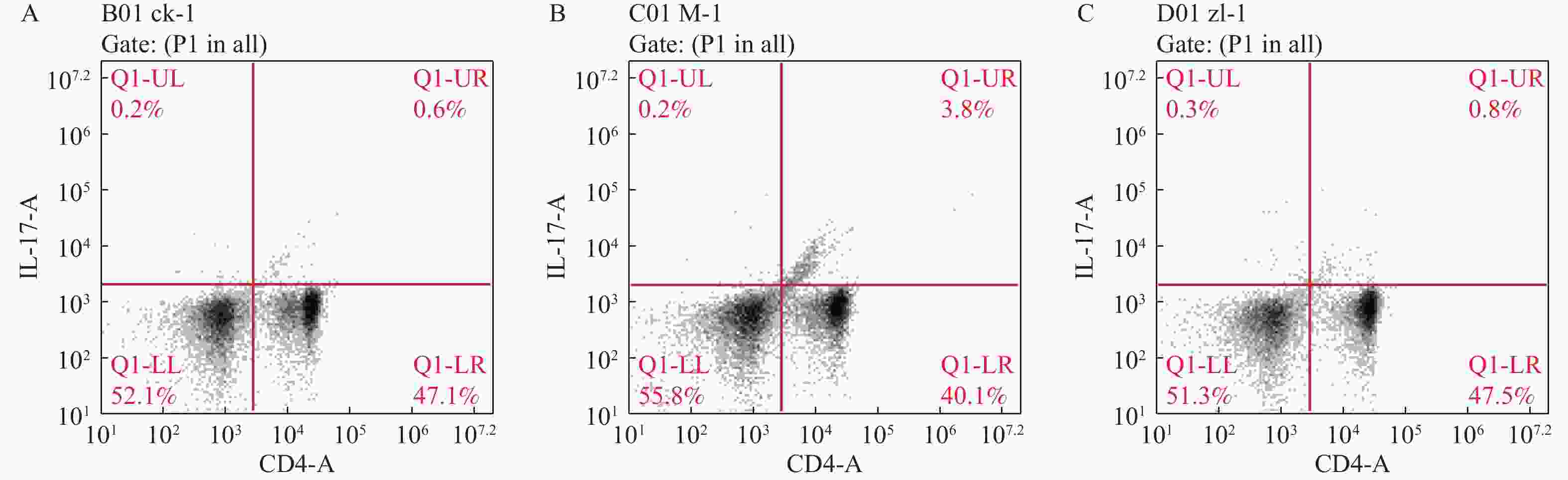
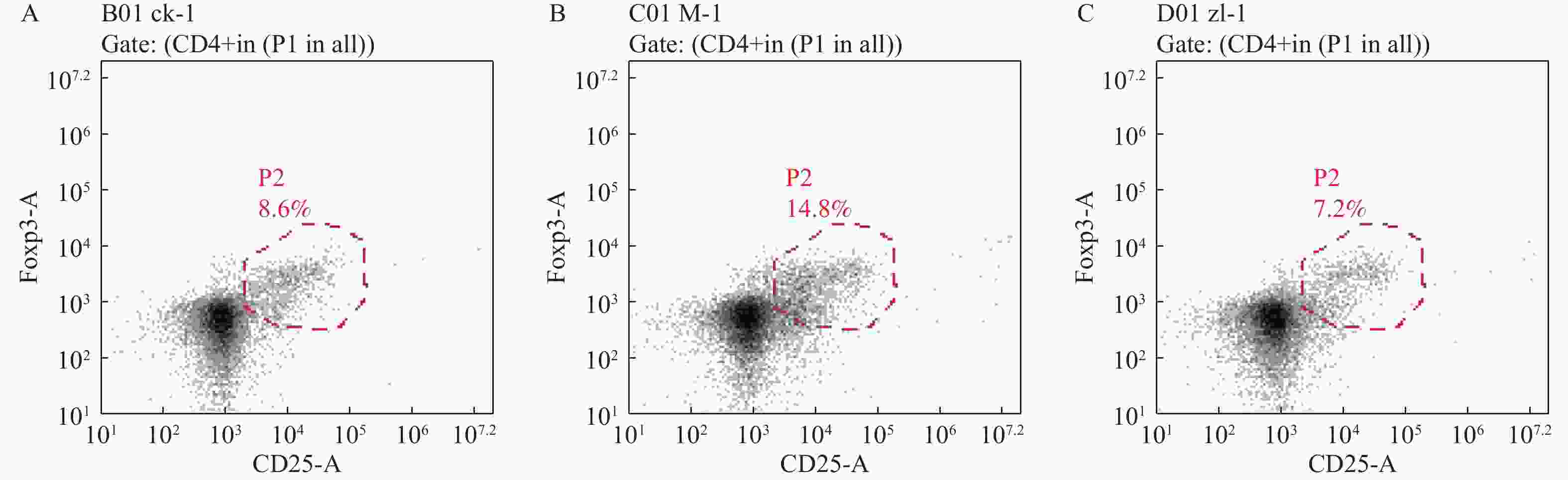
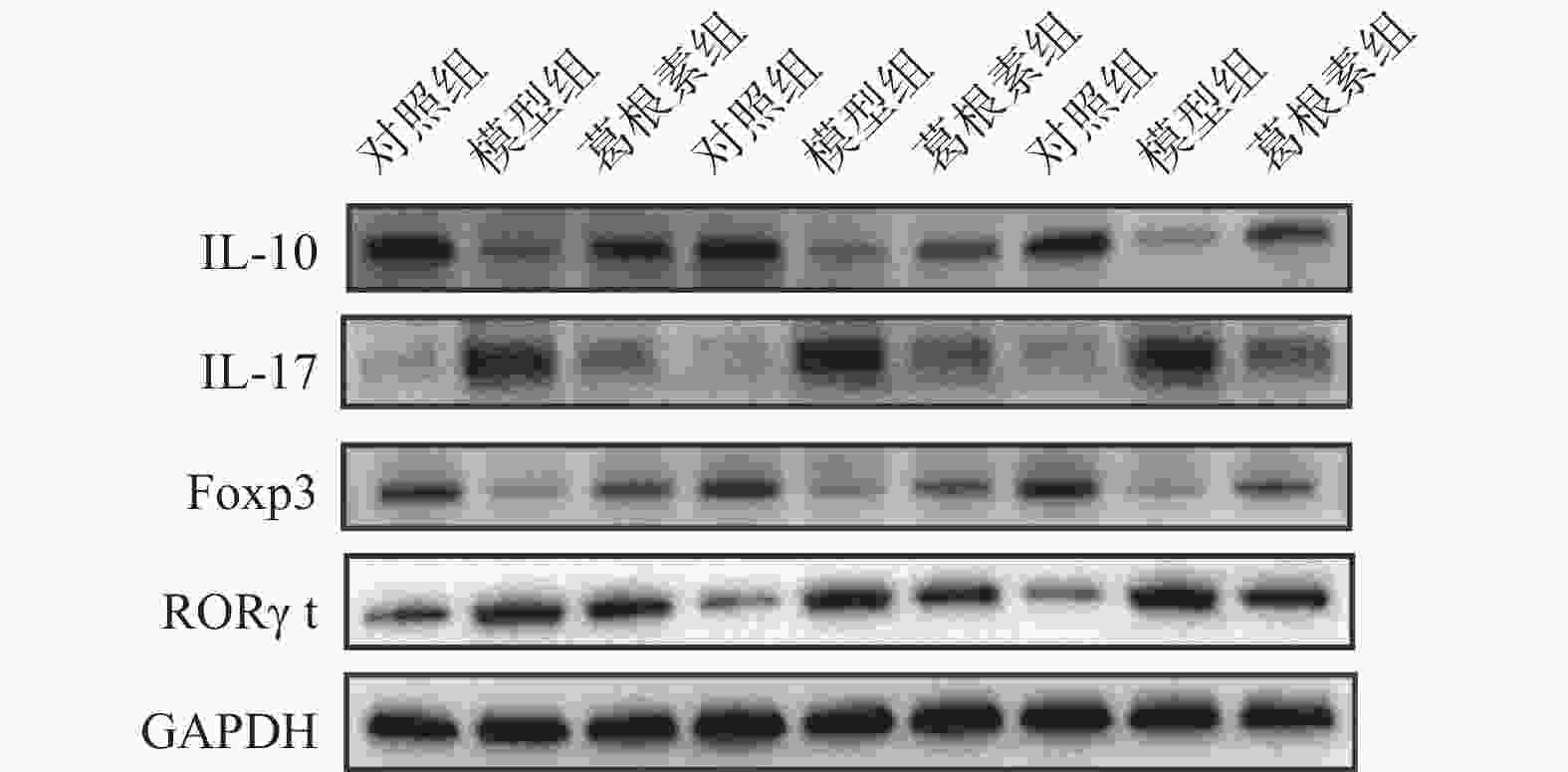
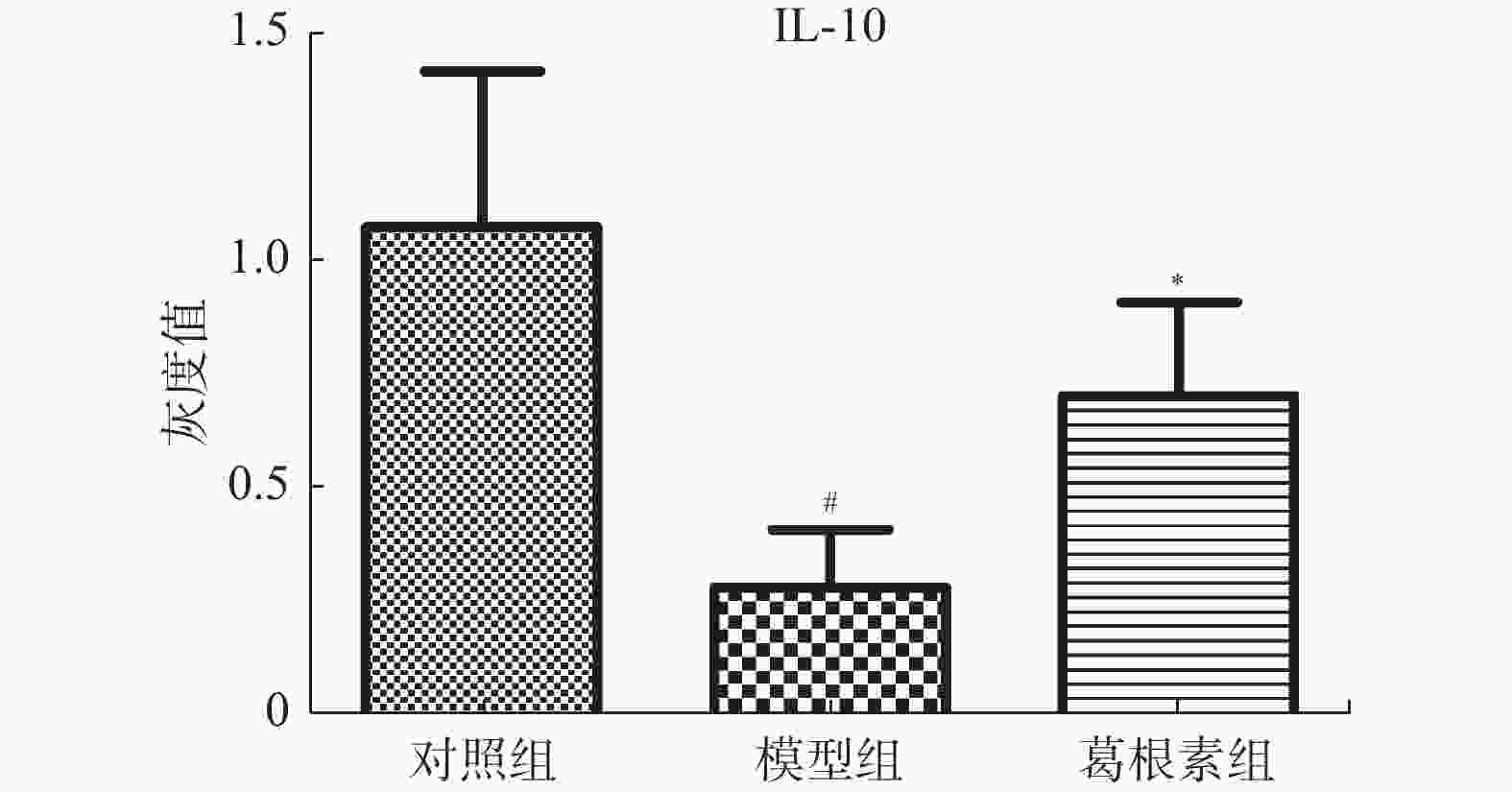
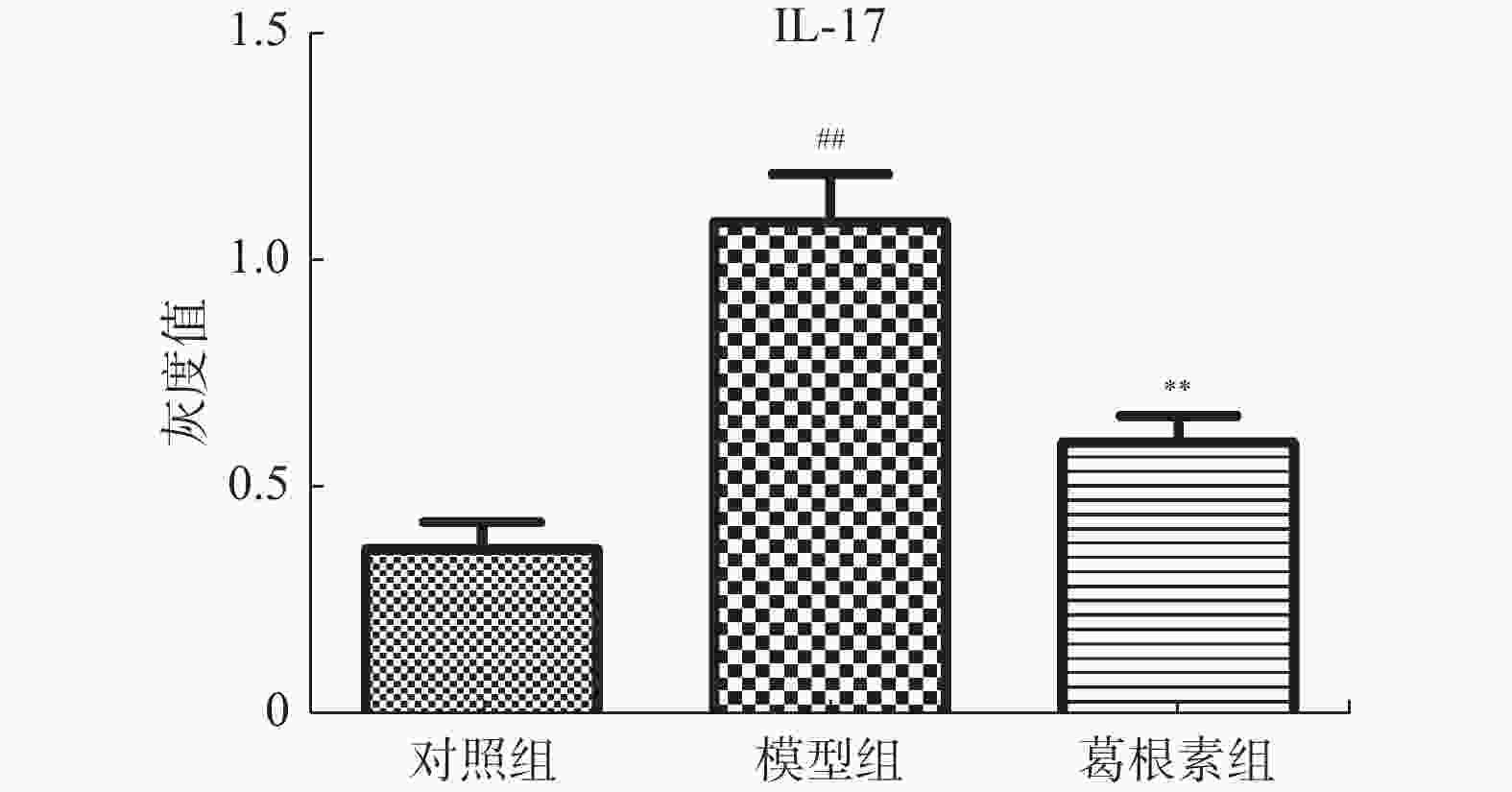
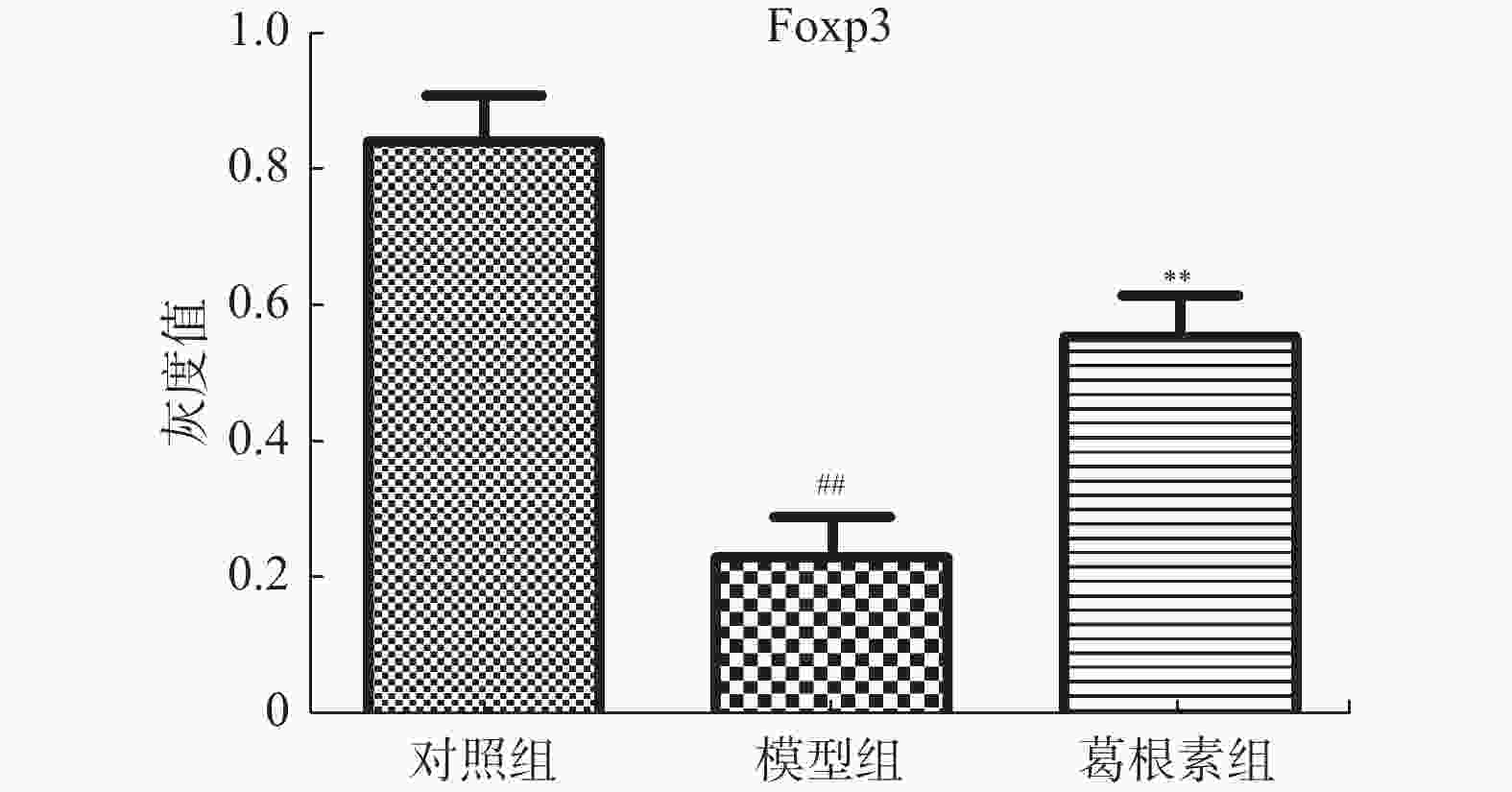
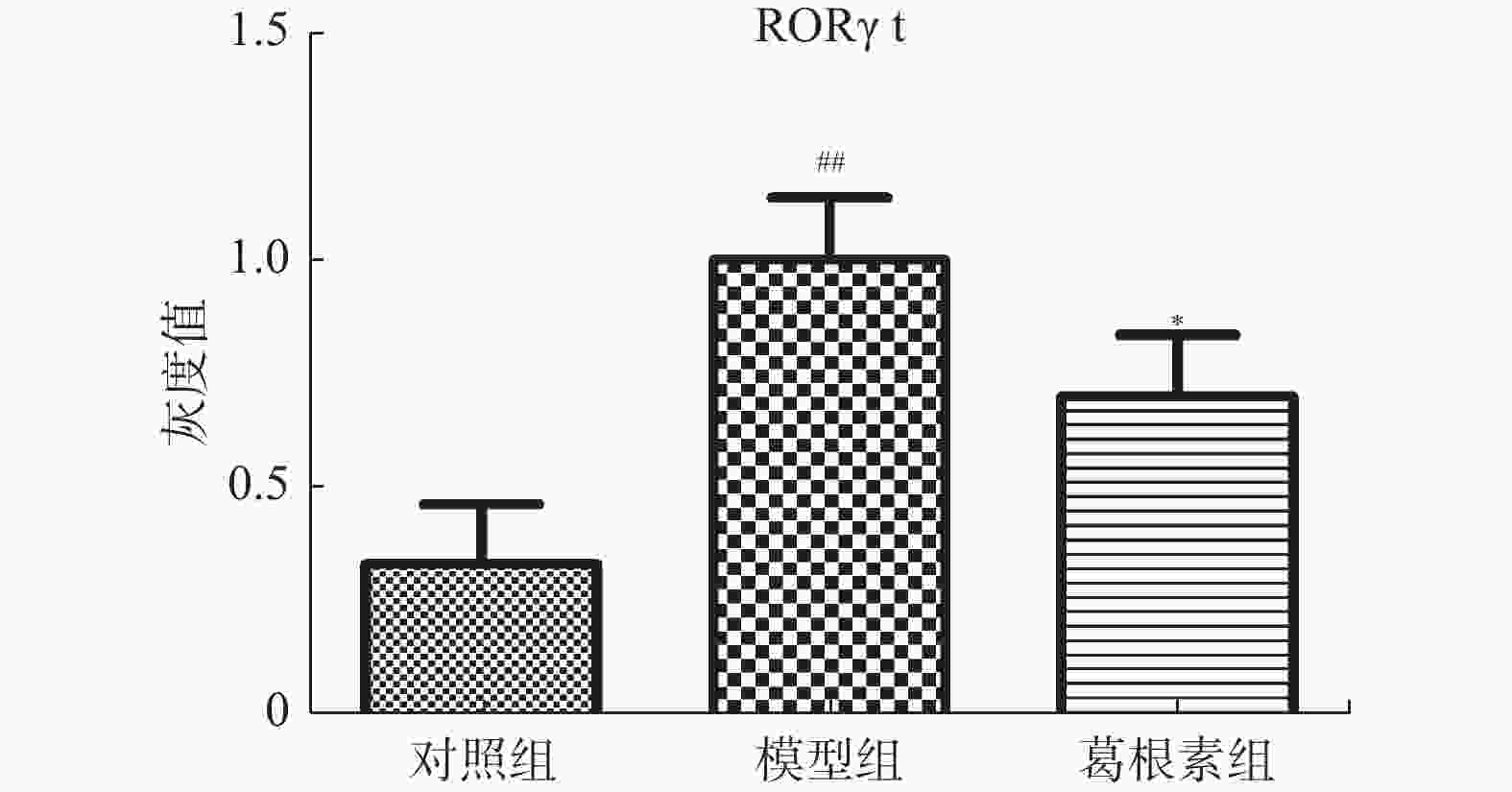
目的 探究葛根素对牙周炎大鼠辅助性 T 细胞 17( T helper cell 17,Th17) /调节性 T 细胞 (Regulatory T cell, Treg) 免疫平衡及相关转录因子的影响。 方法 采用分离牙龈、丝线结扎配合龈下注射大肠杆菌内毒素(E-LPS)法建立大鼠牙周炎模型。将大鼠随机分为正常对照组(A组)、牙周炎模型组(B组)、200 mg/(kg·d)葛根素组(C组)。HE 染色观察牙周组织病理形态学变化。通过Micro-CT对骨生物学参数定量分析牙槽骨吸收情况。流式细胞术、免疫印迹法(western blot,WB) 分别检测牙周组织中 Th17、Treg 细胞比例、白介素-17( IL-17) 、视黄酸相关孤儿受体( RORγt) 、IL-10、叉头状转录因子-3( Foxp3) 蛋白表达。 结果 HE染色中葛根素组大鼠牙根部可见明显新生骨细胞增生,牙周膜可见少量炎症细胞聚集,牙槽骨结构较整齐。Micro-CT显示治疗组大鼠牙槽骨较模型组骨量略有下降,骨质量及强度有所上升。流式细胞术检测全血细胞发现葛根素组的TH17、Treg细胞比例均下降,且TH17/Treg的细胞比例也下降。 IL-10、Foxp3在葛根素组蛋白表达量上调,而IL-17、RORγt在葛根素组蛋白表达量下调,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。 结论 葛根素可缓解牙周炎大鼠牙周组织炎性反应、牙槽骨吸收,通过调节Th17 /Treg 细胞及相关转录因子的表达,使Th17 /Treg 细胞免疫平衡轴往有利于牙周组织愈合方向发展,其作用机制可能与葛根素有效调节Th17 /Treg细胞免疫平衡轴有关。 Abstract:Objective To study the effects of puerarin on the immune homeostasis of T helper 17 (Th17)/regulatory T (Treg) cells and the expression of related transcription factors in rats with periodontitis. Methods A rat periodontitis model was established using gingival isolation, silk ligature application and subgingival injection of Escherichia coli endotoxin (E-LPS). The rats were randomly divided into a normal control group (group A), a periodontitis model group (group B), and a 200 mg/(kg-d) puerarin group (group C). HE staining was used to observe the changes of periodontal tissue. Micro-ct correlated bone indexes were also analyzed to quantify the resorption of alveolar bone. The percentages of Th17 and Treg cells and the expression of interleukin (IL)-17, retinoic acid-related orphan receptor gamma t (RORγt), IL-10 and forkhead transcription factor-3 (Foxp3)in periodontal tissues were monitored by flow Cytometry and Western blot (WB), respectively. Results In the study, the roots of the teeth in the puerarin group were significantly proliferated with new osteoblasts. Flow cytometry showed that the proportion of TH17 and Treg cells in the puerarin group decreased, and the proportion of TH17/Treg cells also decreased . The protein expressions of IL-10 and Foxp3 were up-regulated in puerarin, while the histone expressions of IL-17 and RORγt were down-regulated in puerarin (P < 0.05). Conclusions Puerarin can alleviate the periodontal tissue inflammatory response and alveolar bone resorption in rats with periodontitis and favor periodontal tissue healing by regulating Th17/Treg cell immune homeostasis and the expression of related transcription factors. The mechanism of action may be related to effective regulation of Th17/Treg cell immune homeostasis by puerarin. -
Key words:
- Puerarin /
- Periodontitis /
- Rats /
- Helper T cells /
- Regulatory T cells
-
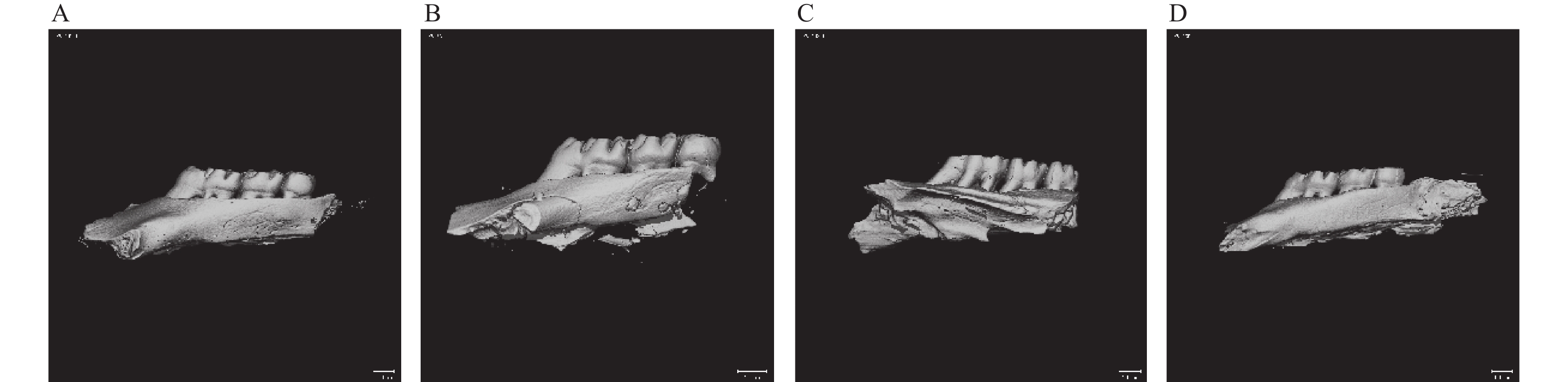
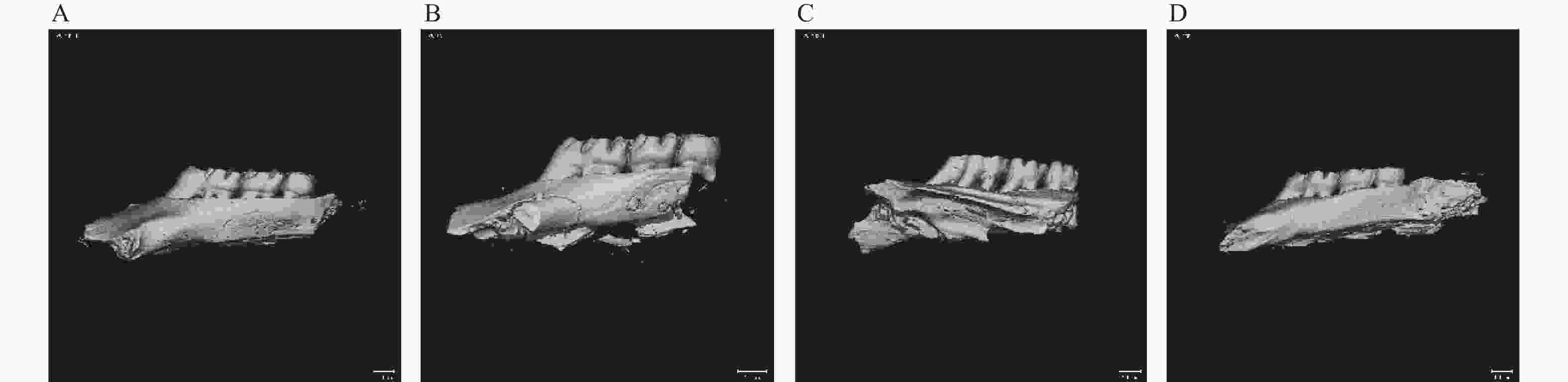
表 1 各组Micro-CT扫描分析后骨体积分数、骨矿物质密度值(n = 12,
$ \bar x \pm s $ )Table 1. BV/TV and BMD values of each group obtained by micro-CT scan analysis (n = 12,
$ \bar x \pm s $ )组别 BV/TV(%) BMD(g/cm3) 对照组 0.720 ± 0.049 1004.269 ± 54.644△ 模型组 0.387 ± 0.0376* 894.119 ± 53.789* 葛根素治疗组 0.337 ± 0.036△ 1046.297 ± 54.565△ 与对照组比较,*P < 0.05;与模型组比较,△P < 0.05。 -
[1] Harvey J D. Periodontal microbiology[J]. Dent Clin North Am,2017,61(2):253-269. doi: 10.1016/j.cden.2016.11.005 [2] Sun Q N,Ge S. Advances in clinical epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori and chronic periodontitis[J]. J Prevent Treatment Stomatological Dis,2016,24(3):190-192. [3] Preshaw P M. Host response modulation in periodontics[J]. Periodontol,2008,48(2):92-110. [4] Golub L M,Lee H M. Periodontal therapeutics:current host-modulation agents and future directions[J]. Periodontol,2020,82(1):186-204. doi: 10.1111/prd.12315 [5] Bullock J,Rizvi S A A,Saleh A M,et al. Rheumatoid arthritis:a brief overview of the treatment[J]. Med Princ Pract,2018,27(6):501-507. doi: 10.1159/000493390 [6] Aletaha D,Smolen J S. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis:a review[J]. AMA,2018,320(13):1360-1372. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.13103 [7] Yang X,Zhang H,Wang J,et al. Puerarin decreases bone loss and collagen destruction in rats with ligature-induced periodontitis[J]. Periodontal Res,2015,50(6):748-757. doi: 10.1111/jre.12261 [8] Wang L,Wang J,Jin Y,et al. Oral administration of all-trans retinoic acid suppresses experimental periodontitis by modulating the Th17/Treg imbalance[J]. Periodontol,2014,85(5):740-750. doi: 10.1902/jop.2013.130132 [9] Ramadan D E,Hariyani N,Indrawati R,et al. Cytokines and chemokines in periodontitis[J]. Eur J Dent,2020,14(3):483-495. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1712718 [10] Zhang L,Liu Y S,Wu Y F,et al. Effects of chitosan oligosaccharide on alveolar bone resorption,Th17/Treg balance and OPG/RANKL/RANK pathway in periodontitis rats[J]. Shanghai J Stomatol,2021,30(3):237-242. [11] Zhu X,Xie M,Wang K,et al. The effect of puerarin against IL-1β-mediated leukostasis and apoptosis in retinal capillary endothelial cells (TR-iBRB2)[J]. Mol Vis,2014,20(2):1815-1823. [12] Husniah B,Ahmed N,Muhammad K,et al. Salivary levels of IL-6 and IL-17 could be an indicator of disease severity in patients with calculus associated chronic periodontitis[J]. Bio Medresearch International,2018,2018:1-5. [13] Bártová J,Krátká-Opatrná Z,Procházková J,et al. Th1 and Th2 cytokine profile in patients with early onset periodontitis and their healthy siblings[J]. Mediators Inflamm,2000,9(2):115-120. doi: 10.1080/096293500411587 [14] Bi C S,Sun L J,Qu H L,et al. The relationship between T-helper cell polarization and the RANKL/OPG ratio in gingival tissues from chronic periodontitis patients[J]. Clin Exp Dent Res,2019,5(4):377-388. doi: 10.1002/cre2.192 [15] Liu H,Zheng J,Zheng T,et al. Exendin-4 regulates Wnt and NF-κB signaling in lipopolysaccharide-induced human periodontal ligament stem cells to promote osteogenic differentiation[J]. International Immunopharmacology,2019,75(9):105801. [16] Yan W,Cao Y,Yang H,et al. CB1 enhanced the osteo/dentinogenic differentiation ability of periodontal ligament stem cells via p38 MAPK and JNK in an inflammatory environment[J]. Cell Proliferation,2019,52(6):e12691. [17] Jia L,Xiong Y,Zhang W,et al. Metformin promotes osteogenic differentiation and protects against oxidative stressinduced damage in periodontal ligament stem cells via activation of the Akt/Nrf2 signaling pathway[J]. Experimental Cell Research,2020,386(2):111717. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.111717 [18] Cardoso C R,Garlet G P,Crippa G E,et al. Evidence of the presence of T helper type 17 cells in chronic lesions of human periodontal disease[J]. Oral Microbiol Immunol,2009,24(1):1-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302X.2008.00463.x [19] Mistry A,Pereira R,Kini V,et al. Effect of combined therapy using diode laser and photodynamic therapy on levels of IL-17 in gingival crevicular fluid in patients with chronic periodontitis[J]. Lasers Med Sci,2016,7(4):250-255. doi: 10.15171/jlms.2016.44 [20] Glowczyk I,Wong A,Potempa B,et al. Inactive gingipains from P. gingivalis selectively skews T cells toward a Th17 phenotype in an IL-6 dependent manner[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol,2017,7(3):140. [21] Garlet G P,Sfeir C S,Little S R. Restoring host-microbe homeostasis via selective chemoattraction of Tregs[J]. Dent Res,2014,93(9):834-839. doi: 10.1177/0022034514544300 [22] Parachuru V P B,Coates D E,Milne T J,et al. FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells,interleukin 17 and mast cells in chronic inflammatory periodontal disease[J]. Periodontal Res,2018,53(4):622-635. doi: 10.1111/jre.12552 [23] Nakajima T,Ueki-Maruyama K,Oda T,et al. Regulatory T-cells infiltrate periodontal disease tissues[J]. Dent Res,2005,84(7):639-643. doi: 10.1177/154405910508400711 [24] Shiomi K,Yamawaki I,Taguchi Y,et al. Osteogenic Effects of Glucose Concentration for human bone marrow stromal cells after stimulation with porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysac-charide[J]. J Hard Tissue Biology,2020,29(1):17-24. doi: 10.2485/jhtb.29.17 [25] De Vries T J,Andreotta S,Loos B G,et al. Genes critical for developing periodontitis:lessons from mouse models[J]. Front Immunol,2017,8(5):1395. [26] Chua C L L,Hasang W,Rogerson S J,et al. Poor birth outcomes in malaria in pregnancy:recent insights into mechanisms and prevention approaches[J]. Front Immunol,2021,15(12):621382. [27] Khanam R,Kumar I,Oladapo-Shittu O,et al. Prenatal environmental metal exposure and preterm birth:a scoping review[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health,2021,18(2):573. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18020573 -





 下载:
下载: