Clinical Value of Ultrasound-guided FNA and FNA-TG in Identification of Lymph Node Metastasis of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
-
摘要:
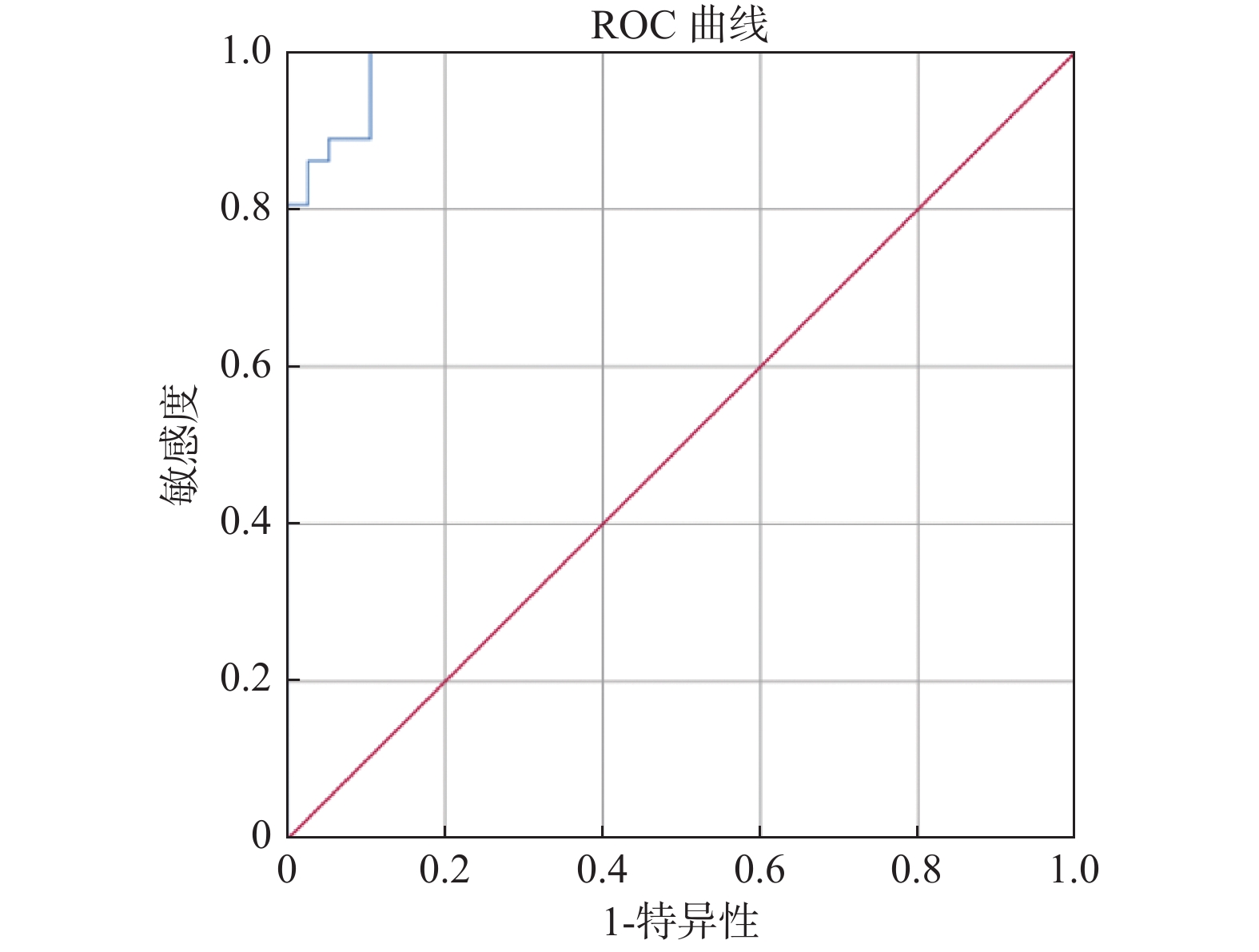
目的 探讨在超声的识别和引导,以及FNA的精确取材基础上,FNA-Tg对可疑颈部甲状腺乳头状癌转移淋巴结的诊断意义,并建立FNA-Tg诊断值。 方法 对74枚甲状腺癌可疑转移淋巴结进行细针穿刺,结合手术病理,分别采用单纯FNA、FNA-Tg值与血清Tg对比、绘制 ROC曲线求取FNA-Tg最佳诊断值3种方法评估淋巴结,并求其判定阳性结果的灵敏性、特异性和准确率。 结果 淋巴结伴钙化、皮髓质分界、血供异常、纵横比在诊断甲状腺乳头状癌颈部淋巴结转移中的差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),以上4项指标诊断甲状腺癌淋巴结转移的敏感度最高,钙化、多发片状高回声、囊性变及弹性成像硬度特异度较高,皮髓质分界及纵横比的准确率最高;FNA的敏感性、特异性及准确率为75%、100%和87.84%;FNA-Tg/血清Tg值 > 1为评判标准时的敏感性、特异性及准确率为97.22%、100%和 98.65%;绘制 ROC曲线求取FNA-Tg最佳诊断阈值为0.575 ng/mL。 结论 FNA-Tg/血清Tg > 1作为诊断甲状腺乳头状癌转移淋巴结的诊断标准能更好的规避因诸多因素带来的弊端,可有效降低误差率,应作为辅助诊断甲状腺乳头状癌淋巴结转移的首选。 Abstract:Objective To explore the diagnostic significance of FNA-Tg for lymph nodes with suspected cervical thyroid papillary carcinoma metastasis on the basis of ultrasonic detection and guidance and accurate biopsy of FNA, and establish the threshold of FNA-TG. Methods 74 lymph nodes with suspected metastasis of thyroid cancer were evaluated by fine needle aspiration and analysed pathologically. Lymph nodes were evaluated by comparing FNA alone, FNA-TG value with serum Tg, and drawing ROC to obtain the best diagnostic value of FNA-TG, and the sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of positive results were evaluated. Results There were significant differences in calcification, cortex-medullary boundary, abnormal blood supply and aspect ratio in the diagnosis of cervical lymph node metastasis of papillary thyroid carcinoma (P < 0.05). The above four indexes had the highest sensitivity in the diagnosis of lymph node metastasis of thyroid cancer. Calcification, multiple hyperecho, cystic changes and elastic imaging had higher hardness specificity, and the accuracy of cortex-medulla boundary and aspect ratio was the highest. The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of FNA were 75%, 100% and 87.84%. The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of FNA-Tg/ serum Tg value > 1 were 97.22%, 100% and 98.65%. ROC curve was drawn to obtain the optimal diagnostic threshold of FNA-Tg as 0.575 ng/mL. Conclusion FNA-Tg/ serum Tg > 1, as the diagnostic criteria for lymph node metastasis of papillary thyroid cancer, can better avoid the disadvantages caused by many factors and effectively reduce the error rate, and should be the first choice for the auxiliary diagnosis of lymph node metastasis of papillary thyroid cancer. -
Key words:
- Papillary thyroid carcinoma /
- Biospy /
- Fine-needle /
- Lymphatic metastasis
-
表 1 颈部淋巴结的超声征象与病理结果对照[n(%)]
Table 1. Comparison of ultrasound indications and pathological results of lymph nodes [n(%)]
指标 非转移淋巴结(n=38) 转移淋巴结(n=36) χ2 P 片状高回声 有 3(7.89) 6(16.67) 1.332 0.249 无 35(92.11) 30(83.33) 钙化 有 2(5.26) 28(77.78) 40.327 < 0.001* 无 36(94.74) 8(22.22) 囊性变 有 7(19.42) 18(50.00) 8.241 0.004* 无 31(81.58) 18(50.00) 纵横比 < 1.5 15(39.47) 20(55.56) 1.918 0.166 ≥1.5 23(60.53) 16(44.44) 皮髓质分界 欠(不)清晰 5(13.16) 31(86.11) 46.111 < 0.001* 清晰 33(84.84) 5(13.89) 血供(SMI) I型 32(84.22) 8(22.22) 28.843 < 0.001* Ⅱ型 2(5.26) 12(33.33) Ⅲ型 2(5.26) 6(16.67) Ⅳ 型 2(5.26) 10(27.78) 弹性成像 I级 28(73.68) 11(30.56) 24.338 < 0.001* Ⅱ级 9(23.68) 6(16.66) Ⅲ级 1(2.63) 10(27.78) Ⅳ 级 0(0) 9(25.00) *P < 0.05。 表 2 FNAC和FNA-Tg/血清Tg比值在诊断甲状腺癌有无淋巴结转移效果与病理结果的对照(%)
Table 2. Comparison of the effects of FNAC and FNA-Tg/serum Tg ratio in the diagnosis of thyroid cancer with or without lymph node metastasis with pathological results (%)
检查方法 检查结果 病理结果(枚) χ2 P 灵敏度 特异度 准确率 阳性预测值 阴性预测值 阳性 阴性 FNAC 阳性 27 0 44.872 < 0.001* 75.00 100 87.84 100 80.85 阴性 9 38 FNAC-Tg/血清Tg值 > 1 阳性 35 0 70.100 < 0.001* 97.22 100 98.65 100 97.44 阴性 1 38 FNAC-Tg > 0.575 ng/mL 阳性 40 0 74.000 < 0.001* 100 100 100 100 100 阴性 0 34 *P < 0.05。 表 3 ROC曲线各项指标
Table 3. ROC curve indicators
指标 AUC 最佳诊断值 敏感度(%) 特异性(%) P 95% 置信区间 下限值 上限 Tg 0.985 0.575 100 89.5 < 0.001* 0.967 1.000 *P < 0.05。 -
[1] Sherman S I. Thyroid carcinoma[J]. Lancet,2003,36(3):501-511. [2] Davies L,Welch H G. Increasing incidence of thyroid cancer in the United States,1973–2002[J]. Am Med Assoc,2006,295(5):2164-2167. [3] Chung J,Kim E K,Lim H. Optimal indication of thyroglobulin measurement in fine-needle aspiration for detecting lateral metastatic lymph nodes in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma[J]. Head Neck,2014,36(6):795-801. doi: 10.1002/hed.23371 [4] Ahn J E,Lee J H,Yi J S. Diagnostic accuracy of CT and ultrasonography for evaluating metastatic cervical lymph nodes in patients with thyroid cancer[J]. World J Surg,2008,32(7):1552-1558. doi: 10.1007/s00268-008-9588-7 [5] 高明,李小龙,于洋. 甲状腺癌的临床病理及PET-CT的诊断价值[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2006,41(6):419-424. [6] 纪丽丽,姜双全,李守强,等. 穿刺洗脱液甲状腺球蛋白测定在诊断甲状腺乳头状癌转移淋巴结肿的应用[J]. 中华超声影像学杂志,2019,28(4):313-317. [7] Pacini F,Fugazzola L,Lippi F,et al. Detection of thyroglobulin in fine needle aspirates of nonthyroidal neck masses:A clue to the diagnosis of metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab,1992,74(6):1401-1404. [8] 岳林先,马懿,邓立强. 超声检测颈部淋巴结对弥漫性硬化型甲状腺乳头状癌的诊断价值[J]. 中国超声医学杂志,2009,25(10):944-946. [9] 赵博,王金锐,胡静. 术前超声在分化型甲状腺癌淋巴结手术选择中的临床价值[J]. 中国超声医学杂志,2014,30(11):964-967. [10] 周建桥,詹维伟. 彩色多普勒超声评估颈部淋巴结疾病血管模式的探讨[J]. 中国医学影像技术,2006,22(7):1031-1034. [11] 任新平,詹维伟,周萍. 实时超声弹性成像在淋巴结疾病诊断中的应用[J]. 华西医学,2010,25(2):294-297. [12] Ghervan C. Thyroid and parathyroid ultrasound[J]. Medical Ultrasonography,2011,13(1):80-84. [13] Kessler A,Rappaport Y,Blank A. Cystic appearance of cervical lymph nodes is characteristic of metastatic papillary thyroid carcinoma[J]. J Clin Ultrasound,2003,31(1):21-15. doi: 10.1002/jcu.10130 [14] Haugen B R,Alexander E K,Bible K C,et al. 2015 American thyroid association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer[J]. Thyroid,2016,26(1):1-133. [15] Sohn Y M,Kim M J,Kim E K,et al. Diagnostic performance of thyroglobulin value in indeterminate range in fine needle aspiration washout fluid from lymph nodes of thyroid cancer[J]. Yonsei Med J,2021,53(1):126-131. -






 下载:
下载: