Effect of miR-130b-3p on the Reprogramming of Human Dental Origin iPSCs
-
摘要:
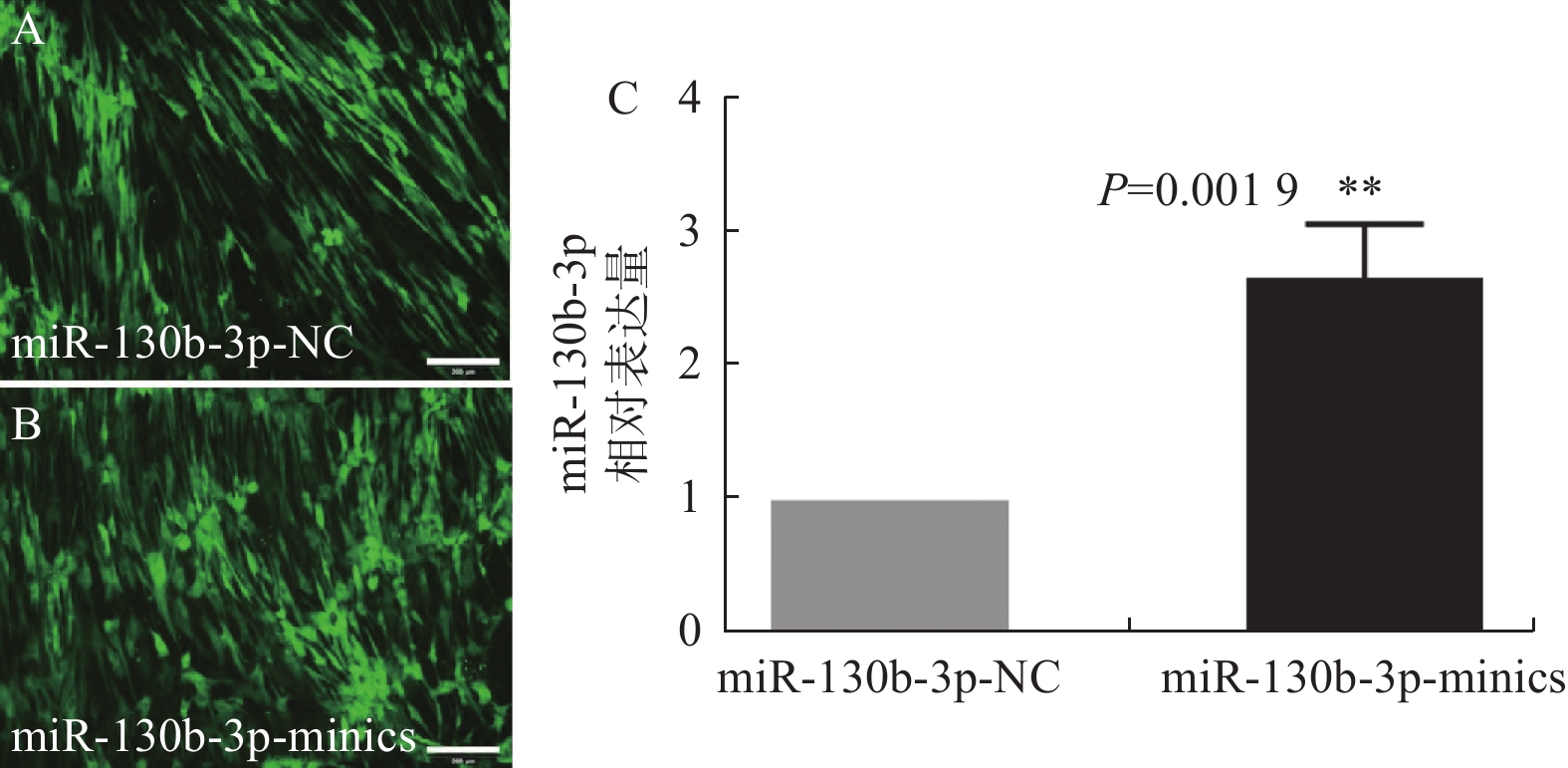
目的 研究hsa-miR-130b-3p对人DPSCs重编程为iPSCs的影响。 方法 设计合成LV3(H1/GFP&Puro)-hsa-miR-130b-3p-mimics质粒,Lipofectamine 3000将质粒转染到人DPSCs,荧光显微镜观察细胞,RT-qPCR验证转染效率。Sendai reprogramming kit将2组DPSCs重编程为iPSCs(实验组为miR-130b-3p-DPSCs,对照组为DPSCs),对比2组iPSCs克隆形态和重编程效率,RT-PCR检测Oct4、Nanog、KOS、Klf4、c-Myc的表达。 结果 hsa-miR-130b-3p过表达质粒转染48 h后在DPSCs内有明显表达,证实高效的转染效率(P < 0.01)。Sev重编程得到的2组iPSCs均呈现为扁平致密的圆形克隆,边缘清晰平滑,集落内细胞形态均一、核质比较大,RT-PCR结果表明2组细胞均可表达干细胞特异标志物Oct4和Nanog,同时外源性病毒SeV或转录因子KOS/Klf4/c-Myc不再表达。实验组的重编程效率高于对照组(分别为0.037%和0.018%,P < 0.05)。 结论 hsa-miR-130b-3p可明显促进人DPSCs重编程的效率,为iPSCs应用于牙髓再生治疗提供研究基础。 Abstract:Objective To explore the effect of hsa-miR-130b-3p on the reprogramming of human dental iPSCs. Methods LV3 (H1/GFP&Puro)-hsa-miR-130b-3p-mimics plasmid was designed and synthesized. The plasmid was transduced into human DPSCs by Lipofectamine 3000 kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Fluorescence microscopy was used to observe the cells and transfection efficiency was verified by RT-qPCR. Sendai reprogramming kit was used to induce two groups of DPSCs (miR-130b-3p-DPSCs in the experimental group and DPSCs in the control group) into iPSCs. The morphology and reprogramming efficiency were compared and the expression of Oct4/Nanog/KOS/Klf4/c-Myc was detected by RT-PCR in two groups of iPSCs. Results hsa-miR-130b-3p overexpression plasmid was significantly expressed in DPSCs 48h after transfection, indicating high transfection efficiency (P < 0.01). The two groups of iPSCs obtained by Sev reprogramming showed flat and dense round clones with clear and smooth edges, uniform cell morphology and large nucleolus in the colonies. RT-PCR results showed that cells in both groups could express the specific markers of stem cells Oct4 and Nanog. At the same time, exogenous virus SeV or transcription factors KOS/Klf4/c-Myc were no longer expressed. RT-PCR showed that cells in both groups all expressed specific markers Oct4 and Nanog, while SeV or KOS/Klf4/ C-MYC were not detected. The reprogramming efficiency of the experimental group was higher than that of the control group (0.037% and 0.018% respectively, P < 0.05). Conclusion hsa-miR-130b-3p could promote the reprogramming efficiency of human DPSCs. Our research provides theoretical foundation for dental iPSCs application in dental pulp regenerative therapy. -
Key words:
- Dental pulp stem cells /
- Reprogramming /
- Induced pluripotent stem cells /
- microRNAs /
- Overexpression
-
表 1 RT-PCR特异性引物的序列
Table 1. Specific primer sequences of RT-PCR
基因 引物 序列(5′-3′) Sev Forward GGATCACTAGGTGATATCGAGC Reverse ACCAGACAAGAGTTTAAGAGA Klf4 Forward TTCCTGCATGCCAGAGGAGCCC Reverse AATGTATCGAAGGTGCTCAA Myc Forward TAACTGACTAGCAGGCTTGTCG Reverse TCCACATACAGTCCTGGATGAT KOS Forward ATGCACCGCTACGACGTGAGGGC Reverse ACCTTGACAATCCTGATGTGG Oct4 Forward GAAGGTATTCAGCCAAACGAC Reverse GTTACAGAACCACACTCGGA Nanog Forward TGCAAATGTCTTCTGCTGAGAT Reverse GTTCAGGATGTTGGAGAGTTC Gapdh Forward GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT Reverse GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG -
[1] Takahashi K,Tanabe K,Ohnuki M,et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors[J]. Cell,2007,131(5):861-872. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.11.019 [2] Yu J,Vodyanik M A,Smuga-Otto K,et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells[J]. Science,2007,318(5858):1917-1920. doi: 10.1126/science.1151526 [3] Hu J,Wang J. From embryonic stem cells to induced pluripotent stem cells-Ready for clinical therapy?[J]. Clin Transplant,2019,33(6):e13573. [4] Yamanaka S. Pluripotent stem cell-based cell therapy-promise and challenges[J]. Cell Stem Cell,2020,27(4):523-531. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2020.09.014 [5] Liu G,David B T,Trawczynski M,et al. Advances in pluripotent stem cells:History,mechanisms,technologies,and applications[J]. Stem Cell Rev Rep,2020,16(1):3-32. doi: 10.1007/s12015-019-09935-x [6] Zeng Z L,Lin X L,Tan L L,et al. MicroRNAs:Important regulators of induced pluripotent stem cell generation and differentiation[J]. Stem Cell Rev Rep,2018,14(1):71-81. doi: 10.1007/s12015-017-9785-6 [7] Zou X Y,Yang H Y,Yu Z,et al. Establishment of transgene-free induced pluripotent stem cells reprogrammed from human stem cells of apical papilla for neural differentiation[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther,2012,3(5):43. doi: 10.1186/scrt134 [8] Tan X,Dai Q. Characterization of microRNAs expression profiles in human dental-derived pluripotent stem cells[J]. PLoS One,2017,12(5):e0177832. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177832 [9] Guo Q,Zhu X,Wei R,et al. miR-130b-3p regulates M1 macrophage polarization via targeting IRF1[J]. J Cell Physiol,2021,236(3):2008-2022. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29987 [10] Song D,Zhang Q,Zhang H,et al. MiR-130b-3p promotes colorectal cancer progression by targeting CHD9[J]. Cell Cycle,2022,21(6):585-601. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2029240 [11] Ye H,Wang Q. Efficient generation of non-integration and feeder-free induced pluripotent stem cells from human peripheral blood cells by Sendai virus[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem,2018,50(4):1318-1331. [12] Okumura T,Horie Y,Lai CY,et al. Robust and highly efficient hiPSC generation from patient non-mobilized peripheral blood-derived CD34+ cells using the auto-erasable Sendai virus vector[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther,2019,10(1):185. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1273-2 [13] Lin S L,Chen J S,Ying S Y. MiR-302-mediated somatic cell reprogramming and method for generating tumor-free iPS cells using miR-302[J]. Methods Mol Biol,2020,2115:199-219. [14] Lin S L,Chang D,Lin C H,et al. Regulation of somatic cell reprogramming through inducible mir-302 expression[J]. Nucleic Acids Res,2011,39(3):1054-1065. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq850 [15] Anokye-Danso F,Trivedi C M,Juhr D,et al. Highly efficient miRNAmediated reprogramming of mouse and human somatic cells to pluripotency[J]. Cell Stem Cell,2011,8(4):376-388. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2011.03.001 [16] Miyoshi N,Ishii H,Nagano H,et al. Reprogramming of mouse and human cells to pluripotency using mature microRNAs[J]. Cell Stem Cell,2011,8(6):633-638. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2011.05.001 [17] Pascale E,Caiazza C,Paladino M,et al. MicroRNA roles in cell reprogramming mechanisms[J]. Cells,2022,11(6):940. doi: 10.3390/cells11060940 [18] Lim J,Sakai E,Sakurai F,et al. miR-27b antagonizes BMP signaling in early differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells[J]. Sci Rep,2021,11(1):19820. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99403-9 [19] Yue W,Sun J,Zhang J,et al. Mir-34c affects the proliferation and pluripotency of porcine induced pluripotent stem cell (piPSC)-like cells by targeting c-Myc[J]. Cells Dev,2021,166:203665. -






 下载:
下载: