Morphological Study of Meniscus Thickness Measurement in Normal Adults Based on MRI
-
摘要:
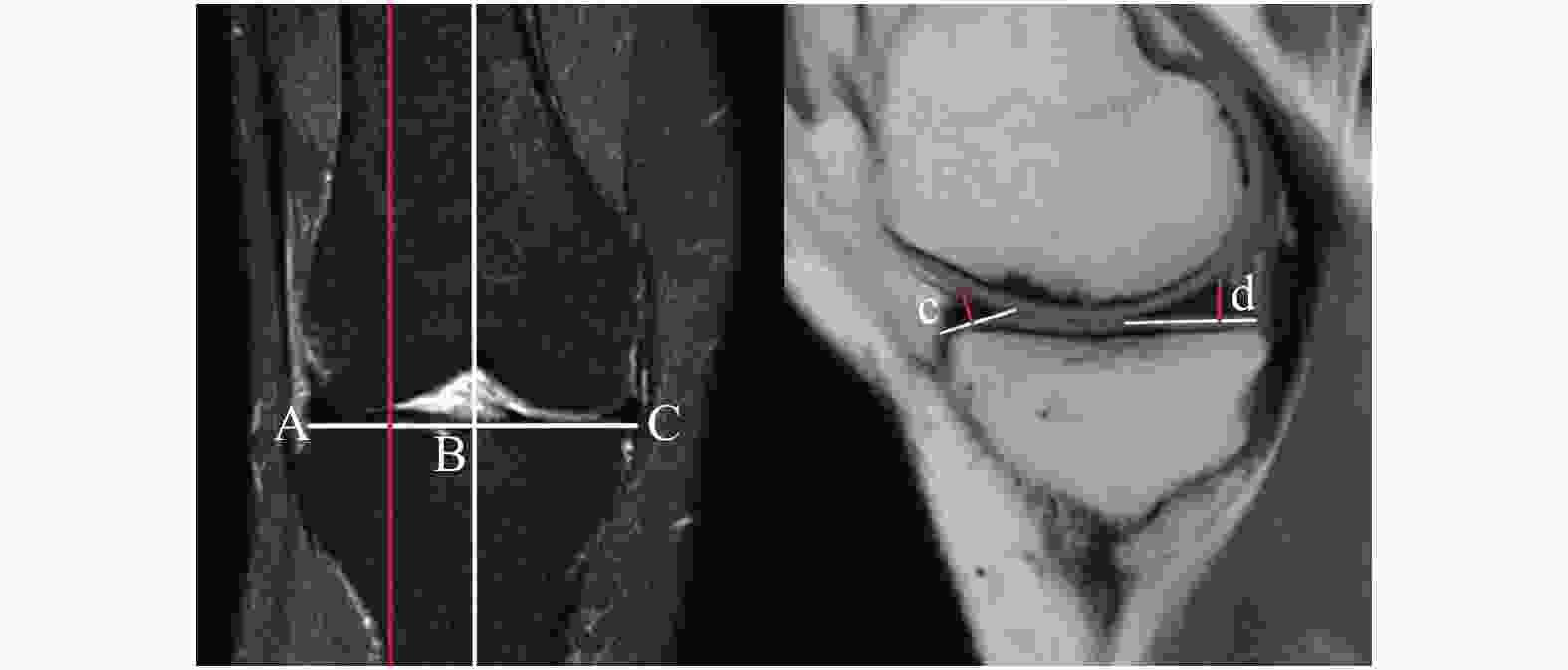
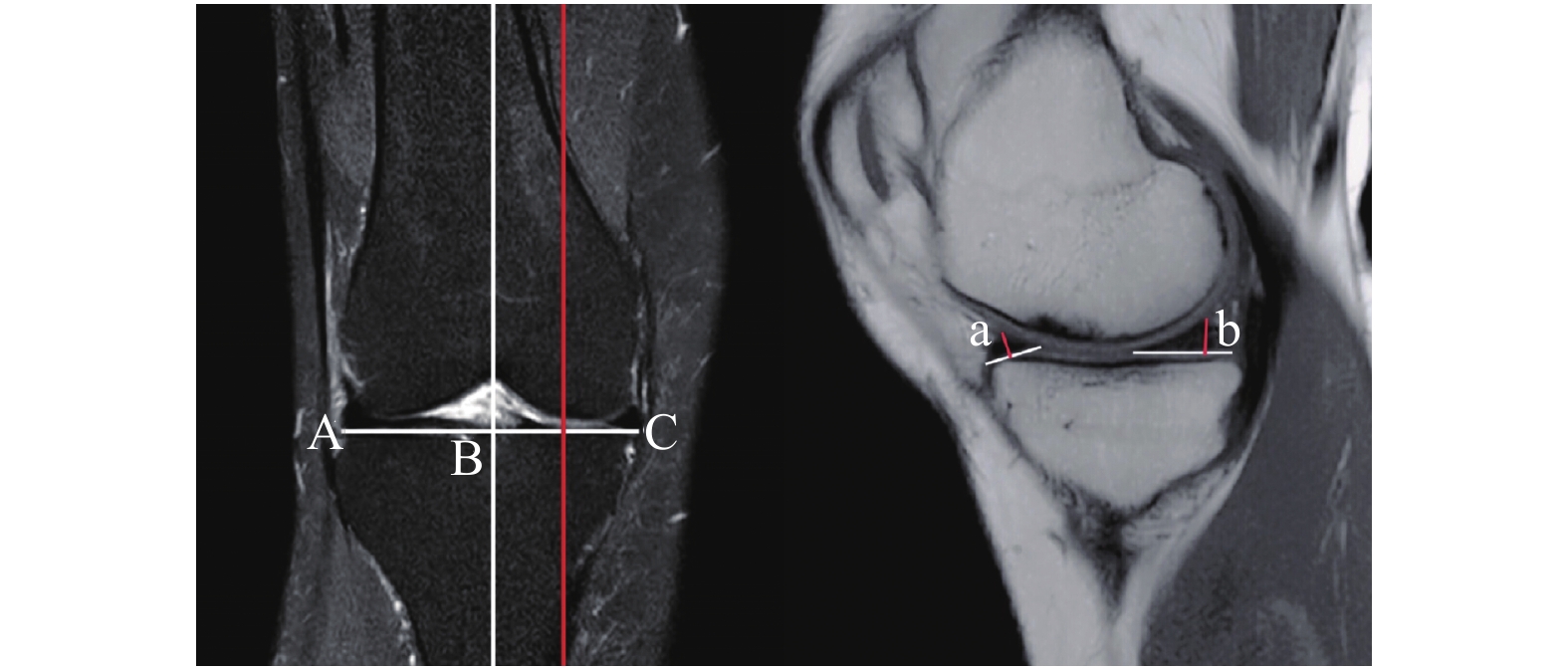
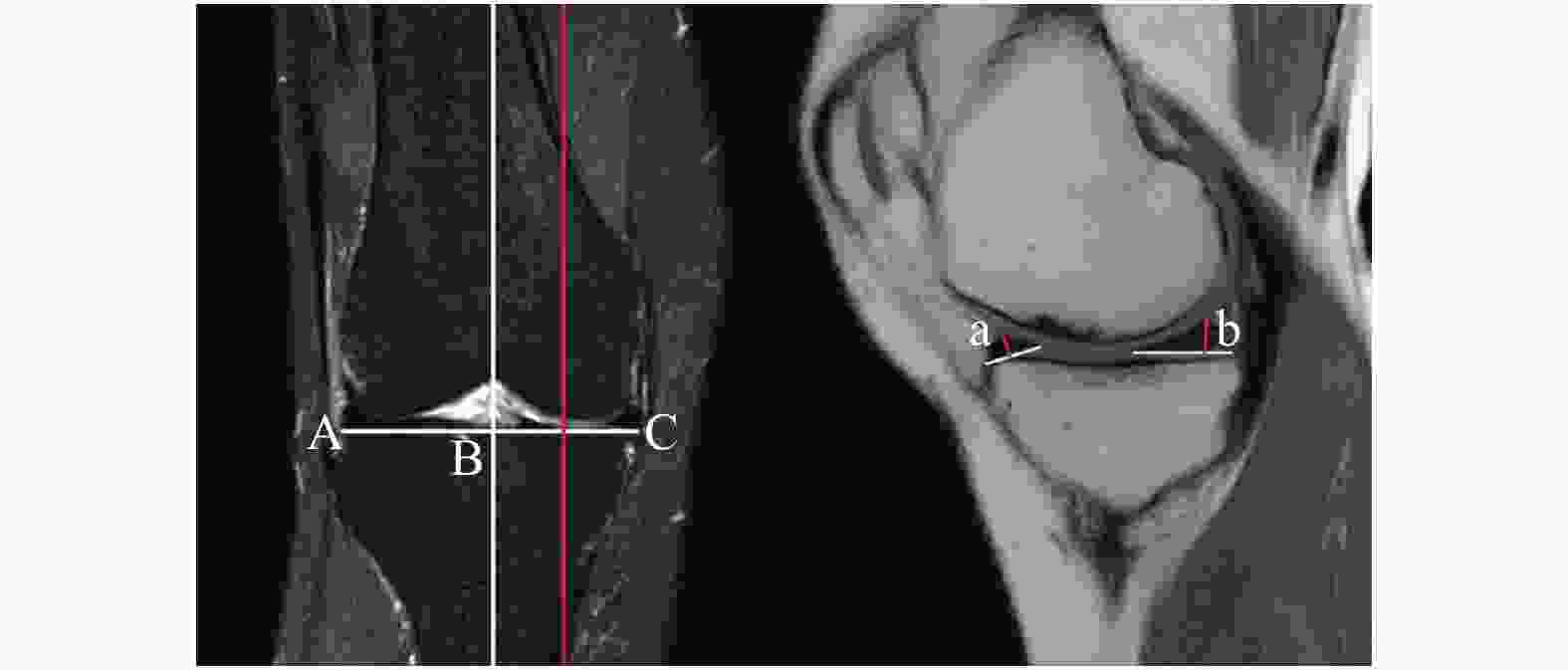
目的 采用MRI扫描成像技术测量正常成人膝关节内外侧间室半月板前后角的厚度,为全膝关节置换假体设计和优化人工半月板设计提供技术手段、参数。 方法 随机抽取 2020年01月至 2022年06月在云南省中医医院就诊的成年患者行单侧膝关节MRI扫描成像的影像学资料,MRI片示无膝关节水肿、半月板明显退变、半月板损伤及撕裂等的248例影像资料作为样本,其中女性137例,男性111例,年龄18~80岁,中位年龄50岁。观察膝关节的矢状面MRI片。由3名资深临床医师测量膝关节内侧间室的半月板前后角厚度、膝关节外侧间室的半月板前后角厚度,并取3次测量结果的平均值作为最终测量结果。测量结果采用SPSS27.0统计学软件包进行统计学分析。 结果 内侧间室半月板前角厚度为(3.65±0.93)mm;内侧间室半月板后角厚度为(5.25±1.17)mm;外侧间室半月板前角厚度为(4.82±1.08)mm;外侧间半月板后角厚度为(6.89±1.03)mm;经两独立样本t检验,男女内侧间室半月板后角厚度,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);左右侧膝关节内侧间室半月板前后角厚度和外侧间室半月板前角厚度,差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05);经Pearson相关性分析,男女性内侧间室半月板前角厚度和内侧间室半月板后角厚度均具有相关性(P < 0.05);男女性外侧间室半月板前角厚度和外侧间室半月板后角厚度均具有相关性(P < 0.05)。 结论 利用MRI成像技术,通过对半月板形态的测量揭示了正常成人半月板形态学的特点及变化规律,有利于全膝关节置换假体设计和优化人工半月板设计,从而更好的指导临床治疗。 Abstract:Objective MRI scanning technique was used to measure the thickness of the anterior and posterior angles of the medial and lateral compartments of the knee joint in normal adults, so as to provide technical means and parameters for the design of total knee replacement prosthesis and the optimization of artificial meniscus design. Methods The imaging data of MRI scanning of unilateral knee joint of adult patients in Yunnan Traditional Chinese medicine hospital from January 2020 to June 2022 were randomly selected. 248 cases without knee edema, obvious degeneration of meniscus, meniscus injury and tear in MRI films were taken as samples, including 137 women, 111 men, 18-80 years old, with a median age of 50 years. The sagittal MRI films of knee joint were observed, Three senior clinicians measured the meniscus anterior and posterior angle thickness of the medial compartment of the knee joint and the meniscus anterior and posterior angle thickness of the lateral compartment of the knee joint, and the average of the three measurements was taken as the final measurement result. The measurement results were statistically analyzed by spss27.0 statistical software package. Results The thickness of anterior horn of meniscus in the medial compartment was (3.65 ± 0.93)mm; the thickness of posterior horn of meniscus in the medial compartment was (5.25 ± 1.17)mm; the thickness of anterior horn of meniscus in the lateral compartment was (4.82 ± 1.08)mm; the thickness of posterior horn of lateral in the lateral compartmentwas (6.89 ± 1.03)mm. The t test of two independent samples showed that the thickness of the posterior angle of meniscus in the medial compartment was statistically significant between men and women (P < 0.05). The anterior and posterior Angle thickness of the meniscus in the medial ventricle of the left and right knee joints was significantly different from that in the lateral ventricle (P < 0.05). According to Pearson correlation analysis, there was a correlation between the anterior angle thickness of medial interventricular meniscus and the posterior angle thickness of medial interventricular meniscus in both sexes (P < 0.05). There was a correlation between the thickness of anterior horn of lateral interventricular meniscus and the thickness of posterior horn of lateral interventricular meniscus in both sexes (P < 0.05). Conclusion In this study, MRI imaging technology was used to reveal the morphological characteristics and changes of meniscus in normal adults through the measurement of meniscus morphology, which is conducive to the design of total knee replacement prosthesis and the optimization of artificial meniscus design, so as to better guide clinical treatment. -
Key words:
- MRI /
- Adult /
- Meniscus /
- Thickness /
- Morphological study
-
表 1 基本资料描述
Table 1. Description of basic data
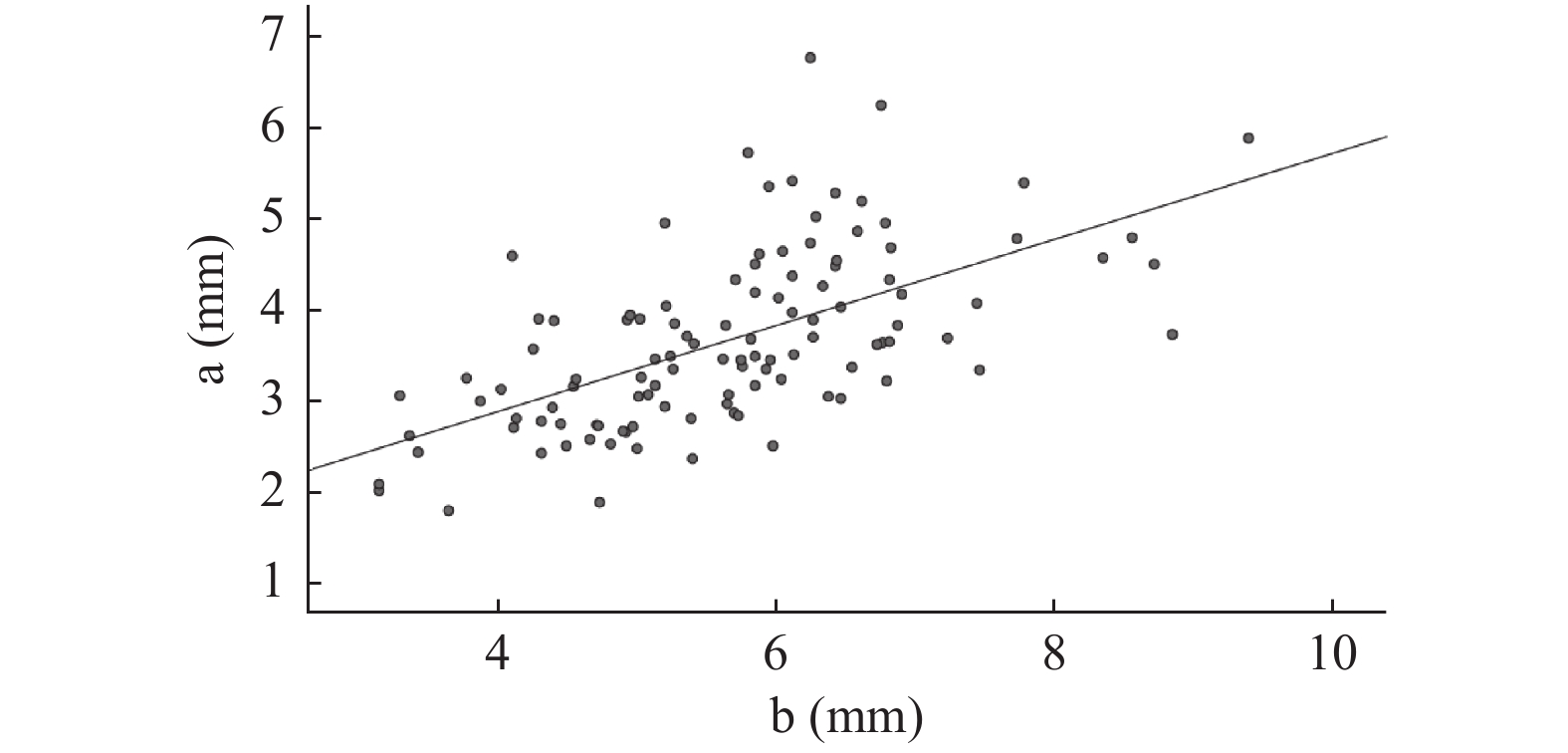
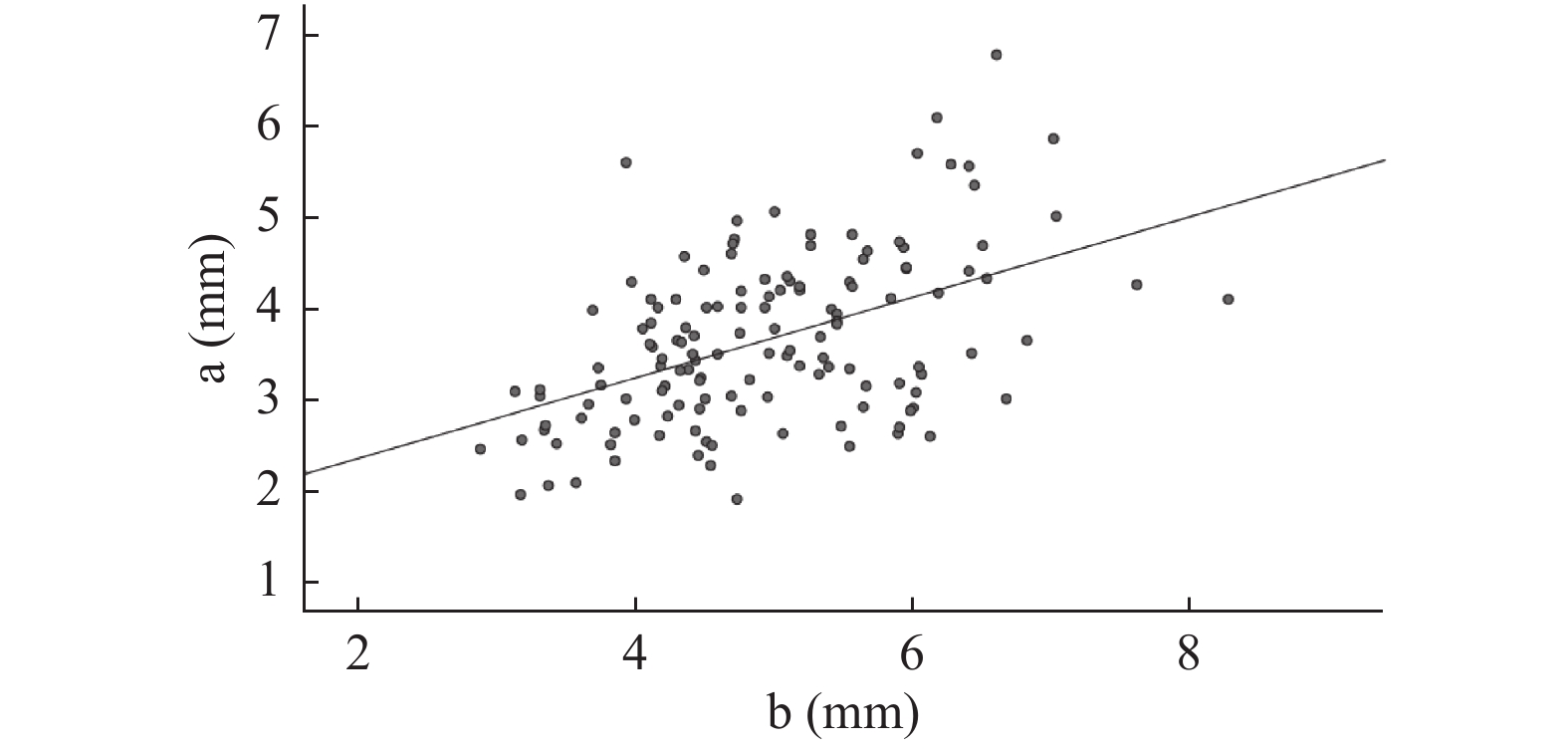
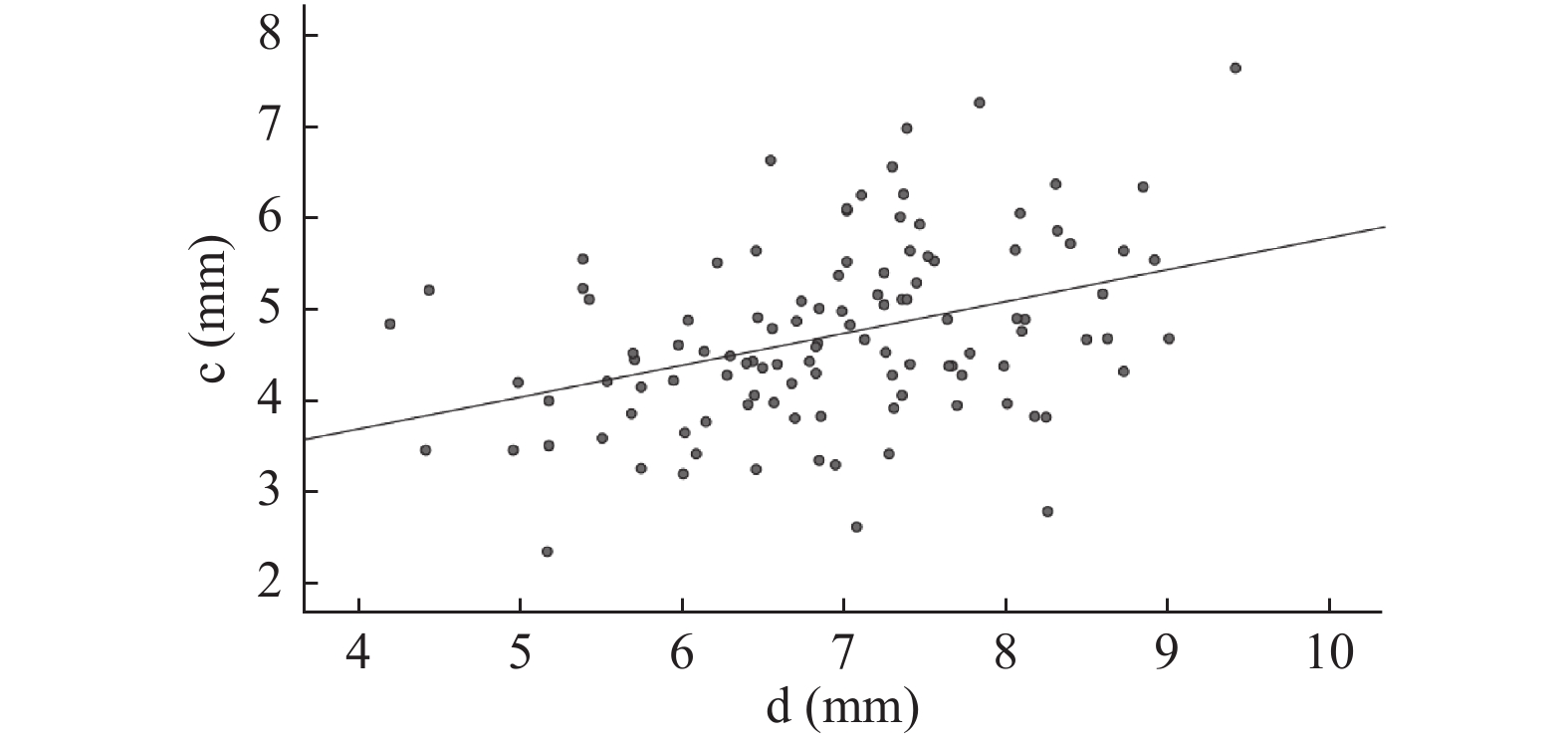
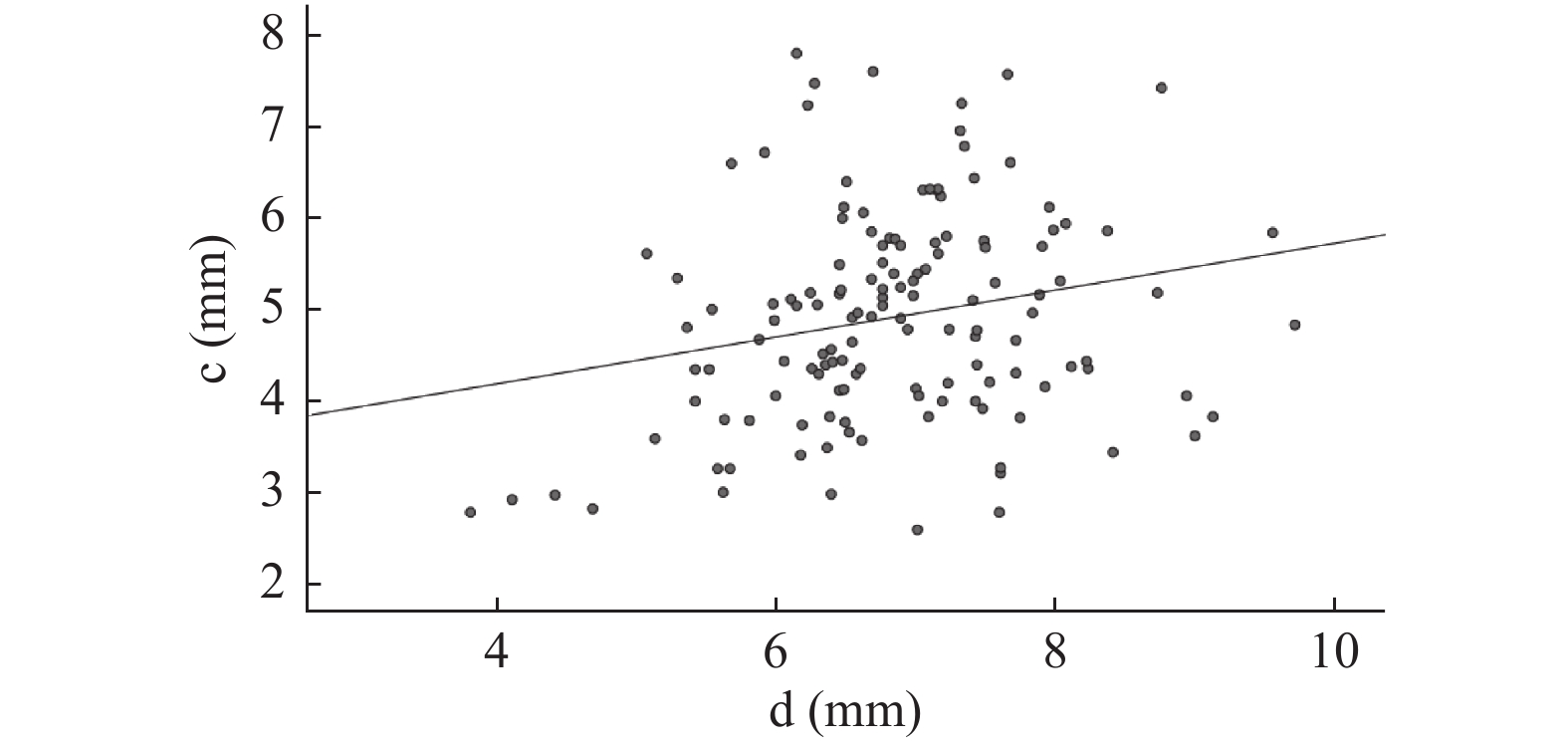
指标 平均值 中位数 SD 最大值 最小值 a(mm) 3.65 3.50 0.93 6.77 1.79 b(mm) 5.25 5.17 1.17 9.39 2.87 c(mm) 4.82 4.77 1.08 7.80 2.34 d(mm) 6.89 6.87 1.03 9.73 3.79 男性年龄(岁) 43.64 43.50 15.52 80.00 19.00 女性年龄(岁) 47.41 48.50 14.12 80.00 18.00 a:内侧间室半月板前角厚度;b:内侧间室半月板后角厚度;c:外侧间室半月板前角厚度;d:外侧间室半月板后角厚度。 表 2 男性和女性情况比较($ \bar x \pm s $)
Table 2. Comparison of male and female ($ \bar x \pm s $)
指标 男性 女性 t P a(mm) 3.66 ± 0.96 3.65 ± 0.92 0.103 0.918 b(mm) 5.65 ± 1.23 4.93 ± 1.00 5.013 < 0.001* c(mm) 4.71 ± 0.98 4.90 ± 1.15 −1.415 0.158 d(mm) 6.94 ± 1.07 6.84 ± 1.00 0.714 0.476 a:内侧间室半月板前角厚度;b:内侧间室半月板后角厚度;c:外侧间室半月板前角厚度;d:外侧间室半月板后角厚度。*P < 0.05。 表 3 左侧和右侧情况比较($ \bar x \pm s $)
Table 3. Comparison of left and right
指标 左侧 右侧 t P a(mm) 3.40 ± 0.87 3.86 ± 0.94 −3.938 < 0.001* b(mm) 4.82 ± 0.98 5.61 ± 1.19 −5.553 < 0.001* c(mm) 4.98 ± 1.06 4.68 ± 1.09 2.203 0.029* d(mm) 6.69 ± 0.99 7.05 ± 1.05 −2.751 0.06 a:内侧间室半月板前角厚度;b:内侧间室半月板后角厚度;c:外侧间室半月板前角厚度;d:外侧间室半月板后角厚度。*P < 0.05。 表 4 相关性分析
Table 4. Correlation analysis
指标 性别 r P a与b 男性 0.604 < 0.001* 女性 0.484 < 0.001* c与d 男性 0.381 < 0.001* 女性 0.222 0.009* a:内侧间室半月板前角厚度;b:内侧间室半月板后角厚度。c:外侧间室半月板前角厚度;d:外侧间室半月板后角厚度。*P < 0.05。 -
[1] 杨顺杰,张明智,李箭,等. 超声检查对膝关节外侧盘状半月板的诊断价值[J]. 中国骨伤,2022,35(3):243-248. [2] 赵章伟,周凯,李琪,等. 膝关节半月板根部附着区的解剖学测量[J]. 中国骨伤,2020,33(3):234-237. [3] 葛宏艳,张丽萍,陈荟,等. MRI测量的交叉韧带松紧度与膝关节半月板损伤程度的相关性研究[J]. 现代医用影像学,2021,30(12):2249-2252. [4] Jiang P,Cui J,Chen Z,et al. Biomechanical study of medial meniscus after posterior horn injury:A finite element analysis[J]. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin,2020,23(4):127-137. [5] 涂有为,刘云鹏,王星亮,等. MRI评估股骨内侧髁和胫骨平台匹配性对内侧半月板后根撕裂的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(12):1872-1876. [6] Choi J Y,Biswas R,Bae W C,et al. Thickness of the meniscal lamellar layer:Correlation with indentation stiffness and comparison of normal and abnormally thick layers by using multiparametric ultrashort echo time MR imaging[J]. Radiology,2016,280(1):161-168. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2016150633 [7] Gee S M,Posner M. Meniscus Anatomy and Basic Science[J]. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev,2021,29(3):e18-e23. [8] 潘惠娟,杨来华,戎慧,等. 高分辨力MRI对膝关节前外侧韧带的评价[J]. 中国中西医结合影像学杂志,2016,14(1):28-30. [9] 张贵荣,周永怀. 研究探讨磁共振(MR)扫描技术与CT检查对急性膝关节外伤的临床效果[J]. 影像研究与医学应用,2020,4(18):103-104. [10] Fan B S,Ye J,Xu B B,et al. Study on feasibility of the partial meniscal allograft transplantation[J]. Clin Transl Med,2022,12(1):e701. [11] Lee K I,Gamini R,Olmer M,et al. Mohawk is a transcription factor that promotes meniscus cell phenotype and tissue repair and reduces osteoarthritis severity[J]. Sci Transl Med,2020,12(567):eaan7967. [12] Murphy C A,Garg A K,Silva-Correia J,et al. The meniscus in normal and osteoarthritic tissues:Facing the structure property challenges and current treatment trends[J]. Annu Rev Biomed Eng,2019,8(21):495-521. [13] Murray I R,Benke M T,Mandelbaum B R. Management of knee articular cartilage injuries in athletes:Chondroprotection,chondrofacilitation,and resurfacing[J]. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc,2016,24(5):1617-1626. doi: 10.1007/s00167-015-3509-8 [14] Sihvonen R,Paavola M,Malmivaara A,et al. Arthroscopic partial meniscectomy for a degenerative meniscus tear:A 5 year follow-up of the placebo-surgery controlled FIDELITY (Finnish Degenerative Meniscus Lesion Study) trial[J]. Br J Sports Med,2020,54(22):1332-1339. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2020-102813 [15] Abram S G F,Hopewell S,Monk A P,et al. Arthroscopic partial meniscectomy for meniscal tears of the knee:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Br J Sports Med,2020,54(11):652-663. [16] Engebretsen L,Moatshe G. Arthroscopic partial meniscectomy for degenerative meniscus tears in middle age patients:why surgeons should change their approach[J]. Br J Sports Med,2020,54(22):1311-1312. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2020-103330 [17] 李钊,杨育晖,吴海贺,等. 基于MRI三维重建的国人正常半月板三维形态学测量[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2018,24(5):468-472. [18] 赵卫民,曹学伟. MRI测量在膝关节半月板中的临床运用[J]. 局解手术学杂志,2017,26(2):98-100. [19] Huang W,Zhang Y,Yao Z,et al. Clinical examination of anterior cruciate ligament rupture:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc,2016,50(1):22-31. -





 下载:
下载: