The Efficacy and Safety of Different Antiviral Treatment Regimens in Patients with ALT Elevation and Low Viral Load in the Indeterminate Phase of Chronic Hepatitis B
-
摘要:
目的 观察初治的低病毒载量不确定期慢乙肝患者采用一线核苷(酸)类药物抗病毒治疗后的临床疗效及安全性。 方法 纳入2019年1月至2022年4月期间在昆明市第三人民医院门诊就诊的96例初治低病毒载量不确定期慢性乙肝患者,根据使用药物不同将患者分为恩替卡韦组(ETV组)、富马酸替诺福韦酯组(TDF组)和富马酸丙酚替诺福韦组(TAF组)。在持续用药的第12周、24周、48周观察3组的临床疗效及安全性差异。 结果 经抗病毒治疗48周后,总共96.88%(93/96)患者HBV DNA获得完全病毒学应答(complete virologic response,CVR,定义为HBV DNA < 100 IU/mL),3组的CVR率为:ETV组96.97%(32/33),TDF组96.97%(32/33),TAF组96.67%(29/30),组间差异无统计学意义(P = 0.997)。治疗48周时HBsAg水平较基线均有显著下降,但3组差异无统计学意义(P = 0.348)。TAF组较ETV组(P = 0.013)、TDF组(P = 0.047)显著提升eGFR水平,AFP水平较ETV组(P = 0.008)和TDF组(P = 0.007)显著下降。48周ALT复常率:TAF组(70%)和TDF组(45.45%),ETV组(60.61%)差异无统计学意义(P = 0.135)。治疗期间无严重不良事件发生。 结论 治疗48周后3组CVR率均达96%以上,AFP水平下降及eGFR水平改善TAF组优于ETV组及TDF组,对ALT升高、低病毒载量慢乙肝不确定期患者行抗病毒治疗可使患者获益。 Abstract:Objective To observe the clinical efficacy and safety of first-line nucleos (t)ide analogues antiviral therapy in newly diagnosed chronic hepatitis B patients with low viral load and uncertain stage. Methods A total of 96 diagnosed treatment-naive chronic hepatitis B patients with low viral load in indeterminate stage who attended Kunming Third People’s Hospital from January 2019 to April 2022 were included and divided into the ETV group, TDF group and TAF group according to the drugs used. The differences in clinical efficacy and safety of the three groups were observed at the 12thW, 24thW and 48thW of continuous dosing. Results After 48 weeks of the antiviral treatment, a total of 96.88% (93/96) patients achieved complete virologic response (CVR, defined as HBV DNA < 100 IU/mL) to HBV DNA, with CVR rates in the three groups: 96.97% (32/33) in the ETV group, 96.97% (32/33) in the TDF group 96.97% (32/33), and 96.67% (29/30) in the TAF group, with no statistically significant difference among the three groups (P = 0.997). HBsAg levels decreased significantly at 48 weeks of treatment compared to the baseline in all three groups, but there was no statistically significant difference among the three groups (P = 0.348). eGFR levels were significantly elevated in the TAF group compared to those in the ETV group (P = 0.013) and the TDF group (P = 0.047), and AFP levels decreased significantly compared to those in the ETV group (P = 0.008) and the TDF group (P = 0.007). There was no significant difference of ALT recurrence rate for 48 weeks among TAF group (70%), TDF group (45.45%) and ETV group (60.61%) (P = 0.135). No serious adverse events occurred during the treatment period. Conclusion The CVR rate of all three groups has reached more than 96% after 48 weeks of the treatment, the ALT normalization rate of the TAF group is better than that of the TDF group, and the decrease in AFP level and improvement in eGFR level of the TAF group are better than those of the ETV and TDF groups. The patients with elevated ALT and low viral load in the indeterminate phase of chronic hepatitis B could benefit from antiviral therapy. -
表 1 入组患者的基线临床特征[
$\bar x \pm s $ /n(%)/ M(P25,P75)]Table 1. Baseline clinical characteristics of enrolled patients [
$\bar x \pm s $ /n(%)/ M(P25,P75)]项目 ETV组(n = 33) TDF组(n = 33) TAF组(n = 30) F/H/χ2 P 年龄 43.30 ± 14.52 36.15 ± 11.52 40.71 ± 10.62 2.828 0.065 性别[n(%)] 2.577 0.276 男 22(66.67) 19(57.58) 23(76.67) 女 11(33.33) 14(42.42) 7(23.33) HBVDNA
(IU/mL)514.23(235.15,872.33) 627.14(283.41,1829.67) 824.26(203.79,1584.07) 1.575 0.455 HbeAg (COI) 0.12(0.09,2.98) 0.12(0.09,6.18) 0.83(0.10,9.55) 6.354 0.052 TBIL
(μmol/L)18.86(13.50,21.69) 13.91(12.46,18.53) 15.83(13.30,10.50) 4.788 0.091 ALB(g/L) 43.08 ± 6.80 45.73 ± 3.27 47.54 ± 8.67 3.298 0.192 GGT (U/L) 31.00(18.50,47.00) 32.50(20.00,63.75) 37.00(25.00,61.00) 0.812 0.666 CR(μmol/L) 72.25 ± 2.31 62.79 ± 16.94 76.10 ± 17.72 5.733 0.057 UA(μmol/L) 327.50(266.75,416.75) 329.00(275.00,429.00) 354.00(284.00,451.25) 1.187 0.572 AFP(ng/mL) 2.94(2.27,5.31) 2.80(1.78,4.34) 3.48(2.27,4.05) 0.662 0.718 表 2 不同治疗方案治疗慢乙肝不确定期患者的病毒学载量情况[n(%)]
Table 2. Virological load of patients with chronic hepatitis B in uncertain stage treated with different treatment regimens [n(%)]
观察指标 分层 ETV组(n = 33) TDF组(n = 33) TAF组(n = 30) χ2 P CVR率 12周 26(78.79) 25(75.75) 25(83.33) 0.551 0.759 24周 31(93.94) 31(93.94) 28(93.33) 0.013 0.994 48周HBV-DNA抑制率 总 32(96.97) 32(97.77) 29(96.67) 0.006 0.997 HBeAg阳性,DNA < 2000 IU/mL 10(100.00) 11(91.67) 15(93.75) 0.814 0.666 HBeAg阴性,DNA < 2000 IU/ mL 22(95.65) 20(100.00) 15(100.00) 1.548 0.416 表 3 不同治疗方案治疗慢乙肝不确定期患者的血清HBsAg滴度水平改变[M(P25,P75)]
Table 3. Changes of serum HBsAg titers in patients with chronic hepatitis B in uncertain stage treated with different treatment regimens [M(P25,P75)]
观察指标 治疗时间 ETV组 TDF组 TAF组 H/Z P HBsAg
(IU/mL)基线 1 215(132,2 371) 1 749(797,7 802) 2 199(813,6 584) 4.887 0.087 12周 1 208(69 ,4 171) 1 409(405,5 030) 1 707(392,4 794) 2.855 0.623 24周 1 159(150,3 069) 1 209(576,3 689) 1 710(284,4 437) 2.434 0.575 48周 1 109(108,2 610) 972 (377,4 913) 1 200(333,2 968) 6.137 0.348 M −0.993 −3.412 −4.397 P 0.003* 0.001* 0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 4 不同治疗方案治疗慢乙肝不确定期患者的ALT生化学应答比较[M(P25,P75)]
Table 4. Comparison of ALT biochemical responses in patients with chronic hepatitis B in uncertain stage treated with different treatment regimens [M(P25,P75)]
观察指标 治疗时间 ETV组 TDF组 TAF组 H/Z P ALT
(U/L)基线 32(23,41) 38(25,58) 34(29,53) 4.584 0.101 12周 31(25,38) 32(23,53) 32(25,43) 0.392 0.822 24周 32(24,37) 37(23,53) 37(28,52) 2.976 0.226 48周 24(19,35) 29(25,41) 30(24,39) 3.315 0.191 M −1.471 −2.603 −3.395 P 0.141 0.009* 0.001* ALT复常率 48周 60.61%(20/33) 45.45%(15/33) 70.00%(21/30) 4.002 0.135 *P < 0.05。 表 5 不同治疗方案治疗慢乙肝不确定期患者的TBIL生化学应答比较[M(P25,P75)]
Table 5. Comparison of TBIL biochemical responses in patients with chronic hepatitis B in uncertain stage treated with different treatment regimens [M(P25,P75)]
观察指标 治疗时间 ETV组 TDF组 TAF组 H/Z P TBIL 基线 18.7(13.2,21.6) 13.9(12.4,18.5) 15.3(13.3,20.5) 4.788 0.091 12周 16.5(13.5,22.2) 14.9(12.3,19.8) 16.1(11.4,21.7) 0.207 0.902 24周 13.7(12.0,19.6) 15.0(11.6,18.7) 16.7(11.6,24.2) 0.908 0.635 48周 11.8(10.2,16.9) 13.1(11.5,16.8) 14.2(10.9,18.0) 0.698 0.705 M 5.143 0.926 11.56 P 0.023* 0.336 0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 6 不同治疗方案治疗慢乙肝不确定期患者的GGT生化学比较[M(P25,P75)]
Table 6. Comparison of GGT biochemical responses in patients with chronic hepatitis B in uncertain stage treated with different treatment regimens [M(P25,P75)]
观察指标 治疗时间 ETV组 TDF组 TAF组 H/Z P GGT
(U/L)基线 25(19,44) 28(18,59) 30(20,50) 12周 25(20,45) 22(16,39) 32(23,17) 1.357 0.503 24周 27(20,44) 25(15,34) 29(20,42) 1.871 0.392 48周 30(20,40) 23(14,39) 25(18,40) 3.291 0.193 M −1.526 −2.326 −2.085 P 0.127 0.020* 0.037* *P < 0.05。 表 7 不同治疗方案治疗慢乙肝不确定期患者的eGFR生化学比较[M(P25,P75)]
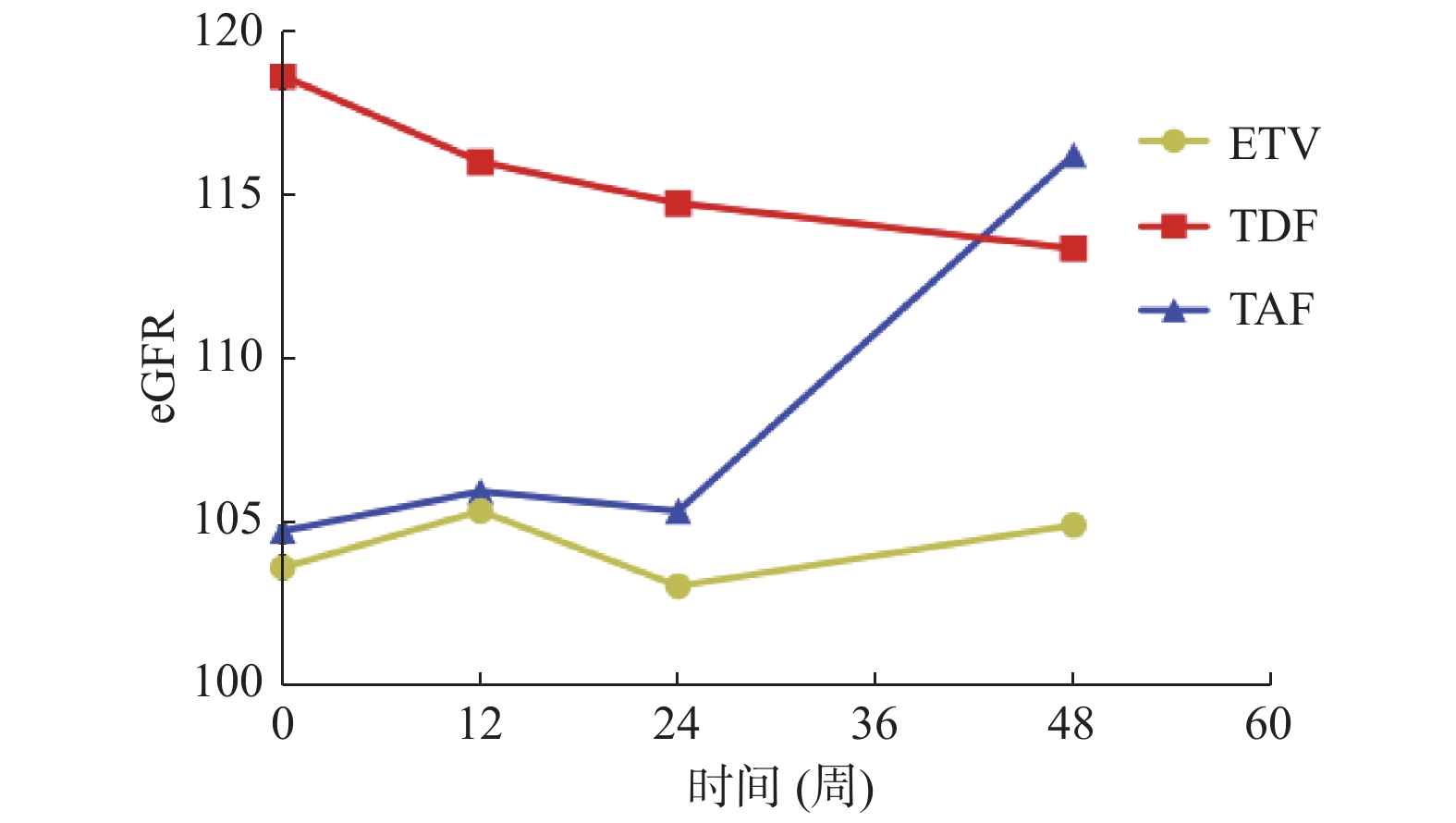
Table 7. Comparison of eGFR biochemical responses in patients with chronic hepatitis B in uncertain stage treated with different treatment regimens [M(P25,P75)]
观察指标 治疗时间 ETV组 TDF组 TAF组 H/Z P eGFR
(mL/min/1.73 m2)基线 102.1(96.9,116.3) 117.6(99.3,128.9) 104.2(97.8,
113.3)5.707 0.058 12周 104.9(98.3,122) 118.2(99.5,128.6) 107.2(93.8,
113.3)3.297 0.192 24周 105.3(92.3,116.9) 114.4(100.4,126.9) 112.2(97.6,
118.6)4.613 0.099 48周 105.5(98.6,120.3) 110.8(103.2,125.5) 118.9(110.4,
122.8)6.579 0.037* M −1.331 −0.412 −2.138 P 0.183 0.040* 0.032* *P < 0.05。 表 8 不同治疗方案治疗慢乙肝不确定期患者第48周的eGFR生化学比较[M(P25,P75)]
Table 8. Comparison of eGFR biochemistry responses in patients with chronic hepatitis B at the 48th week in uncertain stage treated with different treatment regimens [M(P25,P75)]
分组 第48周eGFR(mL/min/1.73 m2) P ETV组VS TAF组 105.5(98.6,120.3) 110.8(103.2,125.5) 0.013* TDF组VS TAF组 110.8(103.2,125.5) 118.9(110.4,122.8) 0.047* ETV组VS TDF组 105.5(98.6,120.3) 118.9(110.4,122.8) 0.128 *P < 0.05。 表 9 不同治疗方案治疗慢乙肝不确定期患者的AFP水平比较[M(P25,P75)]
Table 9. Comparison of AFP biochemical responses in patients with chronic hepatitis B in uncertain stage treated with different treatment regimens [M(P25,P75)]
观察指标 治疗时间 ETV组 TDF组 TAF组 H/Z P AFP 基线 2.91(2.26,4.56) 2.70(1.78,4.34) 3.49(2.28,4.05) 0.466 0.792 12周 3.35(2.71,4.21) 2.81(2.12,5.34) 2.69(2.22,3.64) 1.772 0.423 24周 3.08(2.39,4.28) 3.30(2.37,4.59) 2.73(2.02,3.24) 3.472 0.176 48周 3.10(2.55,3.71) 3.47(2.23,4.71) 2.32(1.51,3.09) 9.489 0.009* M −0.435 −0.284 −2.548 P 0.664 0.776 0.011* *P < 0.05。 表 10 不同治疗方案治疗慢乙肝不确定期患者第48周的AFP生化学比较[M(P25,P75)]
Table 10. Comparison of AFP biochemistry responses in patients with chronic hepatitis B at the 48th week in uncertain stage treated with different treatment regimens [M(P25,P75)]
分组 第48周eGFR(mL/min/1.73 m2) P ETV组VS TAF组 3.10(2.55,3.71) 2.32(1.51,3.09) 0.008* TDF组VS TAF组 3.47(2.23,4.71) 2.32(1.51,3.09) 0.007* ETV组VS TDF组 3.10(2.55,3.71) 3.47(2.23,4.71) 0.821 *P < 0.05。 -
[1] 王贵强, 王福生, 庄辉, 等. 慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2019年版)[J/OL]. 中国病毒病杂志, 2020, 10(1): 1-25. [2] 张会,王欣茹,肖丽,等. 不确定期慢性HBV感染者的分布与治疗[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志,2021,37(12):2778-2779. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.12.008 [3] Sinn D H, Kim S E, Kim B K, et al. The risk of hepatocellular carcinoma among chronic hepatitis B virus‐infected patients outside current treatment criteria[J/OL]. Journal of Viral Hepatitis, 2019, 26(12): 1465-1472. [4] 中华医学会感染病学分会, 中华医学会肝病学分会. 慢性乙型肝炎临床治愈(功能性治愈)专家共识[J]. 中华临床感染病杂志, 2019, 27(8): 594-603. [5] Zoutendijk R, Reijnders J G, Zoulim, et al. Virological response to entecavir is associated with a better clinical outcome in chronic hepatitis B patients with cirrhosis[J/OL]. Gut, 2013, 62(5): 760-765. [6] Huang D Q, Li X, Le M H, et al. Natural history and hepatocellular carcinoma risk in untreated chronic hepatitis B patients with indeterminate phase[J/OL]. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 2022, 20(8): 1803-1812. e5. [7] Spradling P R, Xing J, Rupp L B, et al. Distribution of disease phase, treatment prescription and severe liver disease among 1598 patients with chronic hepatitis B in the Chronic Hepatitis Cohort Study, 2006-2013[J/OL]. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 2016, 44(10): 1080-1089. [8] Jang J W, Choi J Y, Kim Y S, et al. Effects of virologic response to treatment on short- and long-term outcomes of patients with chronic h epatitis B virus infection and decompensated cirrhosis[J/OL]. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 2018, 16(12): 1954-1963. e3. [9] Chan H L Y, Fung S, Seto W K, et al. Tenofovir alafenamide versus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for the treatment of HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3, non-inferiority trial[J/OL]. The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 2016, 1(3): 185-195. [10] Choi J, Kim H J, Lee J, et al. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients treated with entecavir vs tenofovir for chronic hepatitis B: A Korean nationwide cohort study[J/OL]. JAMA Oncology, 2019, 5(1): 30. [11] Choi W M, Choi J, Lim Y S. Effects of tenofovir vs entecavir on risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic HBV infection: A systematic review and Meta-analysis[J/OL]. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 2021, 19(2): 246-258. e9. [12] 庄辉. 不确定期慢性乙型肝炎应否治疗[J]. 临床肝胆杂志,2021,37(9):2033-2036. -






 下载:
下载: